Hair analysis
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
what are the longitudinal components of a hair?
Root-shaft-tip
hair structure from outside in
cuticle, cortex, medulla
Cuticle (Hair)
outermost layer, consists of a single layer of thin, flat cells that are the most heavily keratinized
How are the scales on the cuticle oriented?
Towards the distal end (tip)
What is the main function of the cuticle?
Chemical and structural protection and resistance
What is one of the main conclusions you can draw from analyzing the cuticle of hairs?
Differentiating between human and animal hair
Exocuticle
The rigid, sclerotized outer layer of the procuticle separated into a-layer and exocuticle
a-layer
part of the cuticle, situated just beneath the outermost cuticle layer
- rich in cysteine
Which cuticle layer is Amorphous, Rich in keratin and keratin-associated proteins (KAP)?
Exocuticle
endocuticle
The inner-most layer of the cuticle. It is amorphous and derived from nucleus and cells organelles
Cortex
Main body of the hair shaft made of spindle shaped cortical cells (80 to 115 µm long)
Which layer of hair contains the natural pigments?
cortex
Unit length filament (ULF)
32-mer (8x tetramer)
Keratin --> intermediate filament --> hair shaft
a-helix --> dimer --> tetramer--> 32-mer (ULF)--> elongation of ULF --> KIF --> macro fibrils made by Keratin associated proteins --> disulfide bonds to make shaft
cross linking
a way to harden polymer; disulfide bonds between keratin filaments hold them together
Orthocortical cells
twisted cortical cells
Mesocortical cells
straight cortical cells
Paracortical cells
in between twisted and straight
Hair is a bundle of fibers connected by crosslinks
true
What defines the curvature of hair?
The difference in length of ortho cortical and paracortical cells
Pheomelanin
Melanin that provides yellow pigment yo natural hair colors
Eumelanin
melanin that provides black pigment to hair
medulla (hair)
core of loosely arranged keratin cells and air spaces
The main component of the medulla is
trichohyalin and citrulline
which layer is predominant in thick hair, not always present, and can differ for a single individual in different hairs
medulla
Medulla hair and shape depends on
the curl
The flatter the medulla, the __________ the hair
curlier
If a cross section was done of a hair follicle, the different components (from inside to outside) would be
hair shaft --> inner root sheath --> outer root sheath --> fibrous sheath
Anagen
First stage of hair growth during which new hair is produced/The period of active growth - 80-95% of total hair for humans - 400 µm/day
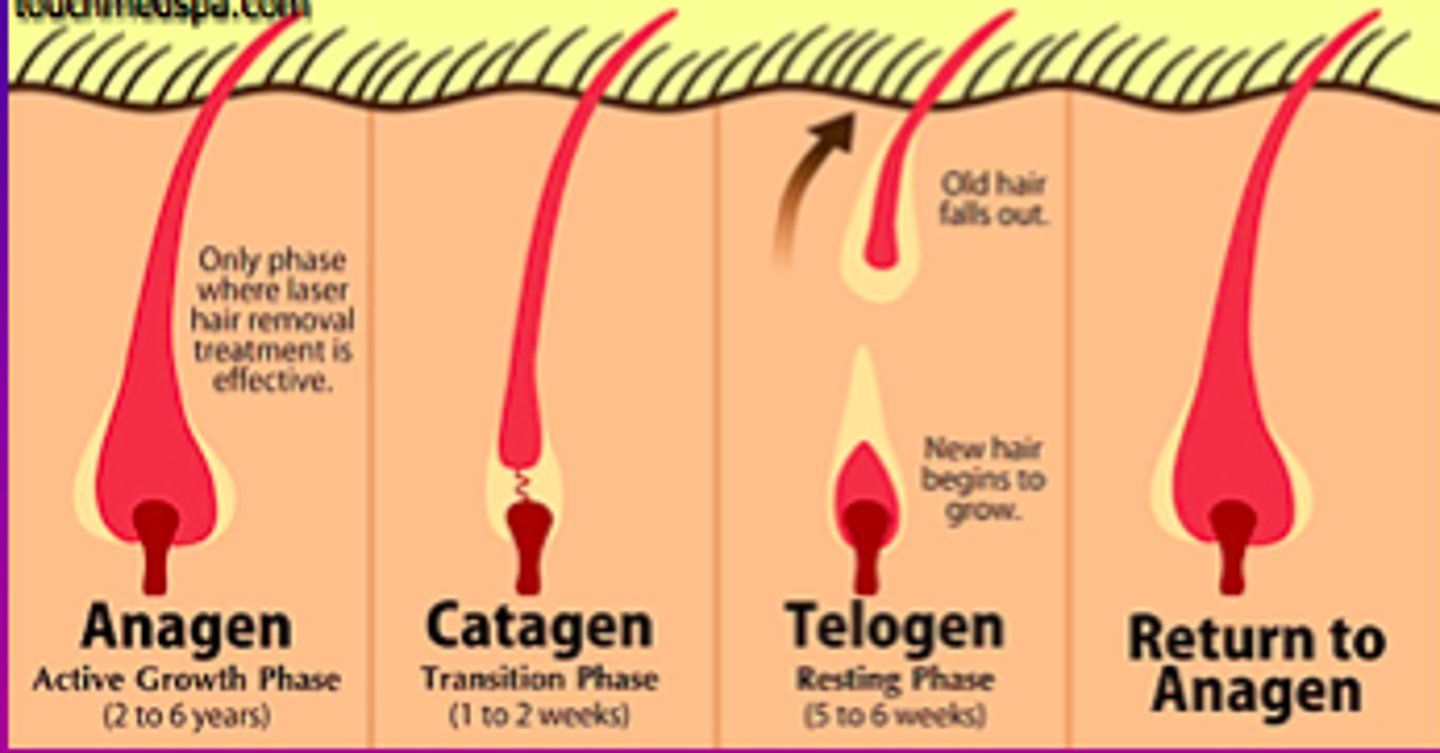
catagen
The period of break down and change of hair growth (1-2 weeks)
telogen
Also known as resting phase; the final phase in the hair cycle that lasts until the fully grown hair is shed. - 2-3 months - 5-15% of total human hair
Exogen
the stage of the hair cycle where old hairs are shed.
Kenogen
balding
most people shed _____ hair/day
50-150
Human hair during life
Luango (fetus hair)--> Vellus (child) --> terminal (puberty)
What characteristic of hair can be used to distinguish it from other fibers?
scales
What characteristic of hair can be used to distinguish it from animal hair?
scale pattern, medulla, root
coronal cuticle
crown like cuticle found in cats
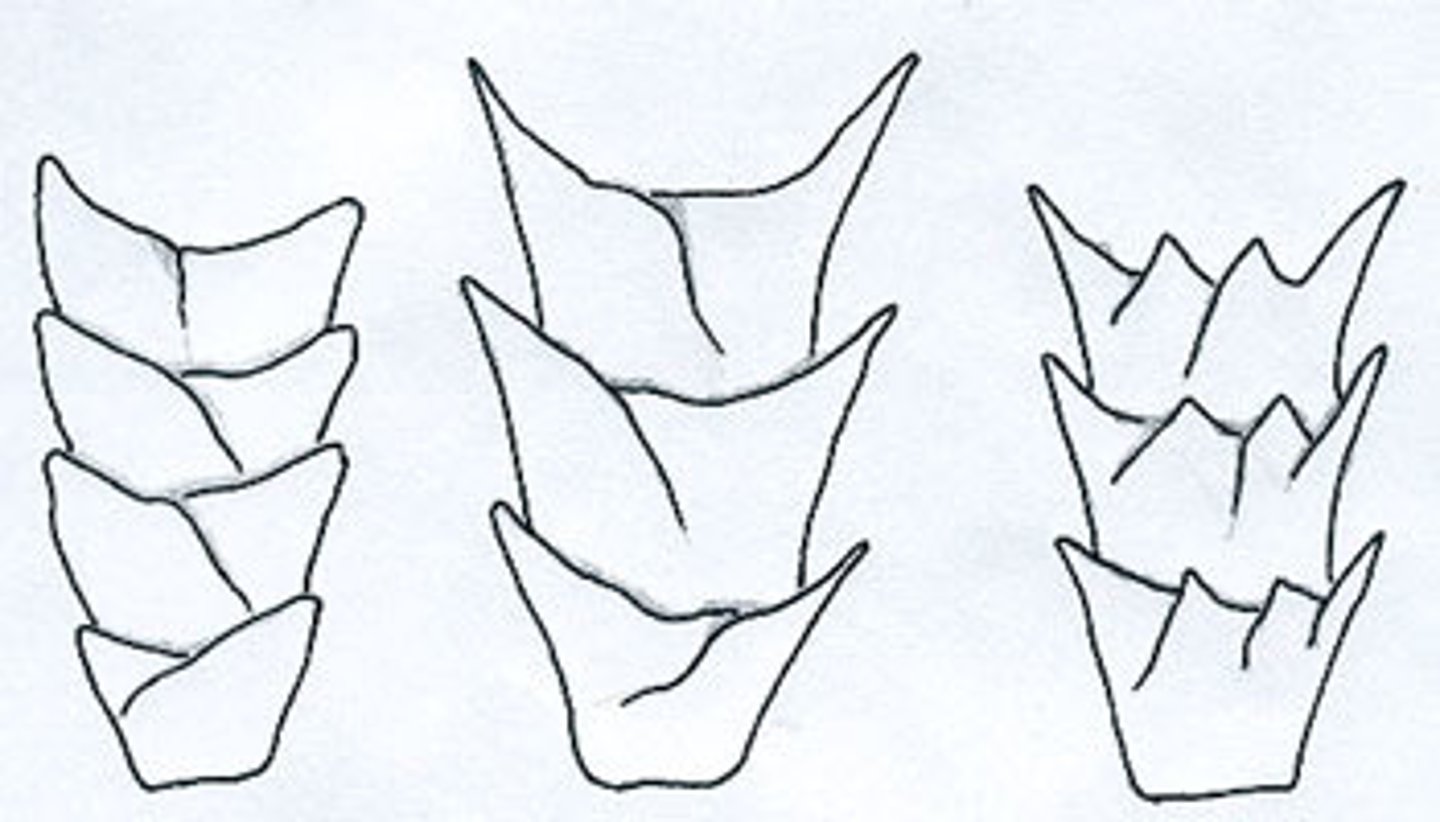
spinous scales
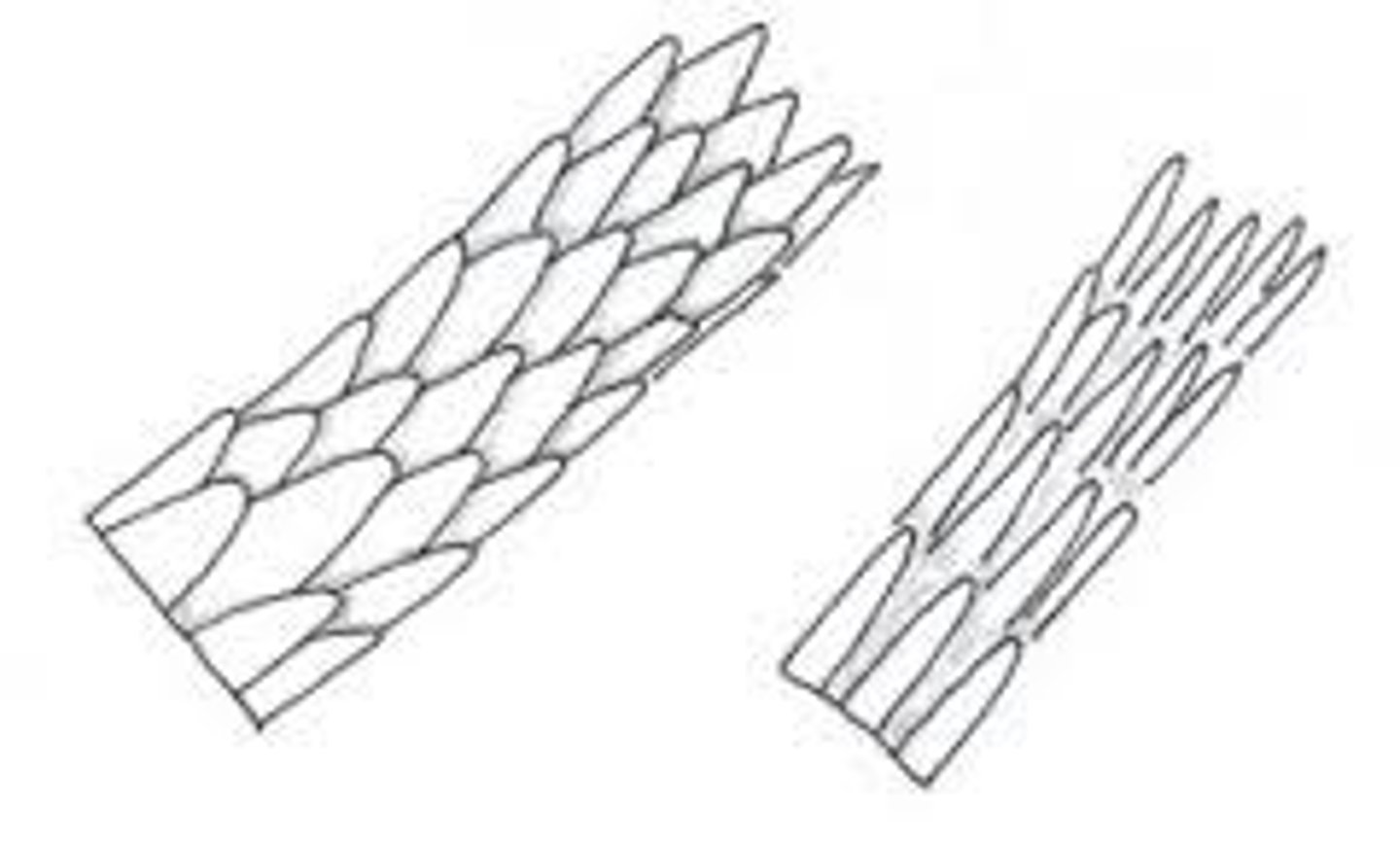
imbricate scales
overlapping scales
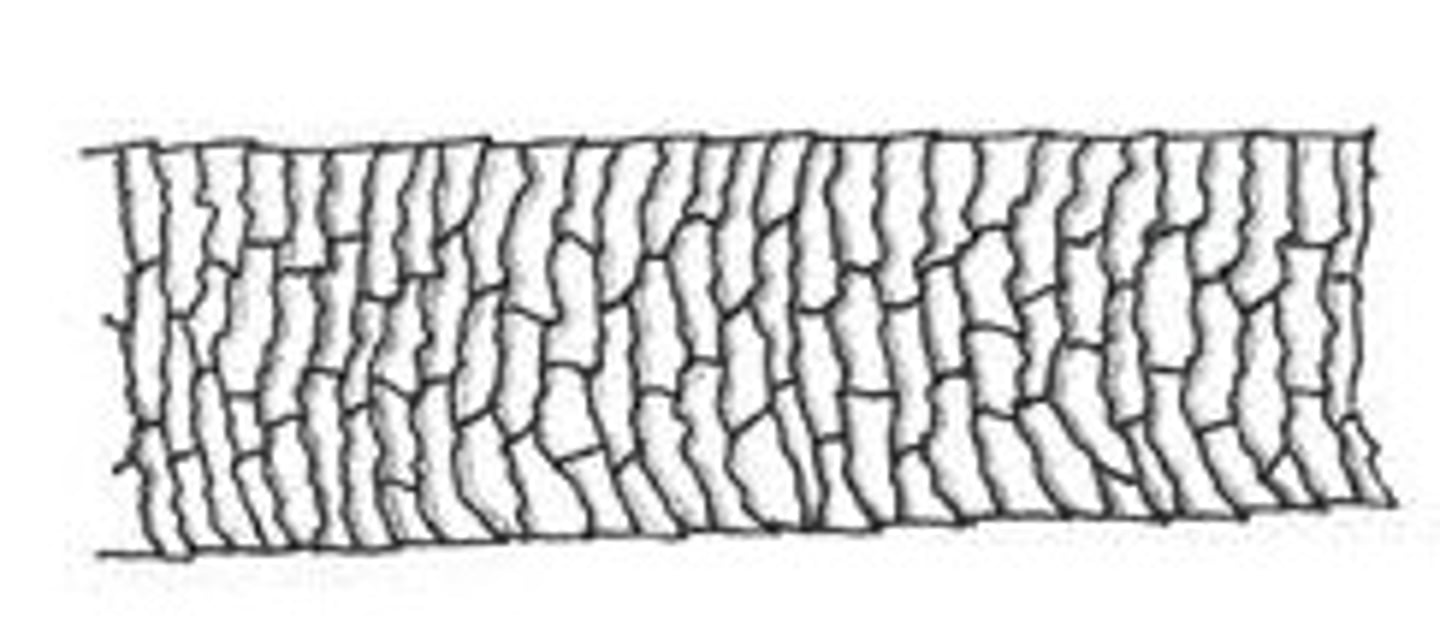
Medullary index
ratio medulla diameter/hair diameter
Human MI
less than 1/3
Animal MI
greater than 1/2
Scalp hair
Long with moderate shaft diameter and diameter variation
- Medulla absent to continuous and relatively narrow
- Often with cut or split tips
- Can show artificial treatment, solar bleaching, or mechanical damage
- Soft texture, pliable
pubic hair
Shaft diameter coarse with wide variations and buckling
- Medulla relatively broad and usuallycontinuous when present
- Root frequently with follicular tissue
- Tip usually tapered, rounded, or abraded
- Stiff texture, wiry
Limb hair
- Diameter fine with little variation
- Gross appearance of hair is arc-like in shape
- Medulla is discontinuous to trace with a granular appearance
- Tips usually tapered, often blunt and abraded, rounded scale ends due to wear
- Soft texture
Facial Hair
- Diameter very coarse with irregular or triangular cross-sectional shape
- Medulla very broad and continuous, may be doubled
- Usually cut
ovoid bodies
Oval or round pigmented bodies usually found in the hair cortex
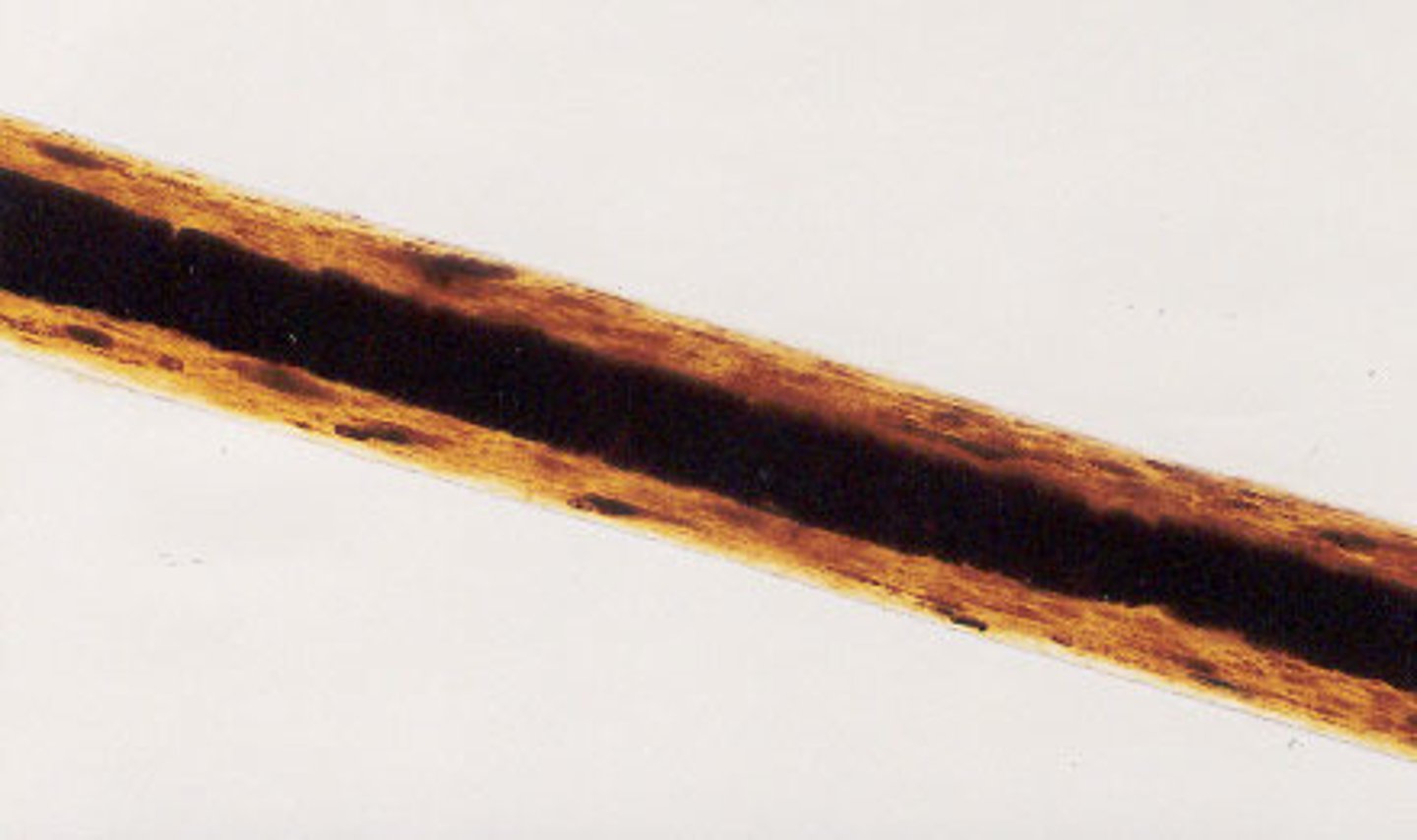

Human hair
- imbricate scale pattern
- medullary index < 1/3
- consistent pigmentation along shaft
- uniform pigmentation towards cuticle
- club shaped root
Animal hair
Spinous or coronal scale pattern
- medullary index > 1/2
- banded pigment along shaft
- pigment centrally distributed towards medulla
- various root shapes