oral histology exam 2
1/177
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
178 Terms
Odontogenesis
The process of tooth development from initiation to maturation
when tensile stress is perpendicular to rod
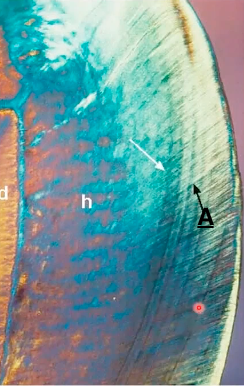
when does enamel fracture occur
lines of retzius
identify A (lines going up)
Initiation, Proliferation, Morphogenesis, Cytodifferentiation, Apposition, and Maturation.
Tooth Developmental processes
initiation
thickening of dental lamina at specific sites in dental arch
bud, cap, bell, crown
Tooth development stages
Enamel organ
A cap-like structure formed during the cap stage that contributes to enamel formation.
Dental papilla
Condensed ECTOMESENCHYME that forms during the cap stage, contributing to the formation of DENTIN and PULP.
Dental follicle
ECTOMESENCHYME surrounding the dental papilla that contributes to the formation of the periodontal ligament and cementum.
Cap Stage
phase in tooth development where the enamel organ, dental papilla, and dental follicle are formed.
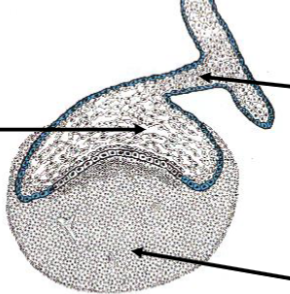
Enamel Knot
A signaling center that regulates the growth and shape of the tooth during development.
Tooth agenesis
A condition where one or more teeth fail to develop due to genetic mutations.
Cervical loop
area where the inner and outer enamel epithelium meet, allowing for ongoing enamel production and root development
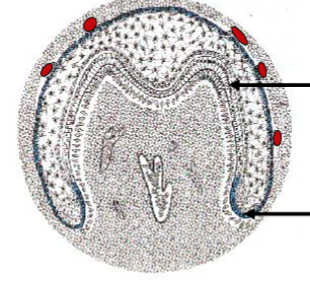
dental lamina breaks up, downward proliferation of cervical loop, differential growth of IEE (inner enamel epithelium)
what occurs during bell stage
bell stage
stage of tooth development characterized by the differentiation of the inner enamel epithelium into ameloblasts and the dental papilla into odontoblasts.
Hyperdontia
A condition characterized by the presence of supernumerary teeth, mutations in signaling molecules (Wnt, FGF, Shh) BEFORE BUD stage
Hypodontia
A condition resulting in a reduced number of teeth due to developmental issues.
Oral epithelium
The epithelial layer involved in initiating the formation and development of teeth.
dentin
what does the ectomesynchyme form during odontogenesis
enamel
what does oral ectoderm form during odontogenesis
directs epithelium to form specific tooth
role of MESENCHYME in CAP and BELL stages
initiate tooth formation in mesenchyme
role of EPITHELIUM BEFORE bud stage
inner enamel epithelium
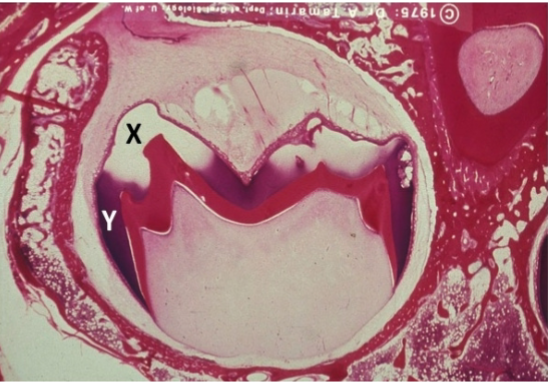
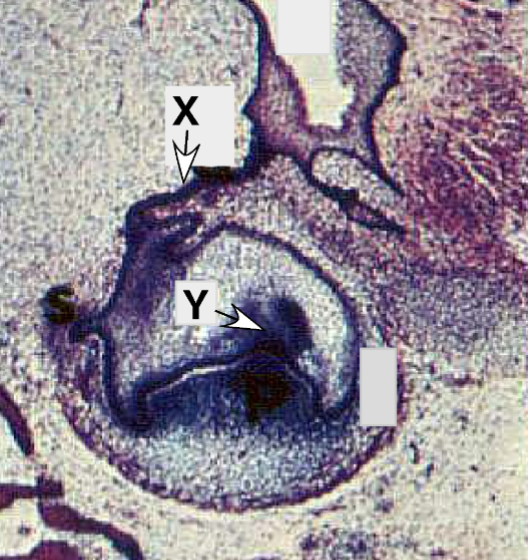
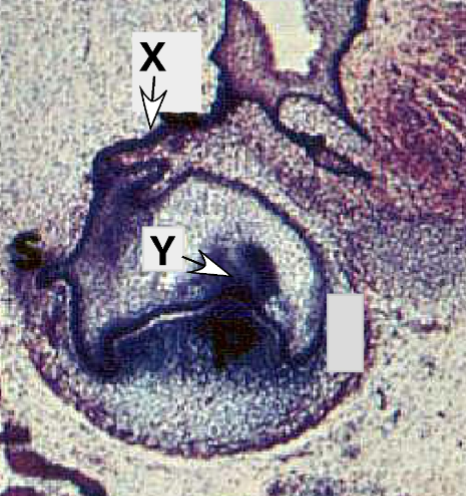
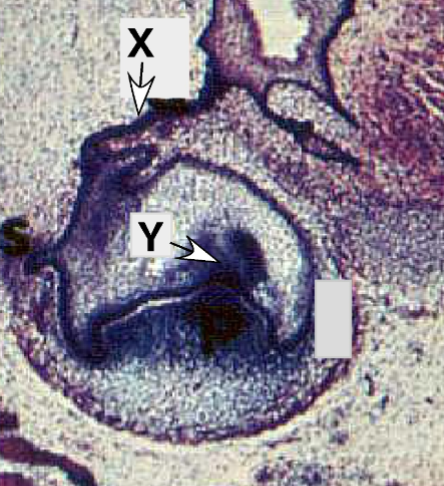
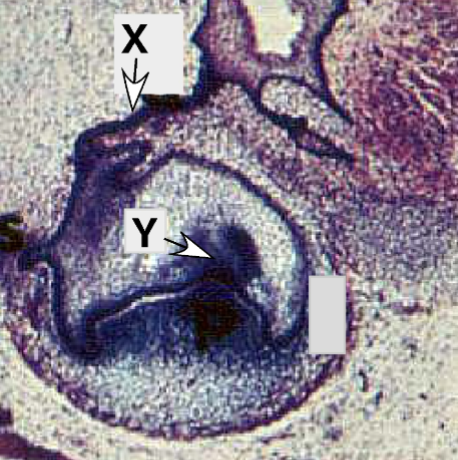
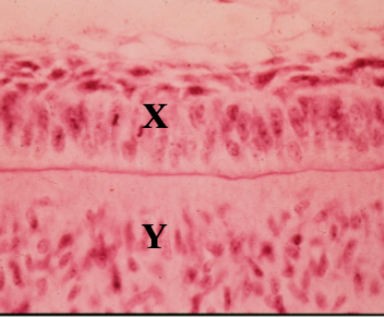
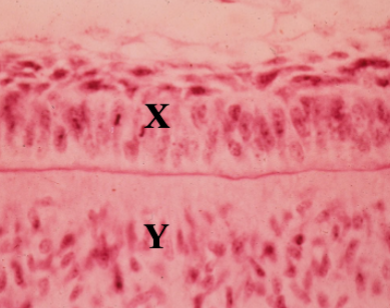
Identify the tissue layer labeled “X”
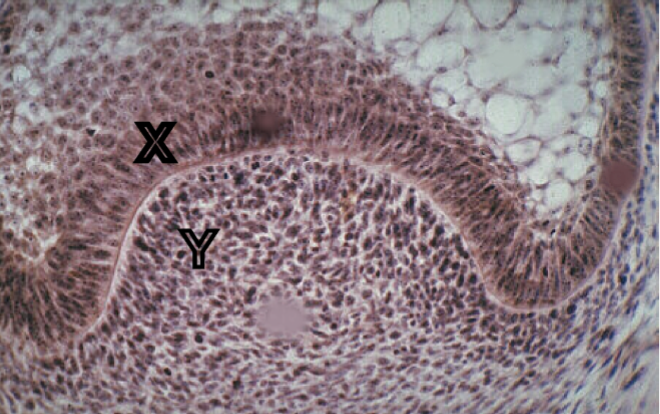
dental papilla
Identify the tissue layer labeled “Y”
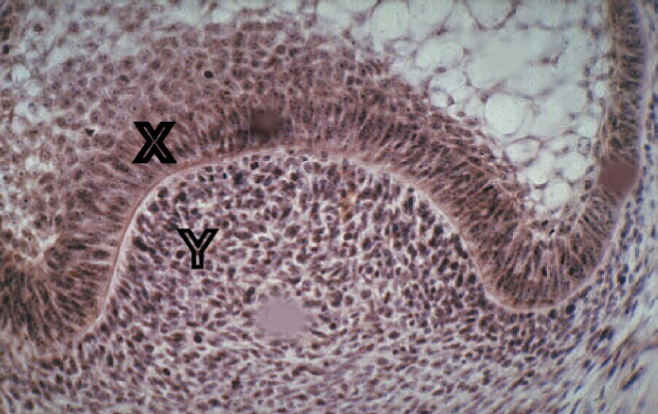
cytodifferentition
What developmental process will
developmental process tissue “X” undergoes in the bell stage to define the future shape of the crown
and cusp development?
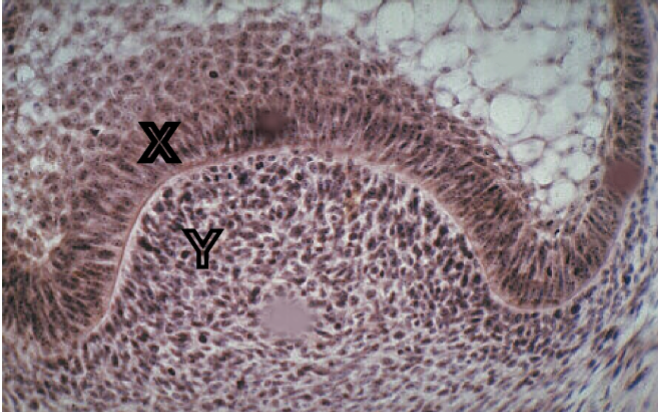
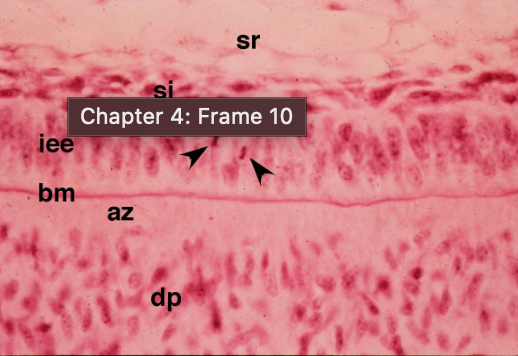
stratum intermedium
Identify the cells present in the tissue layer marked “x”
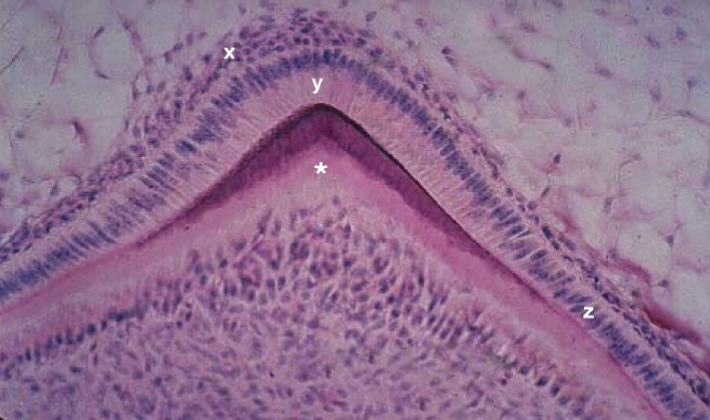
ameloblast
Identify the cells present in the tissue layer marked “y”
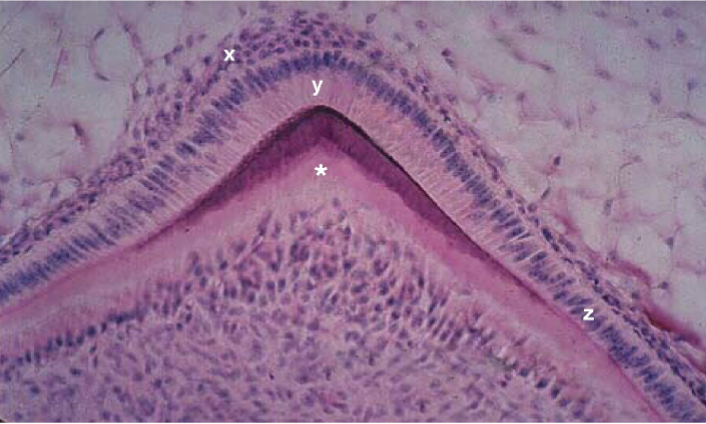
preameloblasts
Identify the cells present in the tissue layer marked “z”
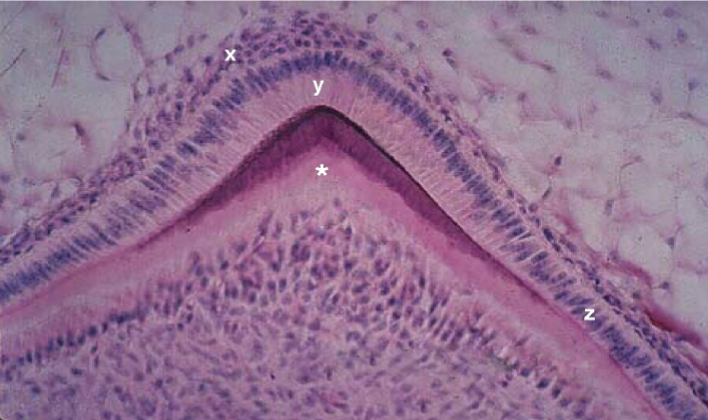
predentin
Identify the tissue marked by the * and stained light pink.
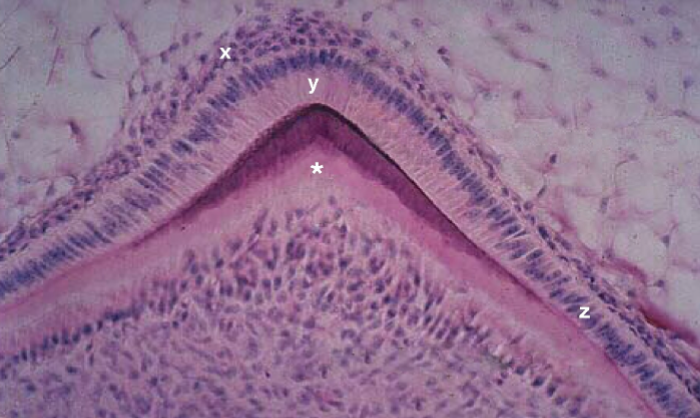
globular dentin/primary dentin
Identify the tissue marked with an “X”
mineralization (globular)
Describe the developmental process occuring at X
enamel
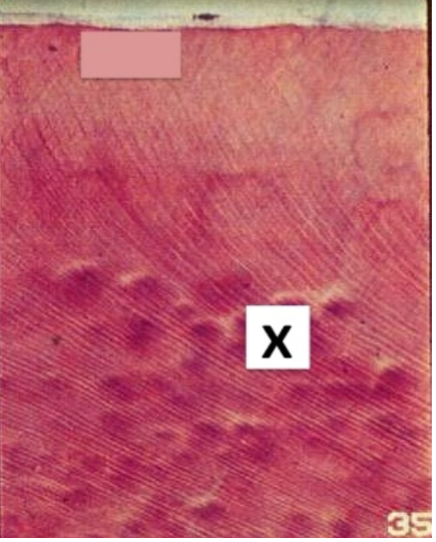
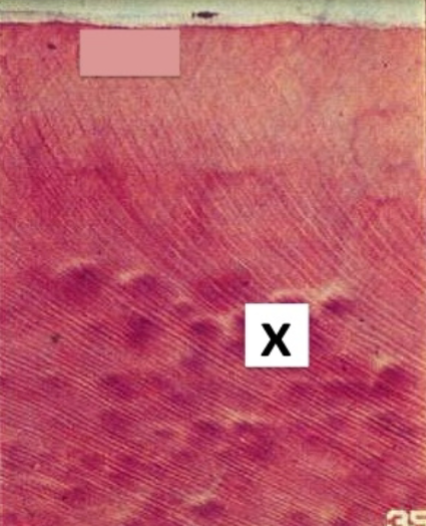
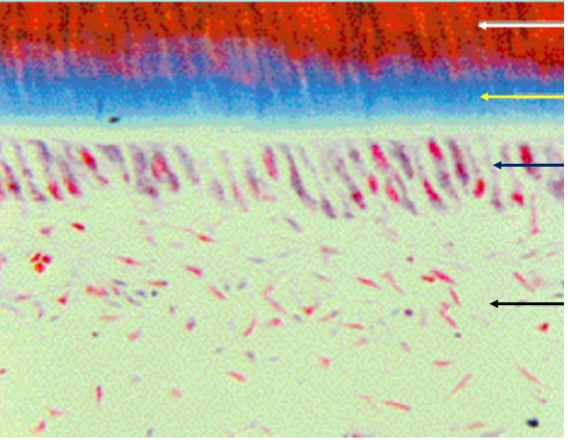
what type of tissue is this picture
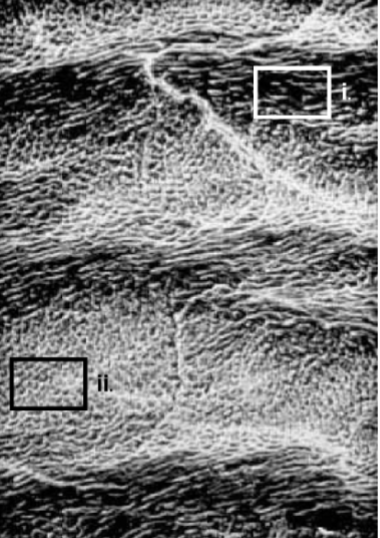
rods at different angles
How does the structure pictured in box (i) differ
from that in box (ii)?
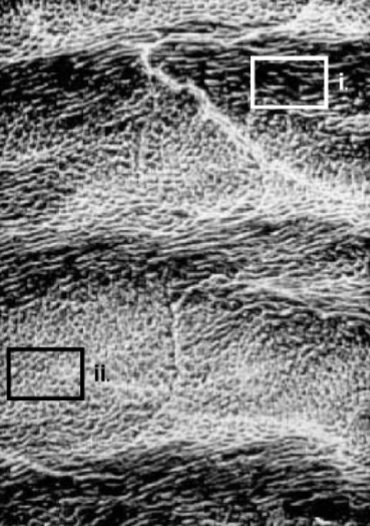
strength (compression mostly)
What is the functional significance of the structural difference between rods in i and ii?
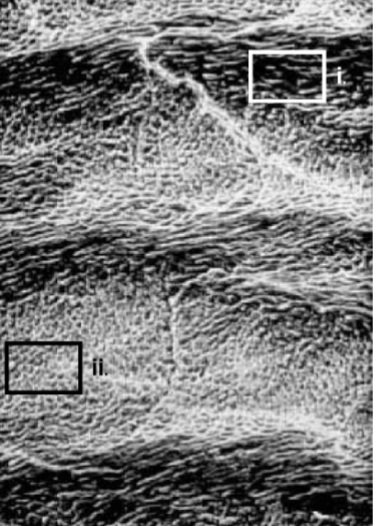
hunter-schreger
What is the name of the enamel structure shown
in this photo?
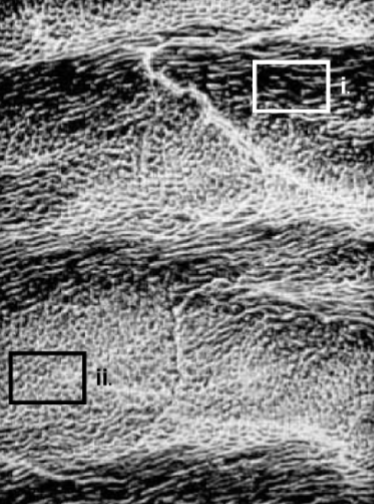
between interrod and rods
weak point of enamel
Y less mature and has more amelogenin
how is the process at Y different from that at X
higher fracture toughness, higher tensile strength, lower stiffness, lower compressive strength
biomechanical properties of dentin compared to enamel
higher compressive strength, lower tensile strength
biomechanical properties of enamel compared to dentin
dentin has collagen
how does the composition of dentin relative to enamel corresponds with higher fracture toughness and lower stiffness
bud stage
what stage
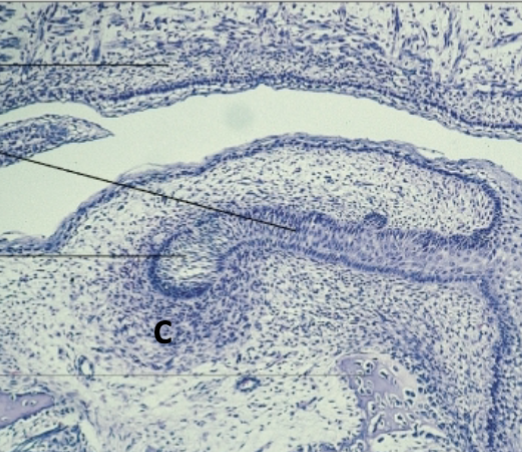
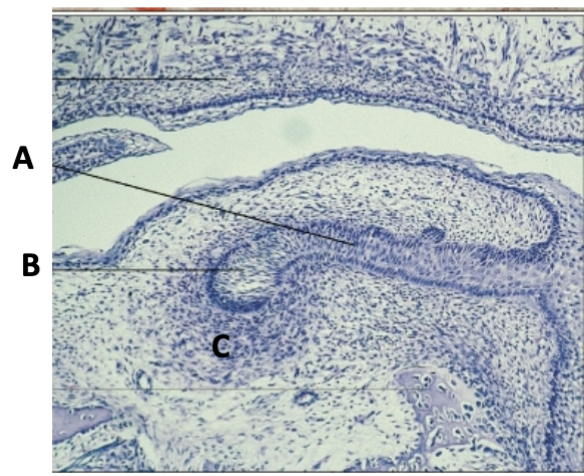
ectomesenchyme
identify cell at C
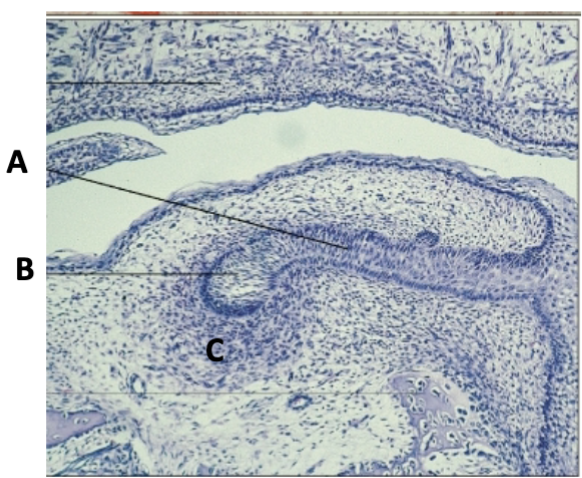
dental lamina
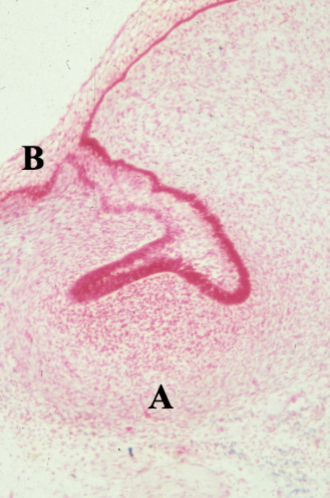
identify A
bud
Identify B
cap
what stage
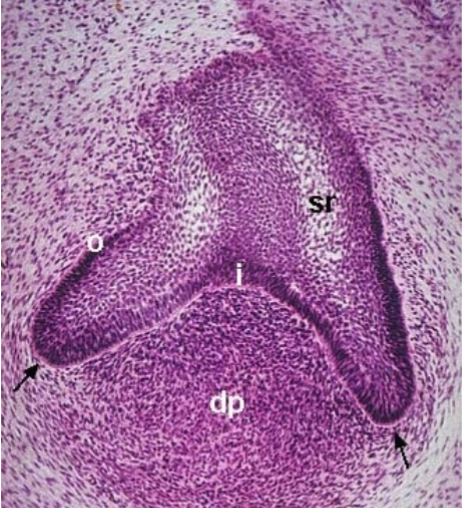
inner enamel epithelium
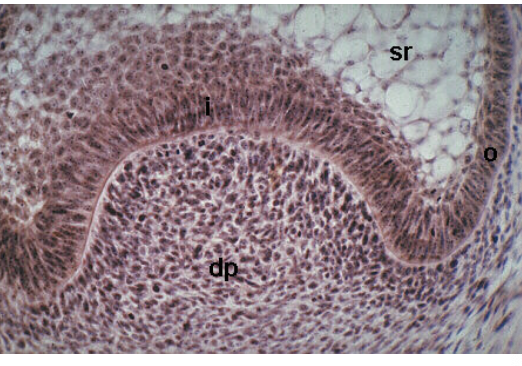
what is i
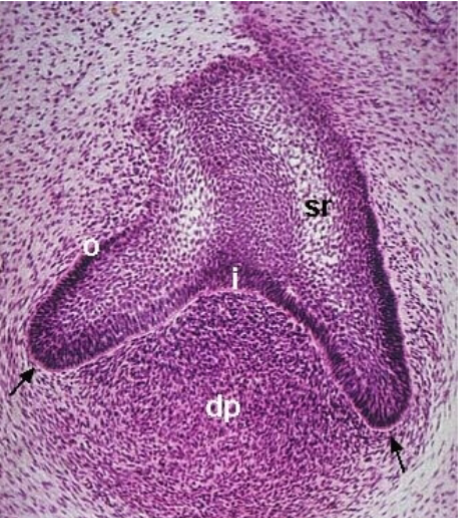
stellate reticulum
what is sr
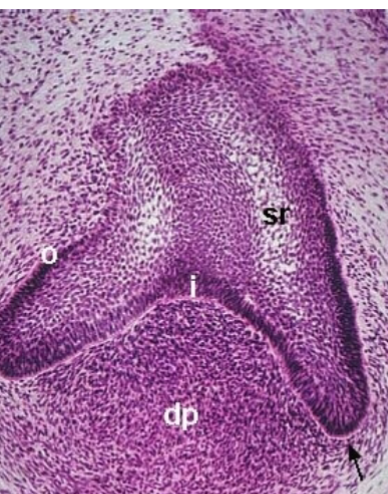
enamel knot
where do cusps come from during this. stage
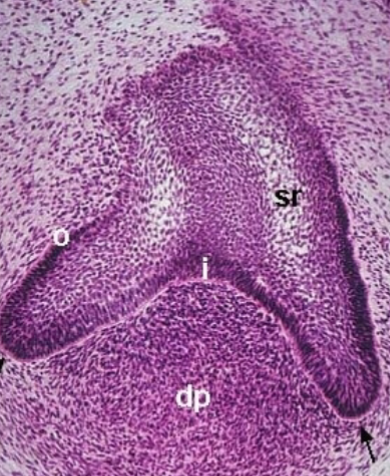
cervical loops
what are the black arrows pointing at
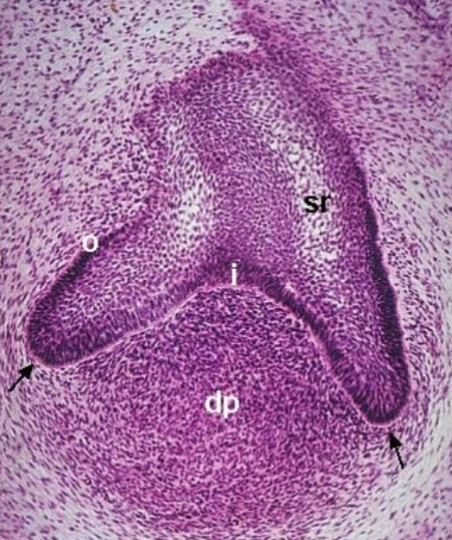
bell
what stage
enamel knot
Identify Y
thinning dental lamina connecting to oral epithelium
identify X
cytodifferentiation
what developmental process is occuring at this stage
dentin, predentin, odontoblast, pulp
what are the layers from top to bottom
peritubular/intratubular
what type of dentin is immediately around dentinal tubules
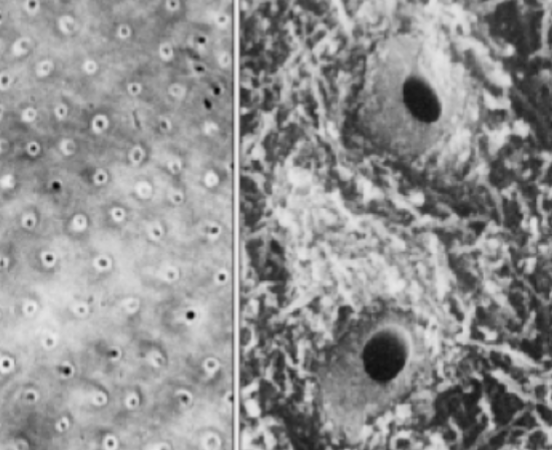
intertubular dentin
what. type of dentin is between dentinal tubules
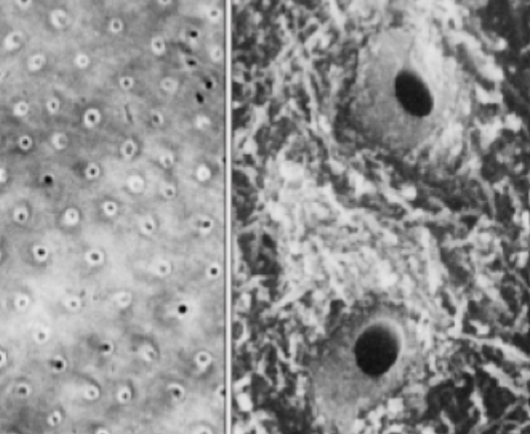
peritubular is hypermineralized with less collagen
what is the difference in composition between peritubular and intertubular dentin
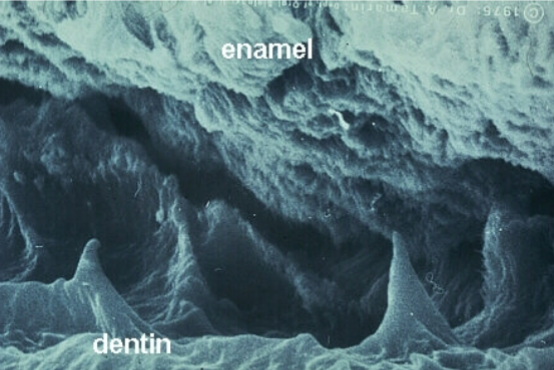
dentinoenamel junction
what space is shown here
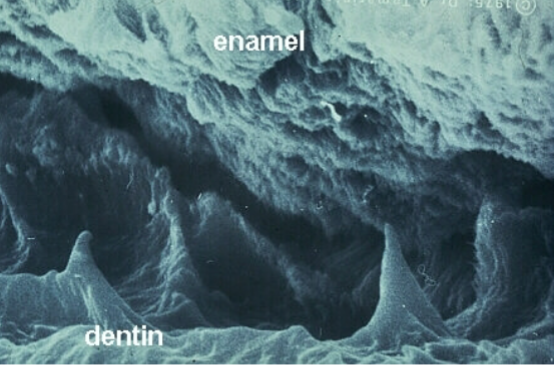
surface area for connection between enamel and dentin
what is the role of this space
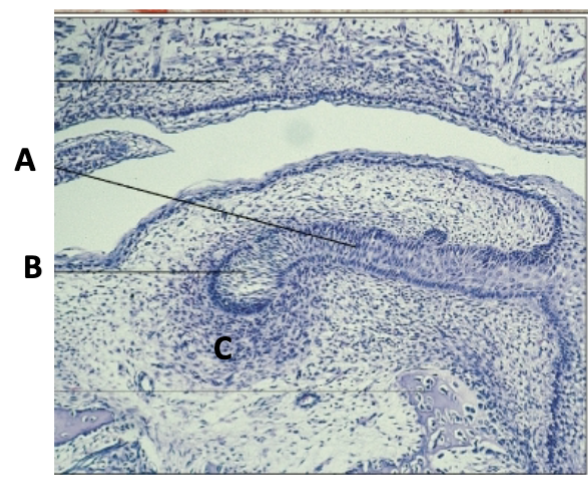
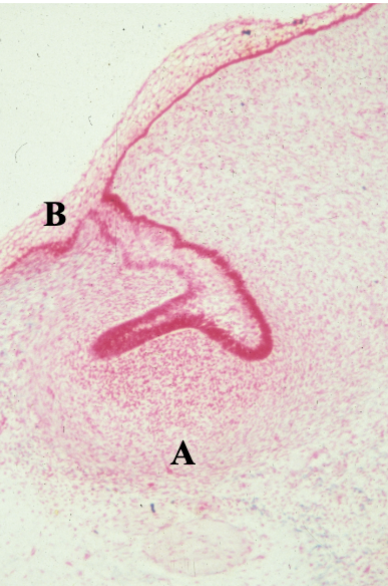
early cap
what stage
ectomesenchyme/dental follicle
what cells are present at A
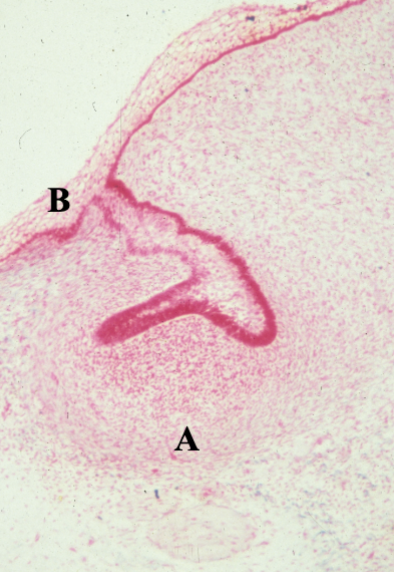
primary epithelial band/oral epithelium
what layer is at B
inner enamel epithelium
identify X
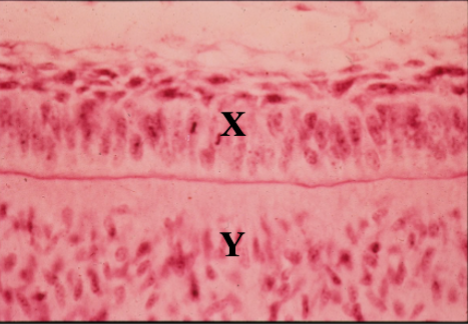
dental papilla
Identify Y
no
is there any apposition of dental material at this point
innerr enamel epithelium
which layer in cap stage generate enamel in the bell stage
increases fracture toughness and tensile strength
how does high density of collagen fibrils organized perpendicular to dentin tubules affect the material properties of dentin
ectoderm
what embryonic tissue is DENTAL LAMINA derived from
neural crest derived from ectomesenchyme
what embryonic tissue are ODONTOBLASTS derived from
ectoderm
where is STELLATE RETICULUM derived from
neural crest cells
where is the DENTAL FOLLICLE derived from
ectoderm
where is REDUCED ENAMEL EPITHELIUM derived from
dental lamina and ectomesenchyme
what is proliferating in the bud stage
enamel epithelia and dental papilla
what is proliferating in the cap stage
cervical loop and dental papilla
what is proliferating in the bell stage
ectomesenchyme
where is the DENTAL PAPILLA derived from
enamel organ and dental papilla
morphogenesis in the cap stage
cervical loop and dental papilla
morphogenesis in the bell stage
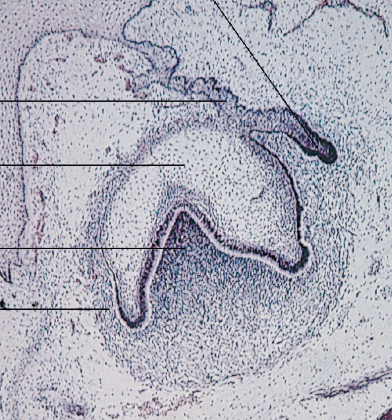
late cap/early bell
what stage
bell stage
what stage
bell stage
what stage
rapid hypertrophy, polarized nucleus, increased organelles, numerous odontoblastic processes
characteristics of odontoblasts
mantle dentin
initial dentin secreted by odontoblasts
large collagen fibrils and matrix vesicles involved in mineralization
components of mantle dentin
fine diameter collagen fibrils and lipid
components of primary dentin
predentin
organic material layer secreted by odontoblasts before mineralization, mainly of collagen
dense meshwork perpendicular to tubules
how do collagen fibrils organize in dentin
globular calcification
mineralization of primary dentin through intracellular deposition of calcium and phosphate within predentin.
calcospherites
small spherical structures formed during the mineralization process in dentin, contributing to the globular calcification of primary dentin.
interglobular dentin/ hypomineralized matrix
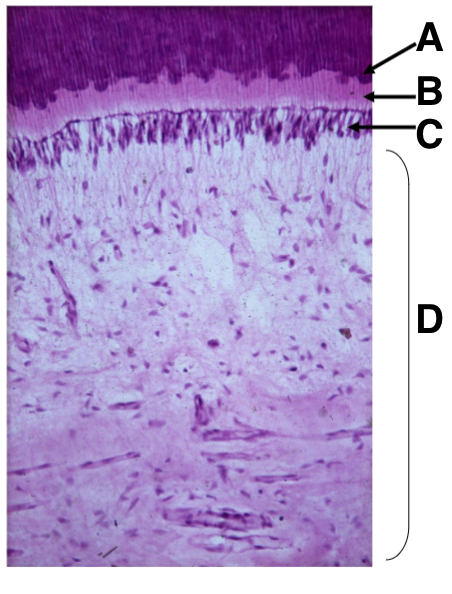
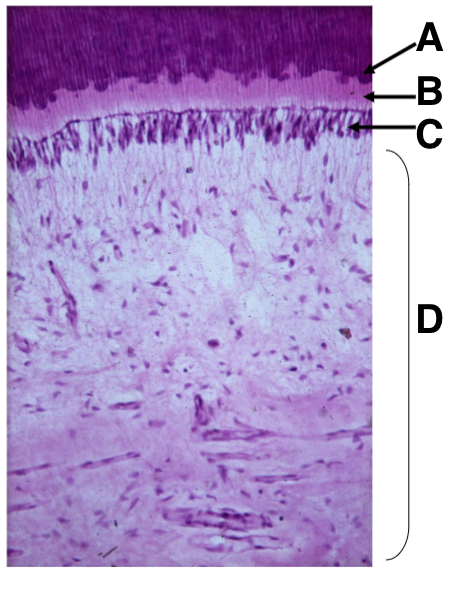
What is A
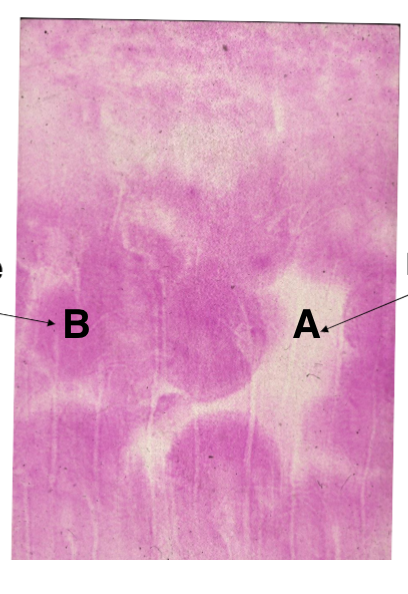
calcospherite
what is B
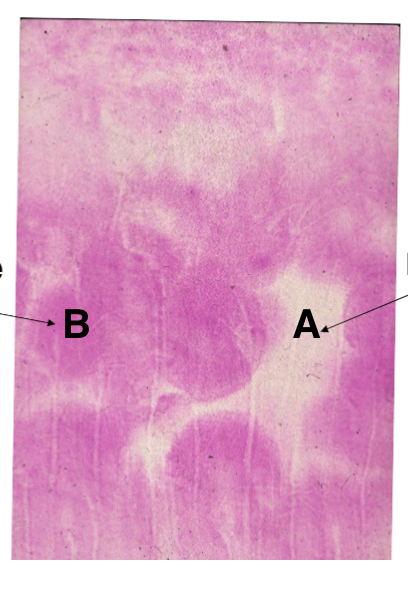
Mineralization front
what is A
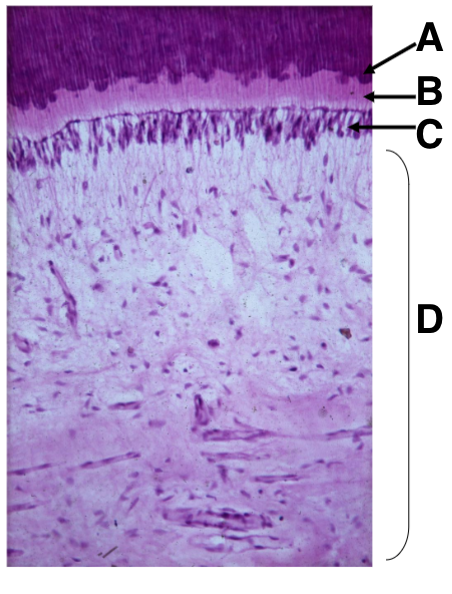
predentin
what is B
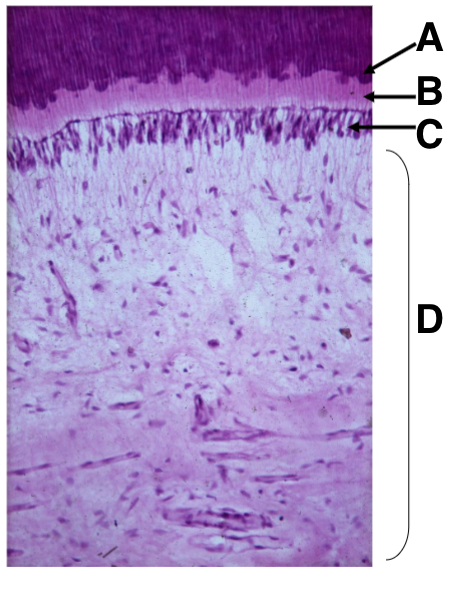
Odontoblasts
what is C
dental pulp
what is D
tomes granular layer
hypomineralized dentin in the root
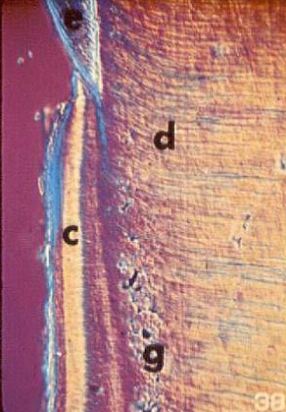
collagen fibrils perpendicular to dental tuble
what contributes to the high tensile strength and fracture resistance of dentin
secondary dentin
Identify A
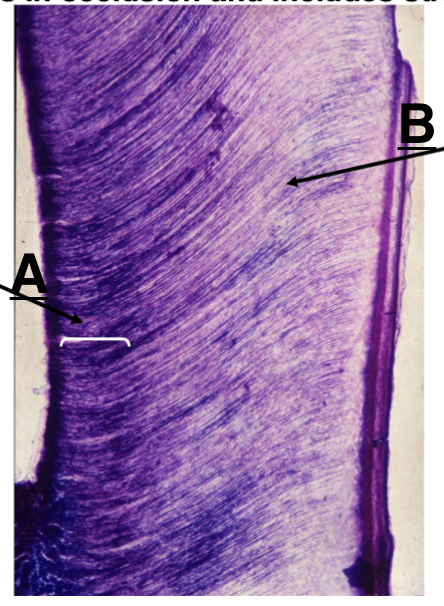
primary dentin
Identify B
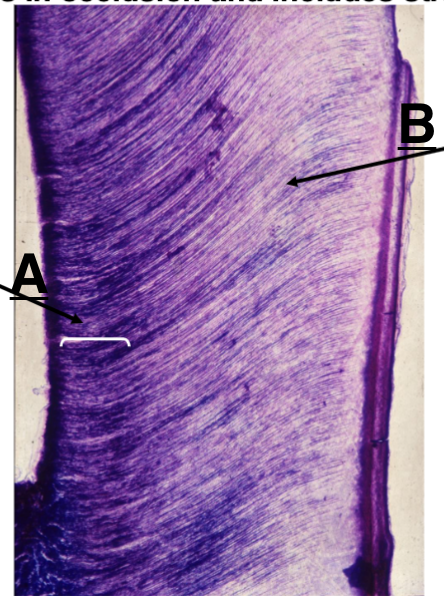
secondary dentin
forms once the tooth is in occlusions and includes straighter tubules