Lec: Fungal Diseases
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Three Basic Forms of Fungal Disease
Mycosis is the direct invasion of cells by fungus
Mycotoxicosis results from ingestion of fungal toxins
Allergic diseases: esp. occur when fungal colonies develop in the lungs
Aspergillus spp.
saprophytic filamentous fungi that occur worldwide
grow in damp soils, decaying vegetation, organic debris, feed grains
species most commonly infected include waterfowl, gulls, and corvids - but all birds and most mammals should be considered potential hosts
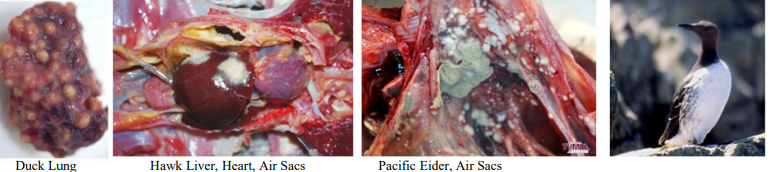
Aspergillosis
aerosolized spores are inhaled, but dissemination through the gut, blood, or lymph is possible
disease is most commonly associated with young animals or w/ stress and immunosuppression
colonization results in erosion of tissues leading to the possibility of dissemination and host response
signs: pneumonia, may open and close their bills when breathing, wings may drop, may seem mildly to severely depressed
Chytrid fungus (Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis (Bd) and B. salamandrivorans (Bsal))
Hosts: amphibians, but not all equally susceptible
found in water or soil, asexual reproduction occurs in the zoosporangium and zoospores are the infective stage
attacks keratin (tough, fibrous protein) that forms a resistant later in animal skin, and this later is damaged by chytridiomycosis
toxic, proteolytic enzymes are released by the fungus
Loss of electrolytes negatively affects osmoregulation and/or oxygen uptake
what are the two hypotheses that explain how Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis (chytrid fungus) directly kills its host
Reduce anthropogenic stress, promote foodwebs to increase micropredators on zoospores, and consider in-situ treatment using itraconazole
what are some management techniques for dealing with chytrid fungus
tadpoles have less keratin in their skin, tooth rows, etc. than adults and this fungus primarily attacks keratin
Why aren’t tadpoles as susceptible to chytridiomycosis as are metamorphosed frogs?
White-Nose Syndrome (caused by Pseudogymnoascus destructans)
DH: Vespertillionid bats in the NE US and SE Canada
No IH
Causes irritation that unnecessarily awakes the bats from torpor, causing them to starve due to inadequate fat reserves necessary to support extra activity
damaged wings = increase heat loss during hibernation, arousal of bats, and impaired flight
regulation of human access to caves, mines, and tunnels that serve as hibernacula
decontamination of tourists, researchers, and spelunkers at cave entrances
temp control to increase cave heat beyond the optimal range of the cold-loving fungus (how would this affect other wildlife)
fungicide spray in caves
treatment/rehabilitation
soil bacteria that inhibits mold growth
a vaccine
what are some of the management tactics for battling white nose syndrome
arousal of bats during hibernation, increased heat loss during hibernation, impaired flight due to wing damage, and skin-mediated fluid loss and dehydration
Although the most common cause of death is still debated, Pseudogymnoascus destructans is thought to kill bats by which of the following mechanisms?
bats provide important ecosystem services, Pseudogymnoascus destructans kills a high % of bats in hibernaculae, several bat species of conservation concern overlap the range of the epizootic, and current management strategies haven’t been enough to stop the spread
The greatest risks of white-nosed syndrome in bats are related to which concept(s)?
Ophidiomyces ophiodiicola
what fungus causes Snake Fungal Disease (SFD)
Snake Fungal Disease (SFD)
opportunistic soil fungus in a variety of snakes in the Eastern US that causes widespread morbidity and mortality
No IH or DH (opportunistic)
fungus attacks keratin
causes lesions, pneumonia, and even liver disease
Management of SFD (caused by Ophidiomyces ophiodiicola)
concern that the pet trade may spread SFD
public education and customs inspectors are essential
fungus is inhibited at a temp below 7 C, snakes that hibernate above this temp may be more susceptible
snakes can be treated with antifungal and treated with thermal and nutritional supportive therapy