22 - Vertebrate Evolution and Diversity
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
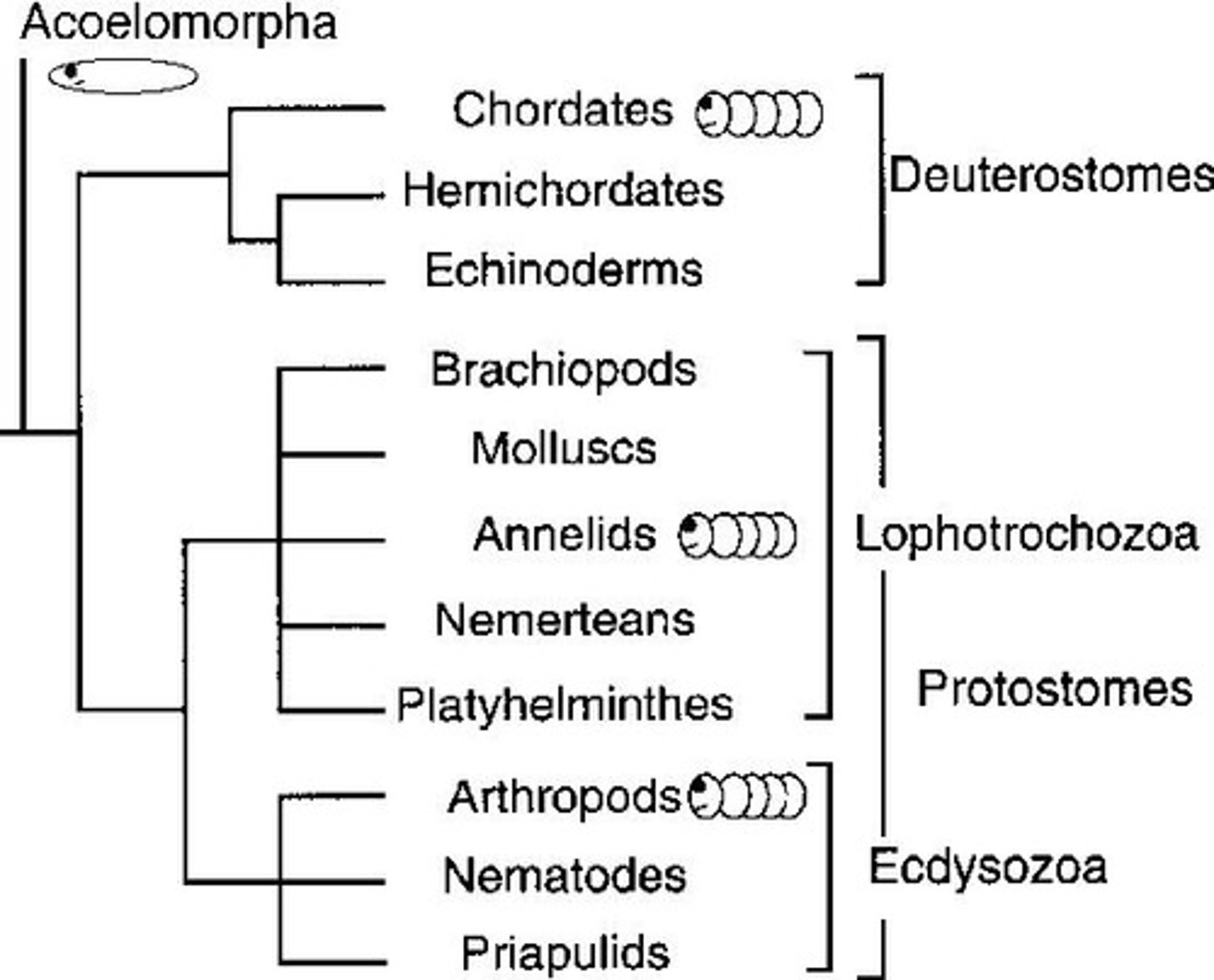
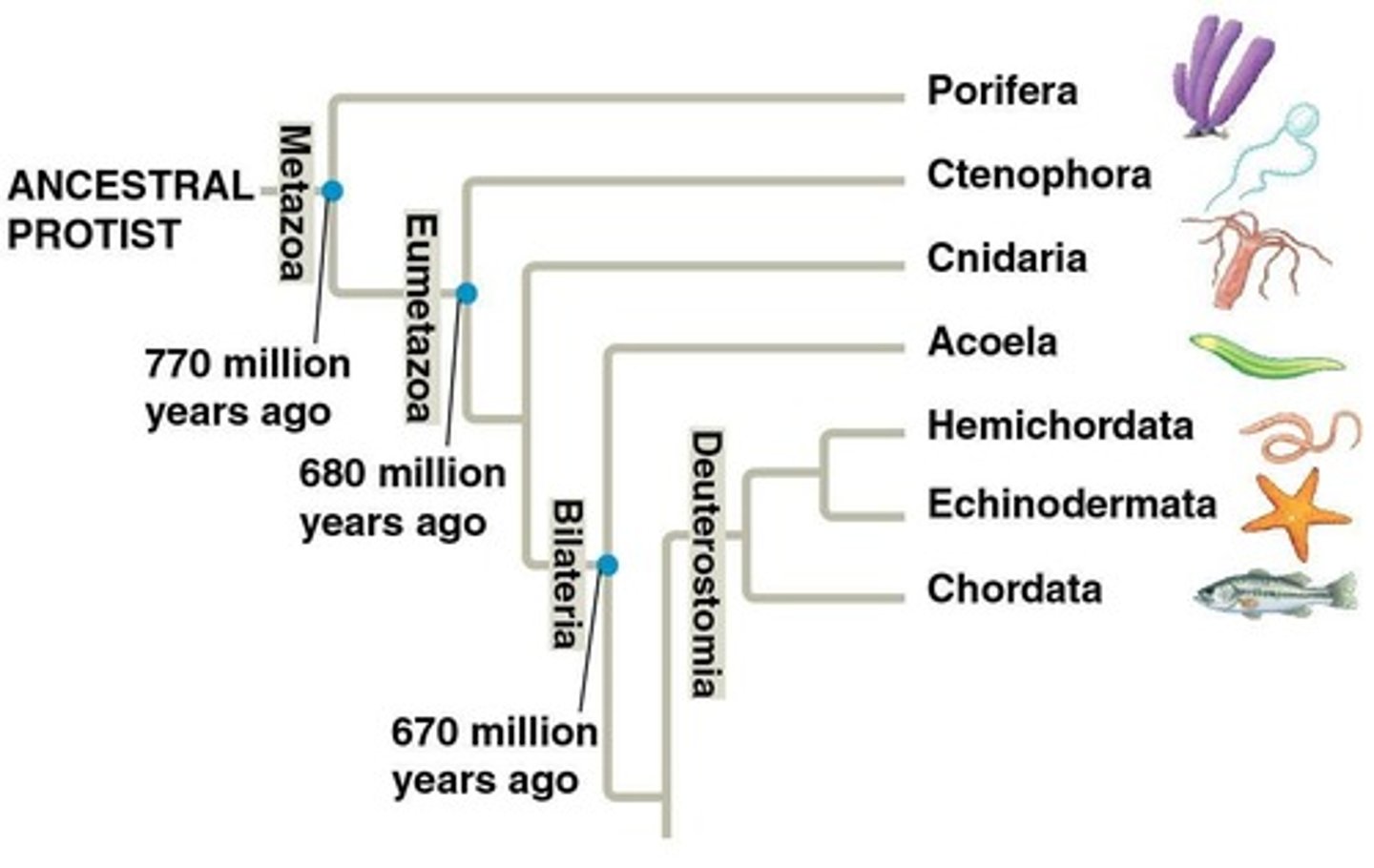
What unites Deuterostomes?
Shared developmental patterns (radial cleavage, indeterminate cells, blastopore → anus) and deep genetic similarities.
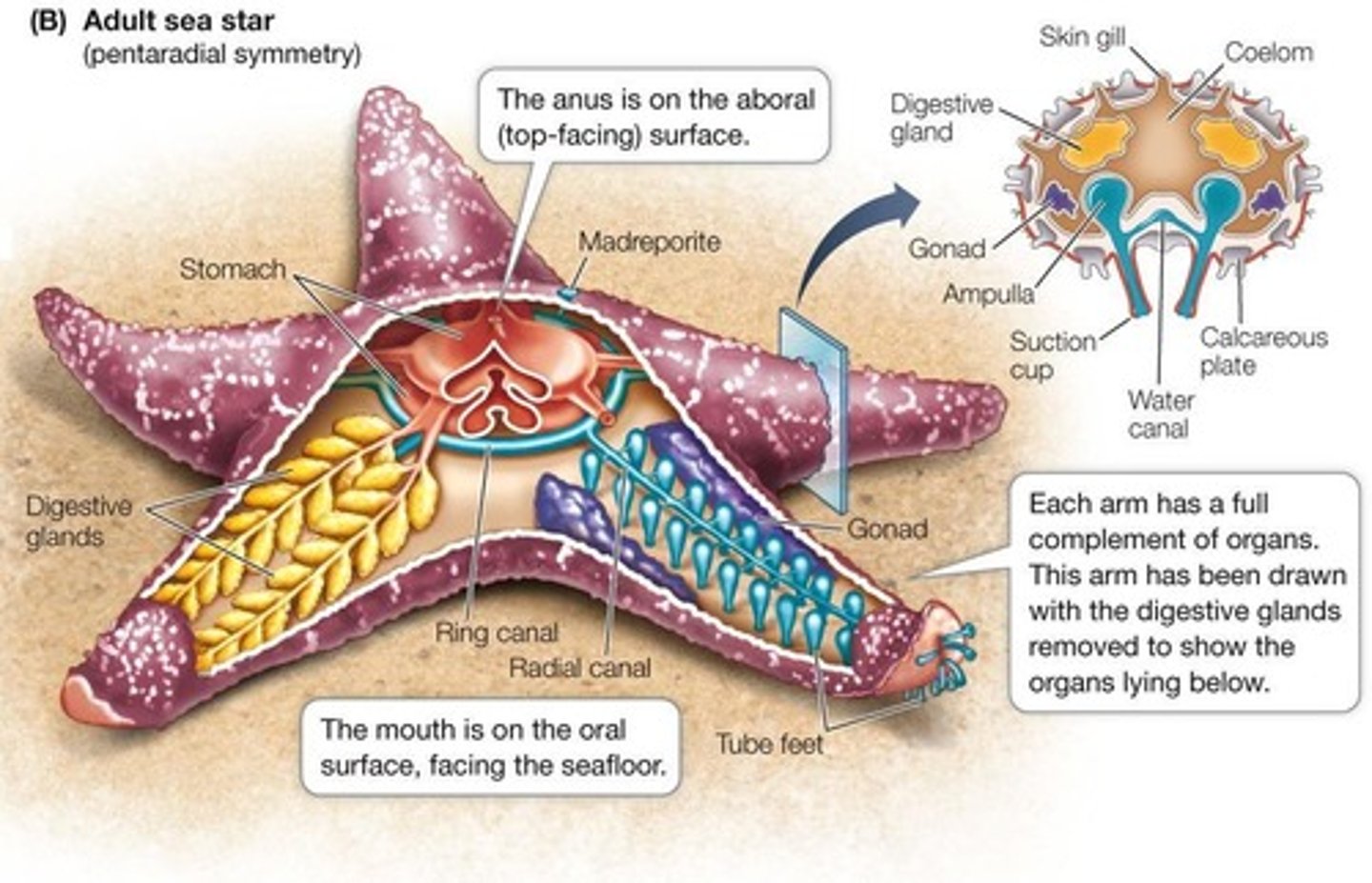
What unique features do Echinoderms display?
Adult radial symmetry, a water vascular system for locomotion, and an endoskeleton of calcareous plates.
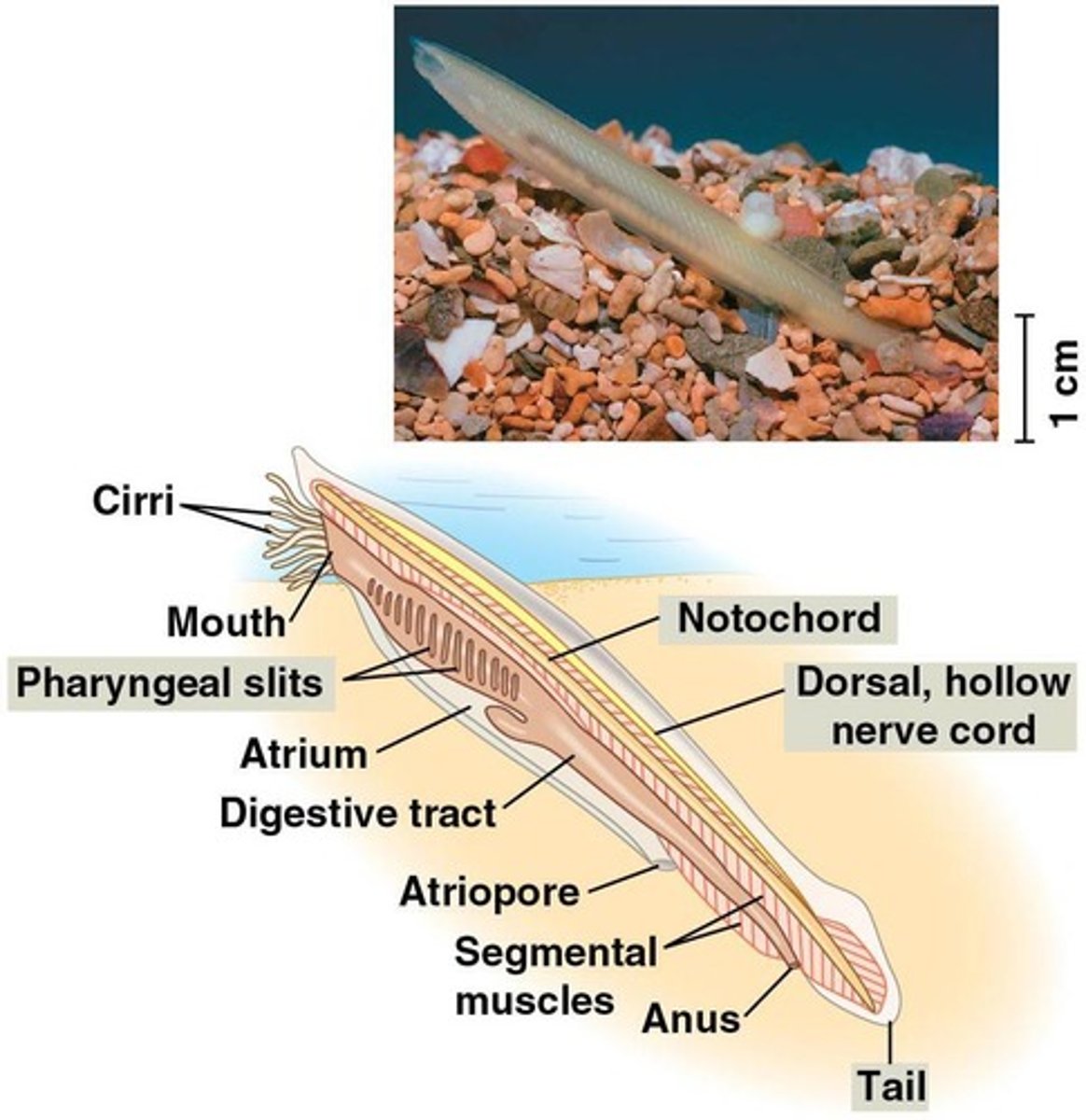
What important evolutionary trends emerged with chordates?
Development of the notochord, dorsal nerve cord, pharyngeal gill slits, and a muscular post-anal tail.
How did life on land contribute to vertebrate diversification?
Life on land led to adaptations such as limbs and lungs, allowing vertebrates to exploit new habitats.
What is the significance of symmetry in animal evolution?
Symmetry trends evolved from none to radial to bilateral, influencing body organization and function.
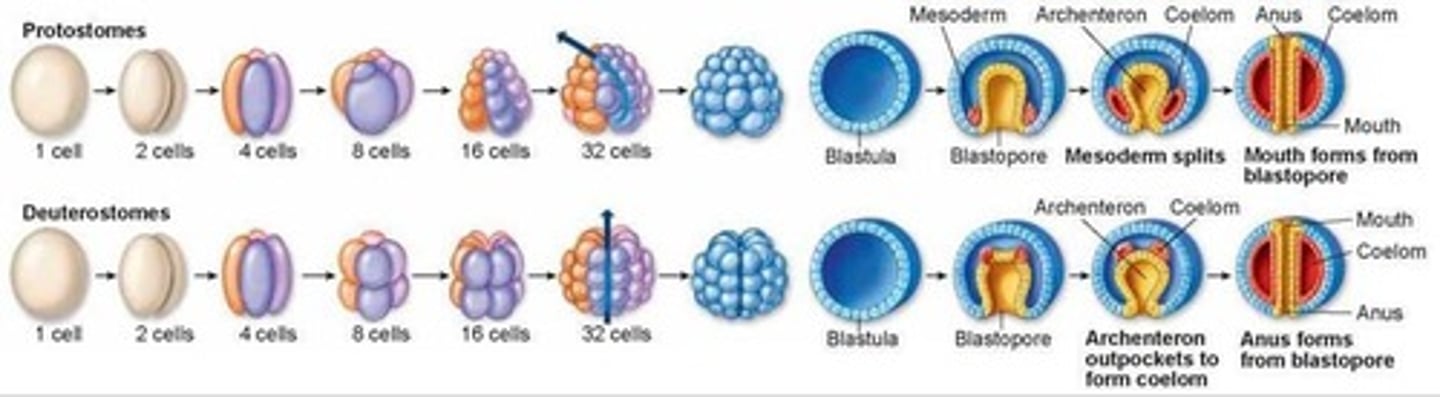
What are the stages of gastrulation in animal evolution?
Gastrulation evolved from no blastopore to protostome and then to deuterostome.
Describe the evolution of body cavities in animals.
Body cavities evolved from none to acoelomate, pseudocoelomate, and coelomate.
What are the trends in segmentation observed in animal evolution?
Segmentation evolved from none to segmented forms, seen in arthropods and annelids.
What types of skeletons are observed in vertebrate evolution?
Skeletons evolved from none to hydrostatic, exoskeleton, and finally to endoskeleton.
What are the three major clades of Deuterostomia?
Echinoderms, Hemichordates, and Chordates.
What is the role of the water vascular system in Echinoderms?
It functions in locomotion and feeding through a network of hydraulic canals and tube feet.
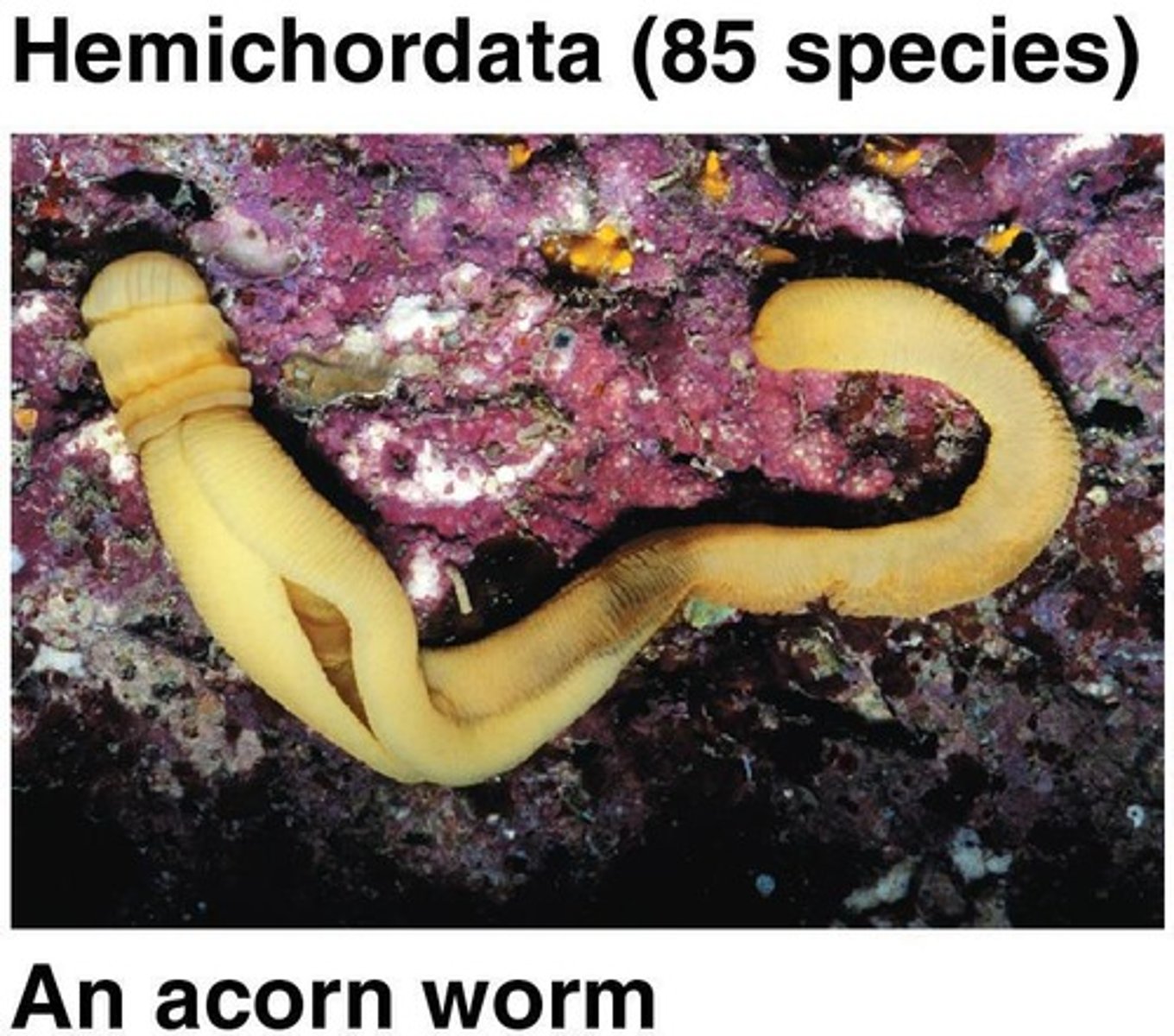
What features do Hemichordates share with Chordates?
Pharyngeal gill slits and a post-anal tail, but lack a notochord and dorsal neural tube.

What are the key innovations of Chordates?
Notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, and pharyngeal slits for filter feeding and respiration.
What characterizes vertebrates?
Jointed skeleton (vertebrae), bony cranium, pair of eyes, and an internal skeleton.
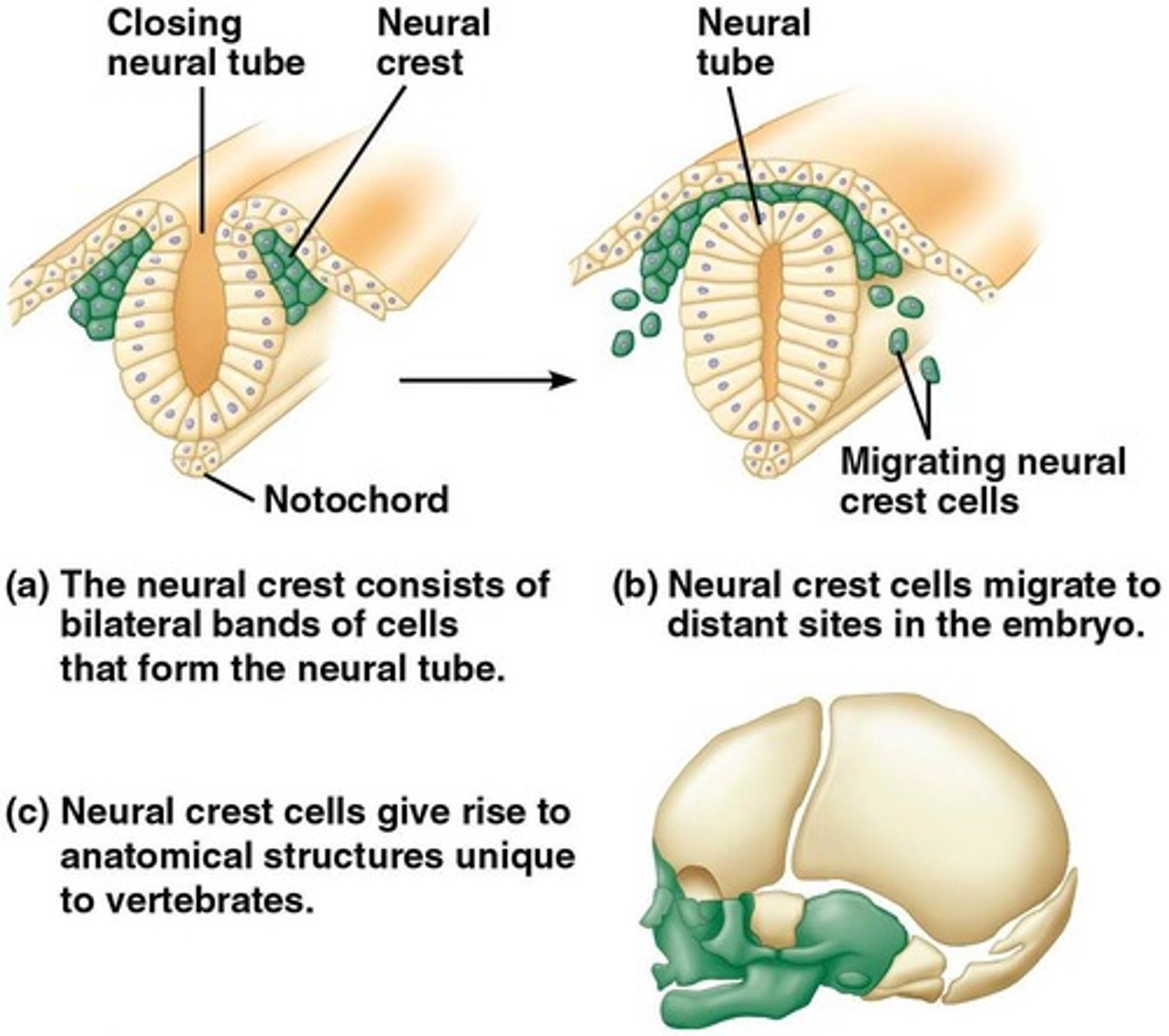
What was the evolutionary significance of the vertebrate leap?
Vertebrae replaced the notochord, allowing for more powerful locomotion and larger body sizes.
What are jawless fish?
The earliest-branching vertebrates with a cartilaginous cranium and vertebral column, lacking jaws.
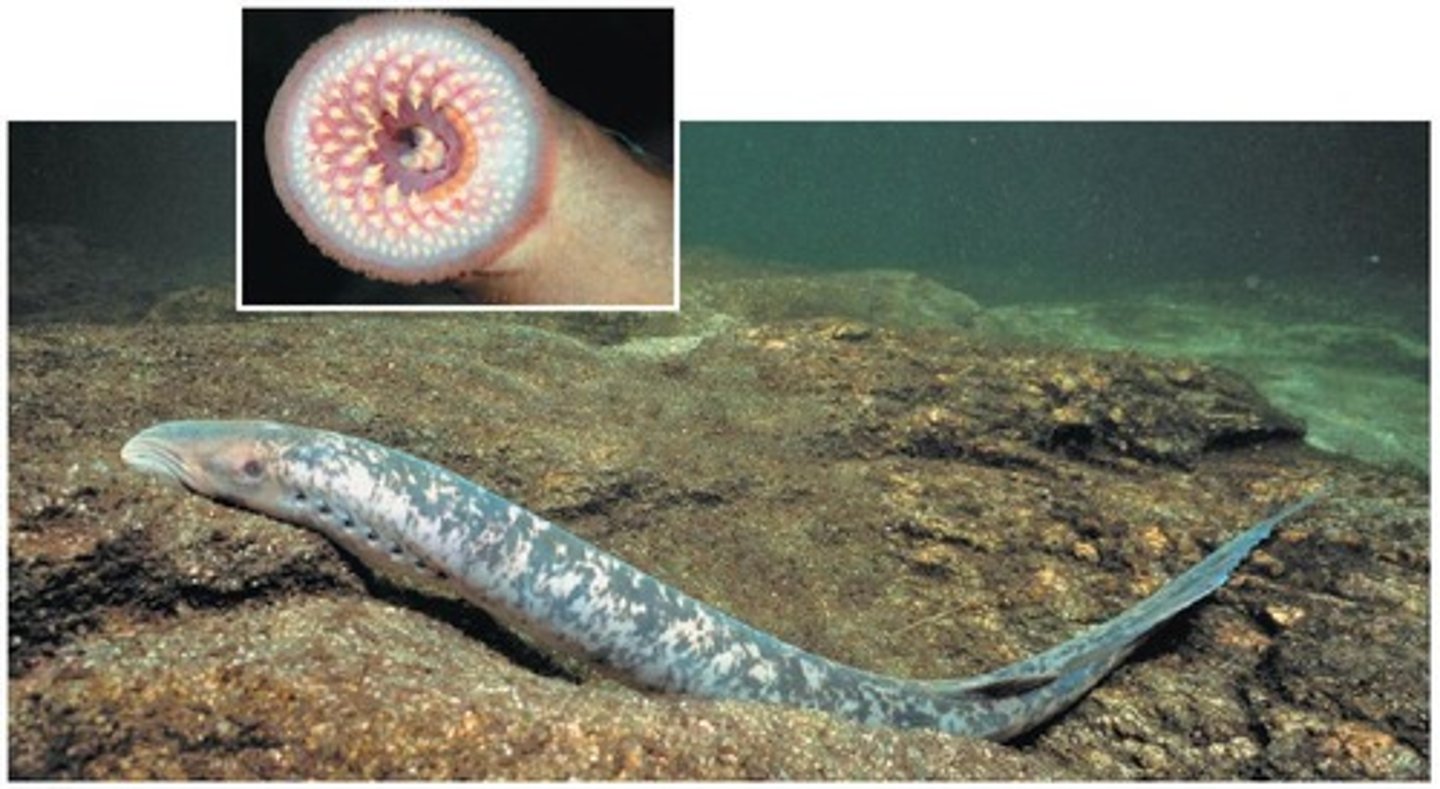

How did jaws evolve in vertebrates?
Jaws evolved from modified pharyngeal arches, enhancing predation capabilities.
What are the main groups of Gnathostomes?
Gnathostomes include cartilaginous fishes (Chondrichthyes) and bony fishes (Osteichthyans).
What adaptations do ray-finned fishes have?
Moveable jaws, swim bladders for buoyancy, and kidneys for water balance.
What distinguishes lobe-fins from other fish?
Lobe-fins have rod-shaped bones in their pectoral and pelvic fins, resembling tetrapod limbs.
What is the significance of lungfish in vertebrate evolution?
Lungfish evolved a gut sac for air breathing, allowing survival in drying habitats.
What is the Devonian period known for in vertebrate evolution?
The Devonian is known as the 'Age of Fishes' due to the diversification of fish and complex reef systems.
What are the evolutionary innovations of Osteichthyans?
Bony endoskeleton, adaptations for buoyancy, and advanced kidney functions.
What role did environmental changes play in vertebrate diversification?
Rising oxygen levels during the Ordovician-Silurian supported active predatory lifestyles in early vertebrates.
What environment favored the evolution of limbs in tetrapods?
Shallow, vegetation-choked Devonian waters.
What type of fish were pre-adapted for movement on land?
Lobe-fins (sarcopterygians) with strong, limb-like bones.
When did early tetrapods radiate?
During the Late Devonian, just before a major extinction.
By what year had the fins of lobe-fins evolved into tetrapod limbs?
By 365 million years ago.
What is a defining characteristic of amphibians?
They must reproduce in water and have a life cycle with aquatic larval and terrestrial adult stages.
What does the term 'amphibian' mean?
Both ways of life.
What happens to frog larvae during metamorphosis?
They develop legs, lungs, and external eardrums, and their gills disappear.
Where must amphibian eggs be laid?
In water or moist environments.
What adaptation allowed amniotes to develop away from water?
Amniotic membranes and shells.
What are the four extraembryonic membranes in amniotes?
Amnion, yolk sac, allantois, and chorion.
What evolutionary advantage do reptiles have for drier environments?
Scales containing keratin protect skin from desiccation.
What major event allowed reptiles to diversify in the Mesozoic?
The Permian-Triassic extinction.
What are the three main lineages of diapsid reptiles?
Turtles, Lepidosaurs, and Archosaurs.
What is the earliest known bird?
Archaeopteryx.
What adaptations do birds have for flight?
Weight-saving adaptations like no urinary bladder, only one ovary, and toothless mouths.
What are the four models for the origin of flight in birds?
Running, wing-assisted running, wing-assisted incline running, and wing-assisted climbing.
What significant evolutionary transitions occurred across Deuterostomes?
Shared developmental patterns and diverse adult body plans.
What innovations did chordates introduce for movement and feeding?
Notochord, dorsal nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, and post-anal tail.
What enabled the Devonian radiation of vertebrates?
Jaws, paired fins, and enhanced gills.
What adaptations broke the dependence on water for amniotes?
Amniotic eggs, keratinized skin, and advanced lungs.
What role did feathers play in the evolution of birds?
Feathers evolved for insulation, display, and eventually powered flight.
What ecological niches did dinosaurs occupy during the Mesozoic?
From apex predators to massive herbivores.
How did early amniotes adapt to their environments?
They lived in warm, moist areas and expanded into diverse environments over time.
What is a key feature of amphibian eggs?
They lack a shell and must be fertilized externally in most species.
What is the significance of the amniotic egg?
It allowed for the full terrestrialization of vertebrates.
What adaptations do reptiles display for reproduction?
Most lay shelled eggs on land and have internal fertilization.
What evolutionary trend is seen in the diversification of reptiles?
Adaptations to drier environments and varied ecological roles.