Composition of Blood- Hematopoiesis, Function
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
hematopoietic stem cell (HSC)
-pluripotent- any type of blood cell differentiation
-three essential attributes: self-renewal, multilineage differentiation, ability to reconstitute hematopoietic system of lethally irradiated host
importance of HSCs
-rare: 1:1000-1,000,000
-quiescent (noncycling) in steady state
-stress → extensive proliferation
-perturbations of hematopoietic process: leukemia, aplastic anemia
-therapeutic usefulness
identifications of HSCs
-functional assays in vivo: clonogenic cells in bone marrow → irradiated mouse/human → rescue hematopoietic system
-in vivo colony forming assays
-monoclonal antibodies and flow cytometry- presence of absence of specific surface markers
characterization of HSC
-monoclonal antibodies have been extensively used: CD34+CD38-Kit+Lin-
fates of HSCs
-three possibilities: self renewal, differentiation, apoptosis
-two models: stochastic (random), intrusive (extrinsic and/or intrinsic signals)
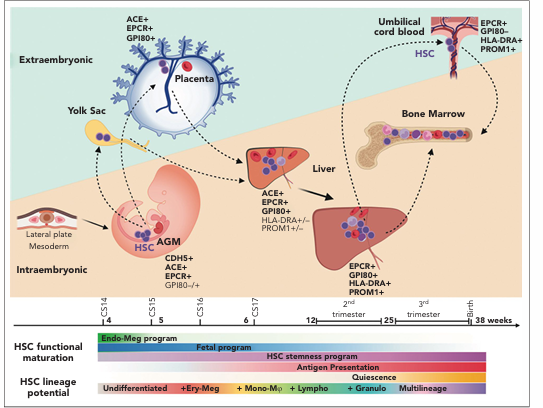
development
-highly conserved among mammals
-primitive hematopoiesis (extra-embryonic yolk sac)
-definitive hematopoiesis (HSC expand and migrate to fetal liver/spleen)
-late fetal stage (HSC migrate to bone marrow)
erythropoiesis
-primary end product is delivery of oxygen to tissues via RBC
-bone marrow releases 3×10^9 retics/kg/day from 5×10^9 precursors/kg
-must respond quickly to increased oxygen demands
erythropoiesis tasks to accomplish
-proliferate
-differentiate
-express key cell surface molecules: receptors (Epo-R, TfR), channels, blood group antigens
-produce hemoglobin: globin chains, heme, incorporate Fe
-degrade organelles
-enucleate
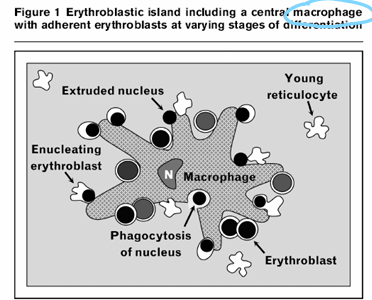
niche
-all of erythropoiesis happens on surface
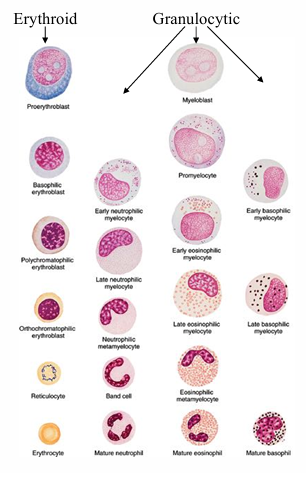
hematopoietic lineages
erythropoiesis development- maturation sequence
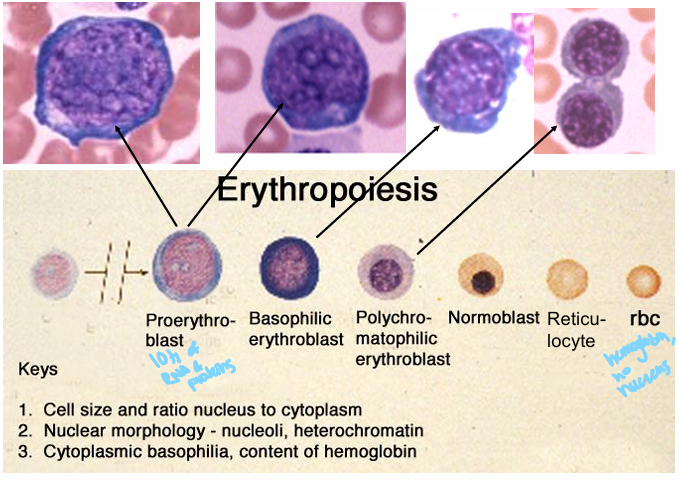
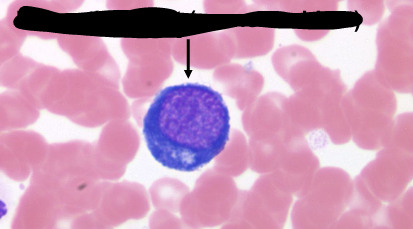
proerythroblast (pronormoblast)
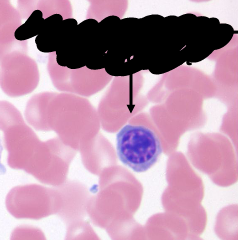
polychromatophilic normoblast
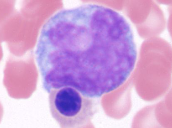
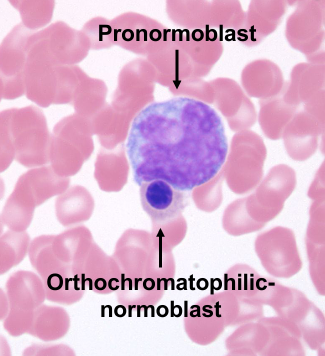
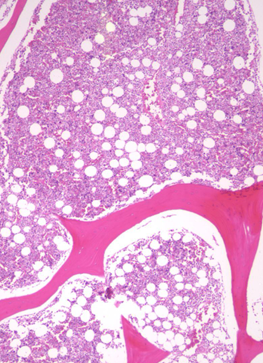
bone marrow
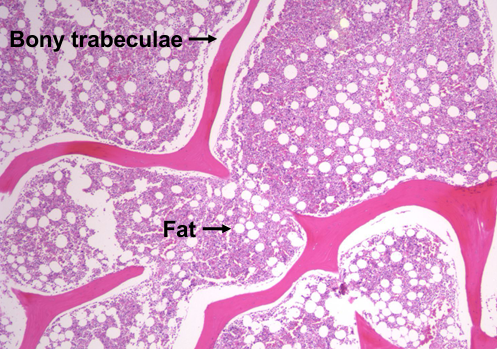
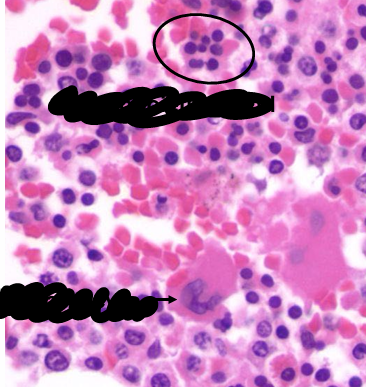
bone marrow
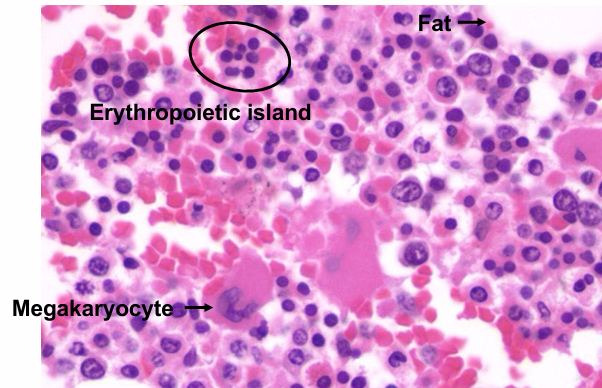
conservation of Fe
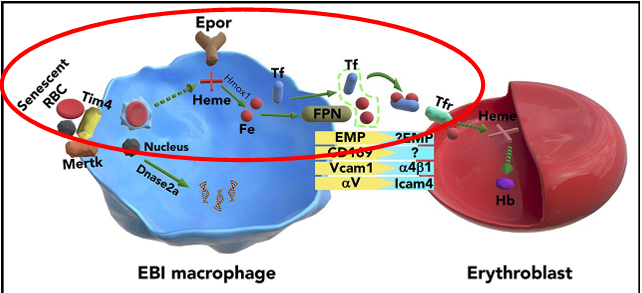
hematopoiesis
-complex process of proliferation and differentiation
functions of blood- delivering products
-food = absorbed amino acids, cholesterol, vitamins
-raw materials = copper, iron, O2
-manufactured goods = hormones, growth factors
-carriers: lipoproteins (cholesterol), transferring (iron), ceruloplasmin (copper), hemoglobin (O2)
functions of blood- remove waste
-local: macrophages
-cross country: urea, creatinine, ammonia, CO2
-carriers: haptoglobin (“free” hemoglobin), hemopexin (“free” heme), hemoglobin (CO2), HDL (lipoprotein- cholesterol), albumin (“drugs”)
functions of blood- facilitate signaling
-classical endocrine hormones- thyroid hormone, insulin, pituitary hormones, epinephrine, glucocorticoids, etc.
-cytokines/chemokines- IL1, IL2, etc., TNF-alpha, MCP-1, etc.
functions of blood- respond to emergencies
-host defense
-local: macrophages, mast cells
-”global”: antibodies, neutrophils, lymphocytes
-”non-specific”: innate or natural immunity- macrophages, neutrophils, complement, “natural” low affinity antibodies
-specific/targeted/training/instruction: antigen presentation (macrophages), T cells, high affinity antibodies
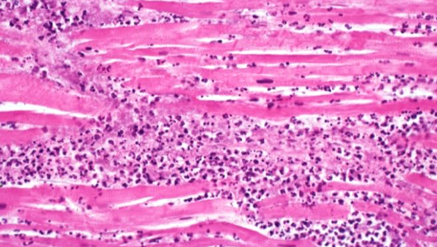
-myocardial infarction
-neutrophils purple dots- make up pus
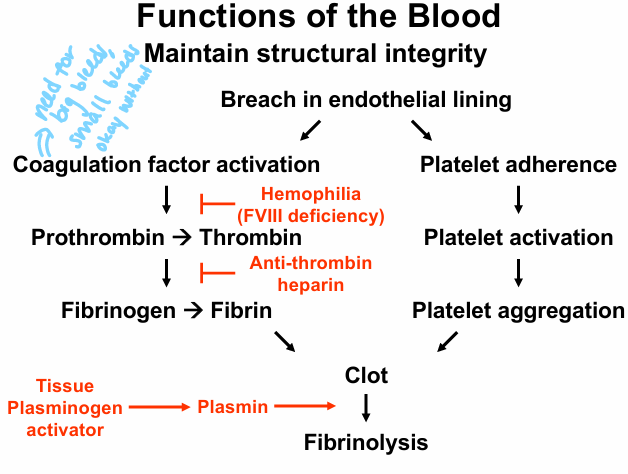
functions of blood- maintain structural integrity
-homeostasis
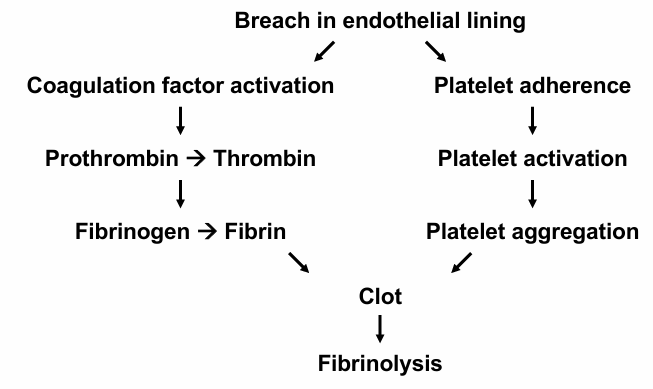
-self-correcting/self-healing: endothelial cells, coagulation factors, platelets, hematopoietic stem cells
-fibrinolysis
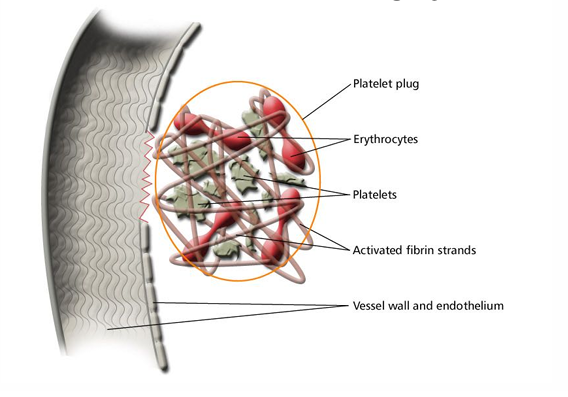
breach in endothelial lining
platelet plug
diseases/interruptions to maintaining structural integrity
sources of components of the blood
-bone marrow: RBC, WBC, platelets
-liver: fibrinogen, albumin
-endothelial cells: von Willebran factor
-endocrine organs: hormones
-lymphocytes, macrophages: cytokines
transfusion medicine
-transfusion of “products”: RBC, platelets, WBC, PBHSC, FFP, cryo
-infusion of (recombinant) proteins: FVIII, FVIIa, AT, IVIg, RHIg, rituxan
-prescription of “drugs”: Epo, G-CSF, GM-CSF, TPA
-removal of “evil humors”: apheresis of cells and solutes
corollary transfusion therapy
-transfuse any unit of RBC into any recipient with perfect acquisition of desired effect (normalizing Hct, diminishing Hgb SS levels, improving O2 delivery) and without adverse consequences (transfusion transmitted diseases, transfusion reactions, missing the therapeutic target, volume overload)
-not currently possible
transfusion in sickle cell disease
-simple transfusion
-RBC exchange fusion- increase or maintain hematocrit, decrease Hgb SS levels, treat or prevent strokes/acute chest syndrome/pain crisis