Complete EESC/GEOG Hydrology 205 Final
1/1429
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
1430 Terms
hydrological cycle
the global-scale, endless recirculatory process linking water in the atmosphere, on the continents, and in the oceans
solar energy
driving force of hydrological cycle, specifically water vapor formation and transport
infiltration
the movement of rain or melted snow into the soil at the earth's surface
infiltration capacity
the maximum rate at which water can infiltrate the soil
percolation
The process by which water moves downward in the soil, toward the water table (porous soil and rocks)
evaporation
the physical process involving a phase change from liquid to vapor by which water is returned to the atmosphere
potential evaporation
the maximum rate of evapotranspiration from a vegetated catchment under conditions of unlimited moisture supply
transpiration
Evaporation of water from the leaves of a plant
surface runoff
water from rainfall or snowmelt that runs over the surface of the earth in sheets, rivulets, streams, and rivers
precipitation
the dominant process by which water vapor in the atmosphere is returned to the earth's surface either as liquid drops (e.g., rain) or solid particles (e.g., snow) under the influence of gravity
precipitation intensity
a measure of the rate of precipitation, commonly computed for a specified duration
interception storage
the process by which precipitation (either liquid or solid or both) is temporarily stored either on vegetation surfaces (canopy interception) or on litter surfaces (litter interception); intercepted water either can return to the atmosphere as evaporation or can become stemflow or throughfall
conservation of mass
the volume of a compartment is the difference of the inflow and outflow
water budget
Balance between the rates of water added and lost in an area
steady-state
inputs = outputs
runoff ratio
the ratio of average annual surface runoff to average annual precipitation for a given land area
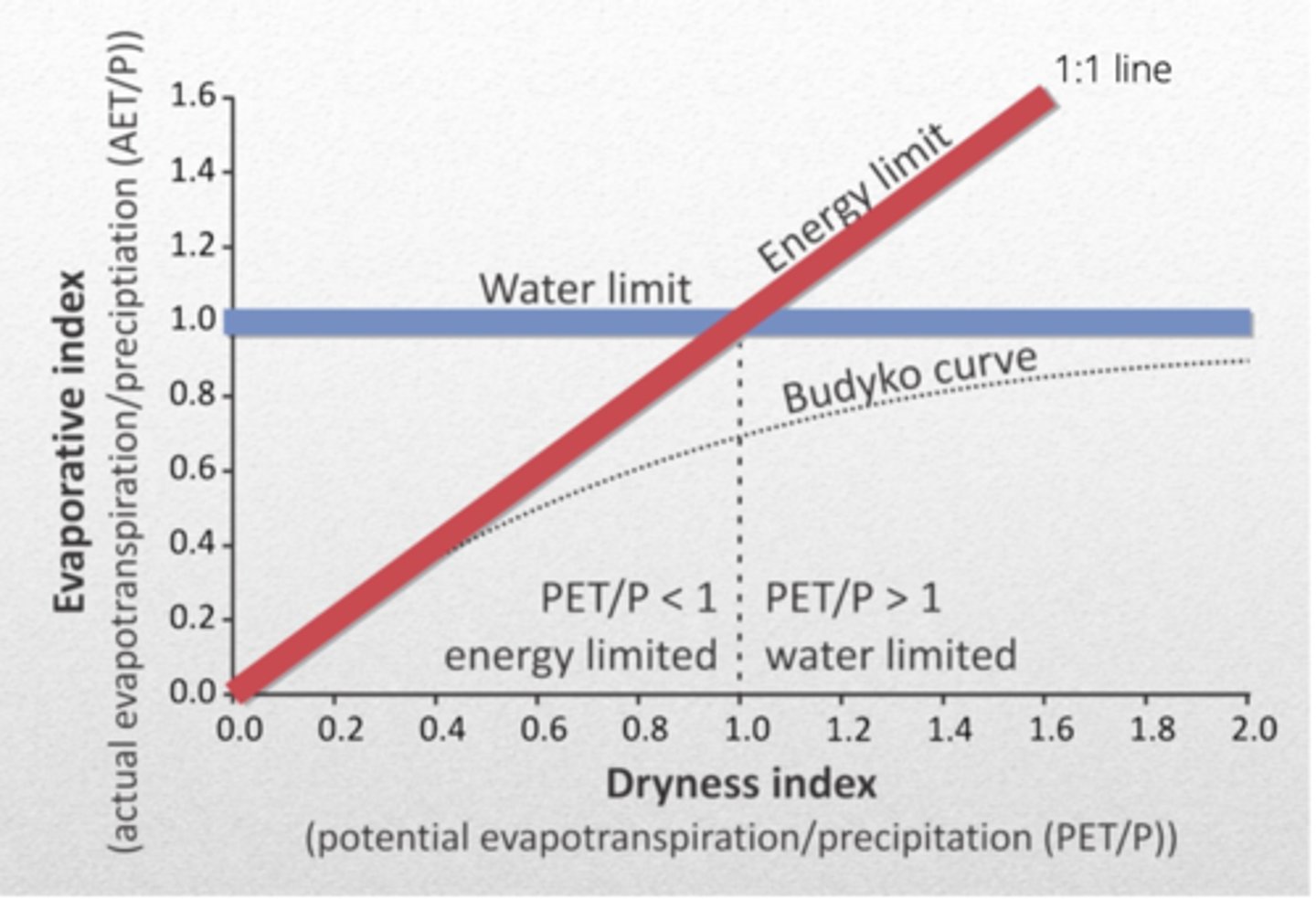
dryness index
DI = PET (demand for water (energy driven evap. demand)) / P (water supply available for ET)
value is low = ratio: low PET to large water supply
value is high = ratio: high PET to limited water supply
budyko
EI(vap) = ET/P
catchment (or watershed)
an area of land, bounded by a divide, in which water flowing across the surface will drain into a stream or river and flow out of the area through a specified point on that stream or river.
vapor pressure
the actual partial pressure exerted by a vapor within an air mass; related to the concentration of water vapor in air
saturated vapor pressure
in a system in which both liquid water and water vapor are present, the partial pressure exerted by the water vapor during an equilibrium condition in which the rates of vaporization and condensation are equal; the saturated state of air increases as a non-linear function of air temperature
rain shadow effect
Precipitation falls on the windward side of a mountain range, resulting in lush vegetation & a warm, moist climate on one side, but a desert area on the leeward side.
orographic effect
The precipitation that occurs when moist air rises up the side of a mountain
continentality
the difference between marine and continental areas
hyetograph
a graph of precipitation vs time
precipitation intensity
Rate of precipitation over a specified time period
isohyetal method
estimate mean precipitation over an area by drawing lines of equal precipitation
frequency analysis
a statistical technique used by hydrologists for estimating the average rate at which floods, droughts, storms, stores, rainfall events, etc., for a specified magnitude recur
exceedance probability
the probability that an event of a given magnitude will occur in a given year
return period
a measure of how often (on average) an event (precipitation, flood, etc.) will occur that is greater than some chosen value, the inverse of the exceedance probability
residence time
a measure of the average time a molecule of water spends in a reservoir. the residence time defined for steady-state systems is equal to the reservoir volume divided by the inflow or outflow rate
Tr = storage size or volume of water / flow or flux (input or output)
intensity-duration-frequency analysis
relates rainfall intensity with its duration and frequency of occurrence
stemflow
precipitation that runs down the trunk or stem of a plant to reach the ground
throughfall
that portion of gross precipitation that is not held in storage by interception. its also the precipitation that directly falls from the leaves to reach the ground
evapotranspiration
the sum of all processes by which water changes phase (from solid or liquid) to vapor and is returned to the atmosphere
penman equation
PET = change in net radiation + (psychometric constant (0.66 mb/ deg C) humidity gradient + windiness / (slope of sat vapor curve (mb/deg C) + psychometric constant (0.66 mb/ deg C)) latent heat of evap

actual evapotranspiration
the real rate of evapotranspiration from a land surface
surface energy balance
determine the amount of energy flux available to evaporative surface water and to raise or lower the temperature of the surface
latent heat of vaporization
the amount of energy per unit mass absorbed during a phase change from liquid to vapor at constant temperature. for evaporation of water at 0 deg C, it is 2.5 million Joules per kilogram of water
specific heat capacity of air
amount of heat that is required for something to change in temperature
sensible heat flux
H - the energy flux from surface to atmosphere carried by winds convection (the warmer the surface, the larger the heat flux)
latent heat
the portion of the internal energy of a substance that cannot be "sensed" (i.e., is not proportional to absolute temperature); latent heat is the internal energy that is released or absorbed during a phase change at constant temperature
ground heat flux
the energy flux from surface to deep soil carried by conduction (direct contact) - tends to be small because not often bare soil
net radiation
incoming SW - outgoing SW + incoming LW - outgoing LW
saturated excess overland flow
a mechanism of runoff generation that is particularly important in vegetated catchments in humid regions in which a shallow water table intersects the ground surface, causing ponding of water at the soil surface and flow across the surface either in sheets or in small rivulets.
infiltration excess overland flow
a mechanism of runoff generation in which the infiltration capacity of a catchment or a portion of a catchment is exceeded by the rainfall intensity, which results in ponding of precipitation at the soil surface and flow across the surface either in sheets or in small rivulets
groundwater
water found in the saturated zone of the subsurface
soil water
water that soaks into and collects in soil
saturated zone
a region of the subsurface where pores are completely filled with water and where water experiences a fluid pressure that is equal to or greater than local atmospheric pressure at the ground surface; the saturated zone is bounded at the top by the water table
unsaturated zone
a zone in a soil or rock between the earth's surface and the water table; pores in the unsaturated zone are partly filled with water and partly filled with air
river discharge
volume of water flowing through a river channel
discharge
the volume of flux of water
hydrology
the study of the occurrence and movement of water on and beneath the surface of the earth, the properties of water, and its relationship with the living and material components of the environment.
recurrence interval
the interval between two events associated with a random variable attaining a value greater than some specified value
soil moisture
water that is held in soils and rocks under pressures less than atmospheric; water in the unsaturated zone
water table
a surface separating the saturated and unsaturated zones of the subsurface, defined as a surface at which the fluid pressure is atmospheric
Properties of water
very abundant, universal solvent, high cohesion, state of aggregation, thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, transparency to EMR
Surface tension
water has a greater attraction internally than for air (high cohesive forces) but is affected by temperature
What is capillarity
suction due to surface tension & wetting
What is the capillary fringe
layer where groundwater deeps up from the water table via capillary action to fill pores
How does water change density as it changes states
Increase density from 100C to 4C (water get colder)
Decrease density from 4C to 0C (to become ice)
How does water temperature affect oxygen content
Lower temperature = more oxygen
Latent heat of vaporization, sublimation and fusion
vaporization: 2256 (100C), 2469 (15C), 2511 (0C) - J/g
sublimation: 2846 J/g (0C)
fusion: 335 J/g (0C)
What is specific heat
energy required to raise one unit mass of water through one unit of temperature
Why does water have a high specific heat capacity
cohesion
How is temperature related to vegetation
Temperature cooler in vegetated areas because energy is put towards evapotranspiration instead of evaporation
Define relative humidity
amount of water in the air vs how much it can actually hold
How does cloud development occur
vapor condense on condensation nuclei to form tiny droplets (many droplets merge to be heavy enough to fall)
what are cloud properties determined by
phase of water
number & size of particles
shape of ice crystals
main way that droplets grow within a cloud
collision & coalescence
what does rain production depend on
cloud's liquid water content
range of droplet sizes
cloud thickness (thin cloud = less water)
updrafts (more updraft = more turbulence = more energy = less likely precip)
electrical charge of droplets & electric field within cloud
State of water at different temperatures in a cloud (ice, water, supercooled)
Ice: < 0
Water: > -40
Supercooled: 0 to -20
What is the Bergeron process
water vapor grow at the expense of ice crystals
vapor pressure difference causes vapor molecules to move from liquid droplet to ice crystal (difference increase as temp decrease)
Ice has a lower vapor pressure than water
Temperature profile for snow
temperatures consistently below 0
Sleet & its temperature profile
rain + snow
<0 --> >0 halfway down
freezing rain/drizzle & temperature profile
supercooled rain that freezes on contact with cold surfaces
> 0 at 1/4 way down and go back to <0 right before reaching ground
ice pellets
frozen rain/drizzle
same as freezing rain/drizzle but temp go back to <0 higher above ground level
Hail & damage it can cause
accretion of supercooled water on graupel, large frozen raindrop or other particle
opaque = freezing instant, transparent = freezing slow
agricultural & infrastructural damage
dew, frost & hoar frost
air becomes saturated around a cooled surface, leading to condensation & deposition
not significant part of hydrological cycle as it doesn't rly change catchment water balance
mist & fog; use as a water supply
low elevation clouds w/ same origin as dew
fog drip where water droplets in air stick to surfaces and can be harvested (normally missed by rain gauges)
rime is similar to fog drip, but its supercooled droplets that freeze on contact
what is cloud seeding
prevent hail damage by injecting enough nuclei to reduce size or induce precipitation
chemical composition of precip depends on
nuclei and aerosols (any solids or liquids suspended in atmosphere)
orographic lifting
air masses are forced up over topography and there's more precipitation on west side of mountain
frontal lifting
warm air forced up & over cold, denser air
cold front - larger area, thunderstorms
warm front
convergent lifting
net horizontal inflow of air into a region - air converge at surface and is forced to rise
normally occurs in areas with low pressure
convectional lifting
heat earth surface -> warm air rise -> cool air sink
very localized, associated with thunderstorms
Rain gauge
Measure precipitation (recording)
manually measure depth of a bucket everyday at the same time
must be put in clearings & usually only located in populated areas
capping/plugging
Weighing gauge
Measure precipitation (recording)
measure total precipitation over a fixed time interval
Tipping bucket
Measure precipitation (recording)
measure number of tips per interval
can get overwhelmed by high intensity precipitation
capping/plugging can be an issue
Radar to measure precipitation
surrogate measurement
record time & intensity of reflection
satellite remote sensing
surrogate measurement of precip
2 sensors - radar (size, type & volume) & microwave sensor (intensity)
wind undercatch
wind turbulence at mouth of gauge result in not all precip getting collected
error increases with windspeed
error can be lessened using shielded gauges
methods of estimating precipitation over a drainage basin
1. arithmetic average (very inaccurate)
2. thiessen weighted average (when gauges not uniformly distributed or large precip differences within area)
3. isohyetal method: req a lot of data (lines of equal precip, measure area between isohyetes & calculate weighted precip)
Probability of exceedance & recurrence interval
how likely rainfall will exceed a certain amount
Intensity-Duration-Frequency (IDF) Analysis
how frequently we get a storm of a certain size & how long it rains at a high intensity
design storm drains, flood control structures, bridges etc.
impacts of land cover or management changes
Annual maxima series
identify the largest rain events each year at different durations
plot intensity vs duration for different return periods
essential factors for evaporation
energy supply, available water supply and a vapor deficit
define transpiration
phase change of liquid to gas occurring through the stomata
define potential evaporation
theoretical evaporation from a terrestrial surface if water supply is unlimited
measured using amt of ENERGY available to drive evaporation
equation for energy available for evap
Eevap = Qsn + Qln + Qh + Qg
Eevap: energy available for evap
Qsn: net SW radiation
Qln: net LW radiation
Qh: sensible heat flux (diff in temperatures)
Qg: soil heat flux