AP Bio Unit 3 Cellular Energetics
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
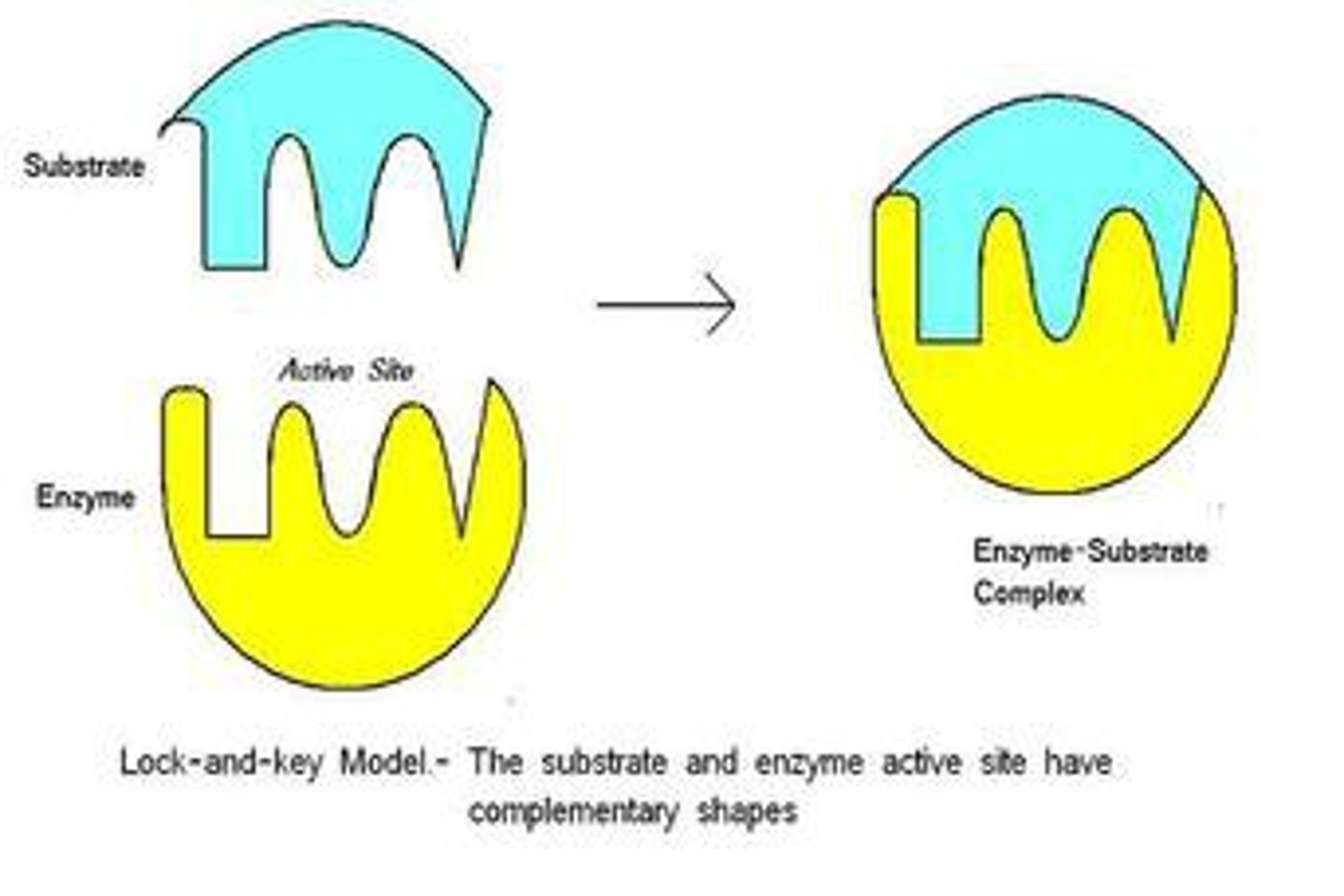
Enzyme
a substance produced by a living organism that acts as a catalyst to bring about a specific biochemical reaction.
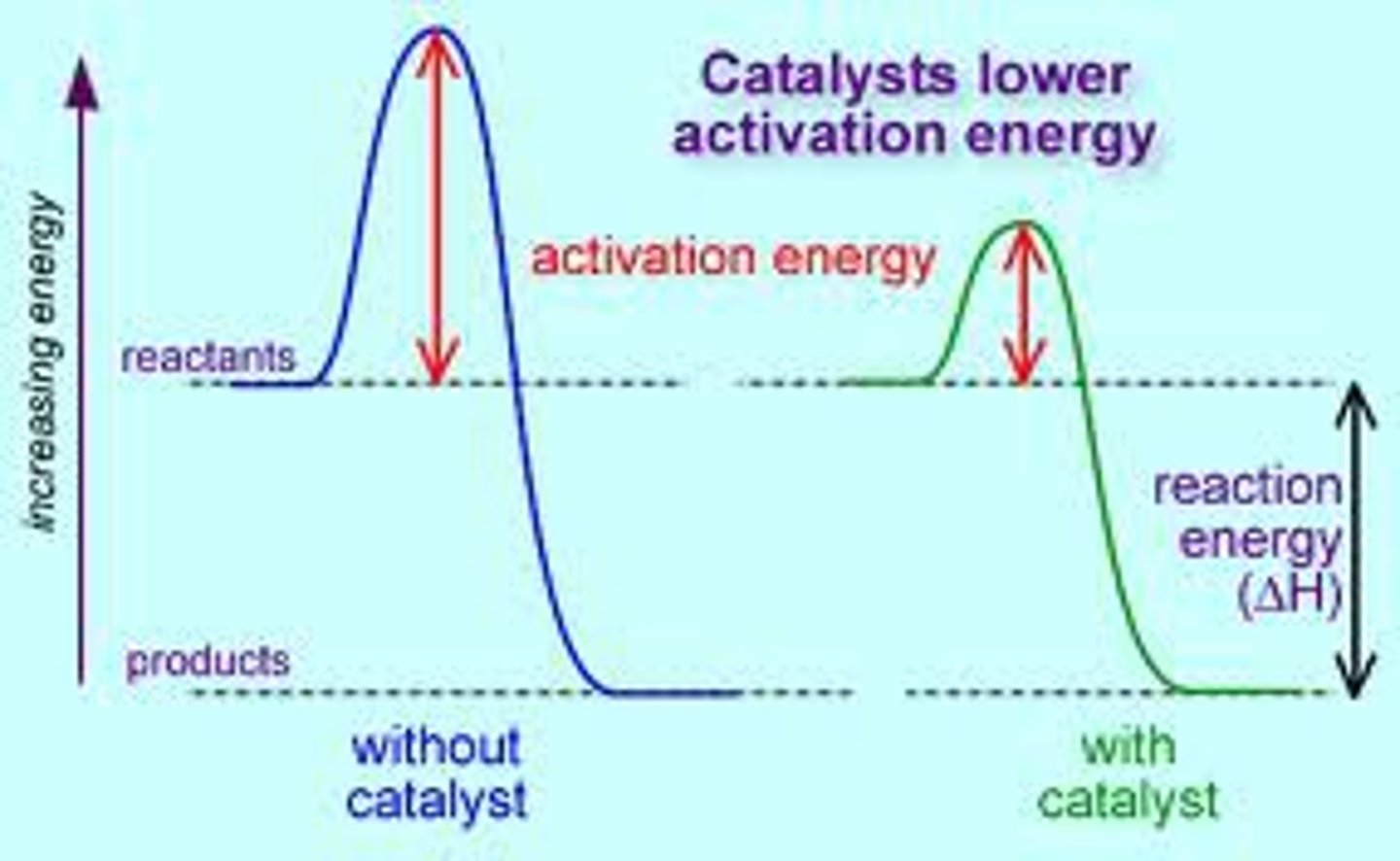
catalyst
substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction by reducing activation energy
Enzyme Properties
- specific, usually only catalyze one reaction because only one complementary substrate will fit into the active site.
- Active site's shape determined by enyzme's tertiary structure.
-Different enzyme = different tertiary structure therefore different shaped active site
- if tertiary structure is altered then shape of active site is altered substrate won't fit into active site so enzyme-substrate complex can't form.

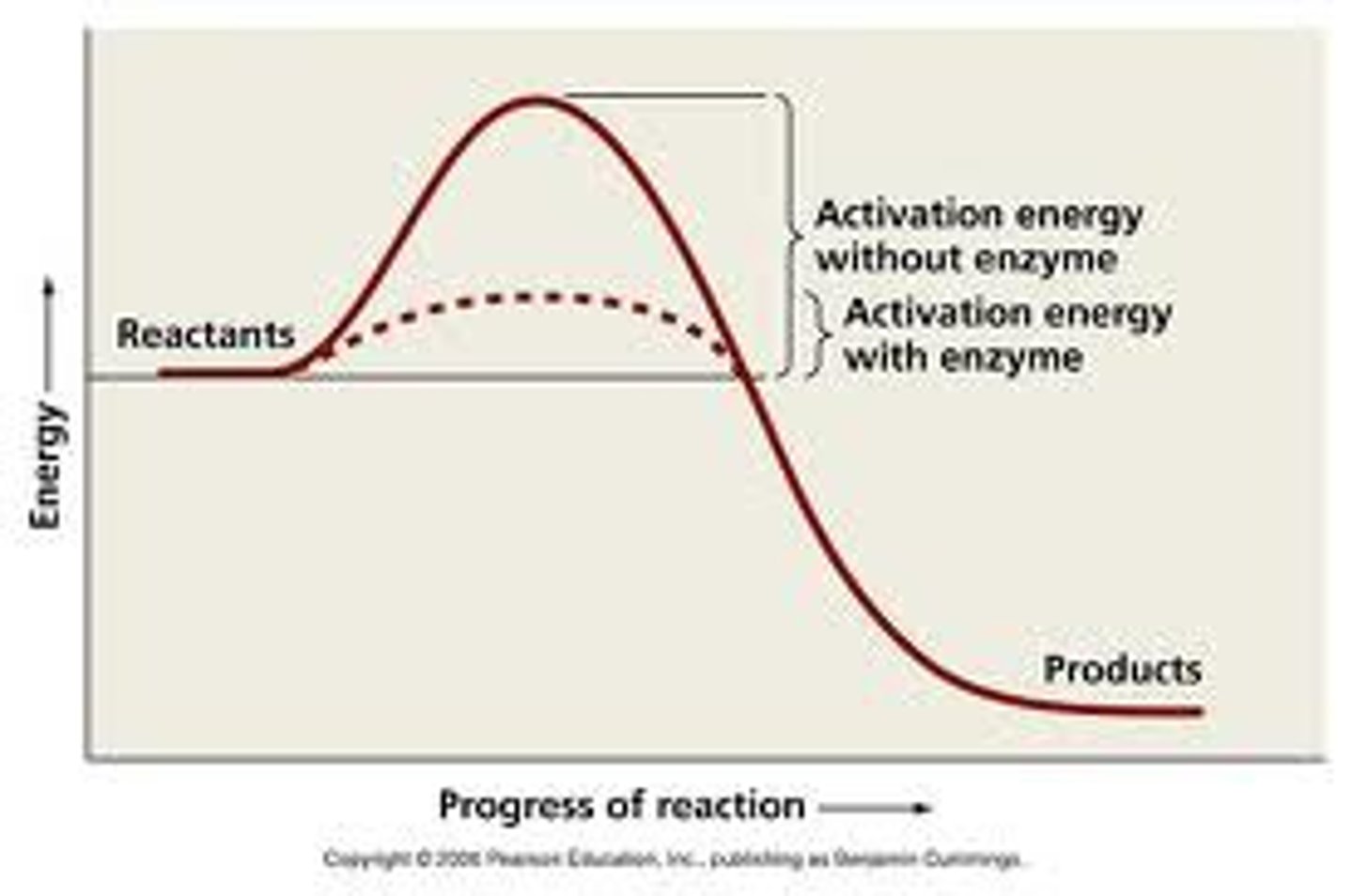
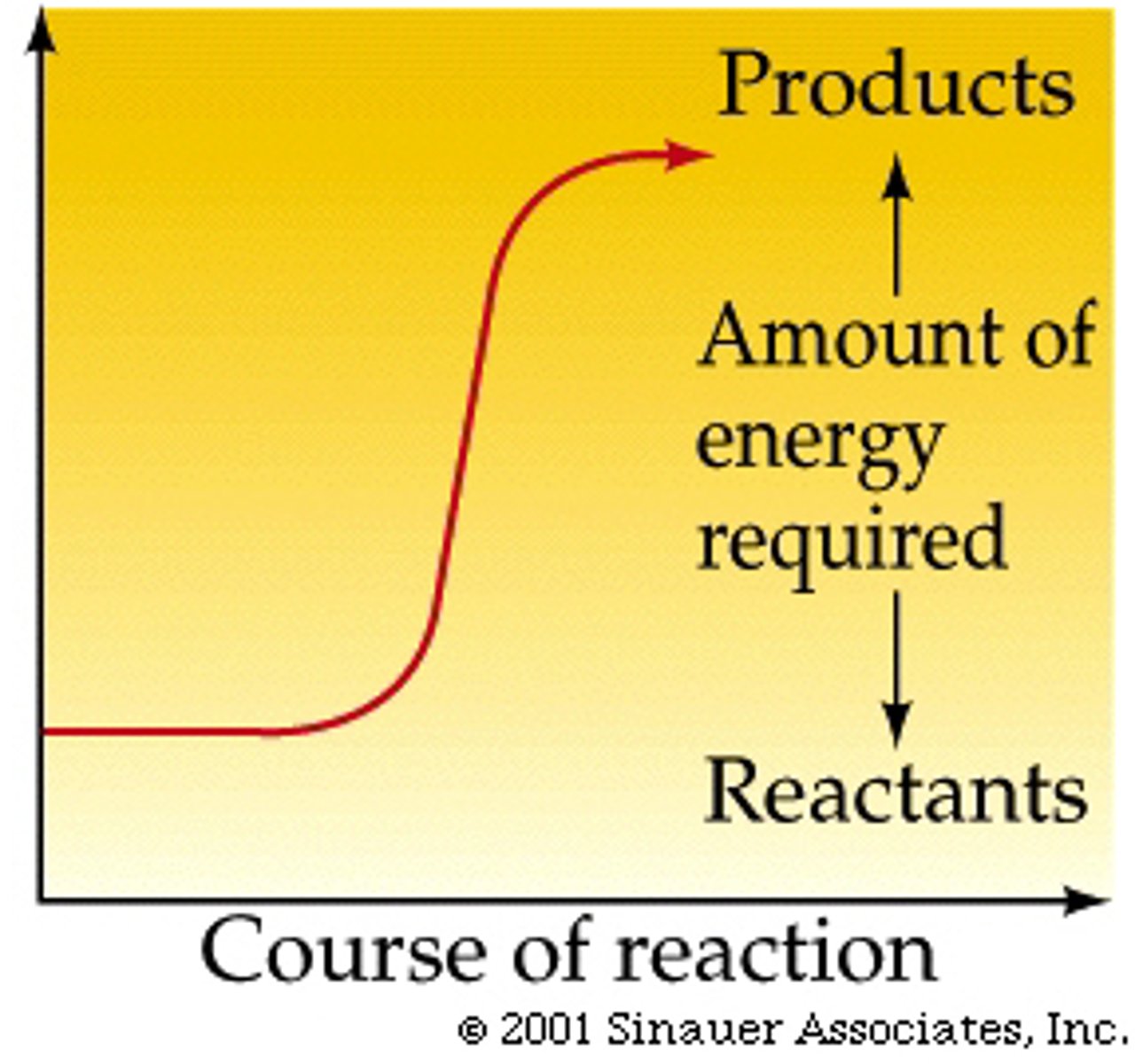
Activation Energy
the minimum amount of energy required to start a chemical reaction
Denaturation
A process in which a protein unravels, losing its specific structure and hence function; can be caused by changes in pH or salt concentration or by high temperature. Also refers to the separation of the two strands of the DNA double helix, caused by similar factors.
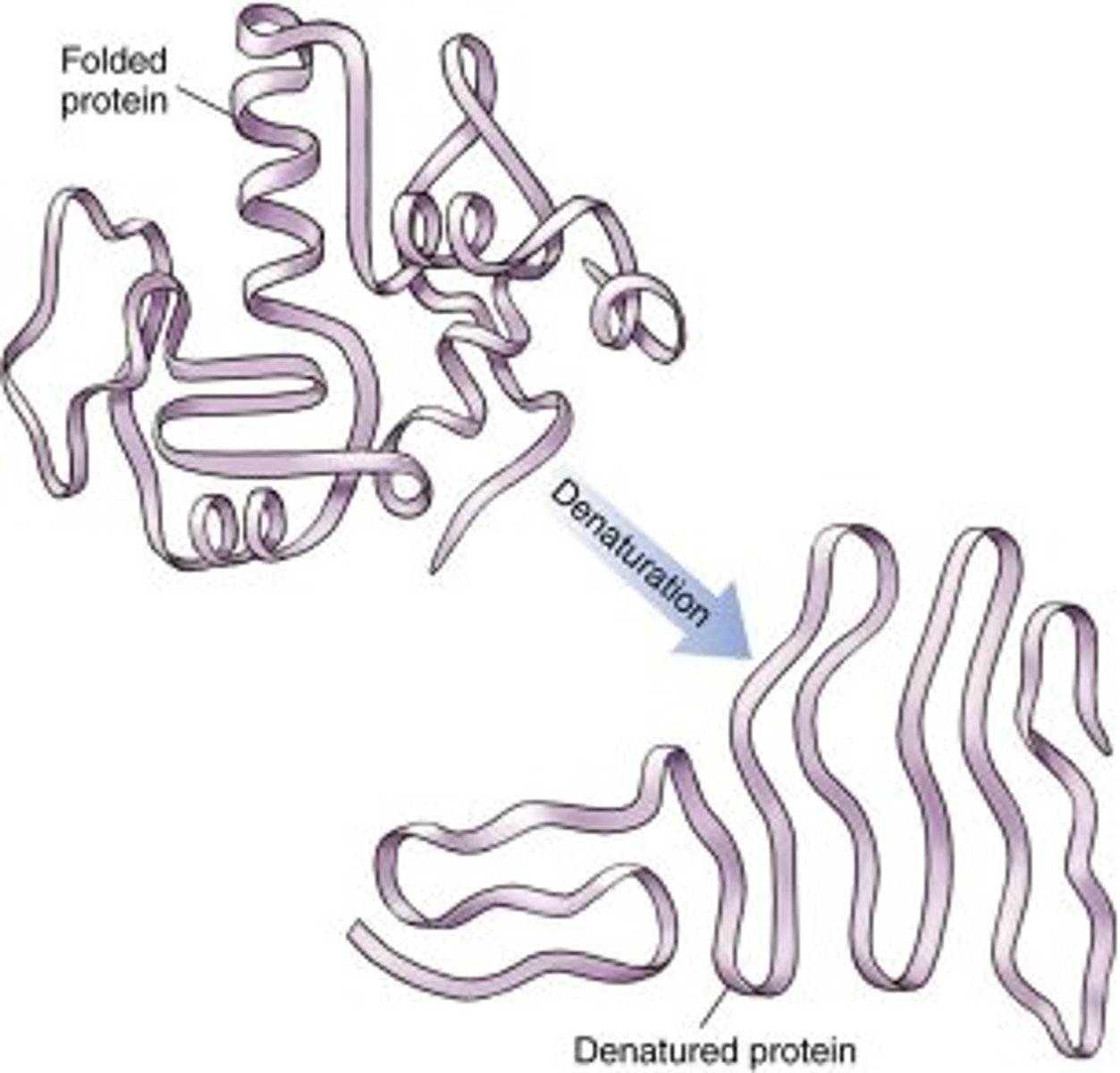
Causes of Denaturation
1. heat
2. acid
3. bases
4. alcohols
5. heavy metals
6. agitation
7. pH

Renaturation
Regaining the correct tertiary structure after denaturation of a protein
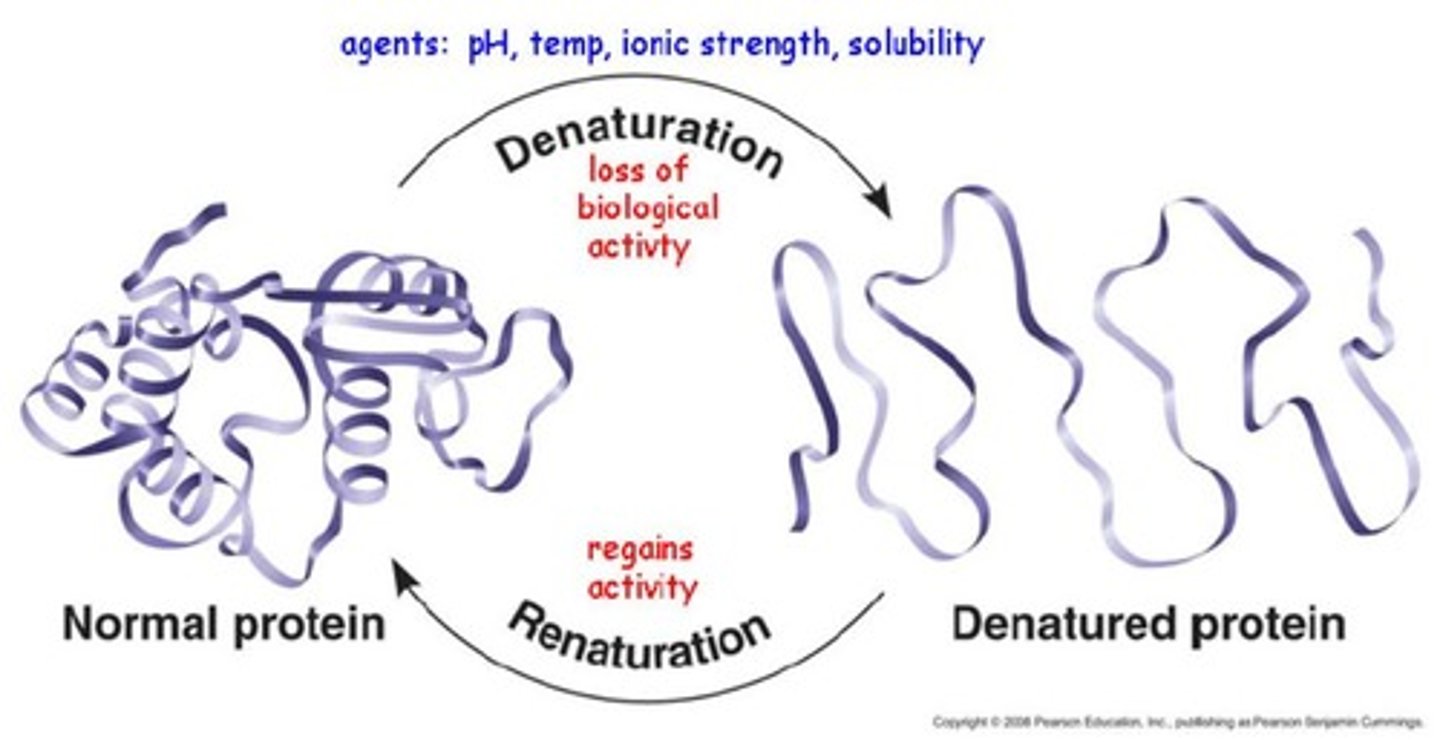
Enzyme efficiency is determined by
relative concentration of substrates and product, temp, pH
pH
measurement of H+ ions in a solution

Base pH
A substance that decreases the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution. Number > 7

Acid pH
A substance that increases the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution. Number < 7
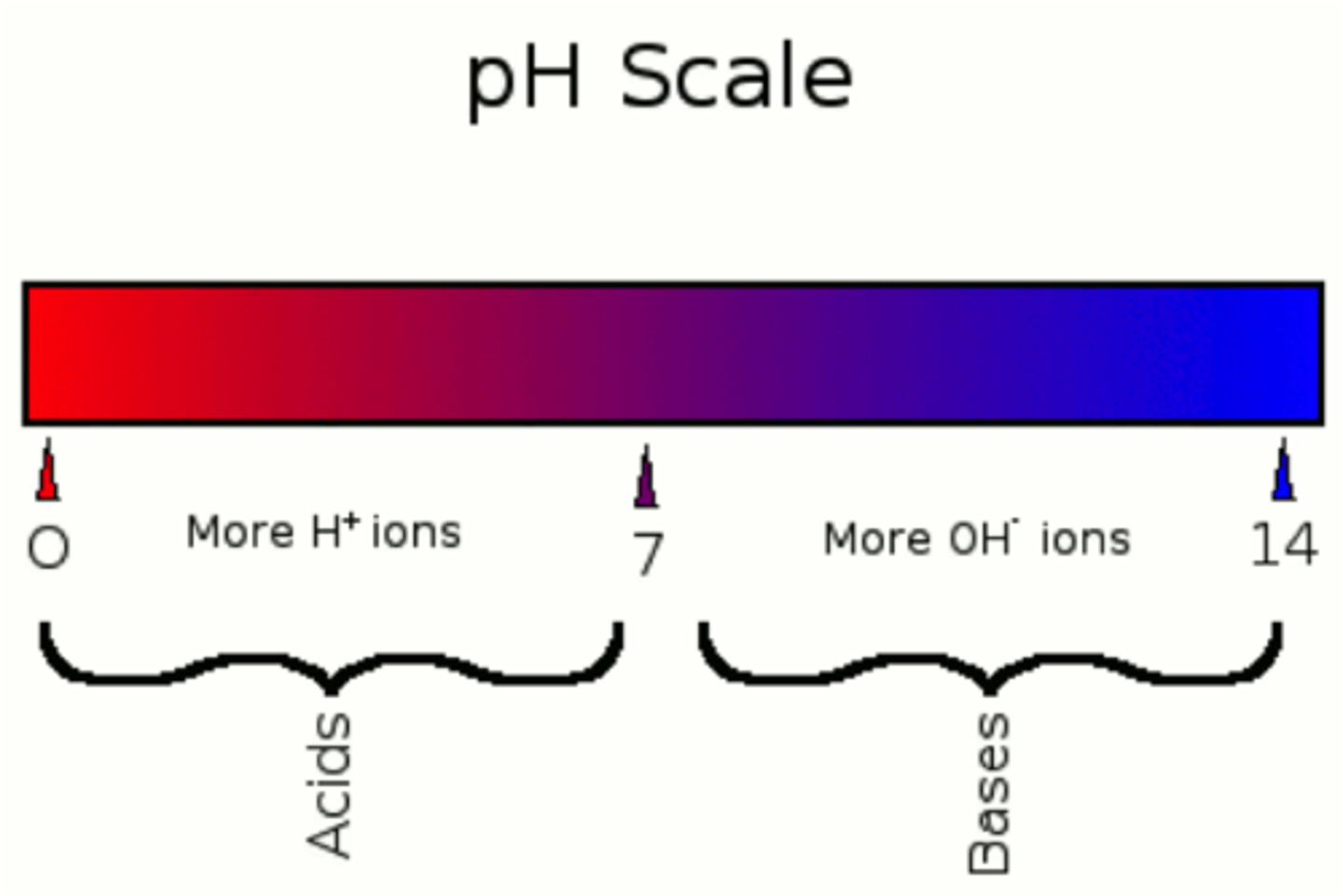
Neutral pH
a balance of H+ and OH—
pure water = 7.0

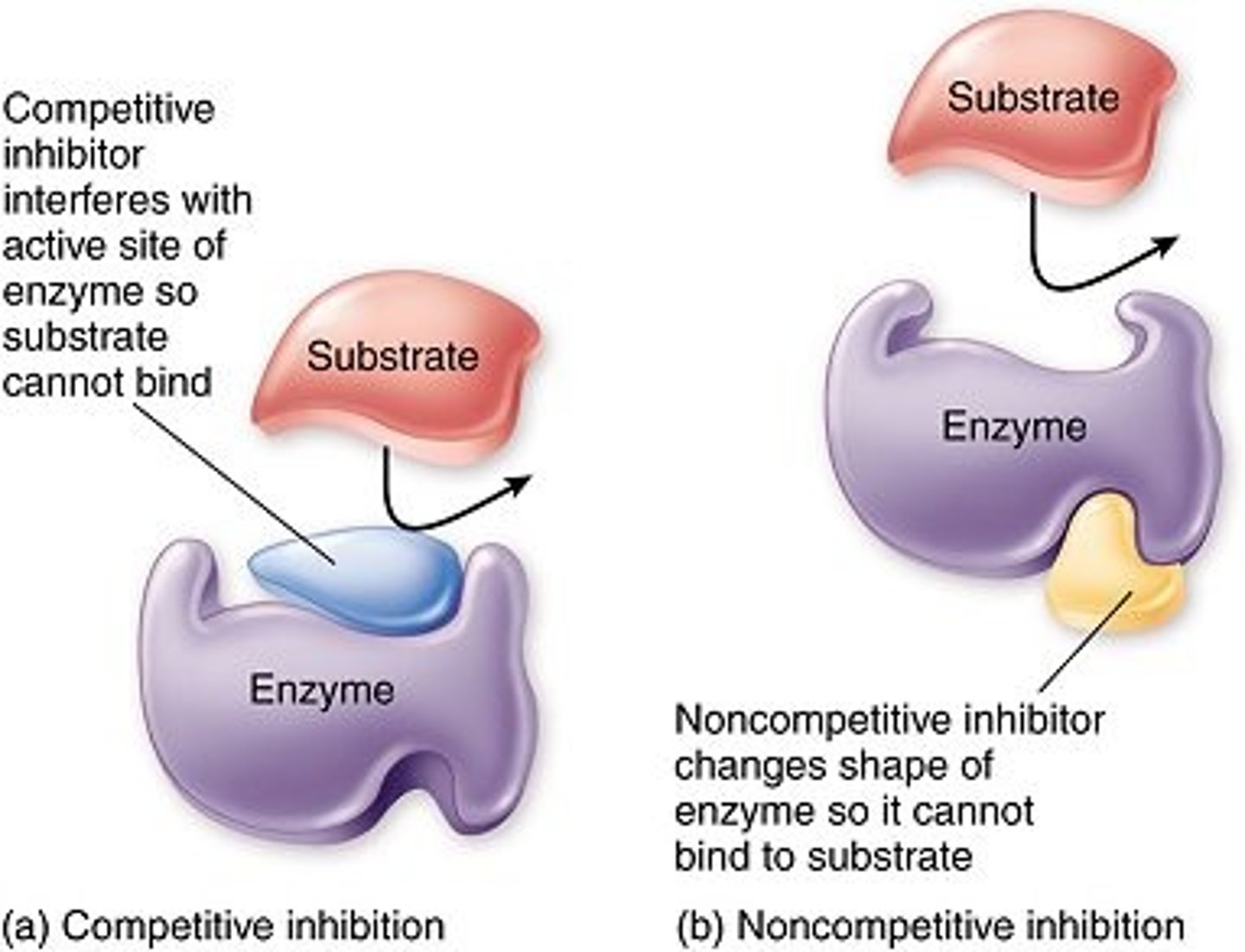
Competitive Inhibition
Inhibition of an enzyme's ability to catalyze a chemical reaction via a non-reactant molecule that competes with the substrate(s) for access to the active site.
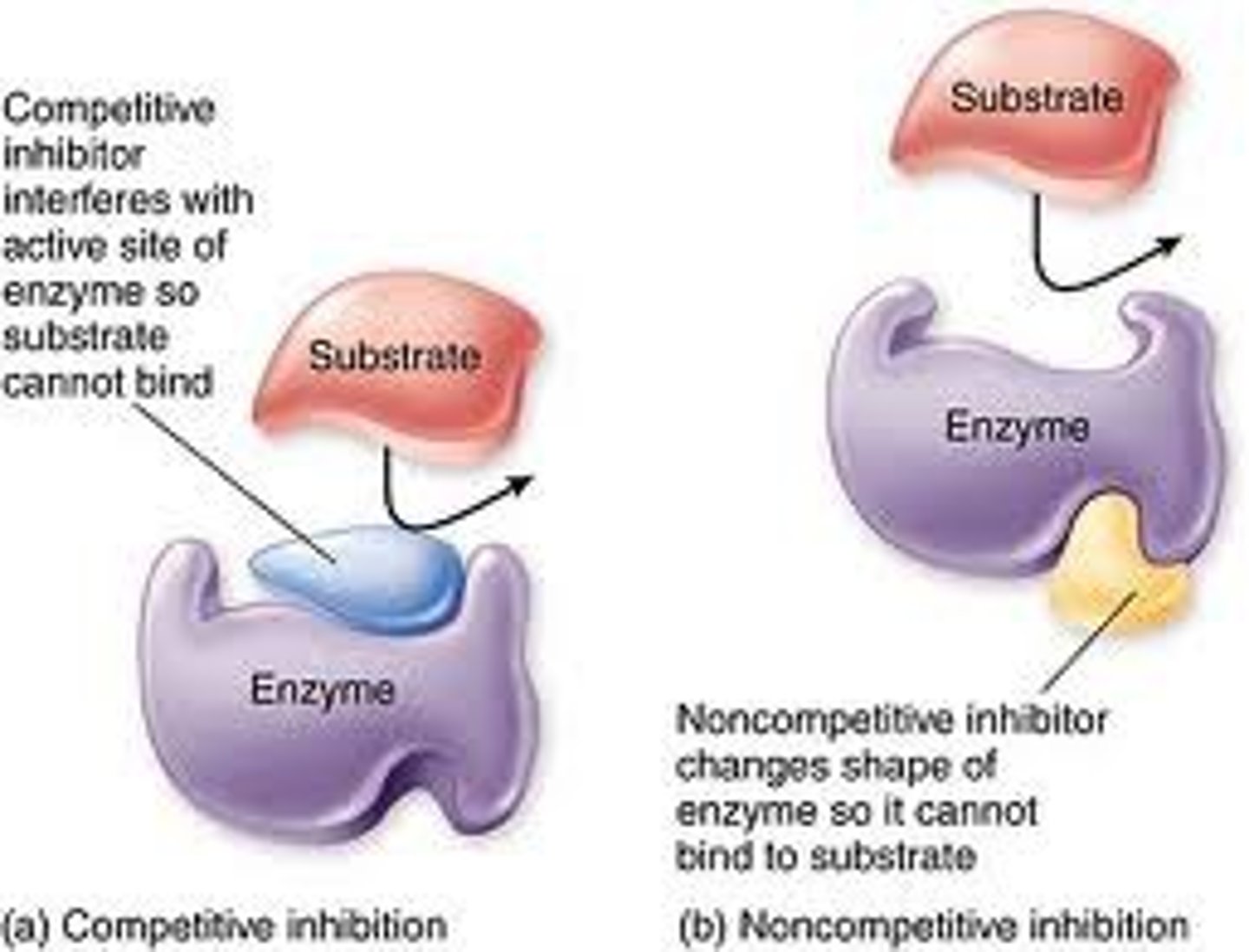
Reversible Inhibition
competitive inhibitors bind to active site; noncompetitive inhibitors bind to allosteric site
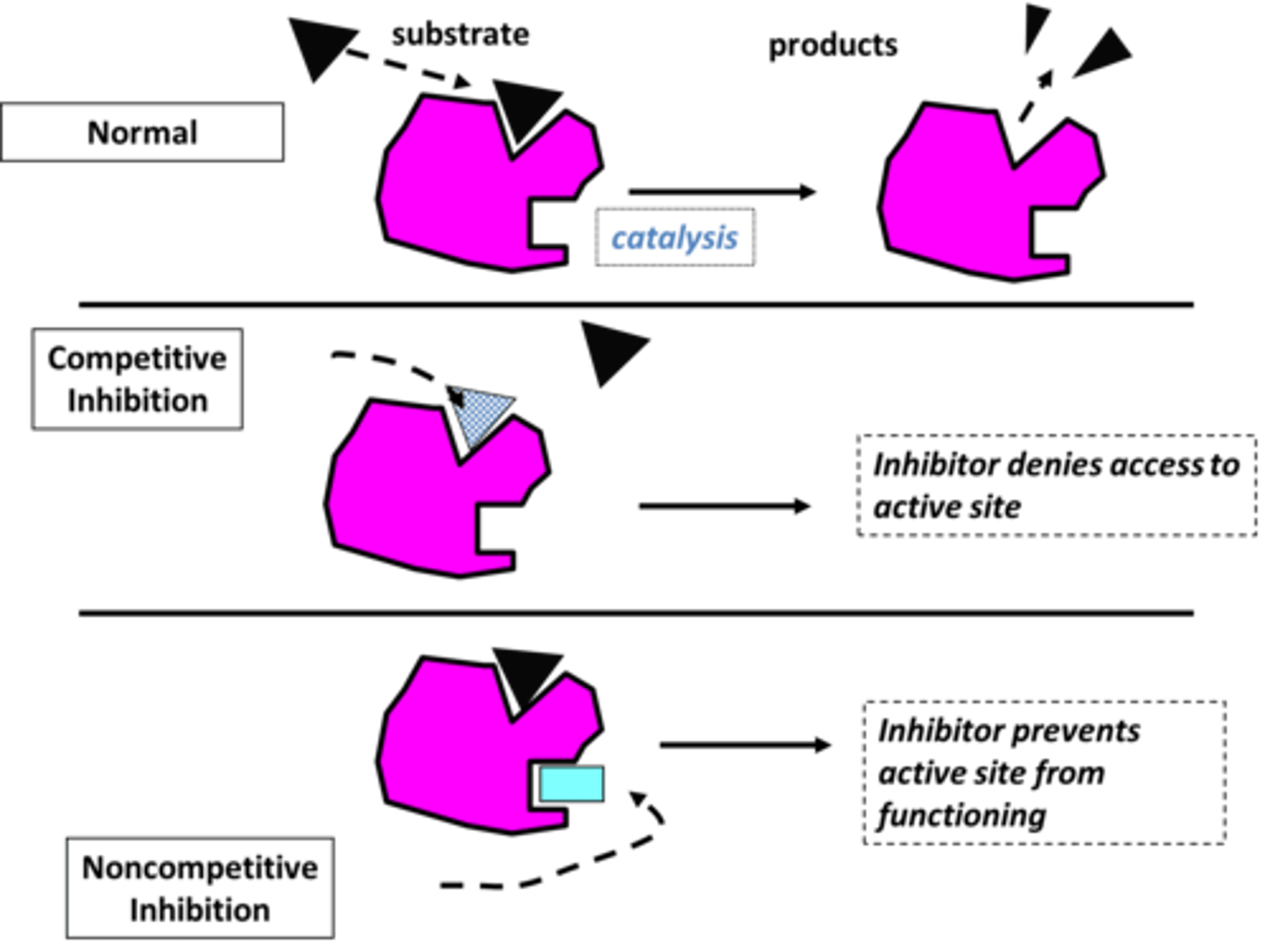
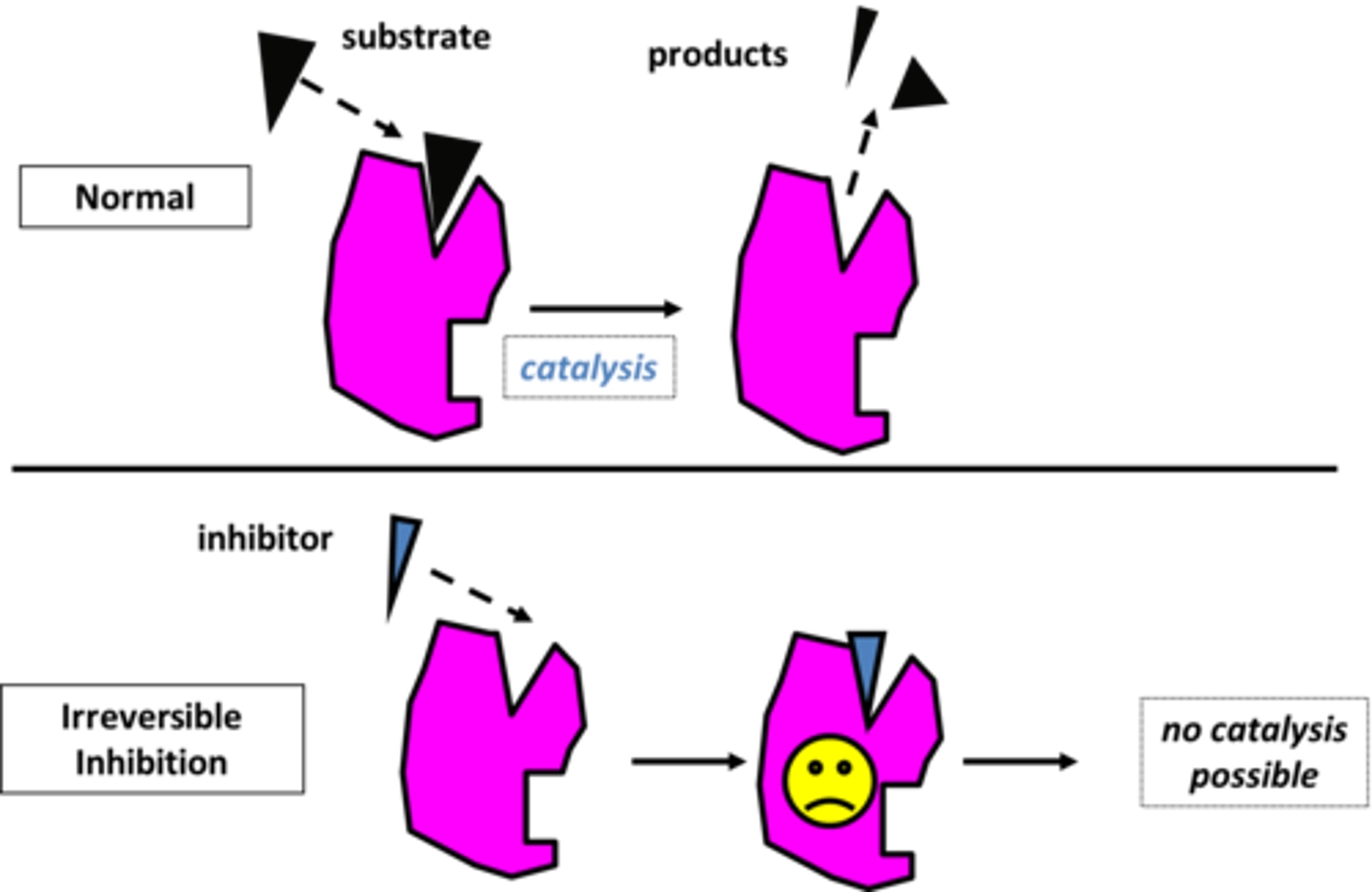
Irreversible Inhibition
alters the enzyme in such a way that the active site is unavailable for a prolonged duration or permanently; new enzyme molecules must be synthesized for the reaction to occur again
Non- Competitive Inhibition
a molecule that binds to an enzyme at a location outside the active site and inhibits the enzyme's function, changes shape of enzyme active site
Cellular Energy
needed by cells to to work; found in ATP; stored in chemical bonds; released when chemical bonds are broken

Endergonic reaction
Reaction that absorbs free energy from its surroundings.
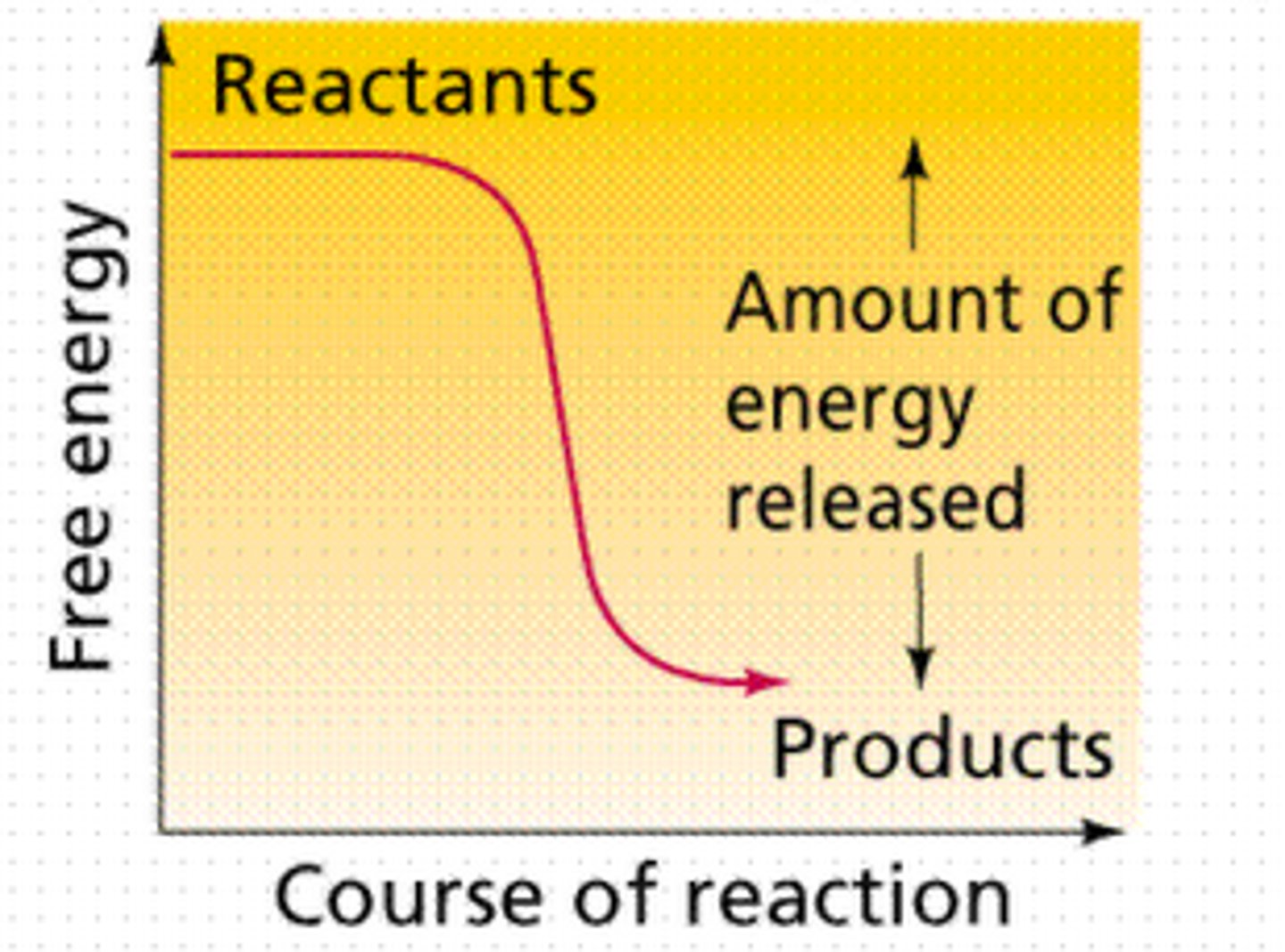
Exergonic Reaction
A spontaneous chemical reaction in which there is a net release of free energy.
Sequential System
Energy related pathways in biological systems are sequential for control and efficiency
Product of reaction in metabolic pathway usually the reactant for the next step
Photosynthesis
Conversion of light energy from the sun into chemical energy, first evolved on prokaryotes (cyanobacteria)
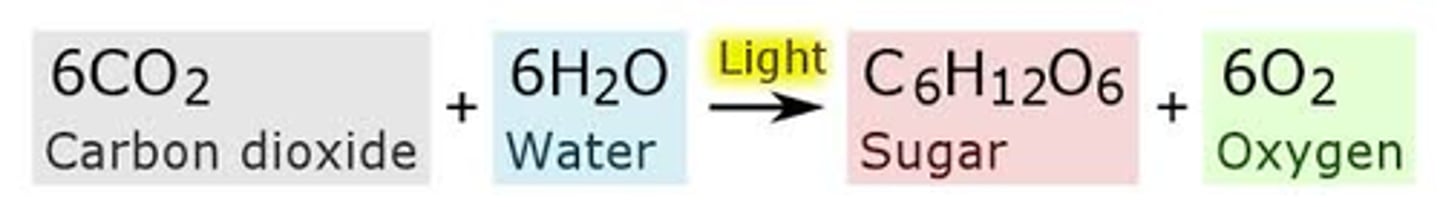
Light Dependent Reactions
reactions of photosynthesis that use energy from light to produce ATP and NADPH
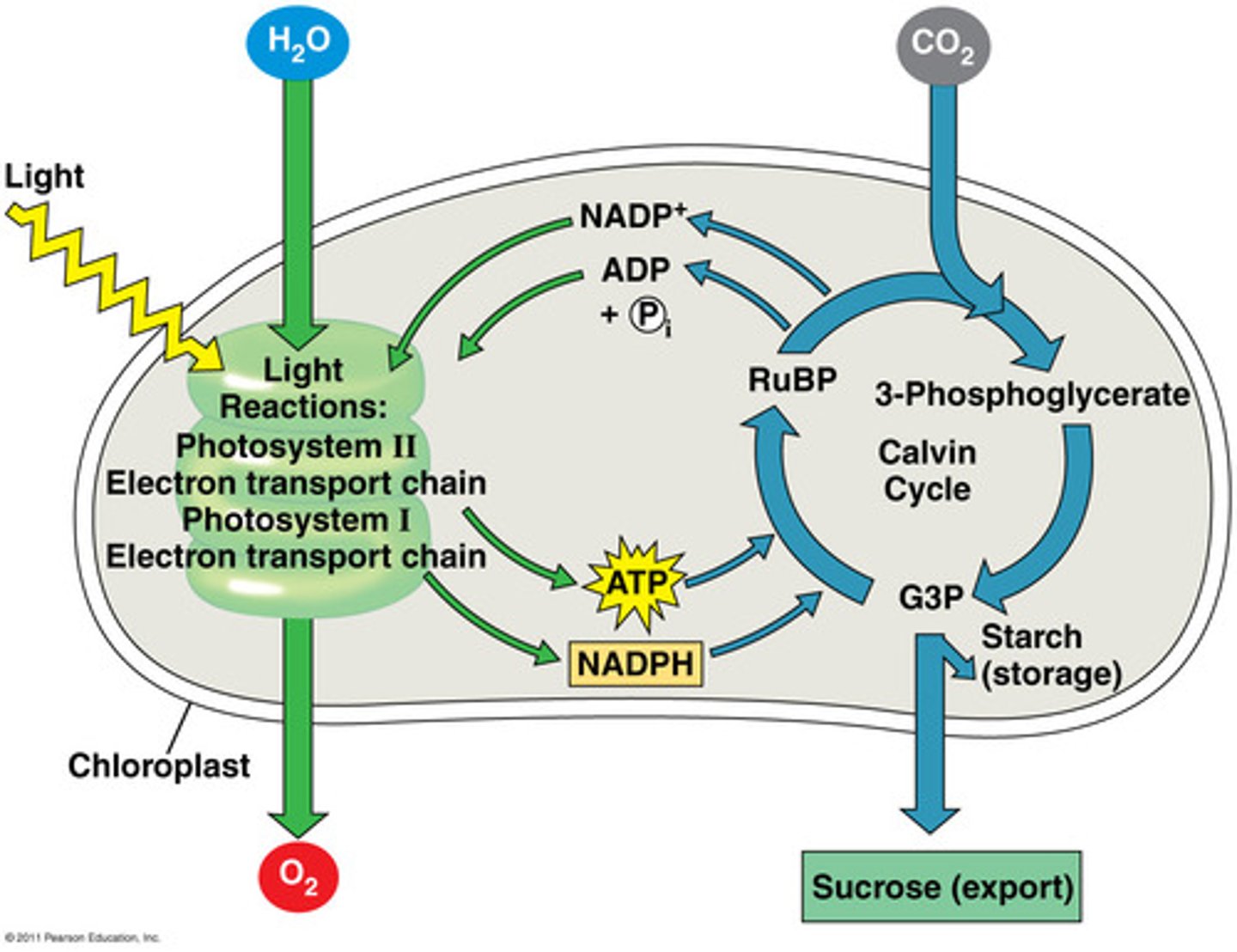
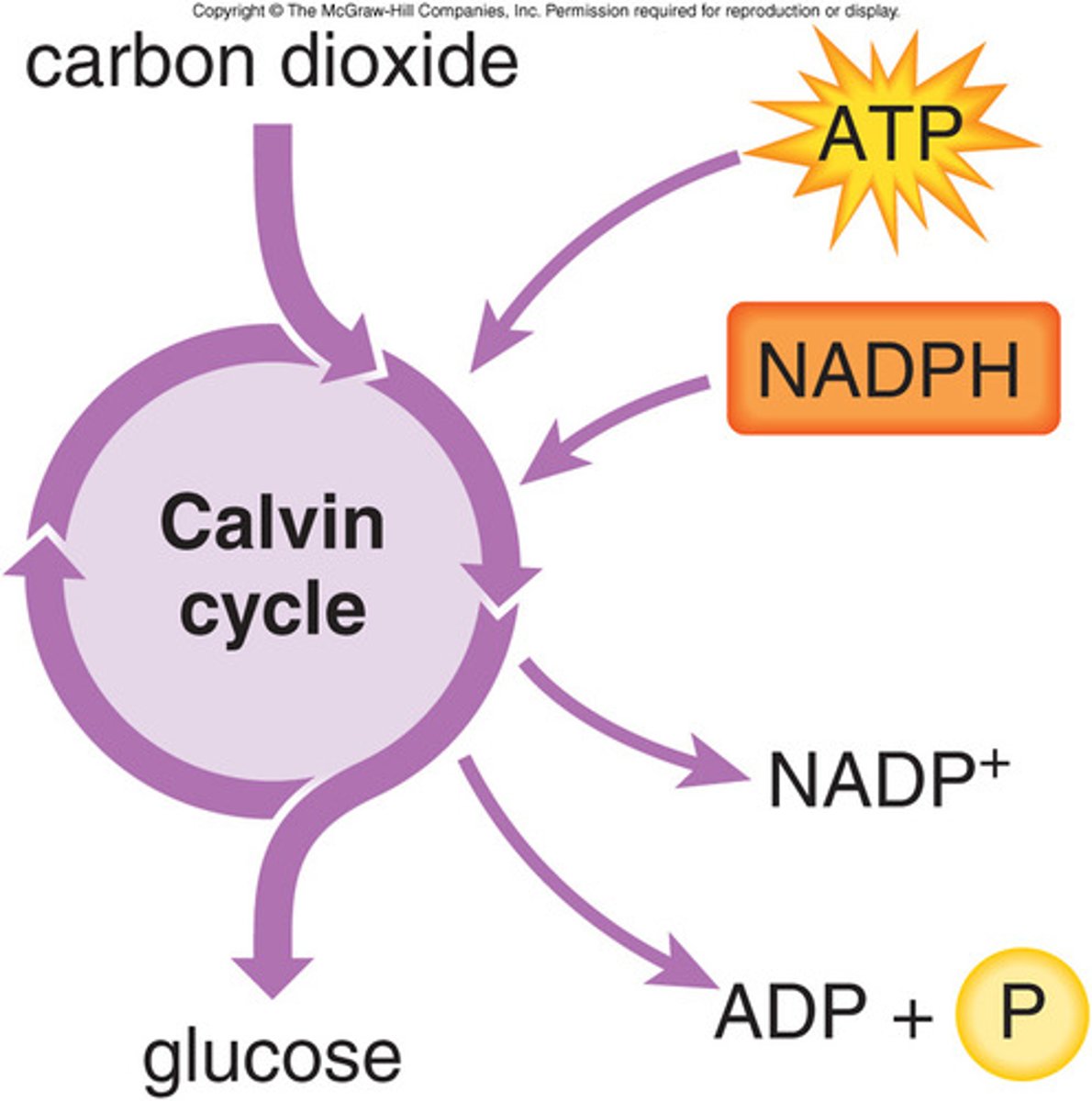
Light Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle)
reactions of photosynthesis in which energy from ATP and NADPH is used to build high-energy compounds such as sugars, occurs in stroma of chloroplast
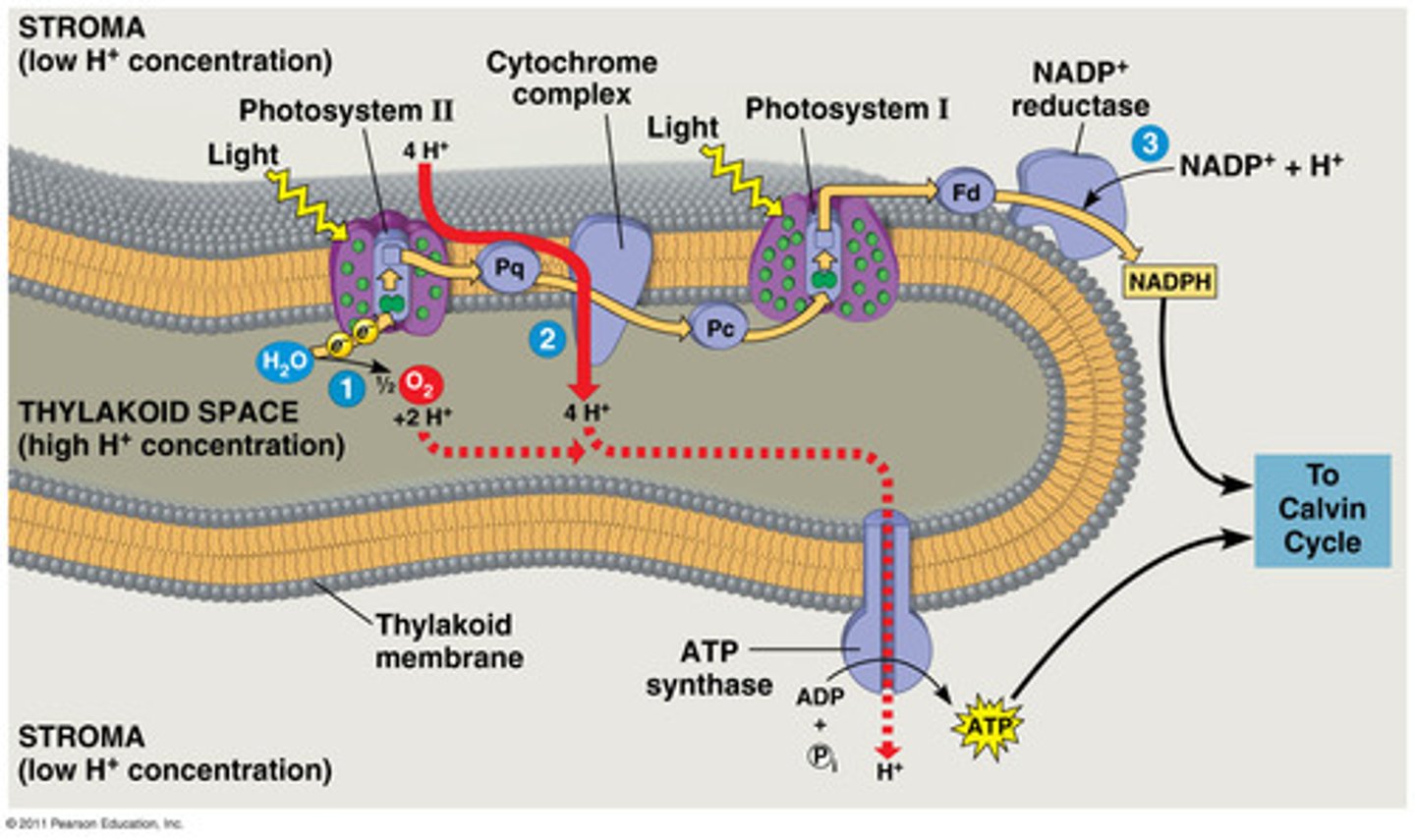
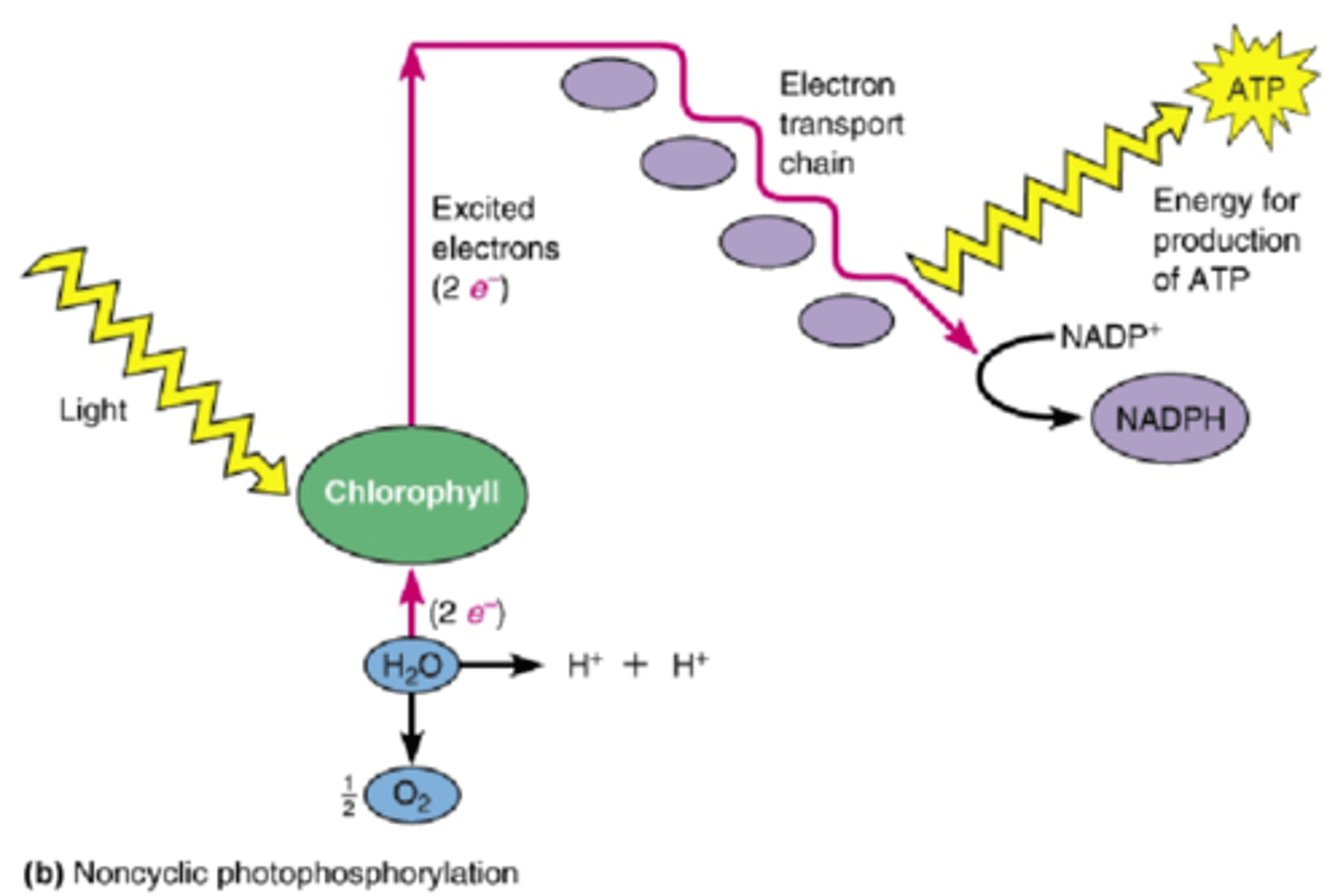
Photosynthesis Electron transport Chain
electron travels through a cascade of reactions to ultimately convert a molecule of NADP to NADPH, so NADP+ is terminal acceptor
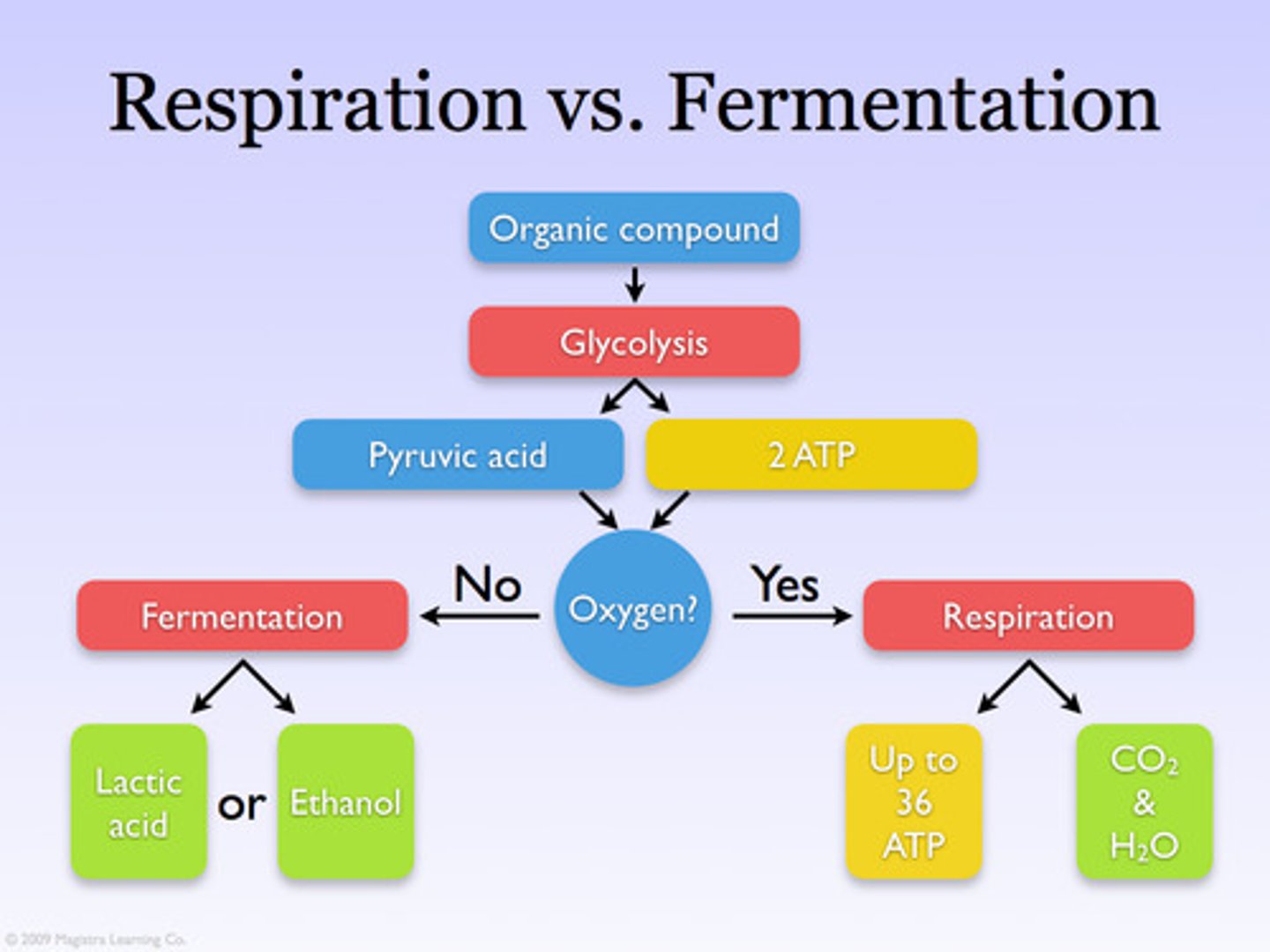
Cellular Respiration
Process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen

Aerobic Respiration
Respiration that requires oxygen, in mitochondria
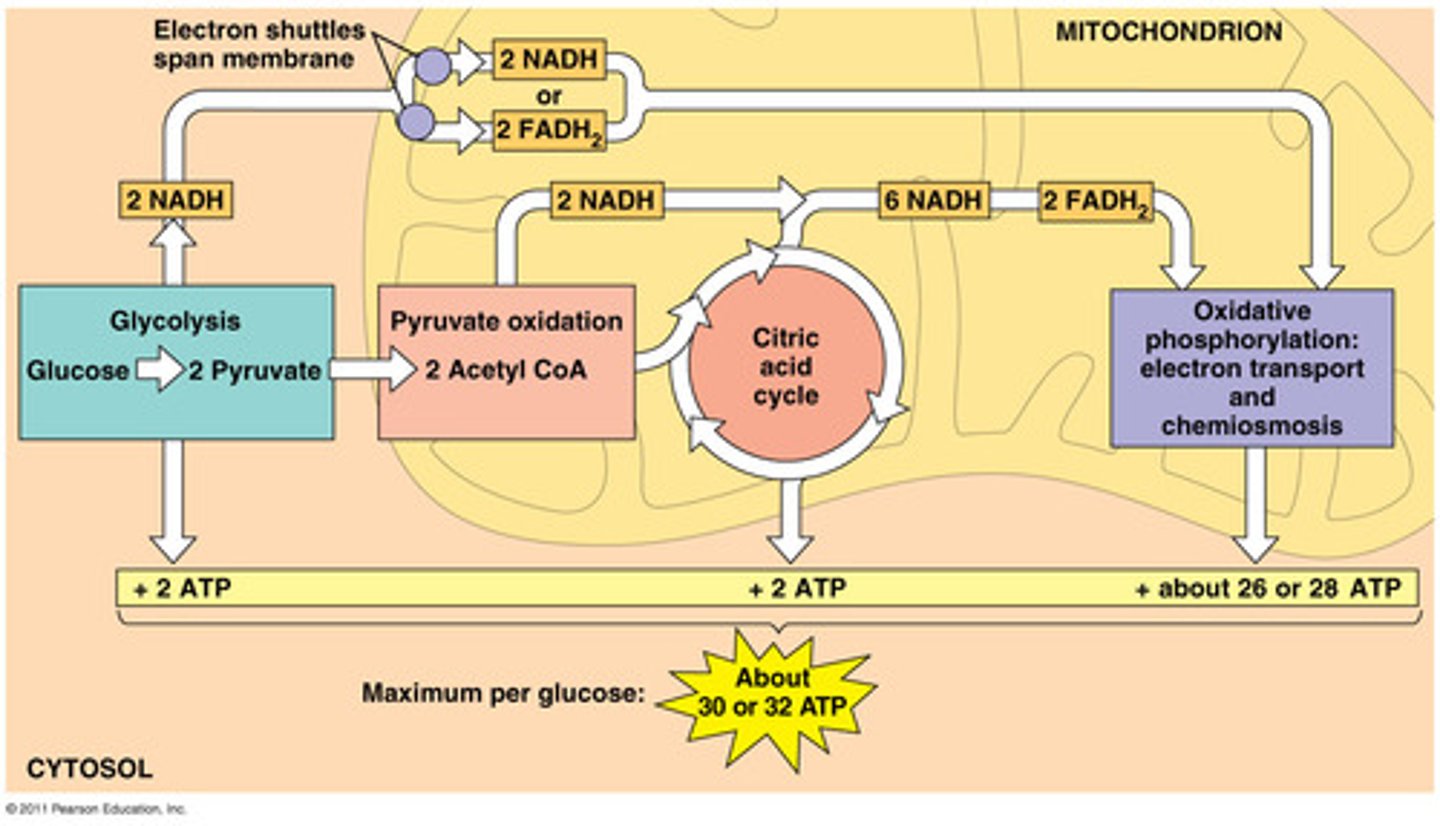
Anaerobic Respiration ( fermentation)
Respiration that does not require oxygen, prokaryotes, yeast, muscles
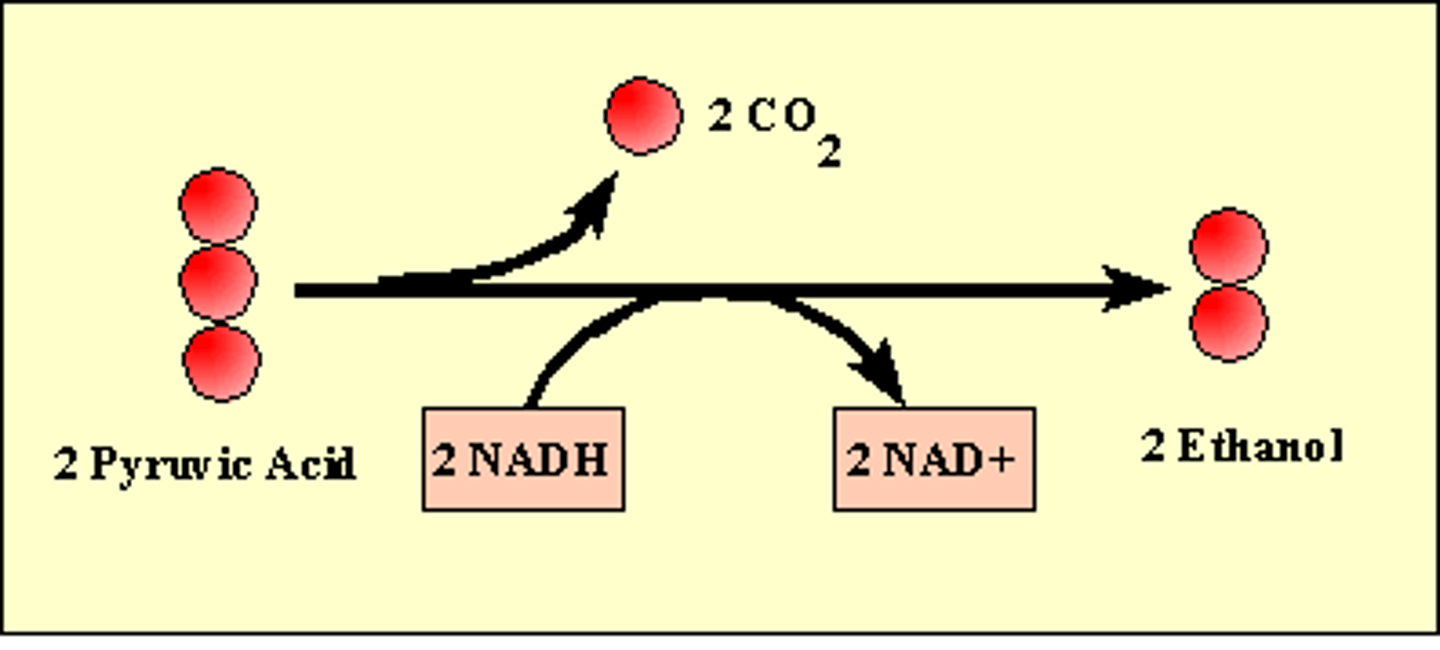
Alcoholic Fermentation
the anaerobic process by which yeasts and other microorganisms break down sugars to form carbon dioxide and ethanol
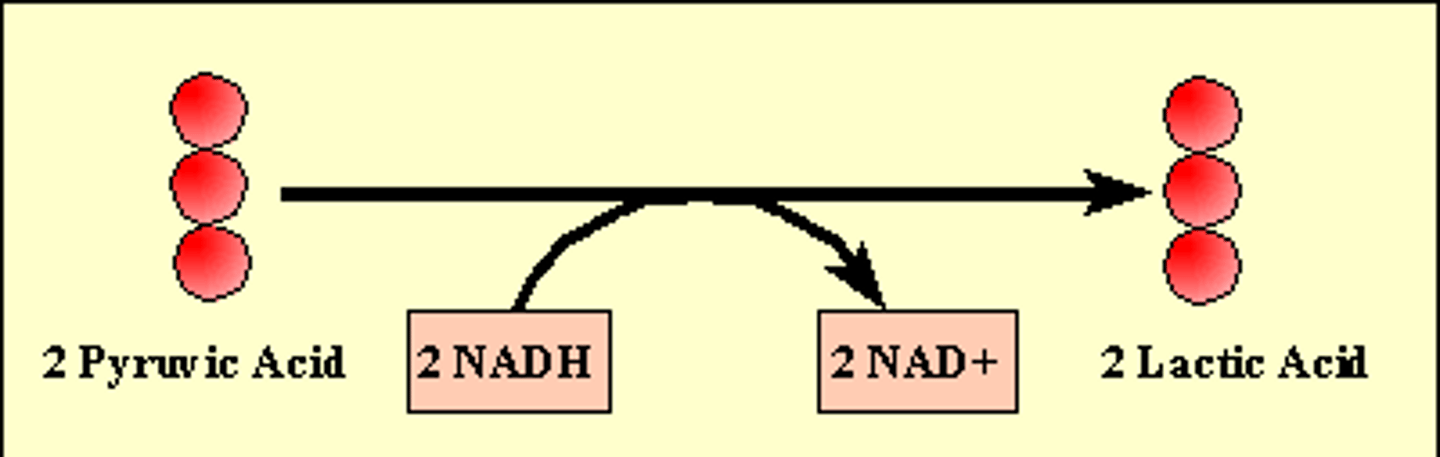
Lactic Acid Fermentation
the chemical breakdown of carbohydrates that produces lactic acid as the main end product, muscle cells
Respiration Electron transport Chain
accepts electrons from NADH and FADH2, O2 terminal acceptor

ATP Synthase
membrane bound enzyme that allows flow of protons by chemiosmosis
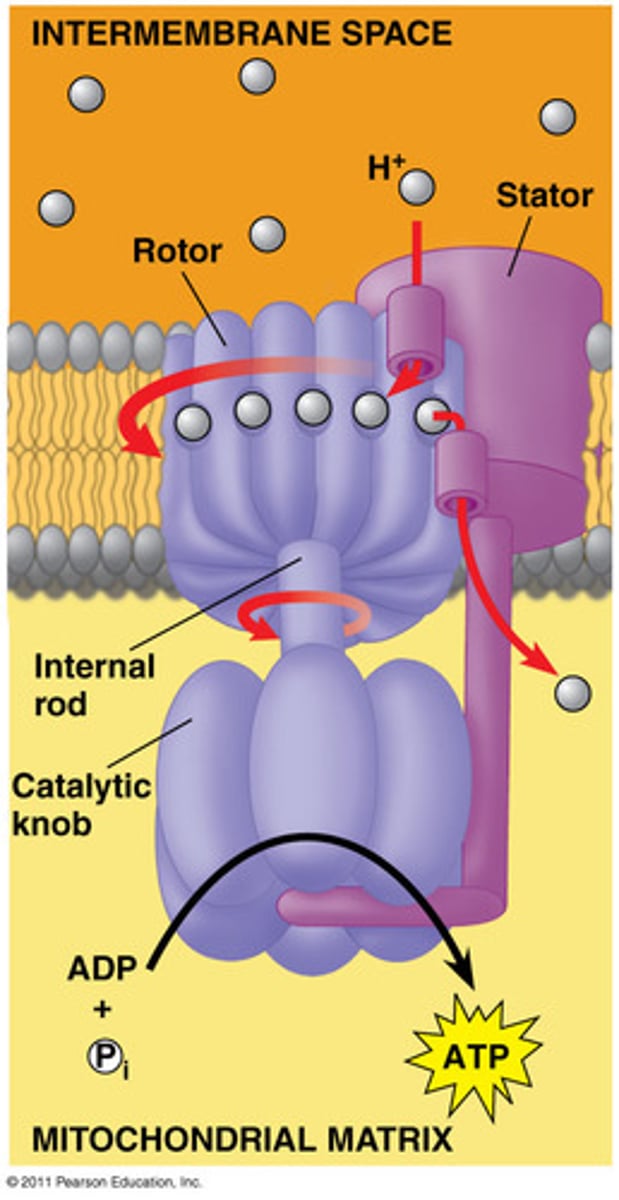
Chemisosmosis
the use of energy in a H+ gradient to drive cellular work
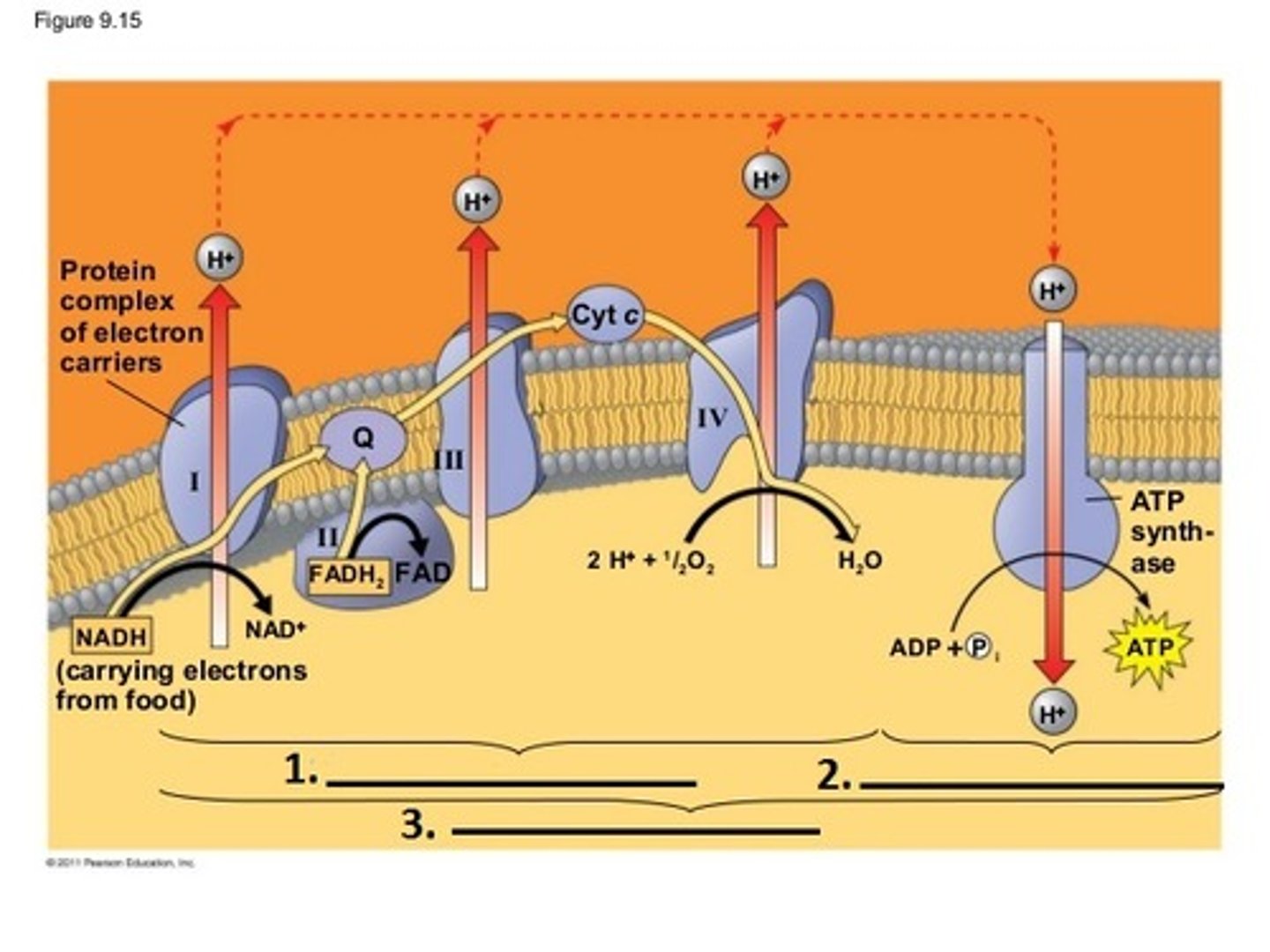
Oxidative Phosphorylation
When energy is released at each step of the chain is stored in a form the mitochondrion can use to make ATP, respiration
Photophosphorylation
The production of ATP by chemiosmosis during the light reactions of photosynthesis.
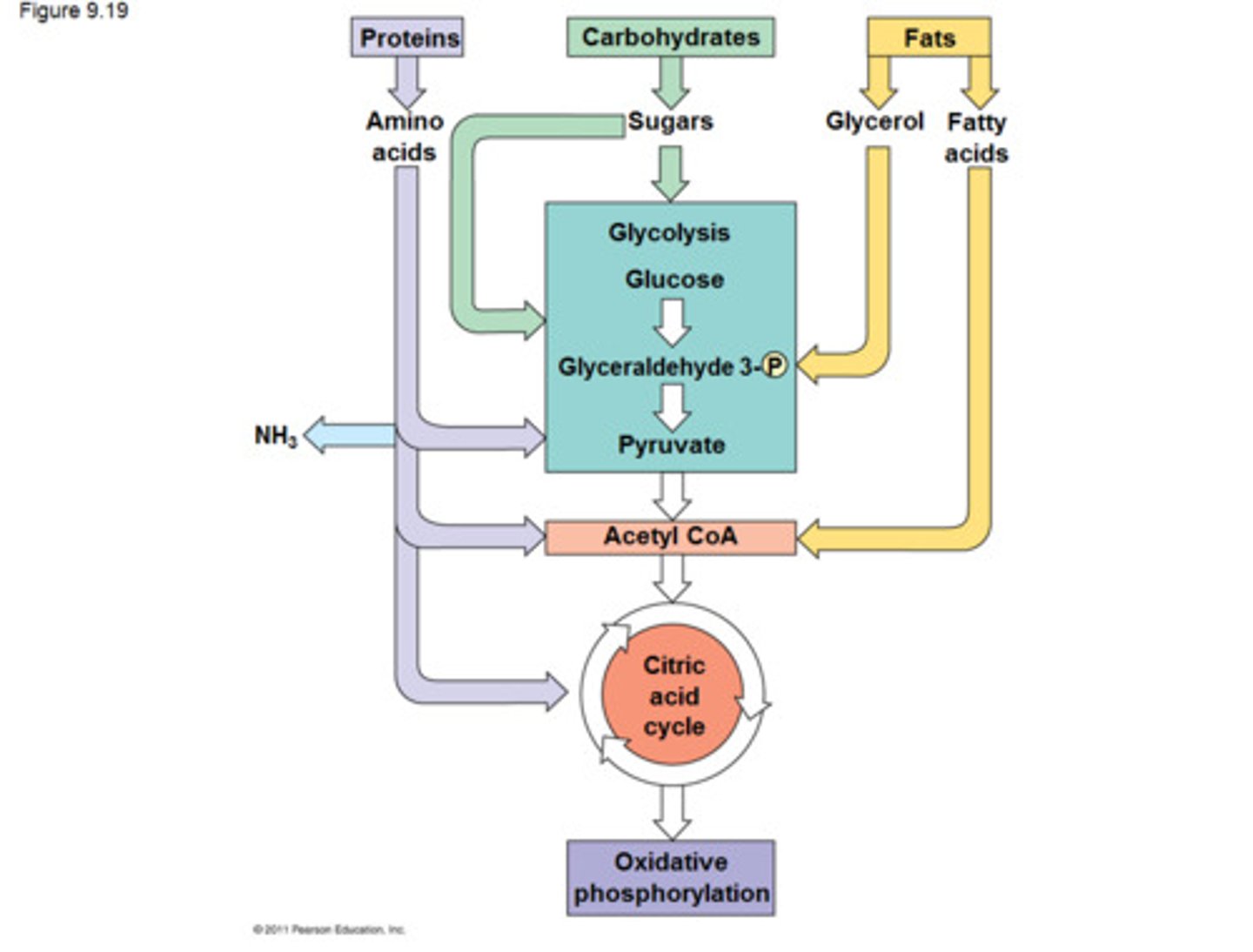
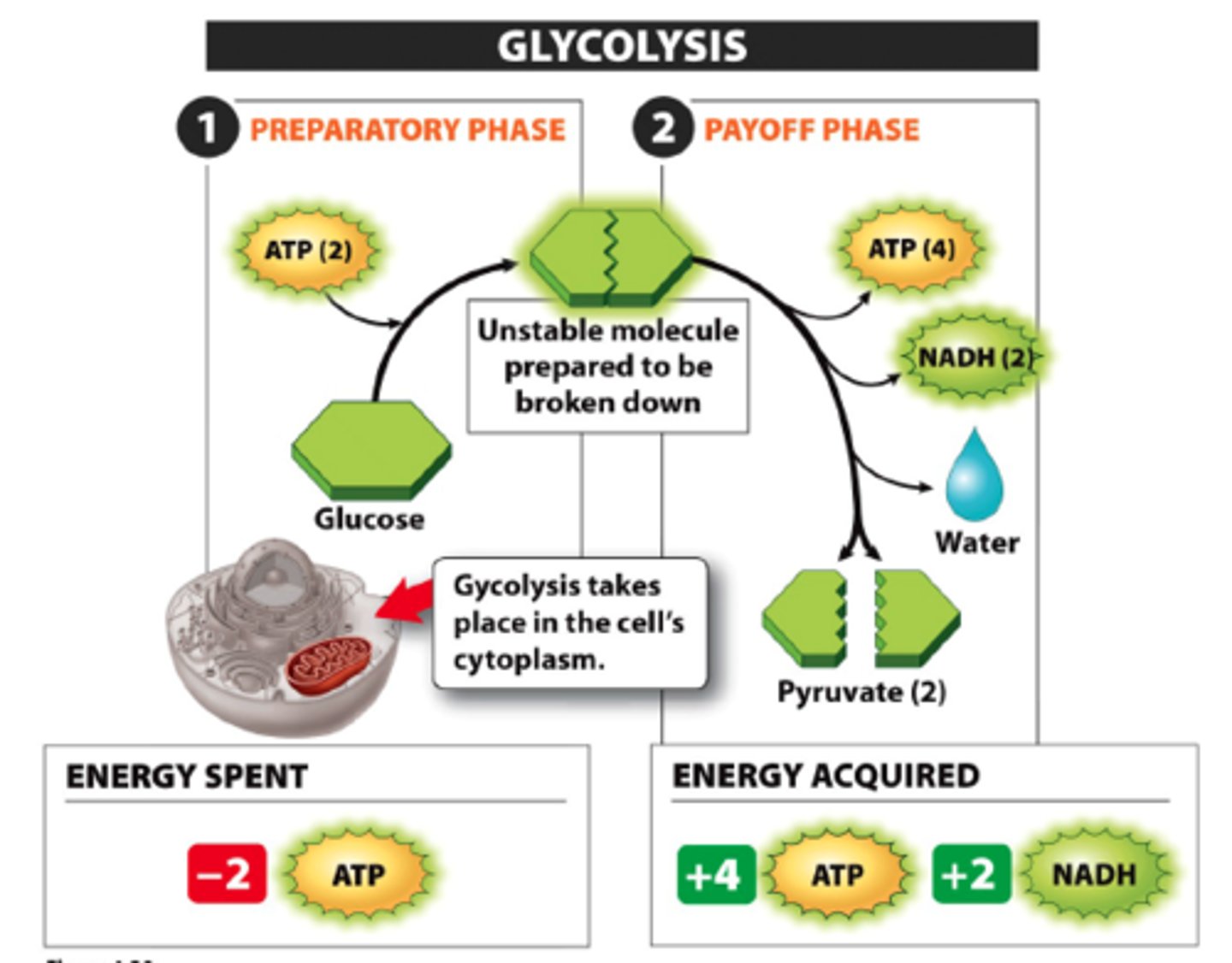
Glycolysis
first step in releasing the energy of glucose, in which a molecule of glucose is broken into two molecules of pyruvic acid OR stand alone fermentation
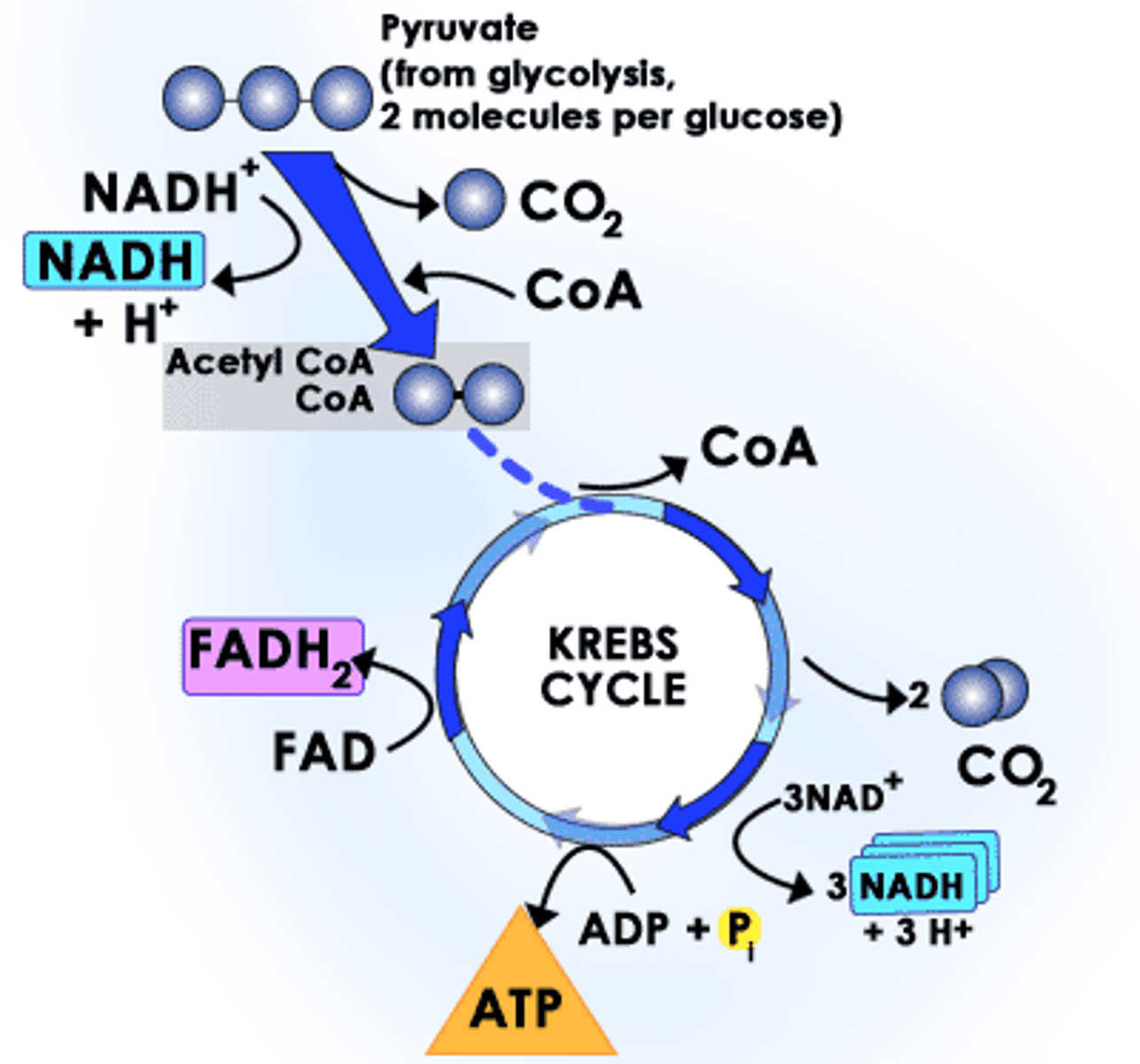
Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
Aerobic Respiration, in mitochondrial matrix
CO2 released
ATP synthesized
e- transferred to coenzymes NADH and FADH2
control group
the group that does not receive the experimental treatment.

Dependent Variable
The outcome factor; the variable that may change in response to manipulations of the independent variable. GRAPHED ON y AXIS
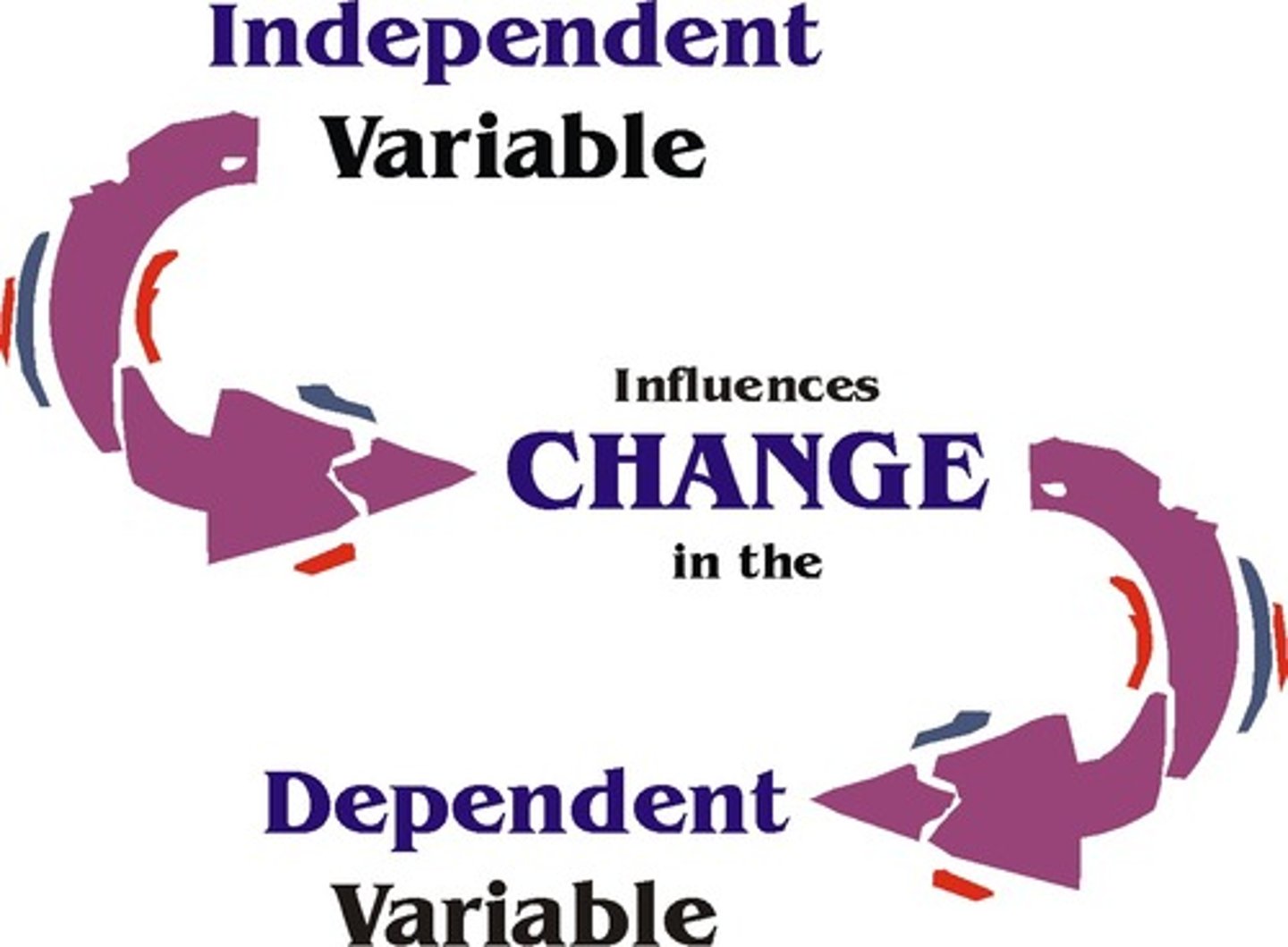
Independent Variable
The experimental factor that is manipulated; the variable whose effect is being studied. GRAPHED ON x AXIS
Hypothesis
a supposition or proposed explanation made on the basis of limited evidence as a starting point for further investigation.
