Science Exam Revision - Semester 2 - ALL TOPICS
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All 4 topics combined
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
Reactants
A starting material in a chemical reaction
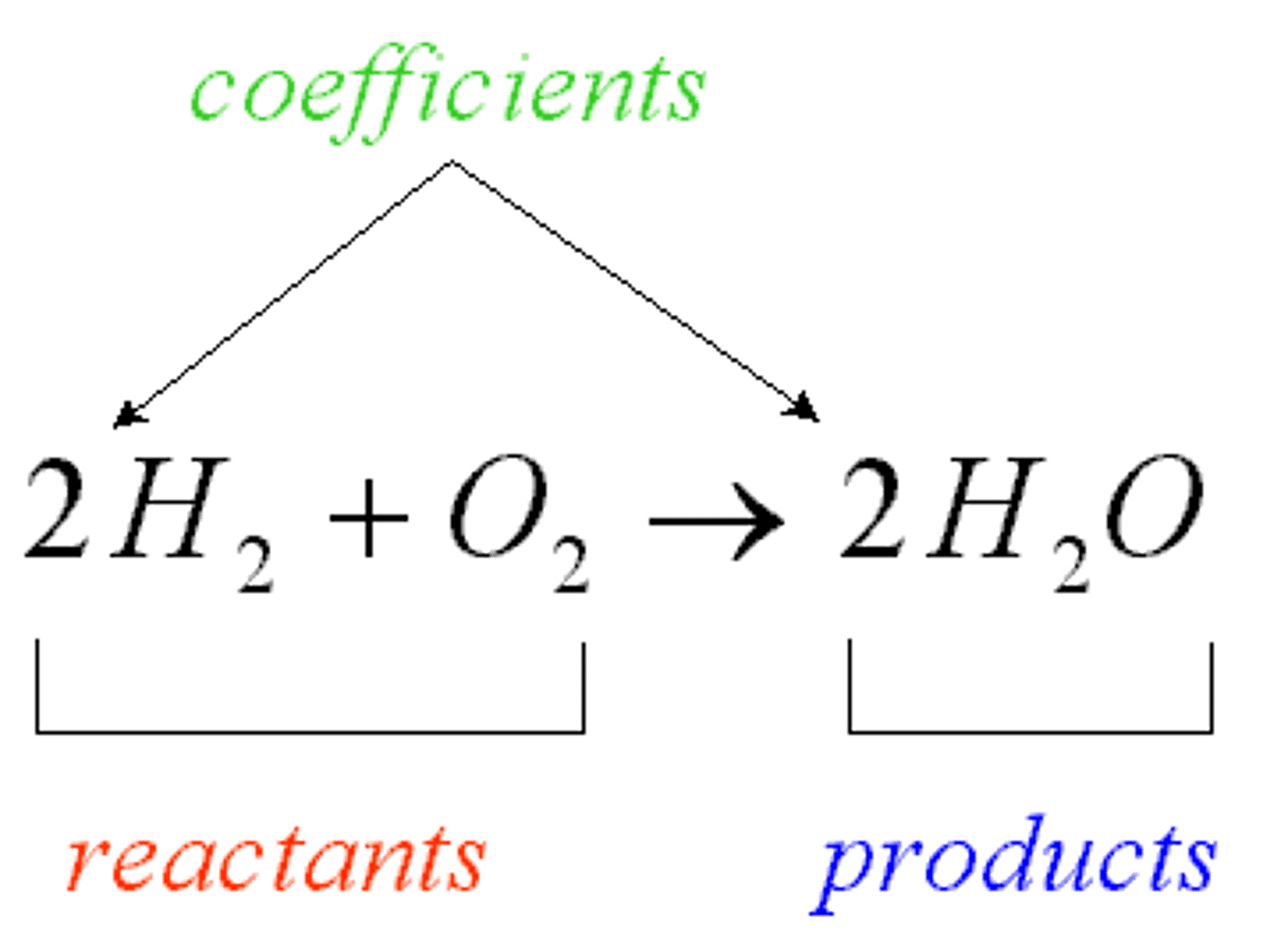
Products
The elements or compounds produced by a chemical reaction.
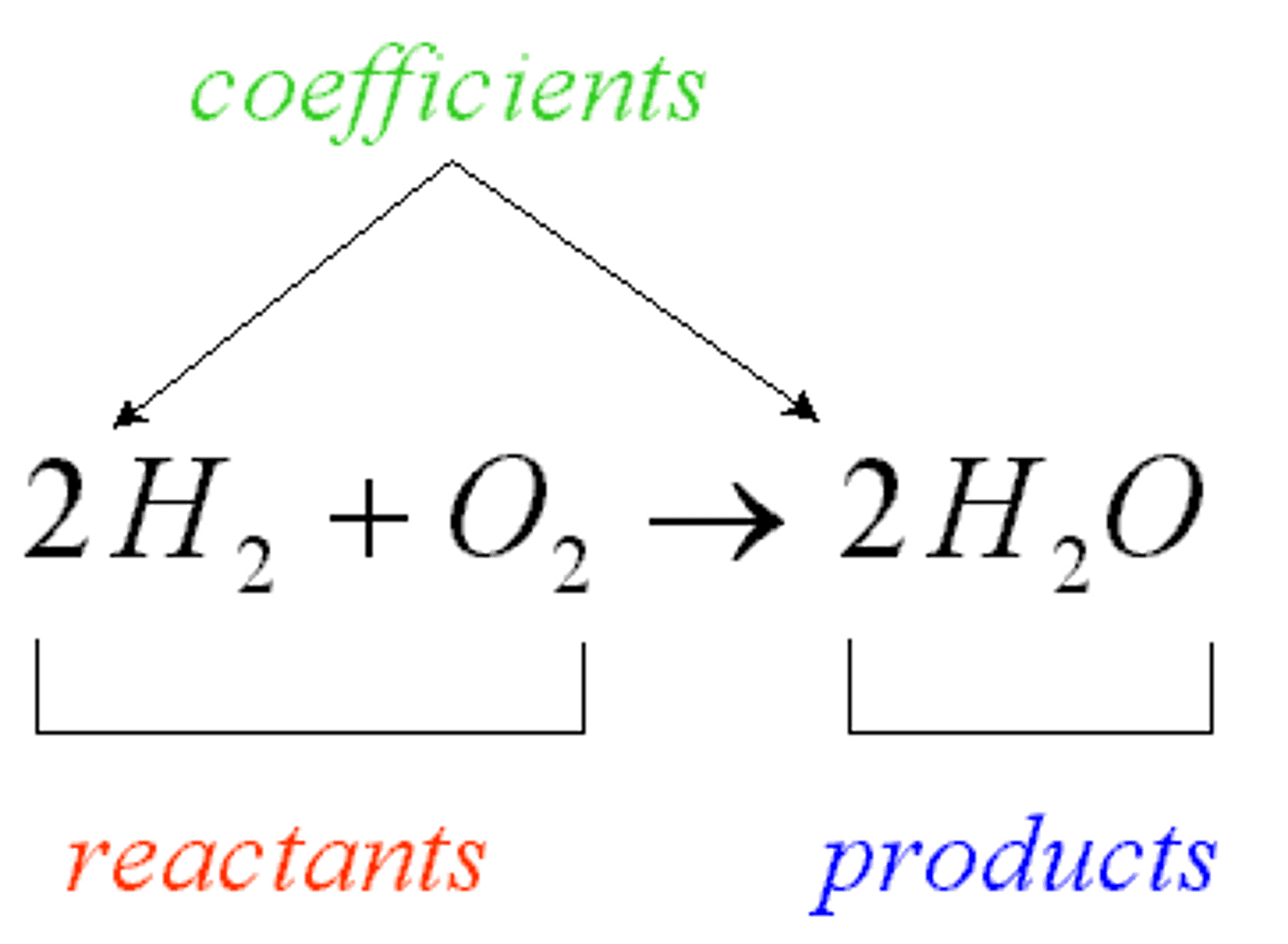
Chemical Reaction
the process by which one or more substances change to produce one or more different substances

Chemical change
A change in matter that produces one or more new substances
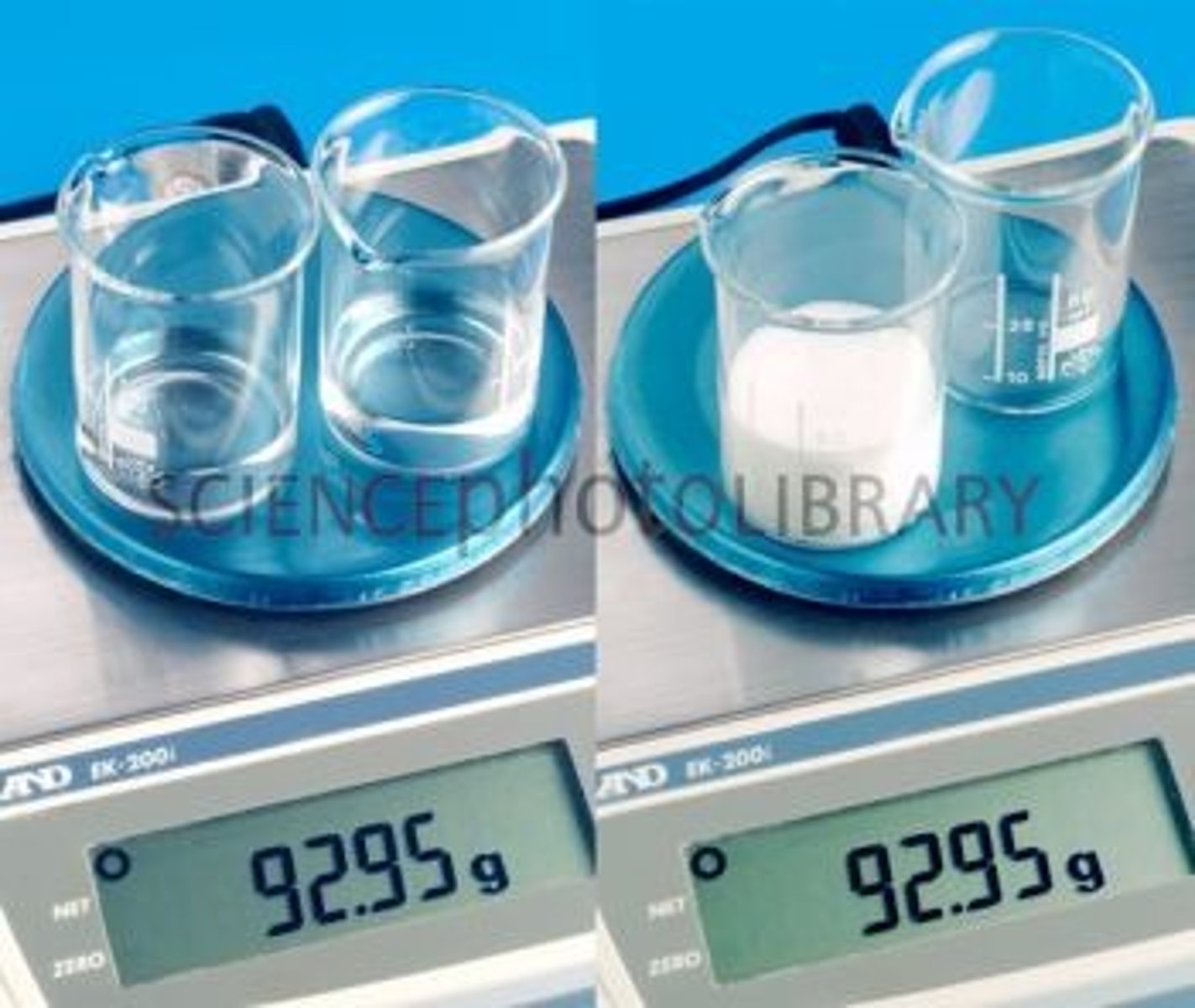
Law of Conservation of Mass
Matter is not created nor destroyed in any chemical or physical change

Chemical Formula
A combination of chemical symbols and numbers to represent a substance
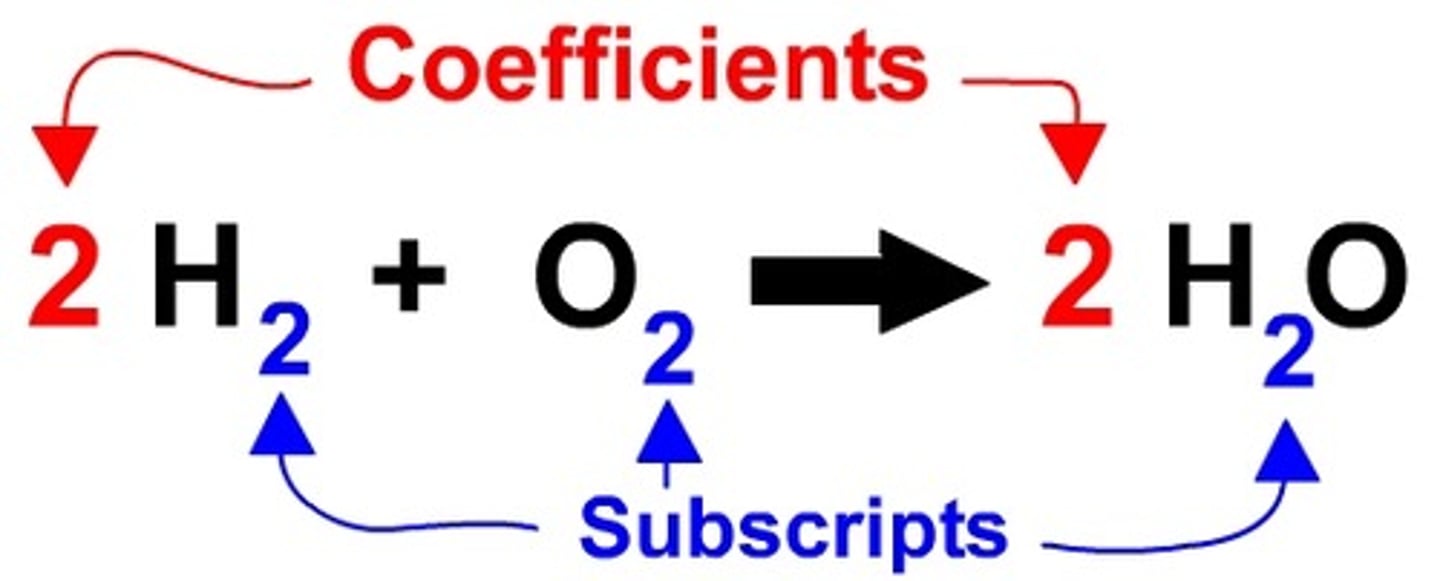
Coefficient
A number in front of a chemical formula in an equation that indicates how many molecules or atoms of each reactant and product are involved in a reaction.
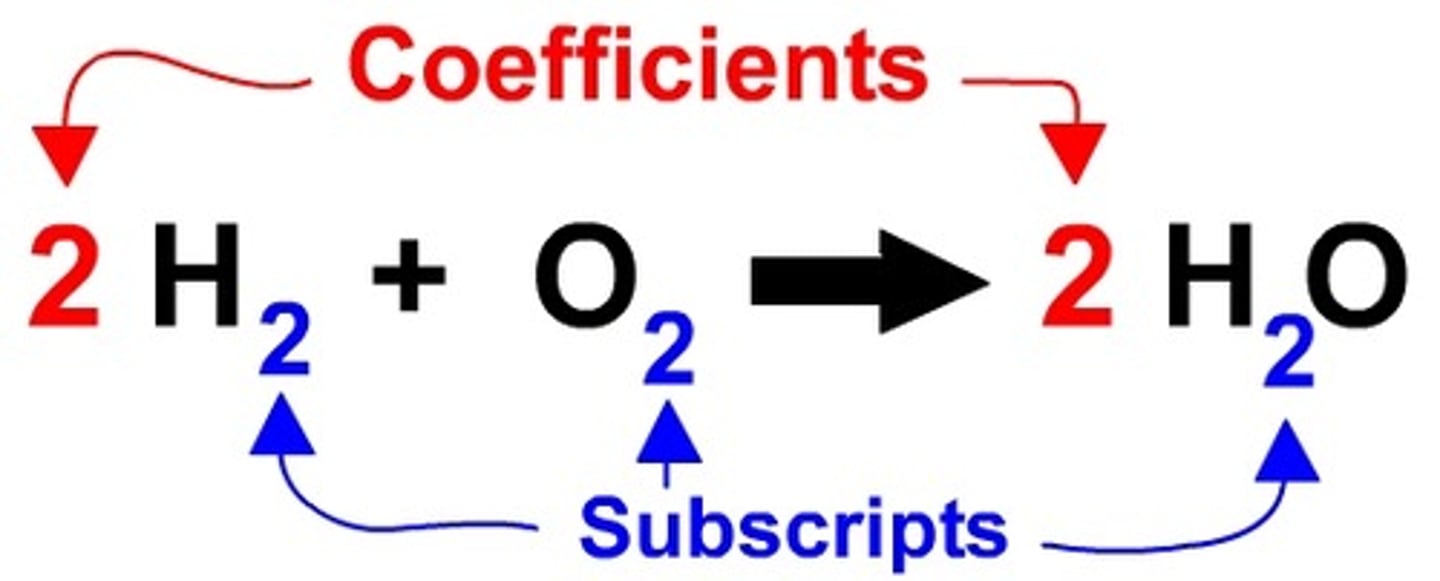
Subscript
A number in a chemical formula that tells the number of atoms in a molecule or the ratio of elements in a compound
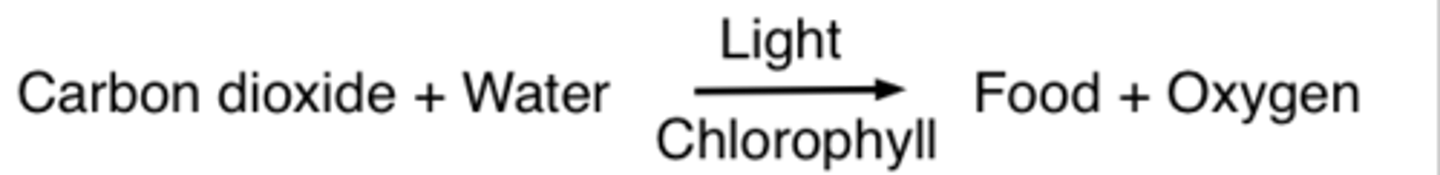
word equation
an equation in which the reactants and products in a chemical reaction are represented by words
Chemical Equation
A representation of a chemical reaction that uses symbols to show the relationship between the reactants and the products
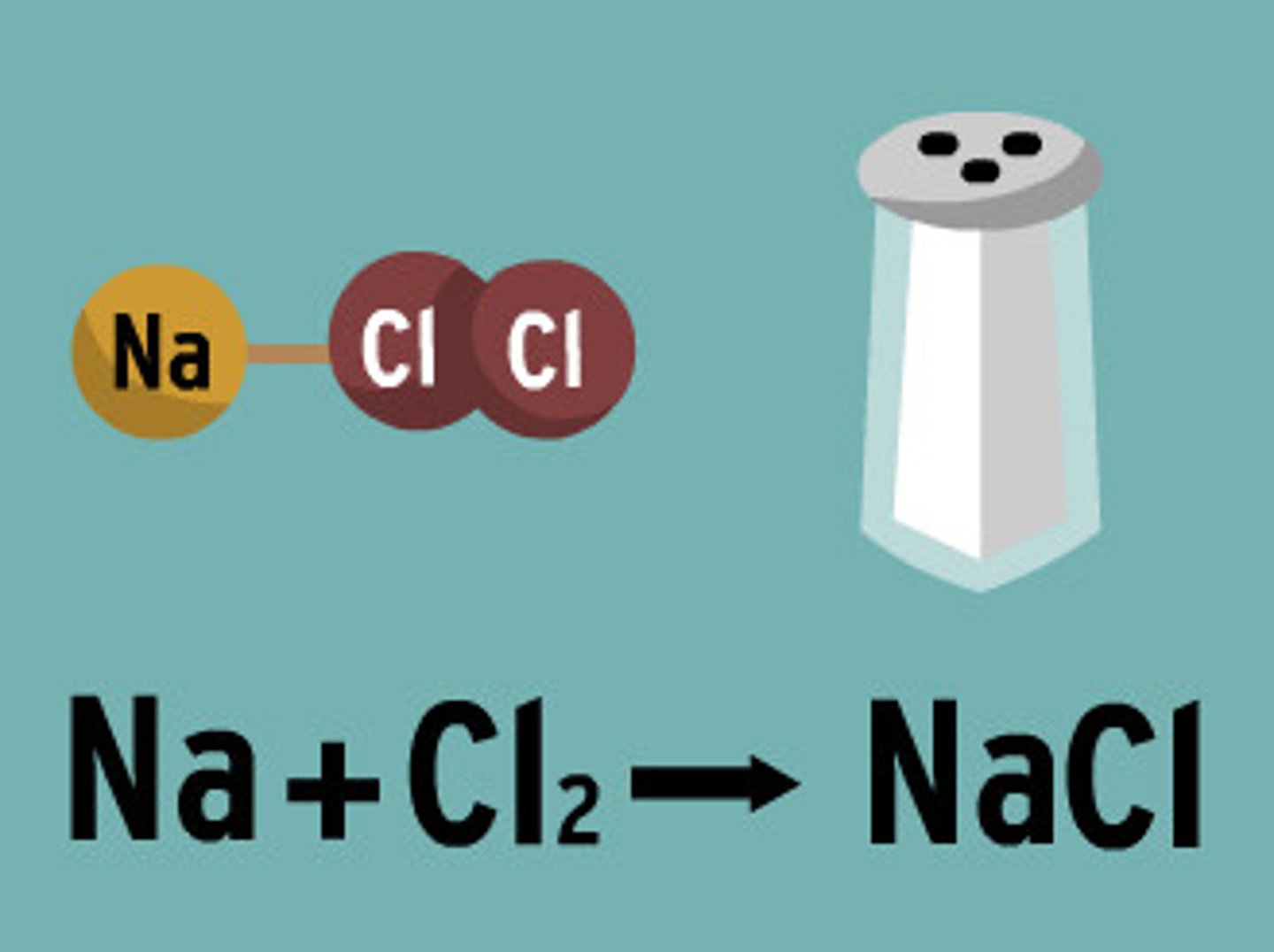
balanced chemical equation
chemical equation with the same number of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation
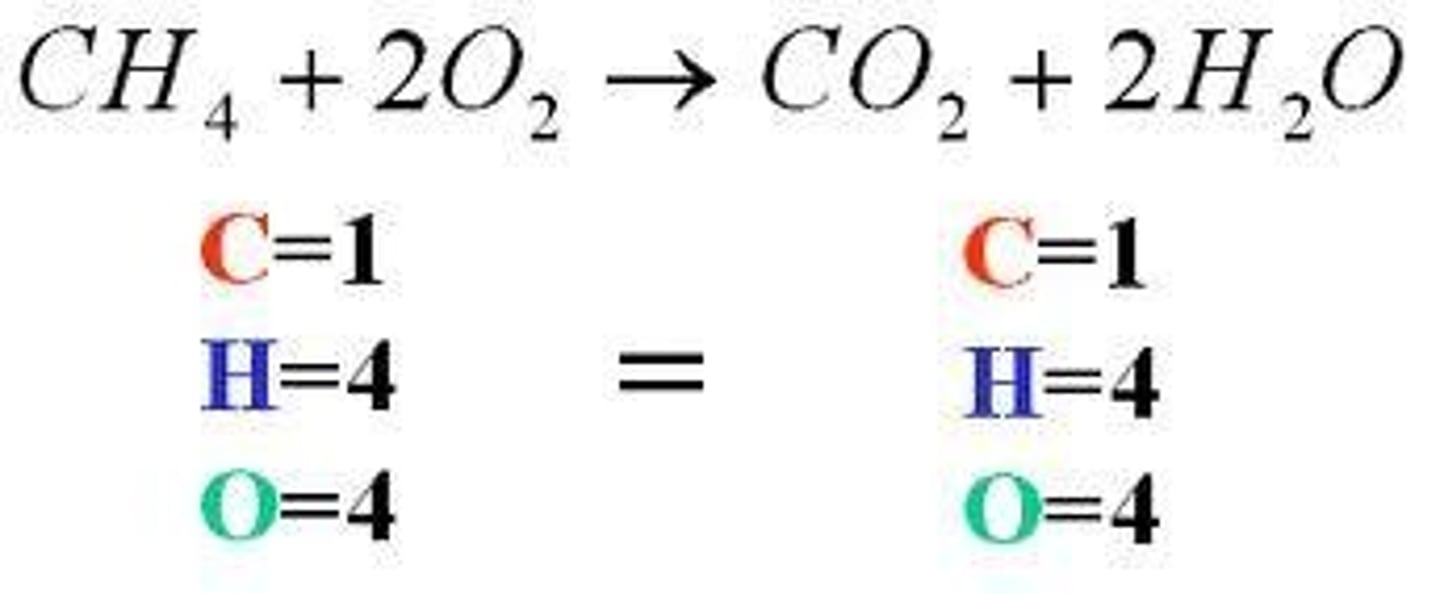
endothermic reaction
A reaction that ABSORBS energy in the form of heat

exothermic reaction
A reaction that releases energy in the form of heat

decomposition reaction
a reaction in which a single compound breaks down to form two or more simpler substances
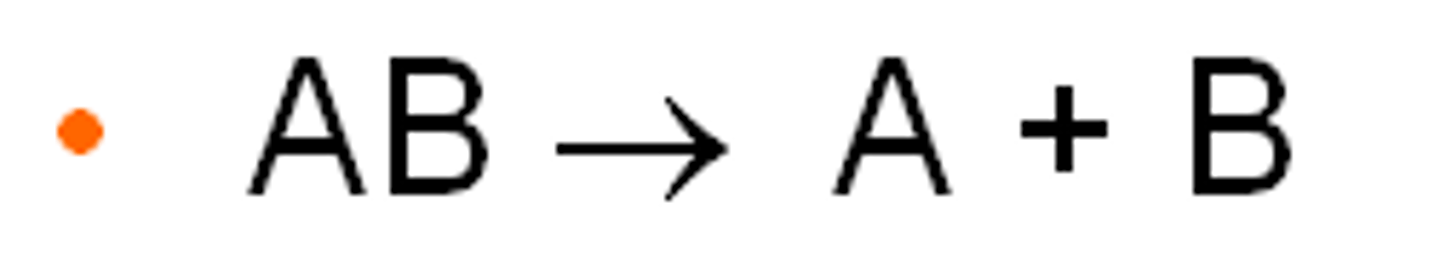
synthesis reaction
a reaction in which two or more substances combine to form a new compound
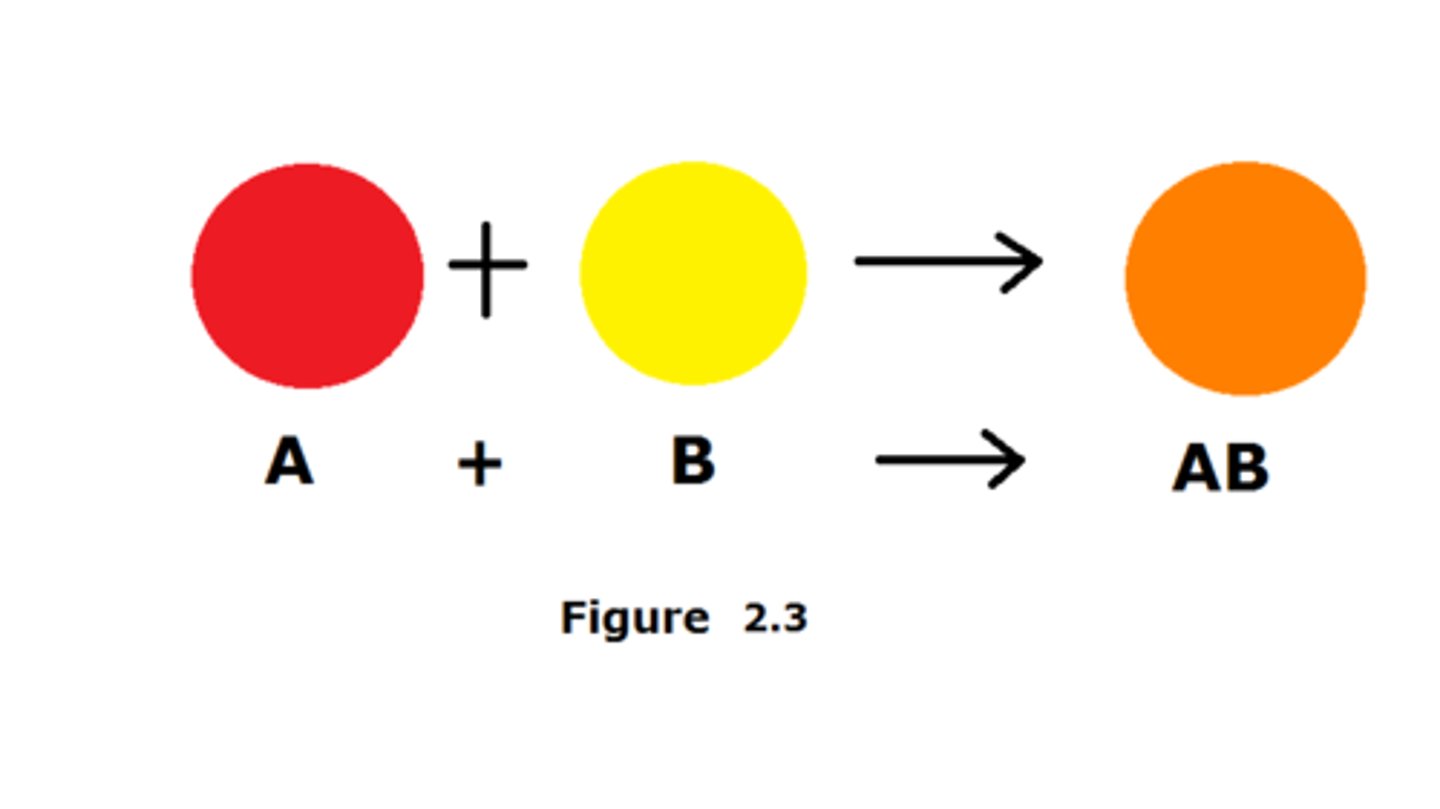
single replacement reaction
a chemical change in which one element replaces a second element in a compound
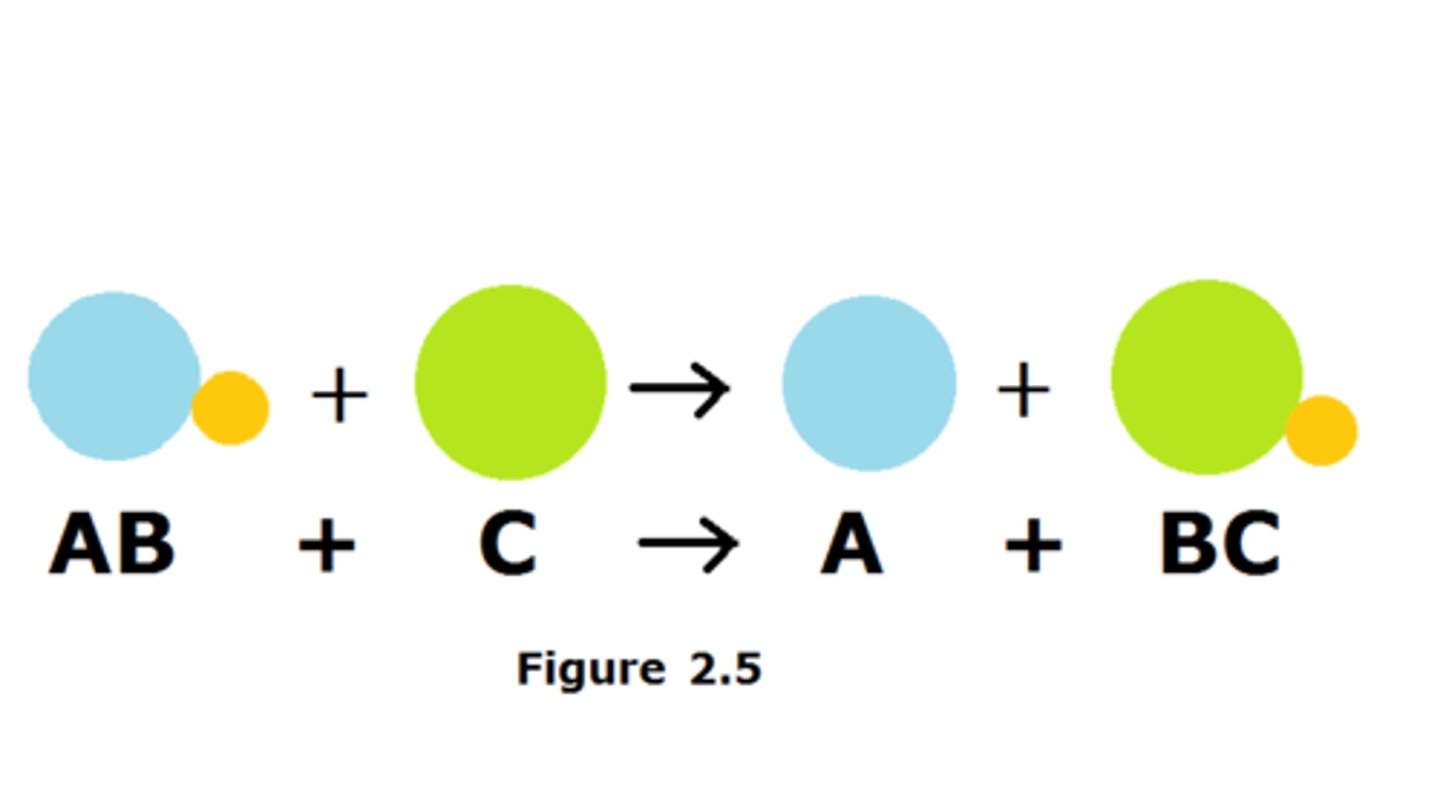
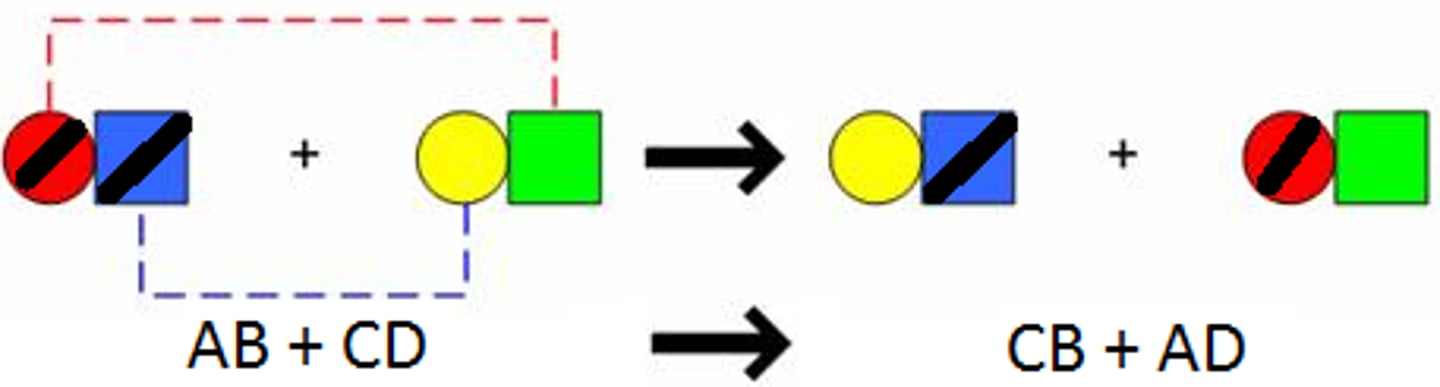
double replacement reaction
a chemical change that involves an exchange of positive ions between two compounds
combustion reaction
a chemical reaction that occurs when a substance reacts with oxygen, releasing energy in the form of heat and light
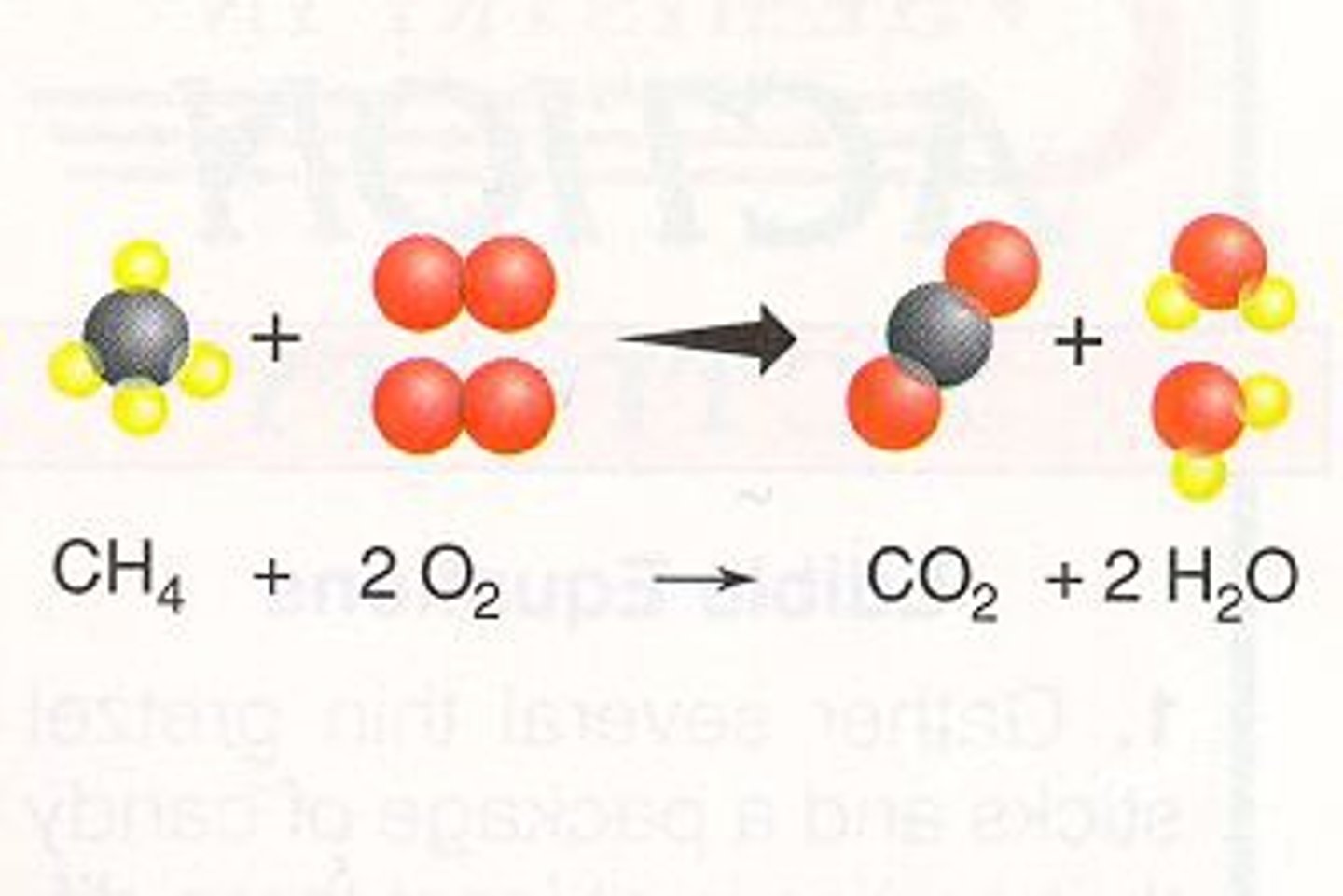
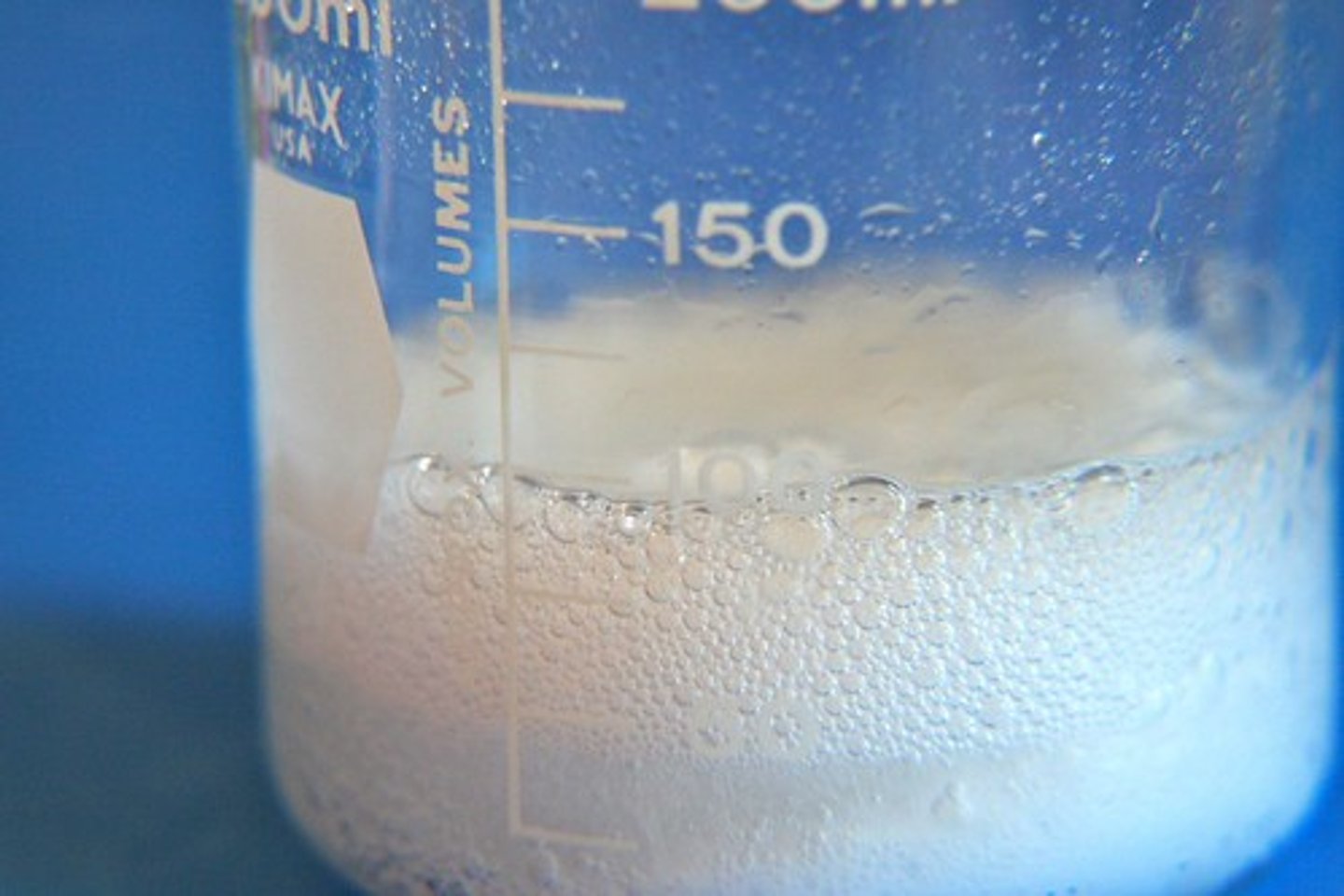
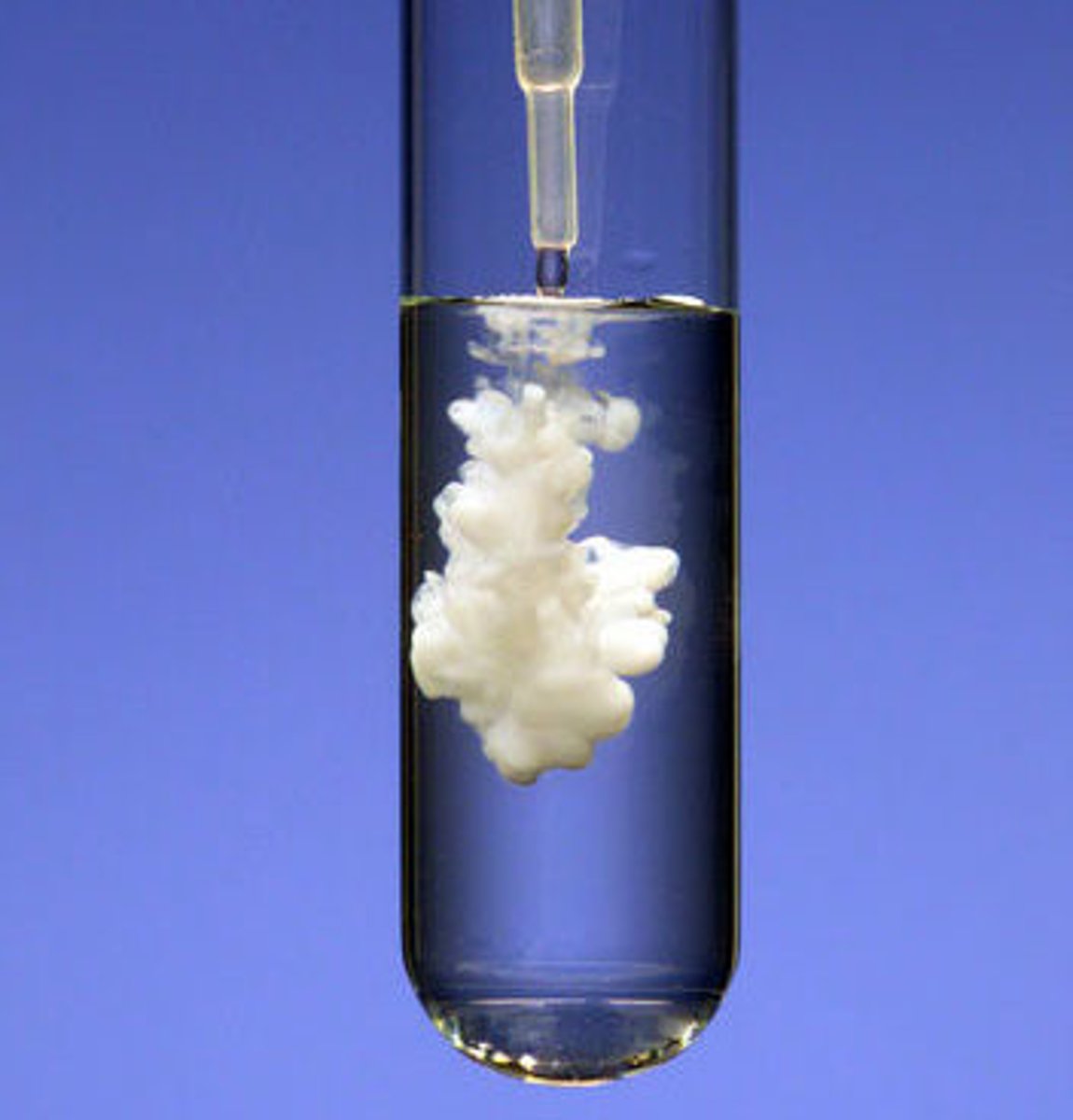
precipitation reaction
a reaction in which an insoluble substance forms and separates from the solution

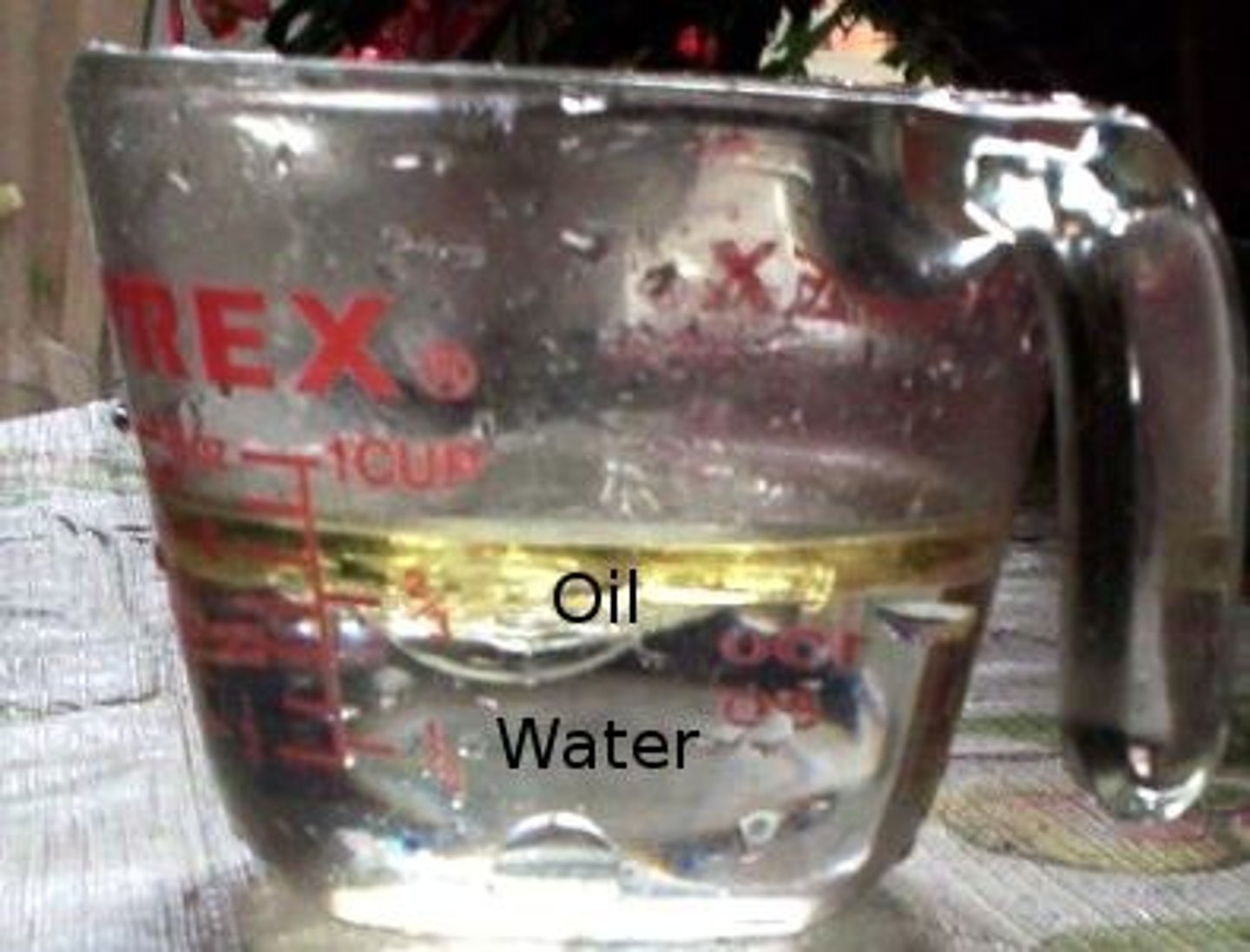
soluble
capable of being dissolved

Insoluble
incapable of being dissolved

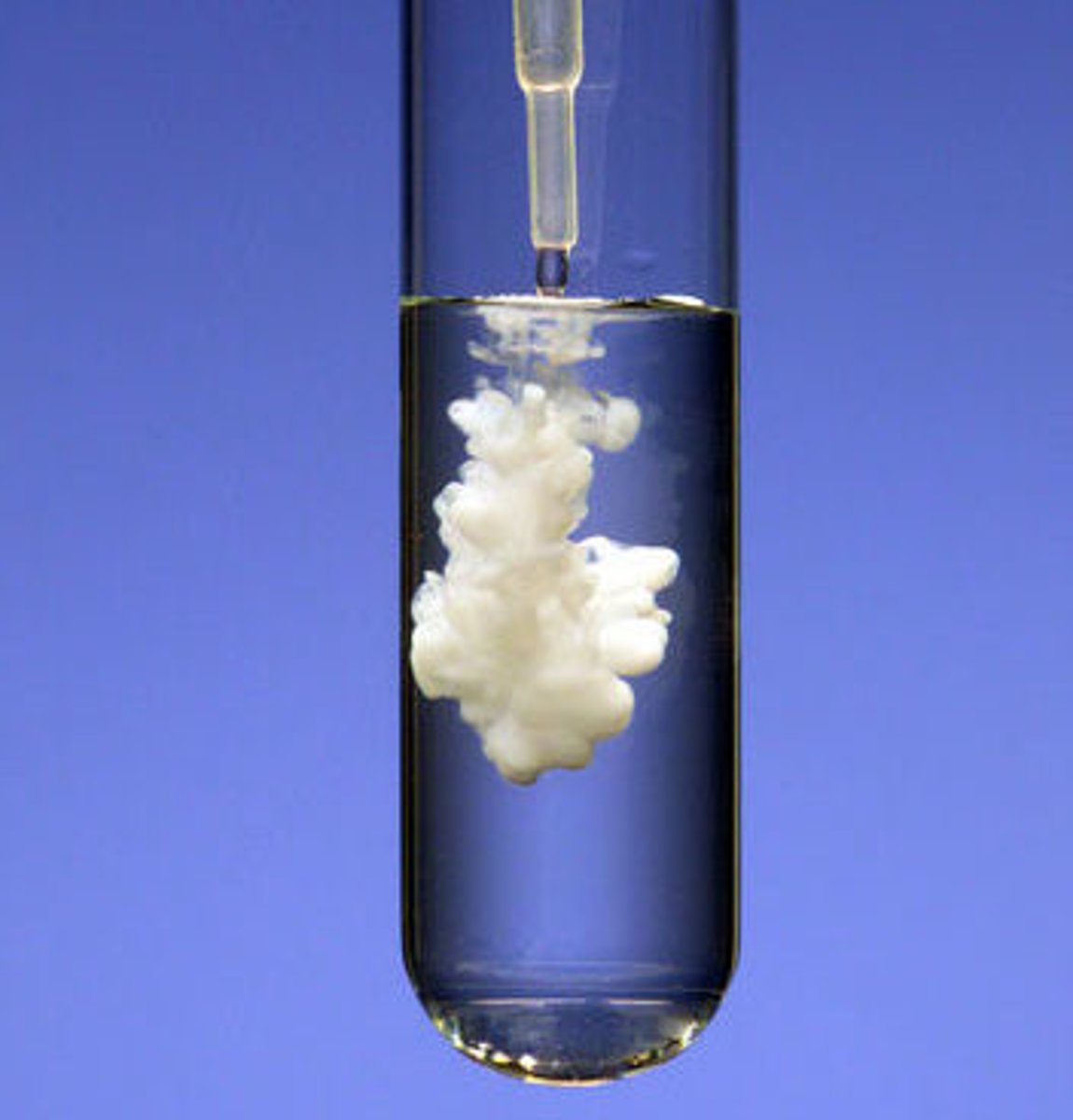
precipitate
A solid that forms from a solution during a chemical reaction.

reaction rate
the rate at which reactants change into products over time
Temperature & reaction rate
usually the higher the temperature the faster the reaction rate
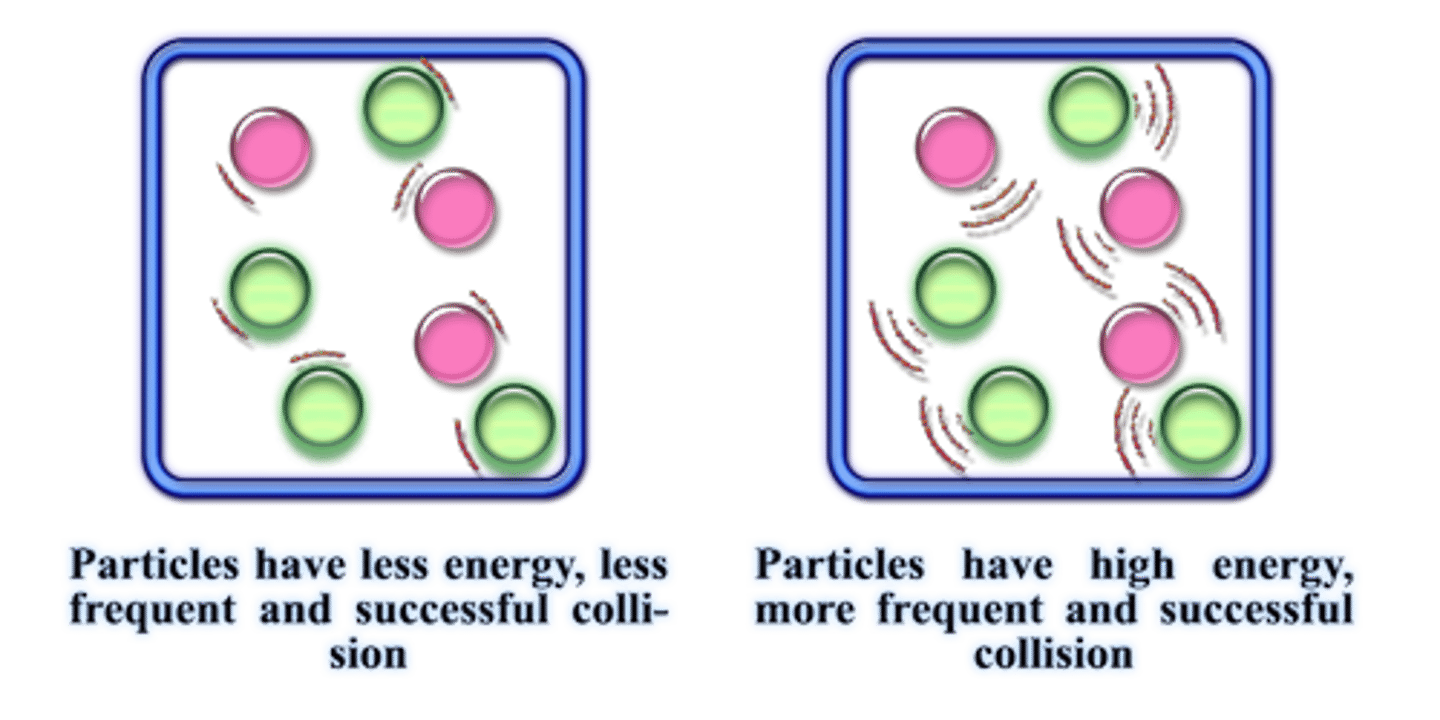
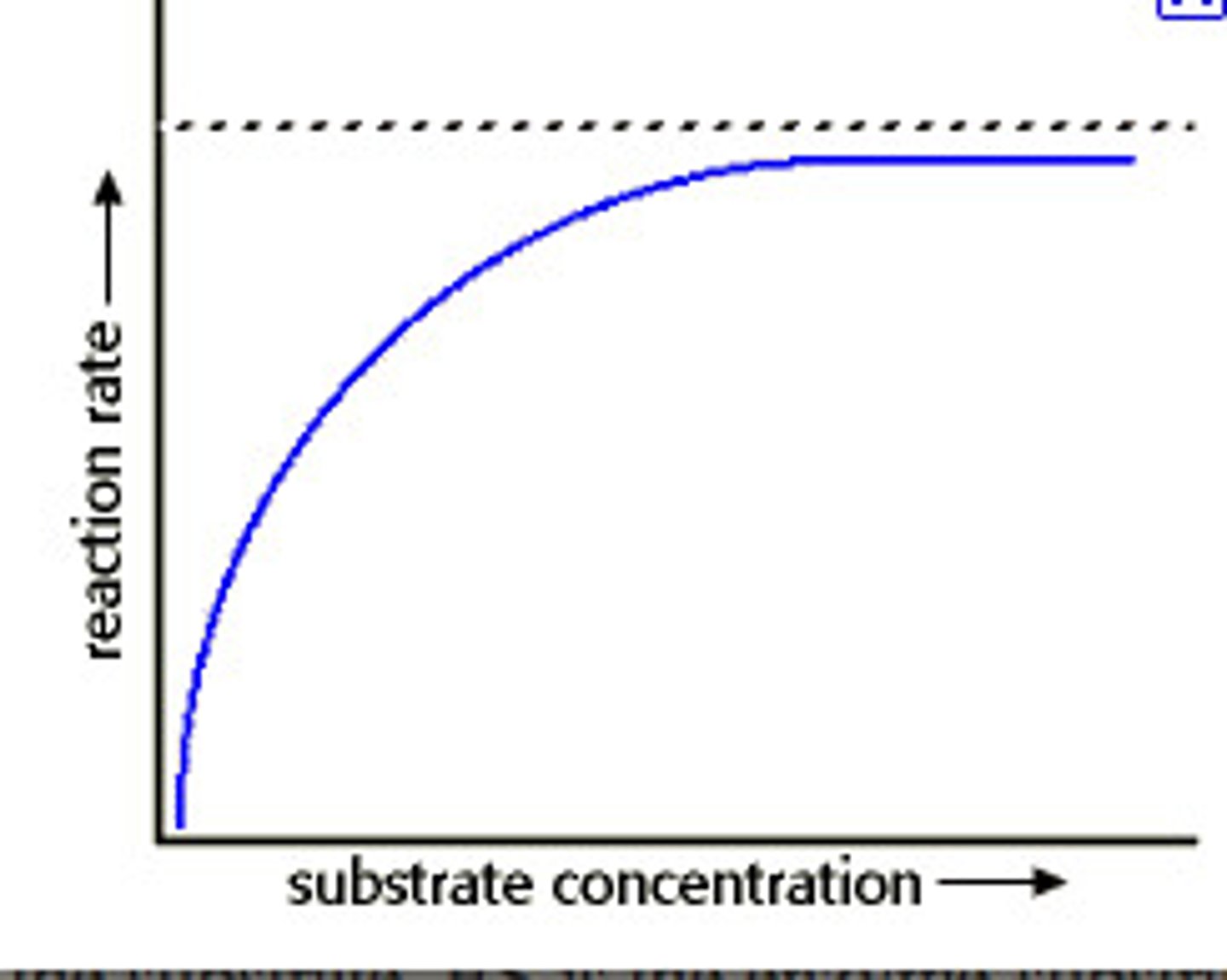
Concentration & Reaction Rate
the higher the concentration of starting materials, the more rapidly the reaction takes place (more collisions taking place). as more reactants are consumed the rate of reaction slows down
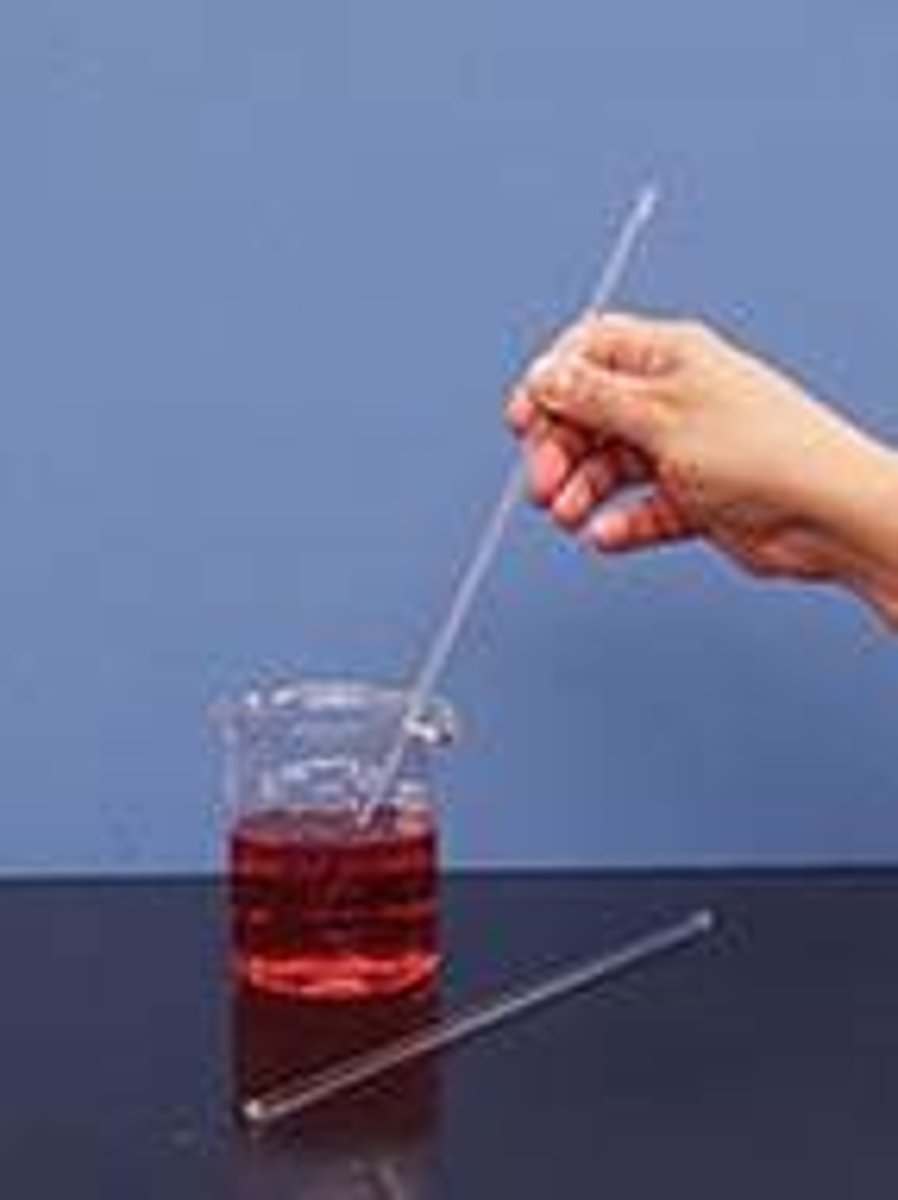
Agitation
Stirring up the reactants - increasing the reaction rate

catalyst
substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction
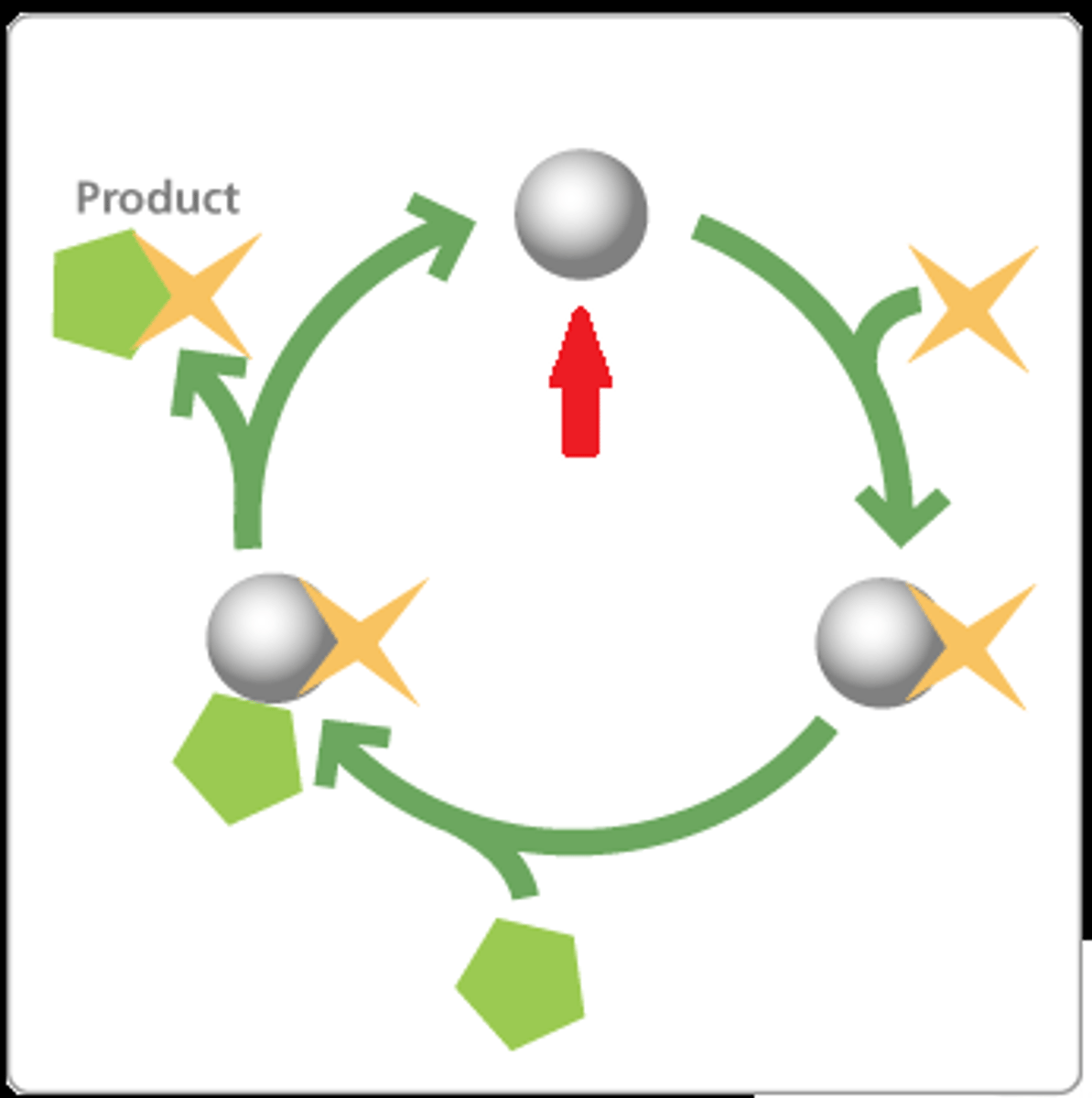
Enzymes
Catalysts for chemical reactions in living things
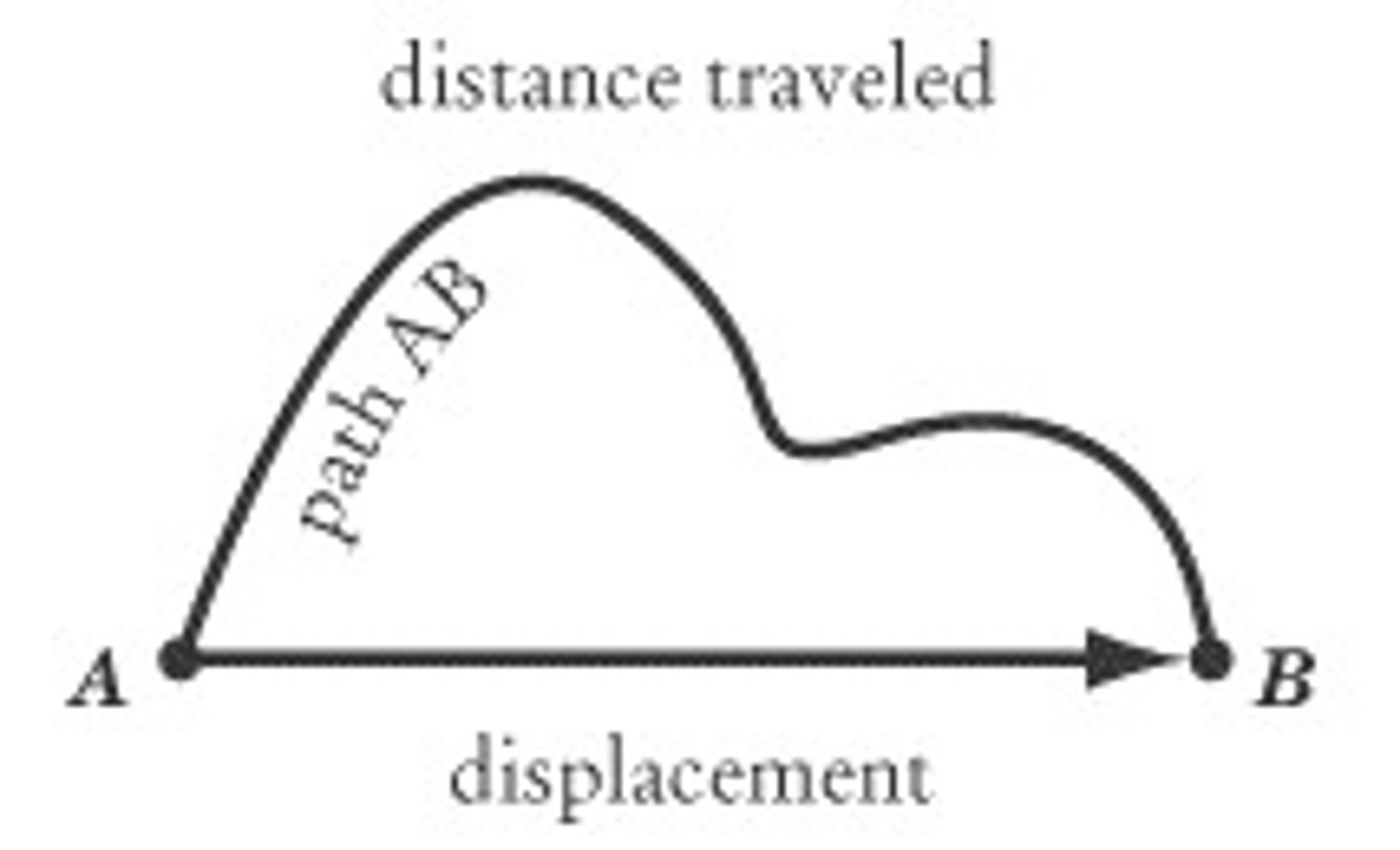
Displacement
Distance and direction of an object's change in position from the starting point.
Speed
The distance an object travels per unit of time

v=d/t
Formula for average speed
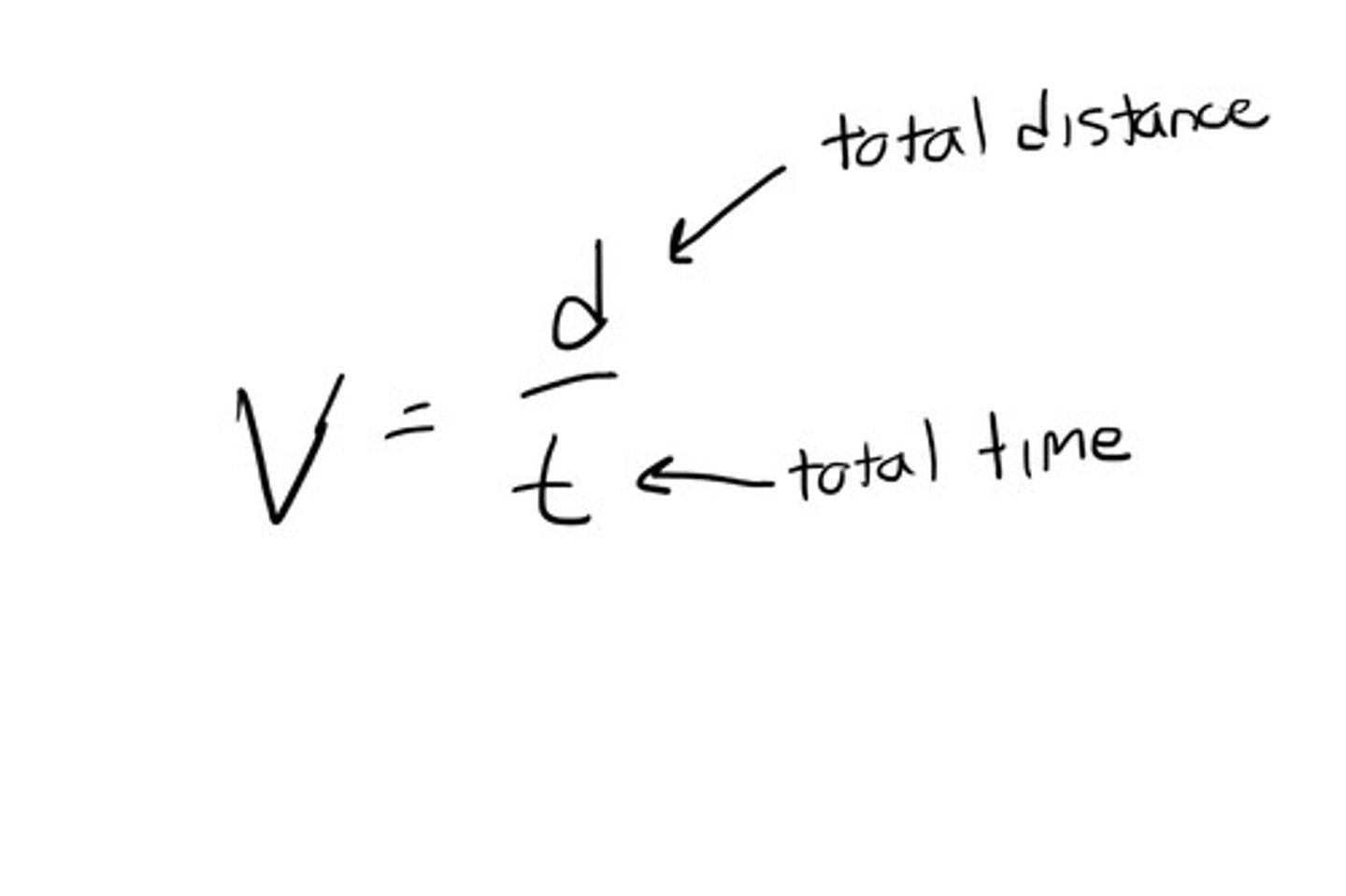
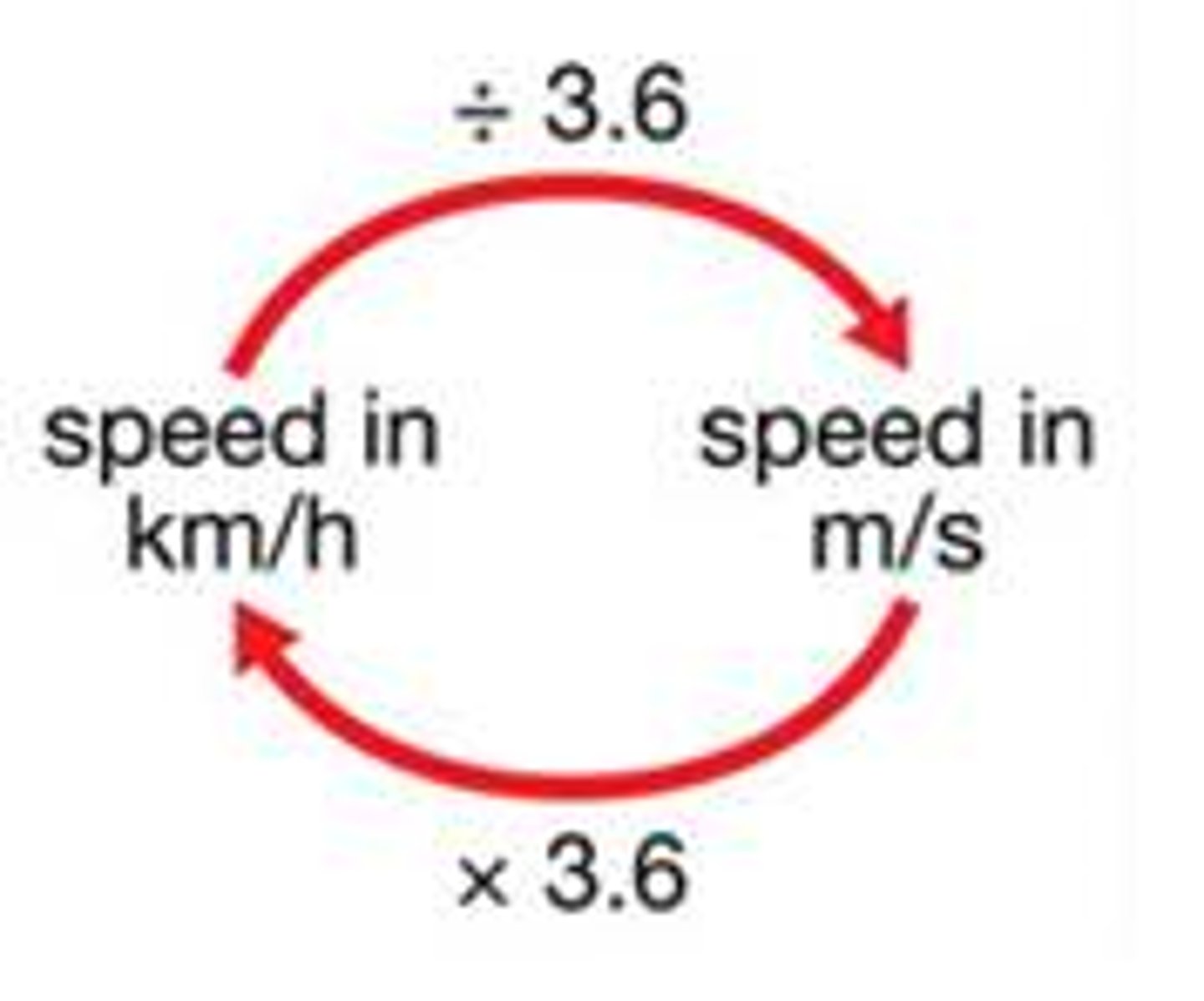
multiply or divide by 3.6
Convert from m/s to kmph
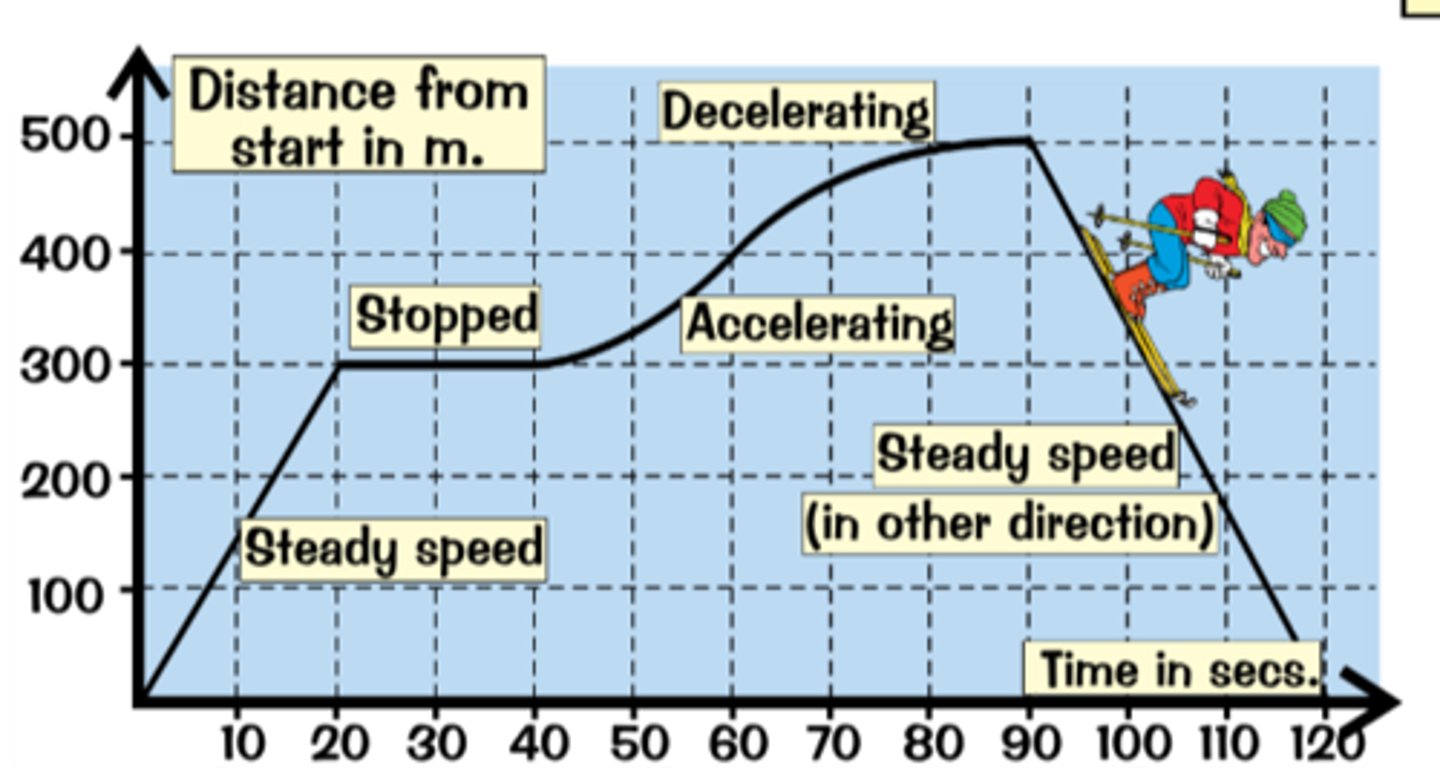
Distance time graph
A graph with distance on the vertical axis and time on the horizontal axis
Acceleration
The rate at which velocity changes

a=(delta)v/t
acceleration equation
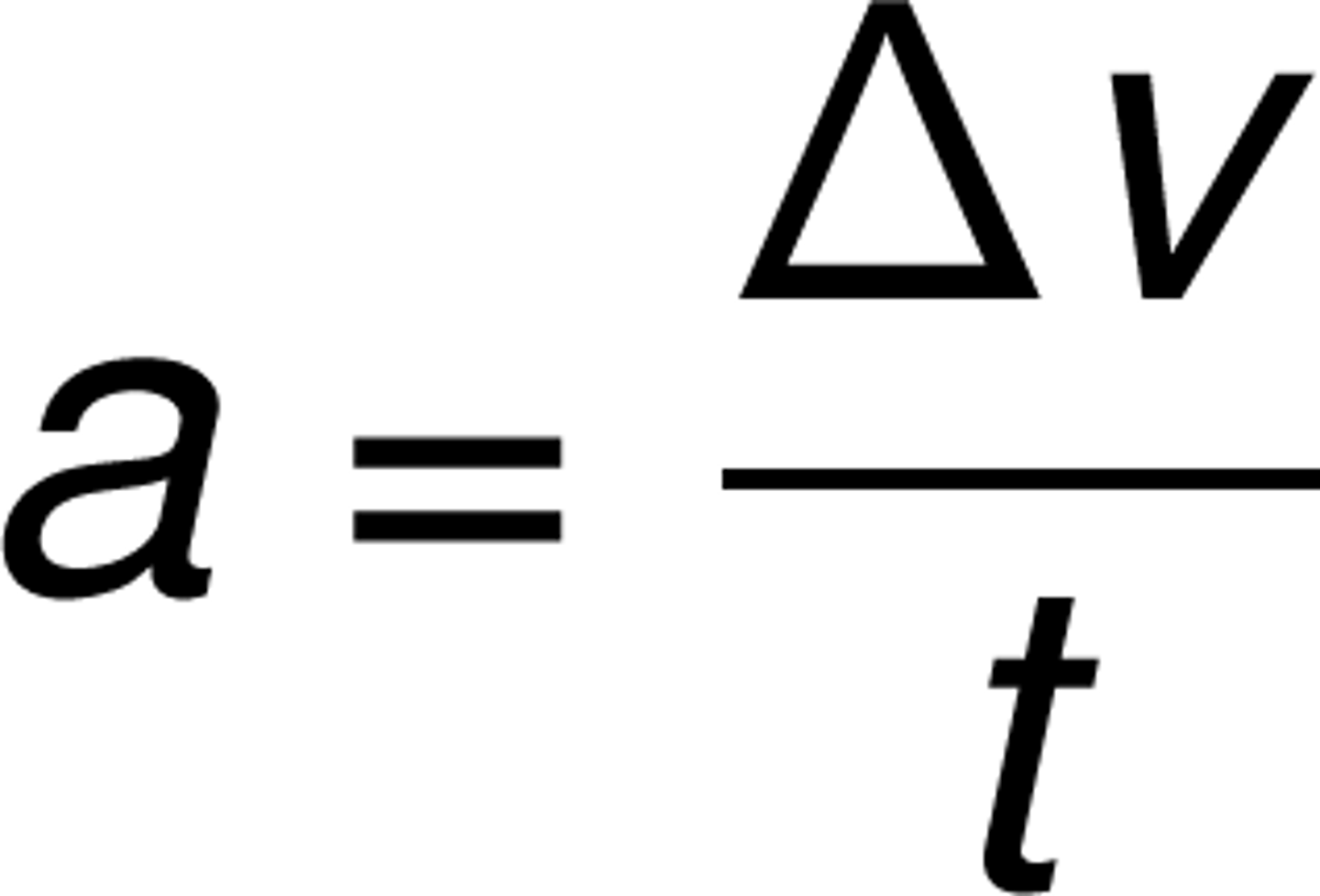
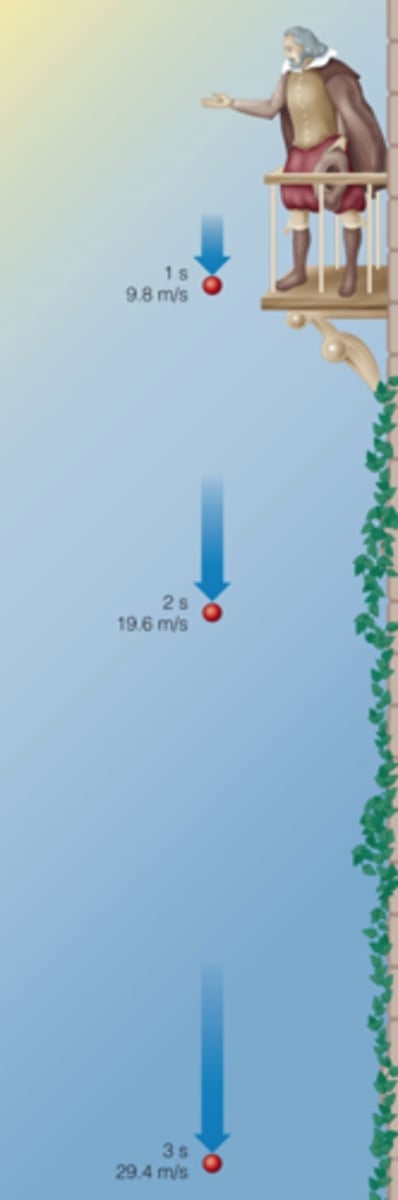
9.8m/s/s
acceleration due to gravity
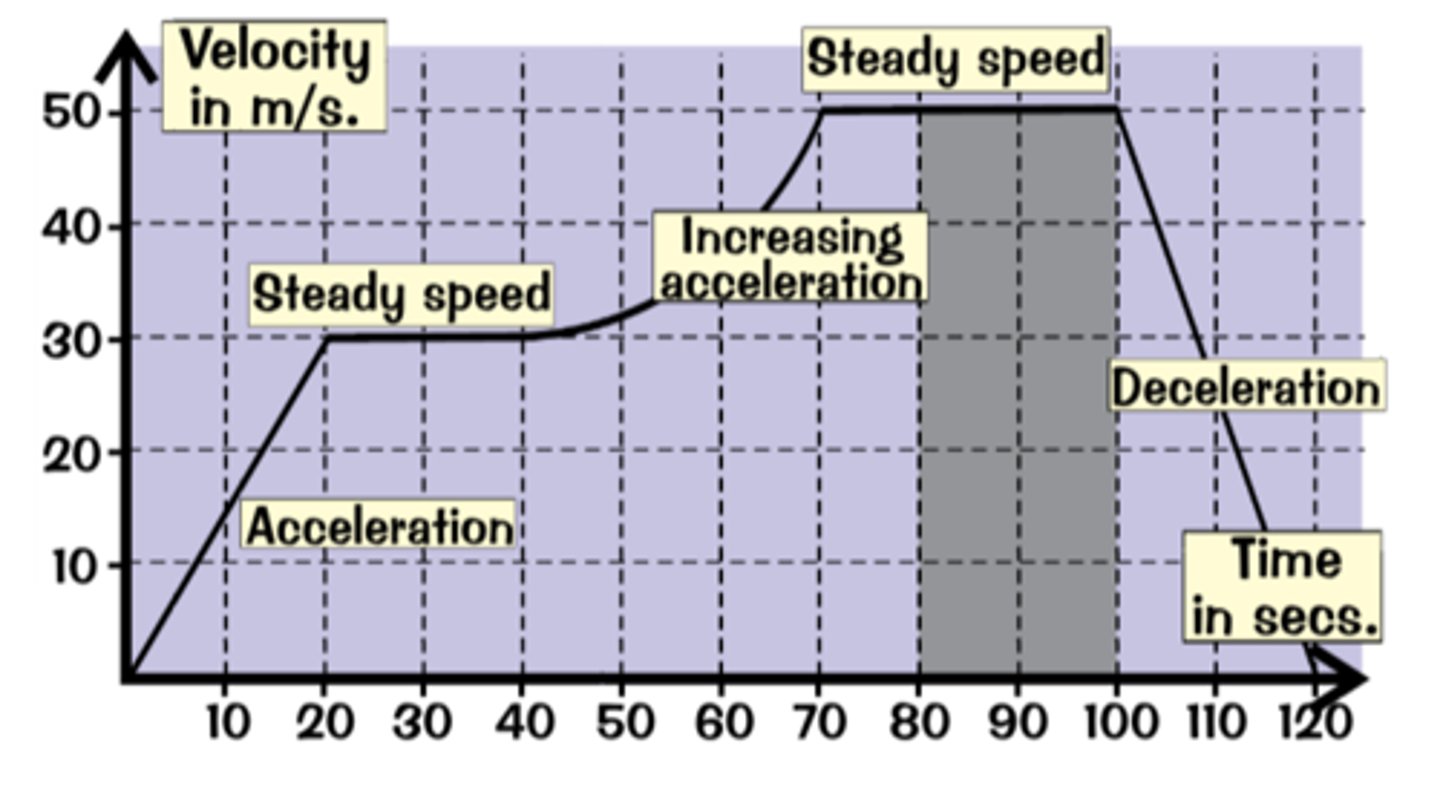
Velocity time graph
a graph that can be used to plot the velocity of an object versus time and to determine the sign of an object's acceleration
Newton's laws of motion
Laws proposed by Isaac Newton that explain how force and motion work.

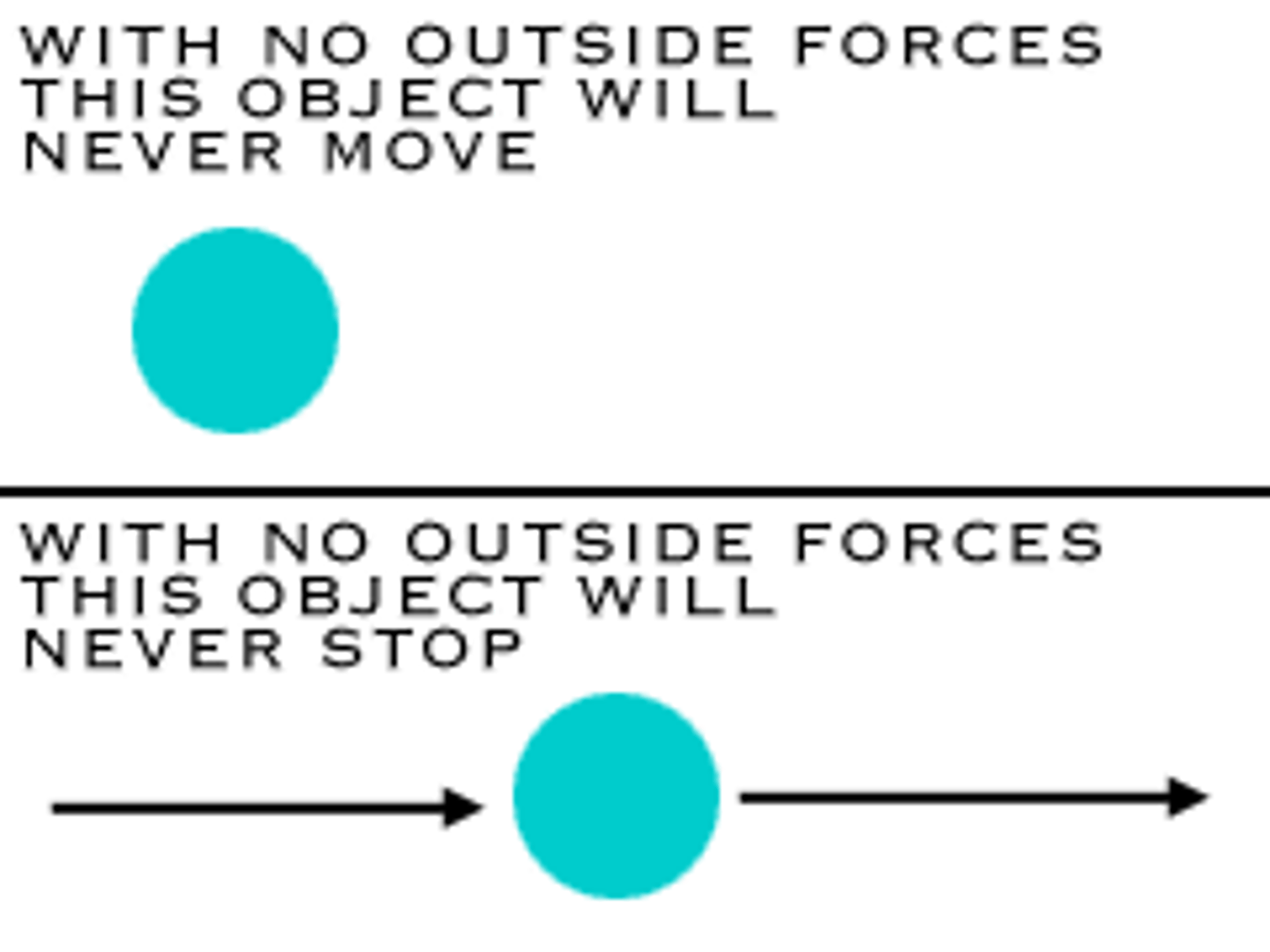
Newton's 1st Law
(Law of Inertia) an object in motion tends to stay in motion & an object at rest stays at rest unless acted upon by an outside force.
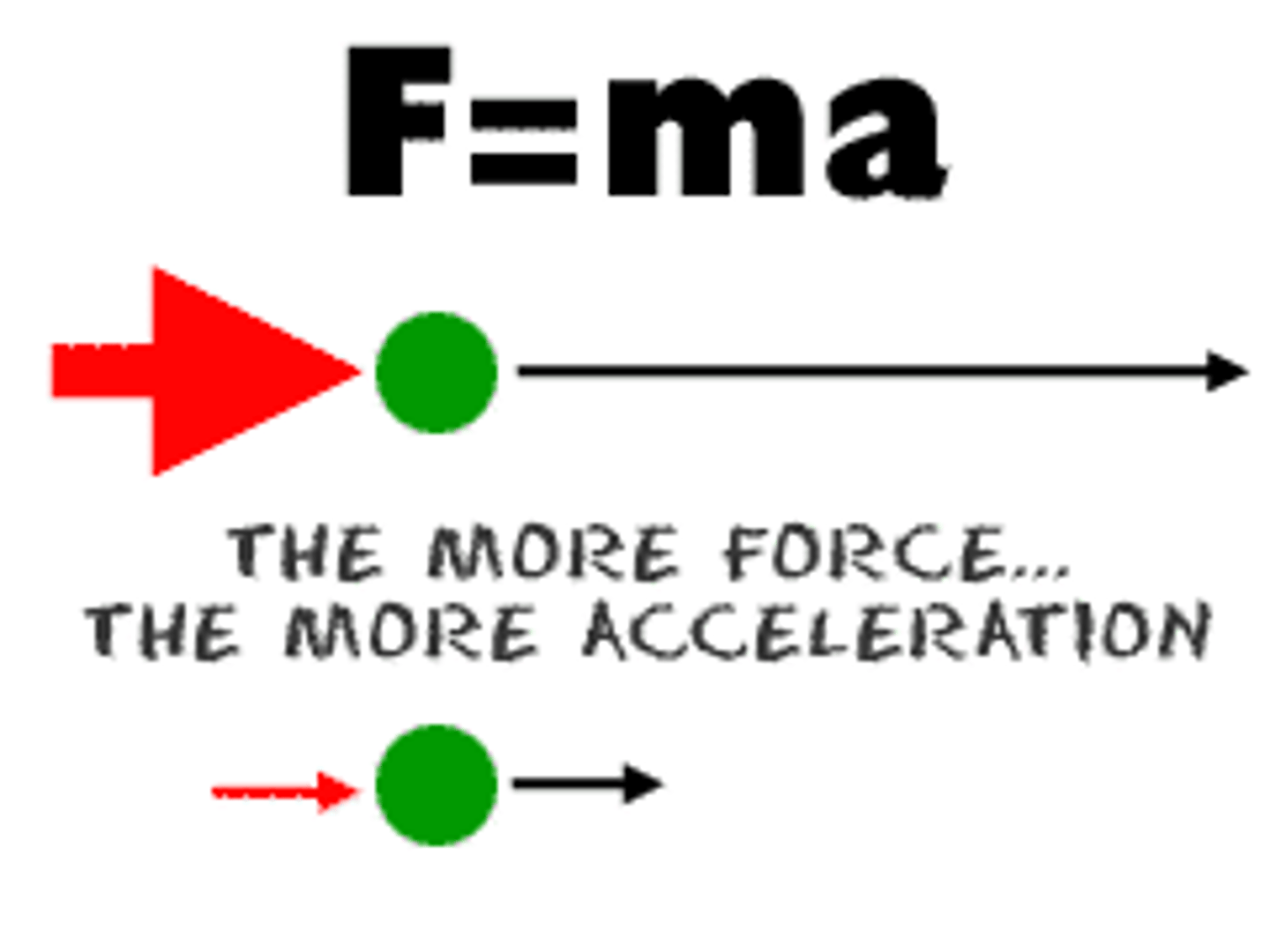
Newton's 2nd Law
The acceleration of an object depends on the mass of the object and the amount of force applied.
Newton's 3rd Law
For every action force there is an equal and opposite reaction force

F=ma
Formula for force
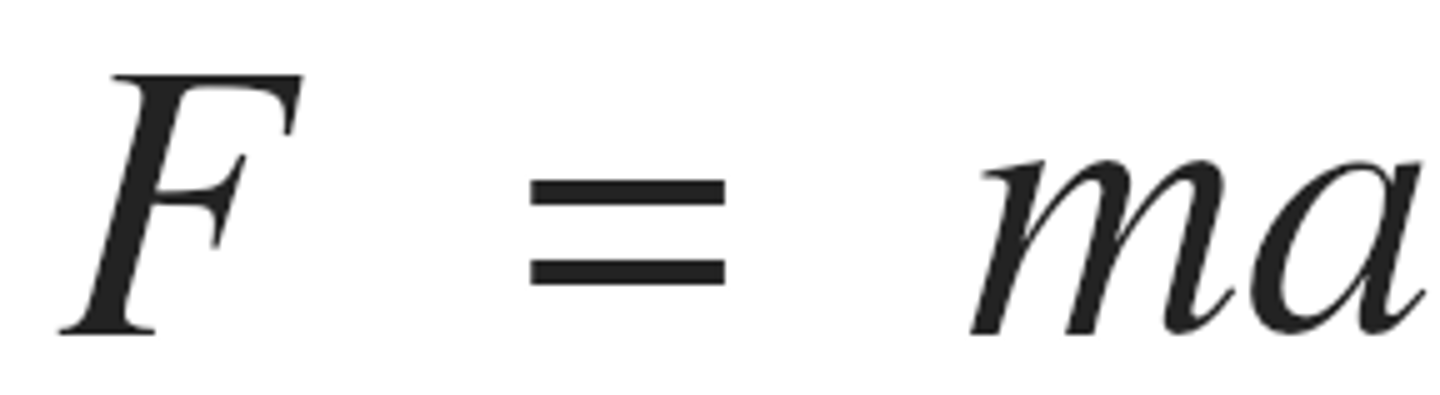
Species
A group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring.

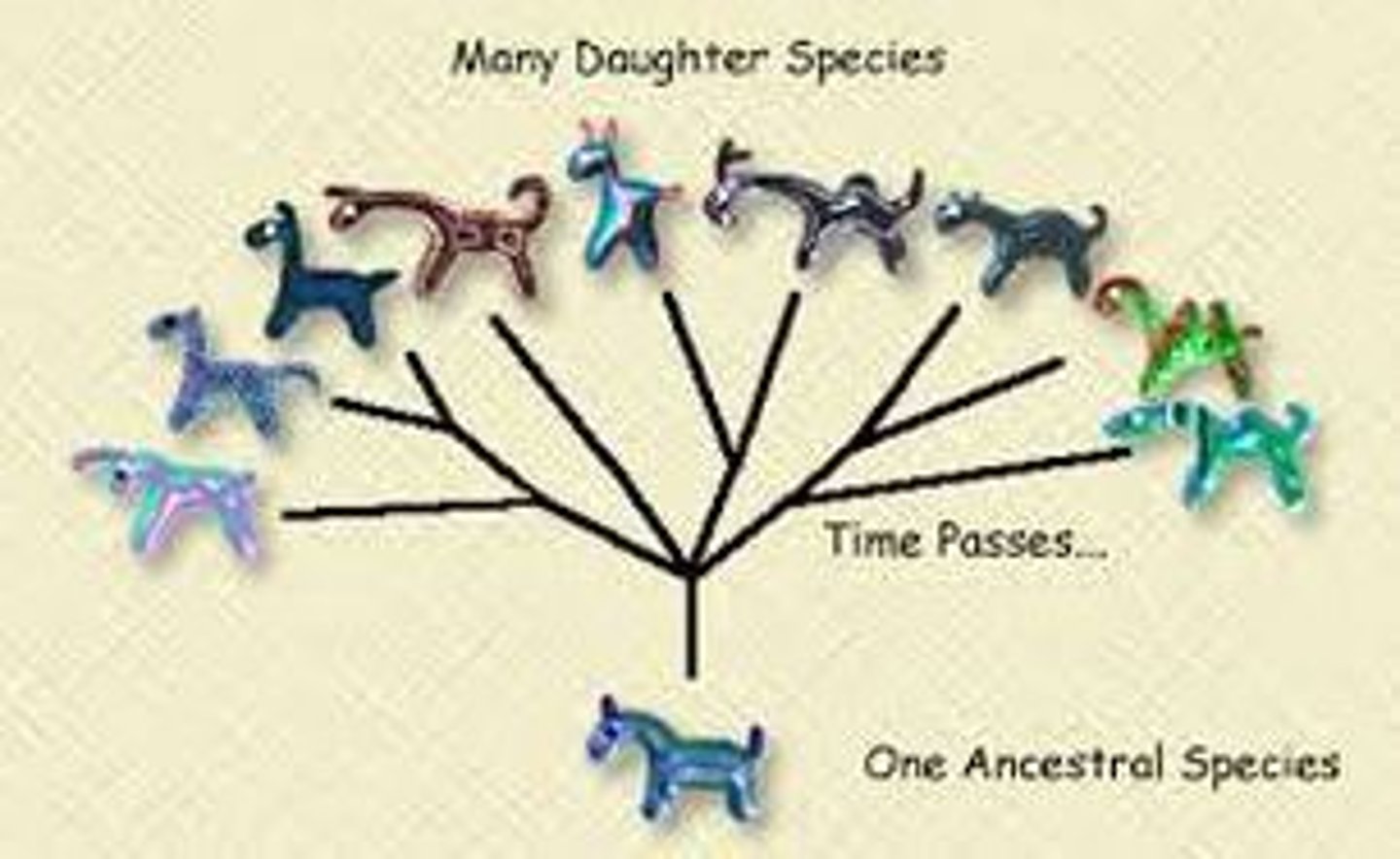
Evolution
The process of change in all forms of life over generations.
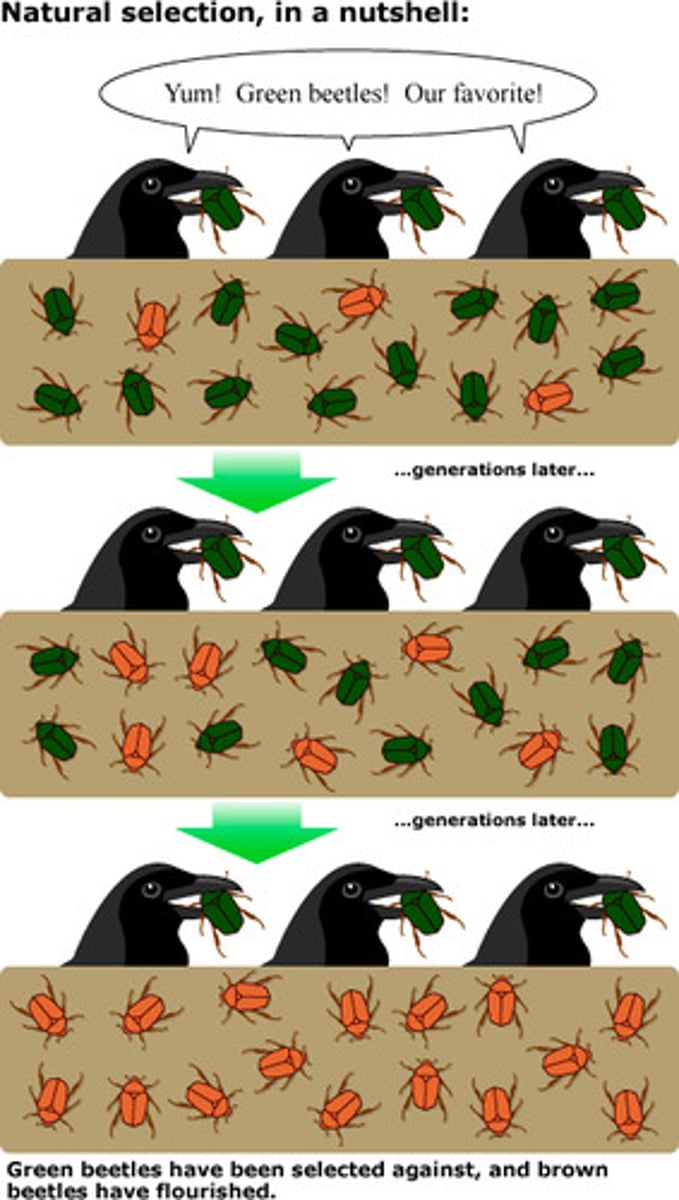
Natural Selection
The process by which organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and reproduce.
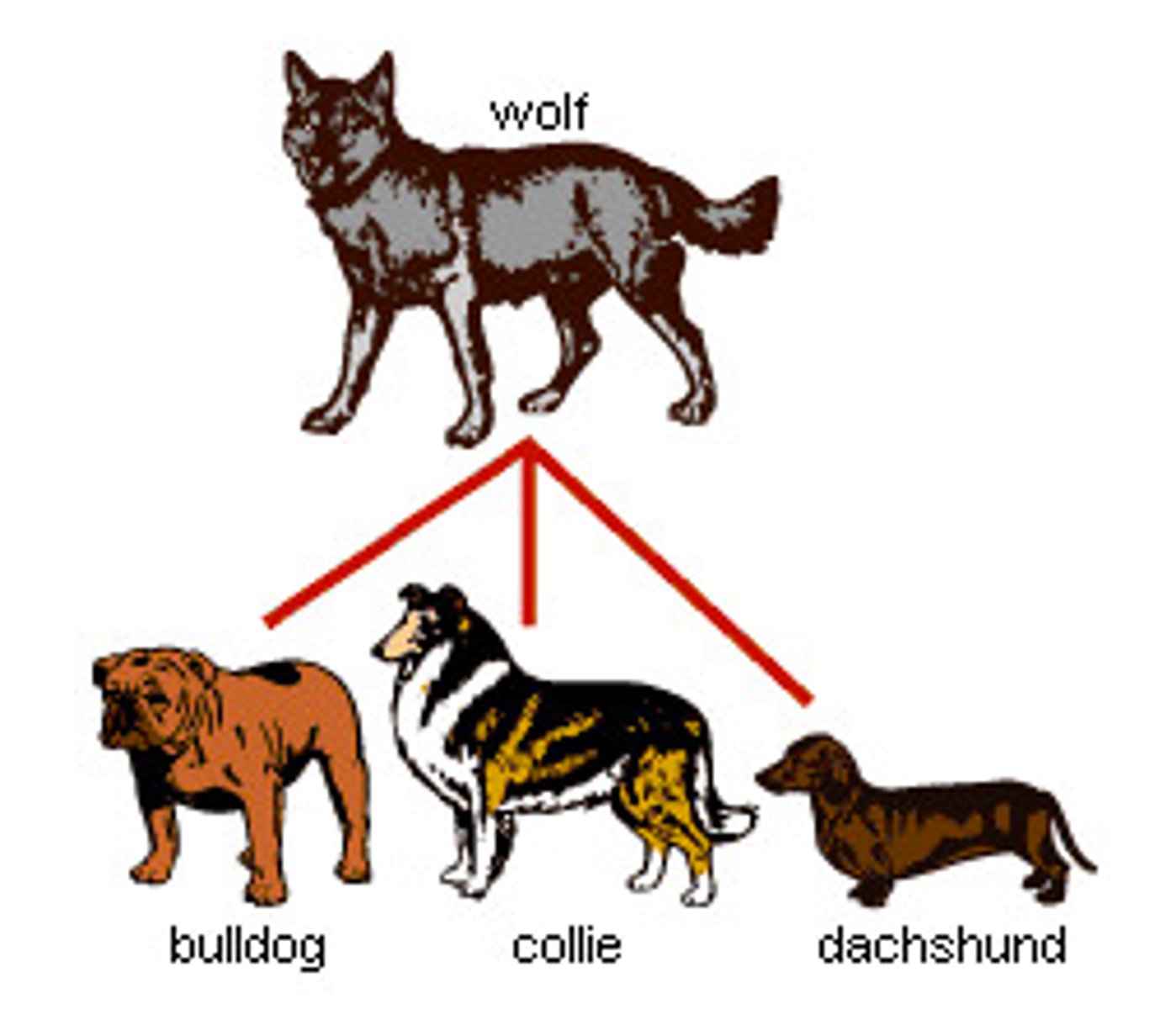
Artificial Selection
The process of intentional selection and breeding of organisms by humans for desirable traits.
Charles Darwin
A British naturalist who proposed the theory of evolution by natural selection.

Genetic Change
Changes in the genetic material of a population over time.
Biodiversity
The variety of life in a particular habitat or ecosystem.

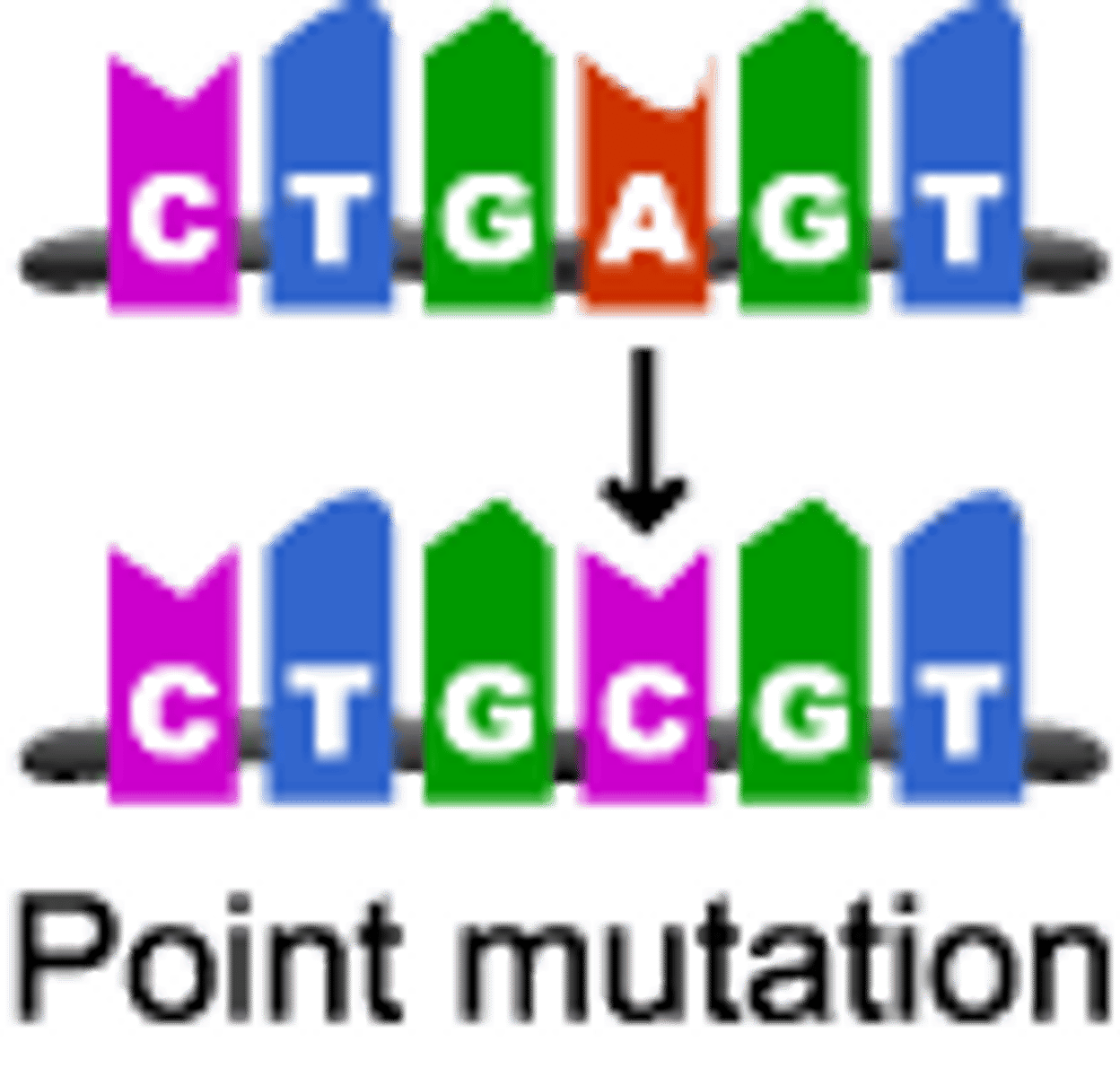
Mutation
A change in the DNA sequence of a gene.
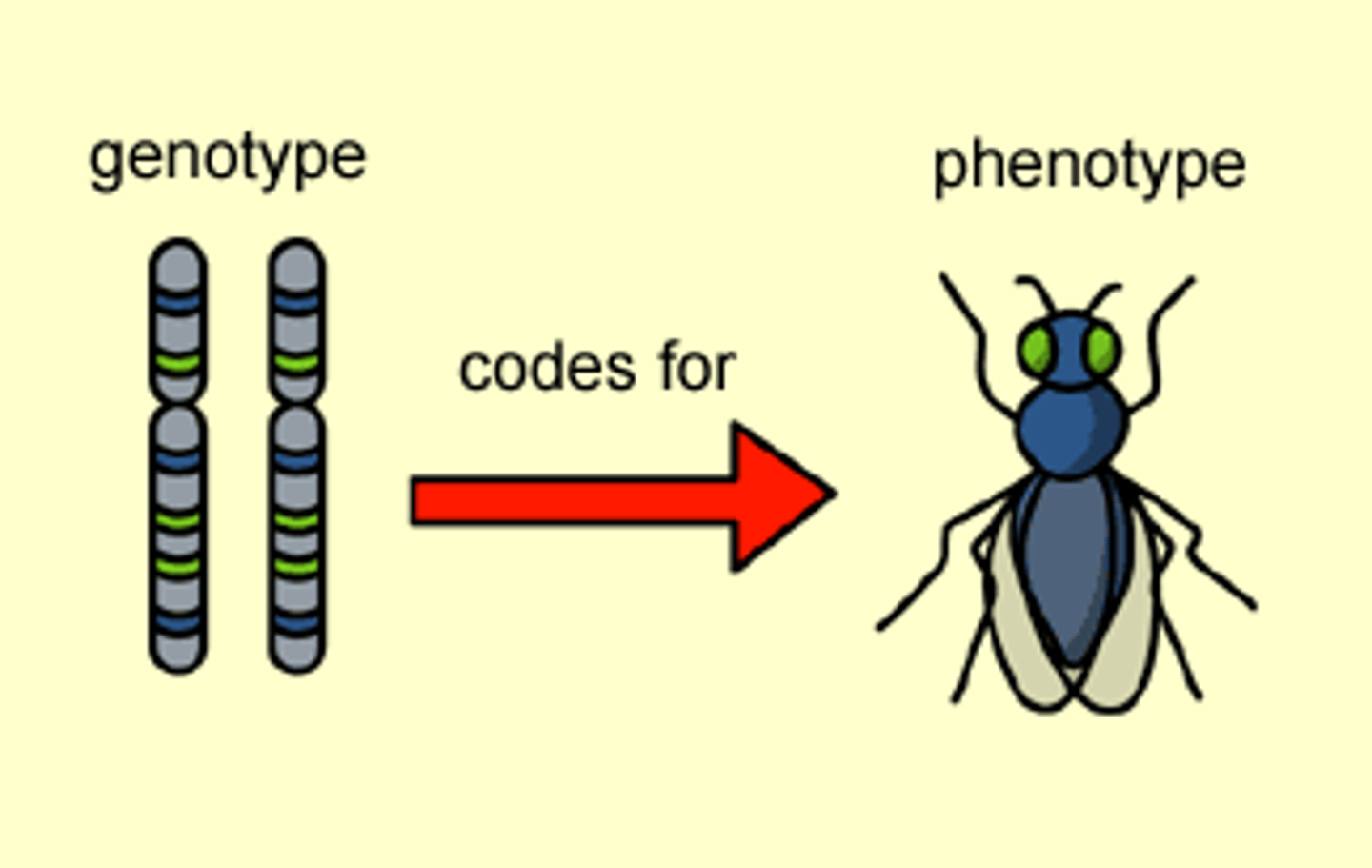
Phenotype
The observable physical or biochemical characteristics of an organism.
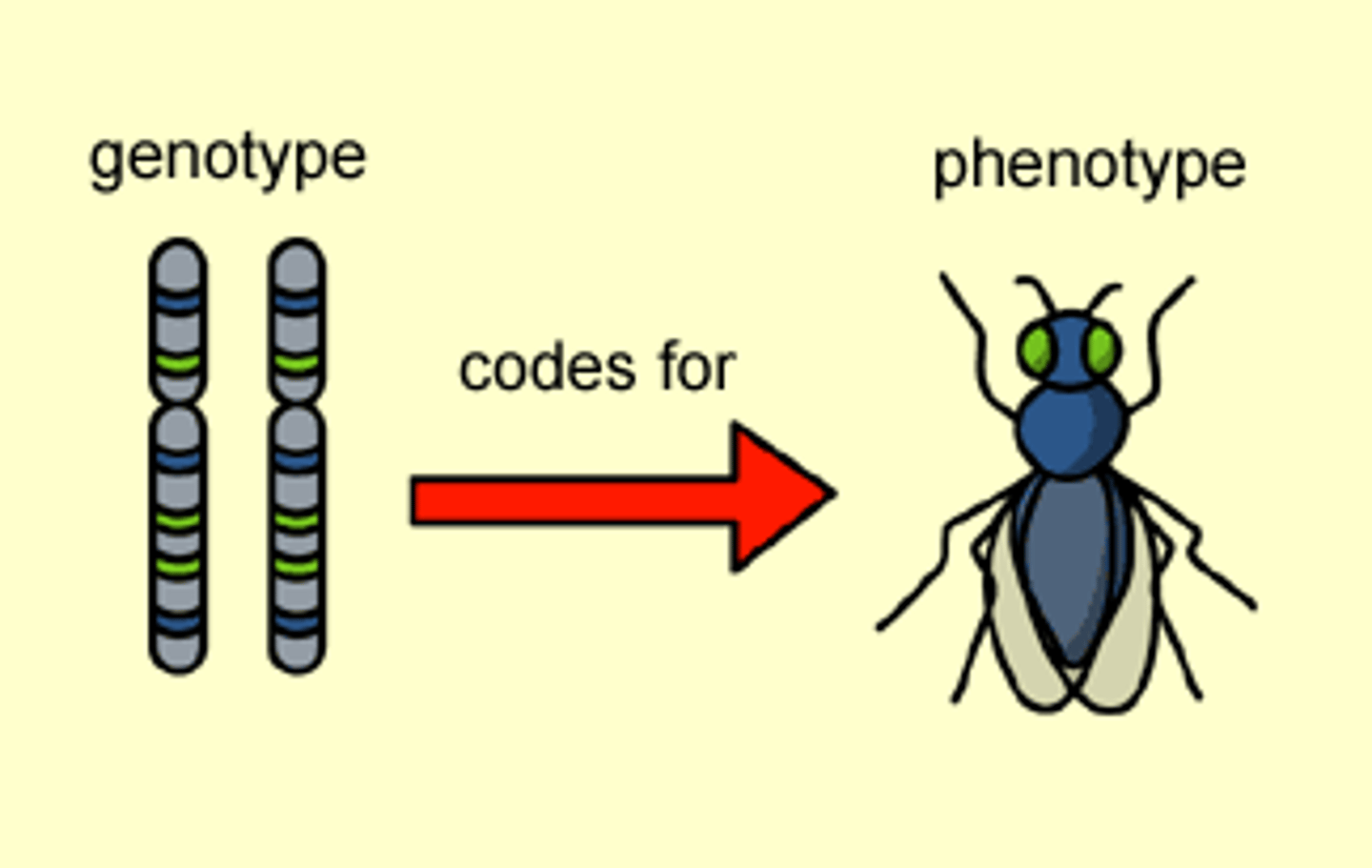
Genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism.
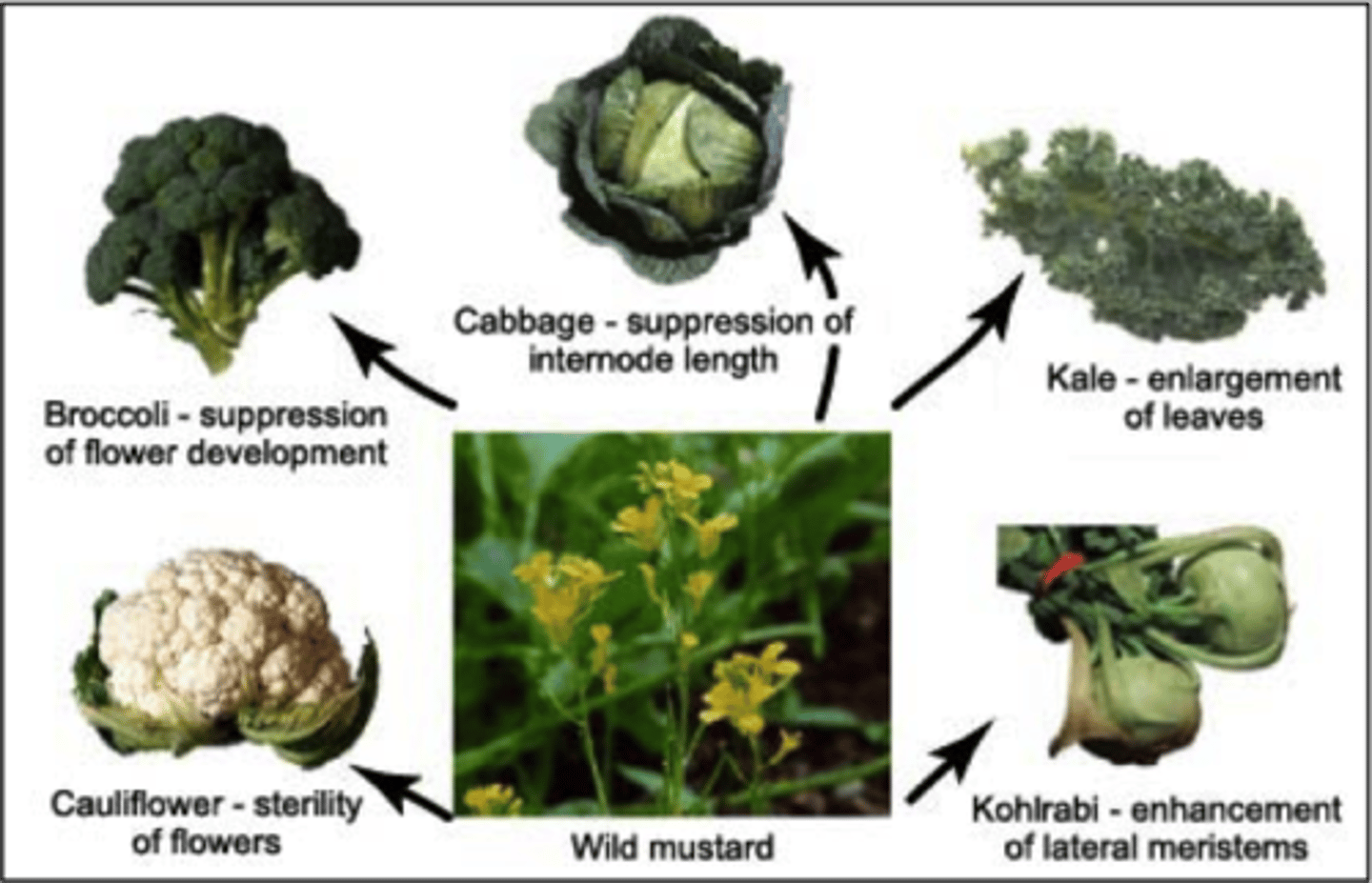
Selective Breeding
The intentional breeding of organisms with desirable traits to produce offspring with those traits.
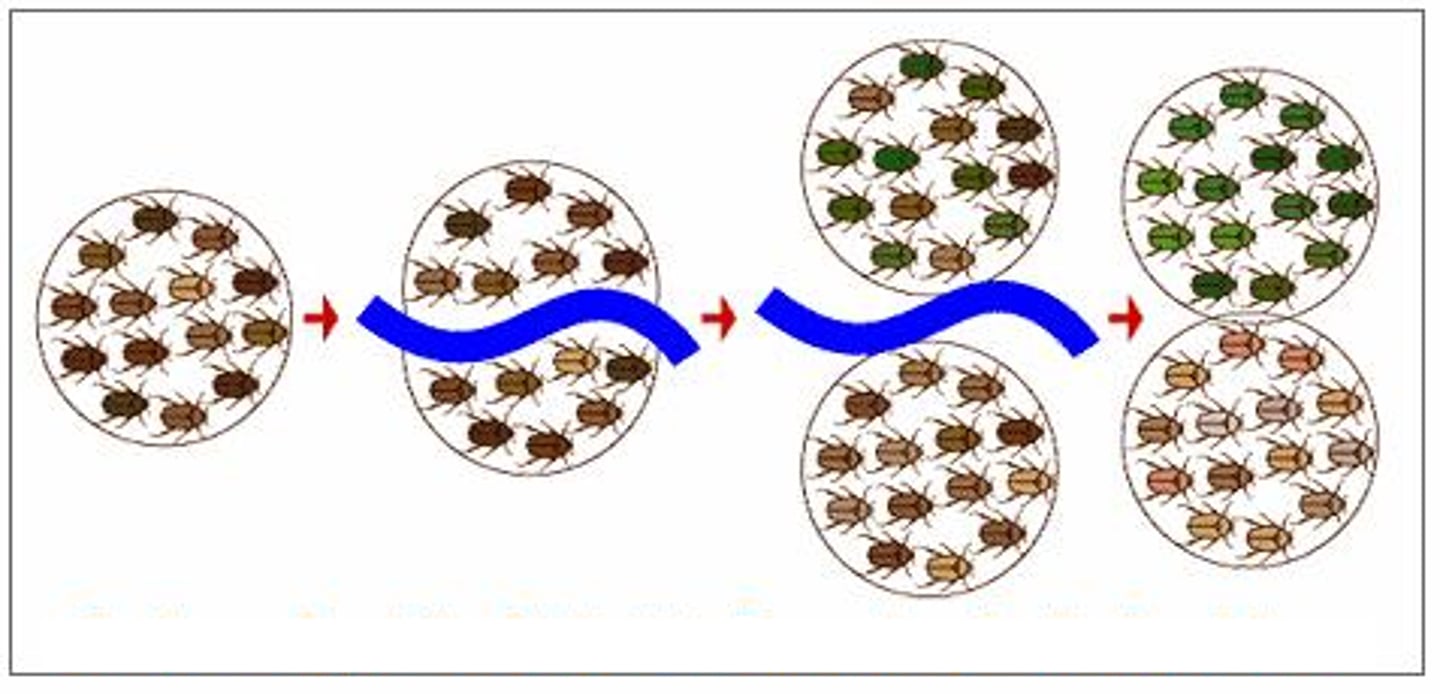
Variation
Differences in traits or characteristics within a population.

Variability
The range of possible values for a trait within a population.

Adaptation
A trait or characteristic that helps an organism survive and reproduce in its environment.

Speciation
The process by which new species arise from existing species.
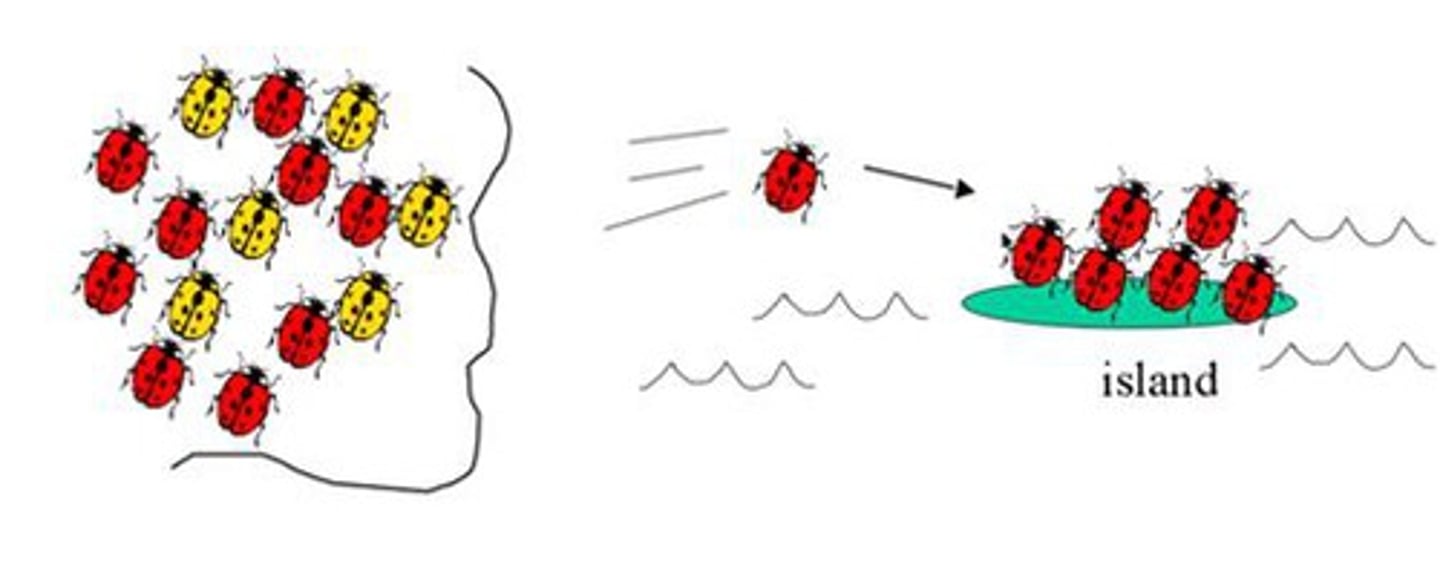
Genetic Isolation
The separation of populations of organisms that prevents them from interbreeding.
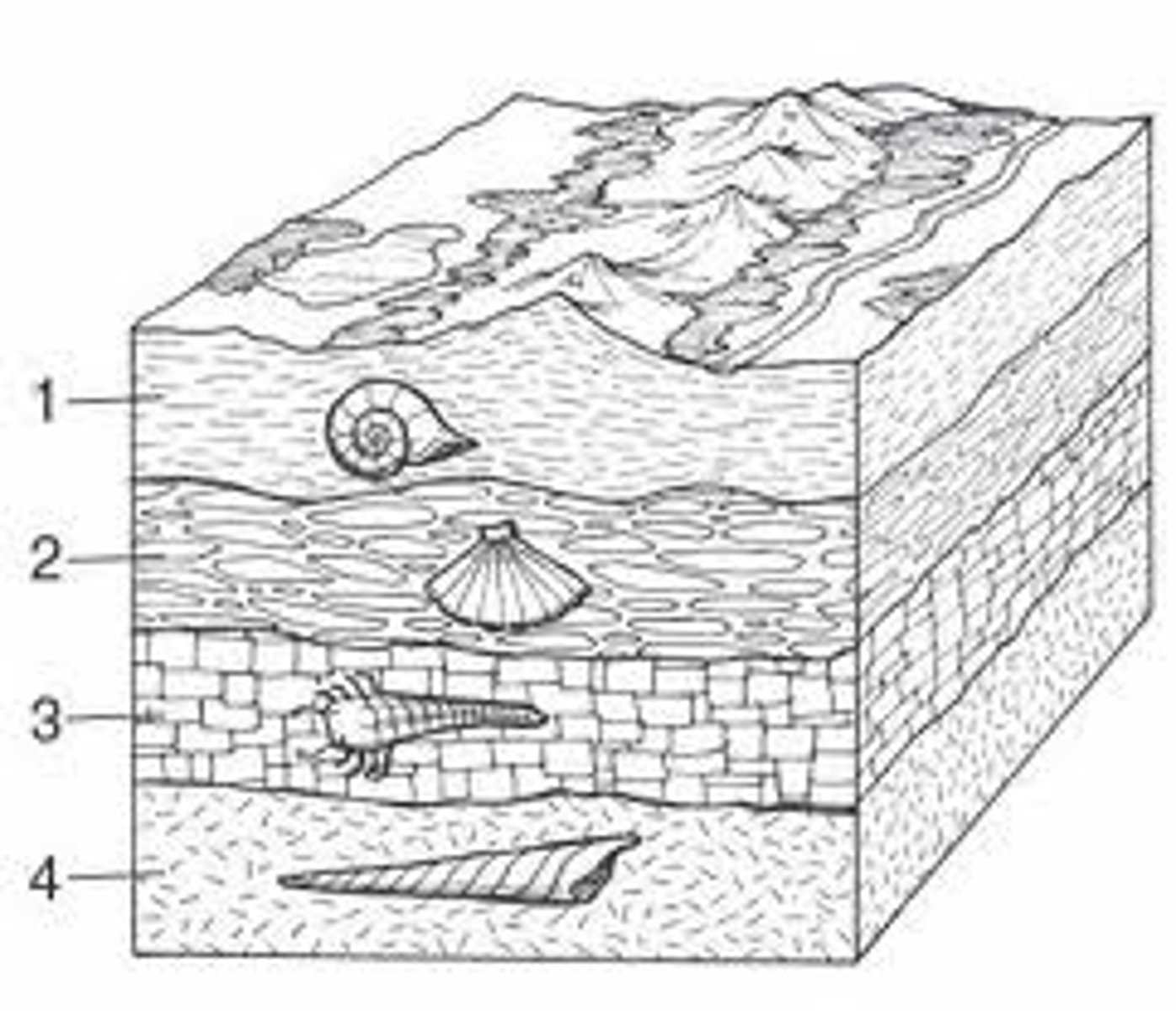
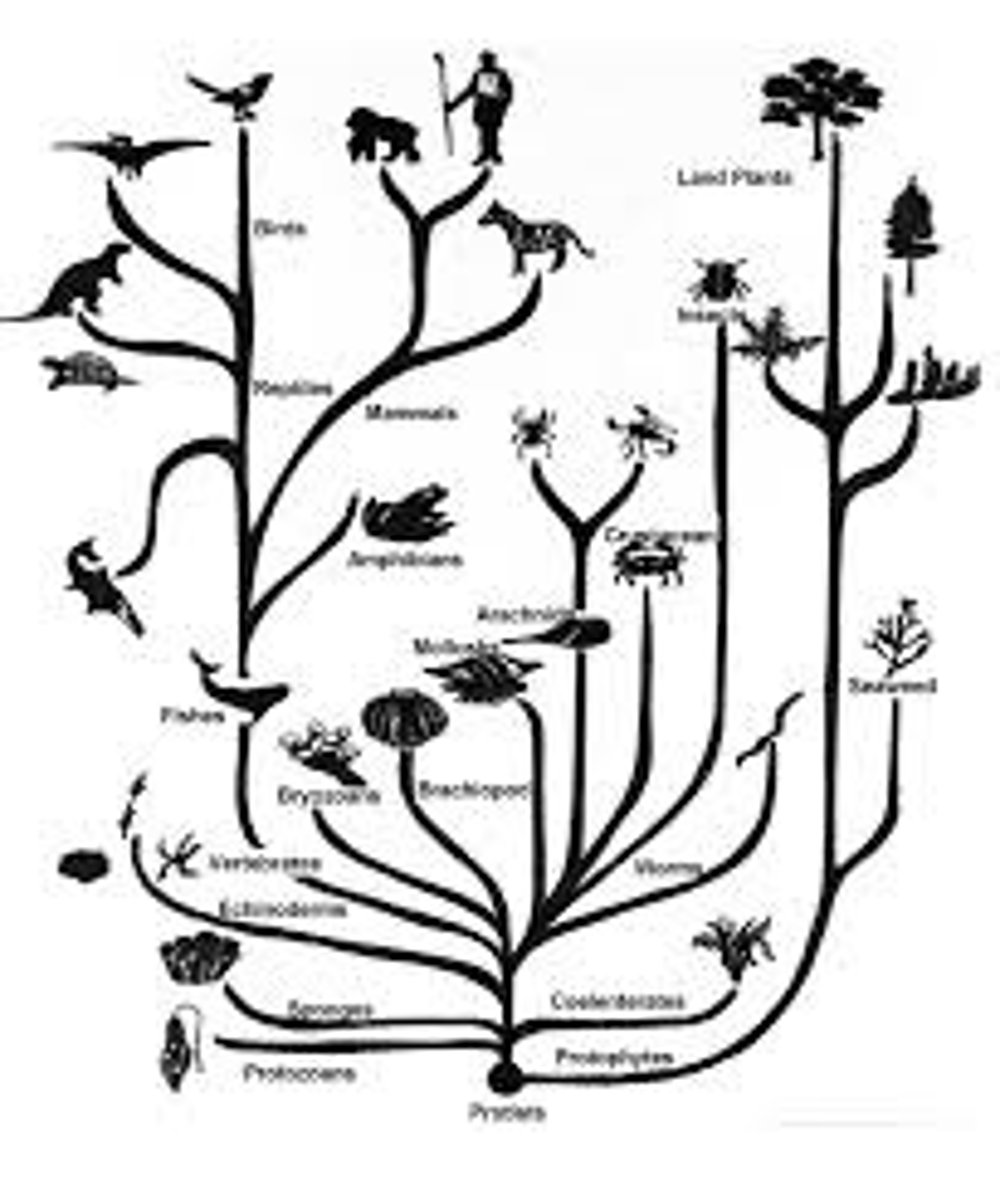
Sources of Evidence for Evolution
Fossils, comparative anatomy, embryology, molecular biology, biogeography.
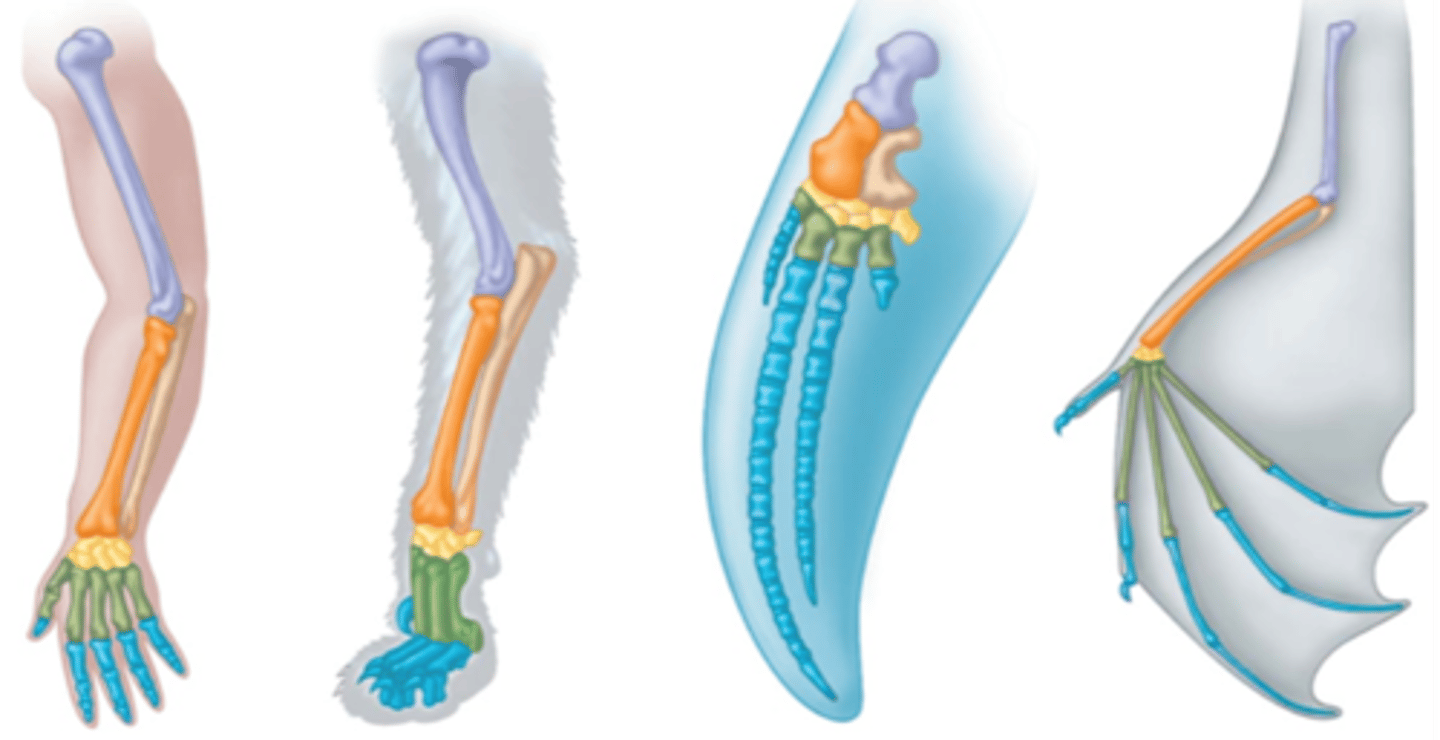
Homologous Structures
Structures that have a similar origin but may have different functions.
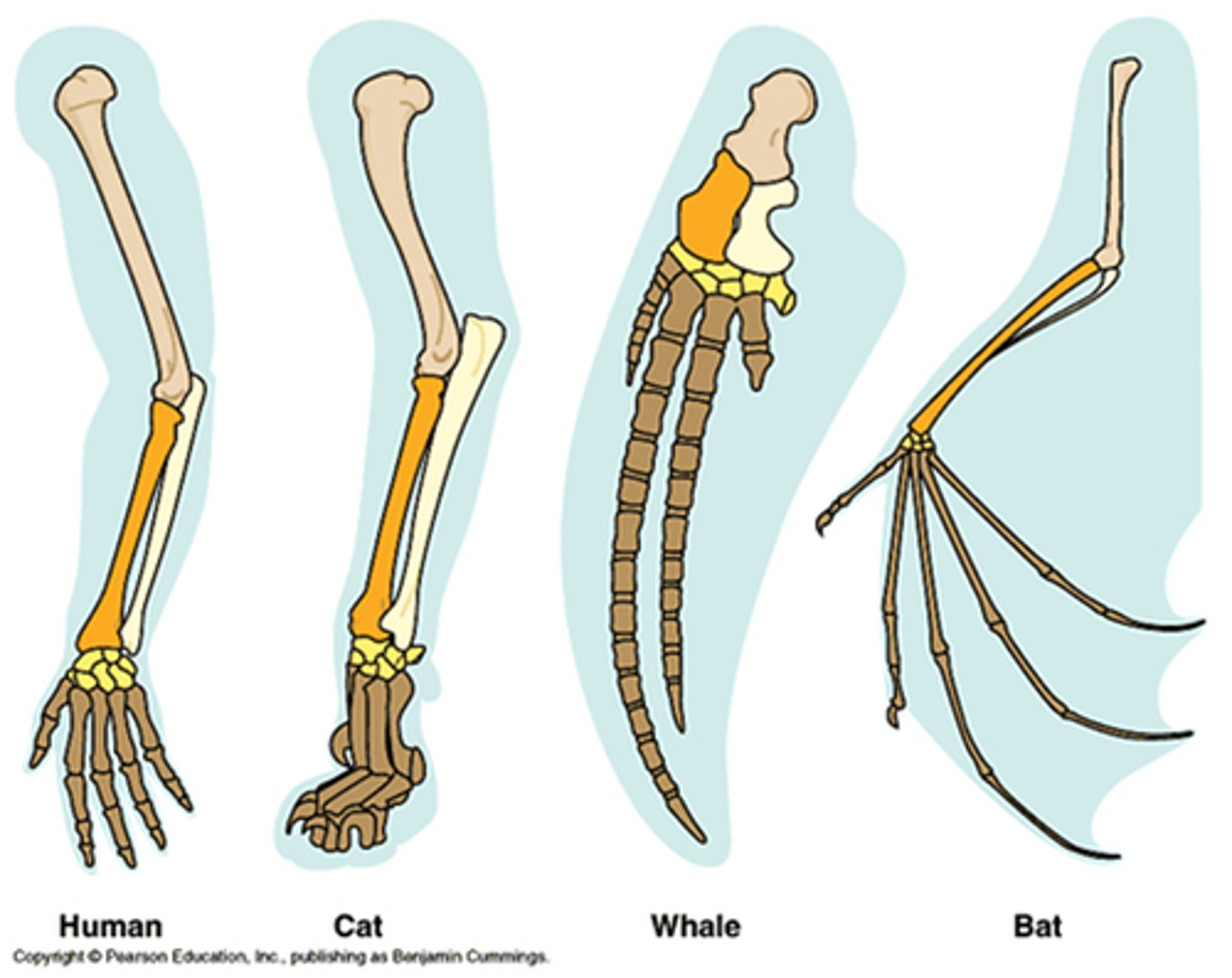
Comparative Anatomy
The study of similarities and differences in the anatomy of different species.
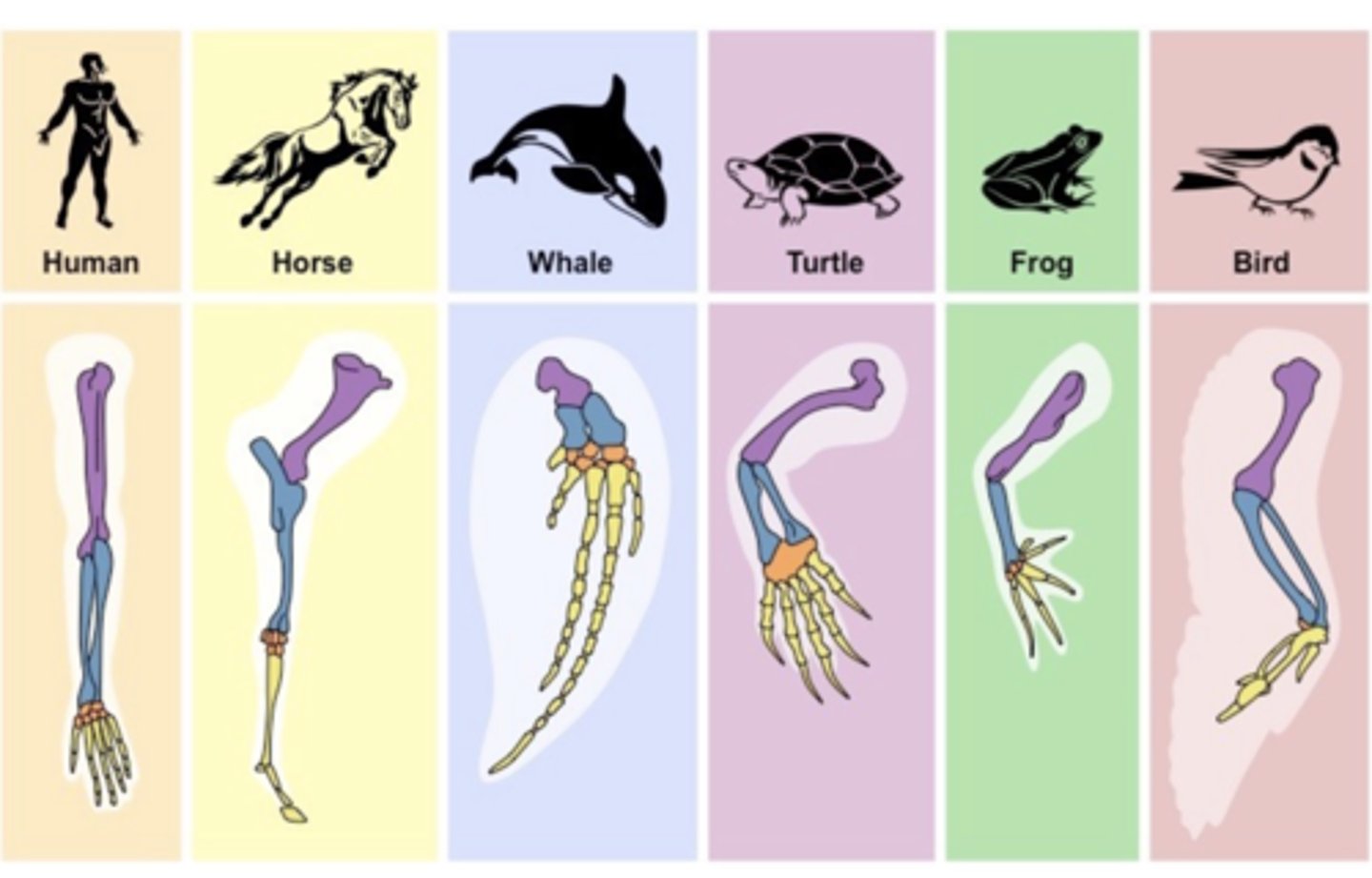
Pentadactyl Limb
A limb with five digits, found in many different vertebrate species.
Theory of Evolution
The scientific explanation for the diversity of life on Earth, based on the process of natural selection.
Alternative Theory to Evolution
Creationism, the belief that life was created by a supernatural being.

Lightyear (ly)
a measure of distance equal to that traveled by light in one year

Parralax
the apparent change in position of an object when seen from different places
star formation
When stellar nurseries or nebulas, collapse to form stars.

spectrum
colored band produced when a beam of light passes through a prism
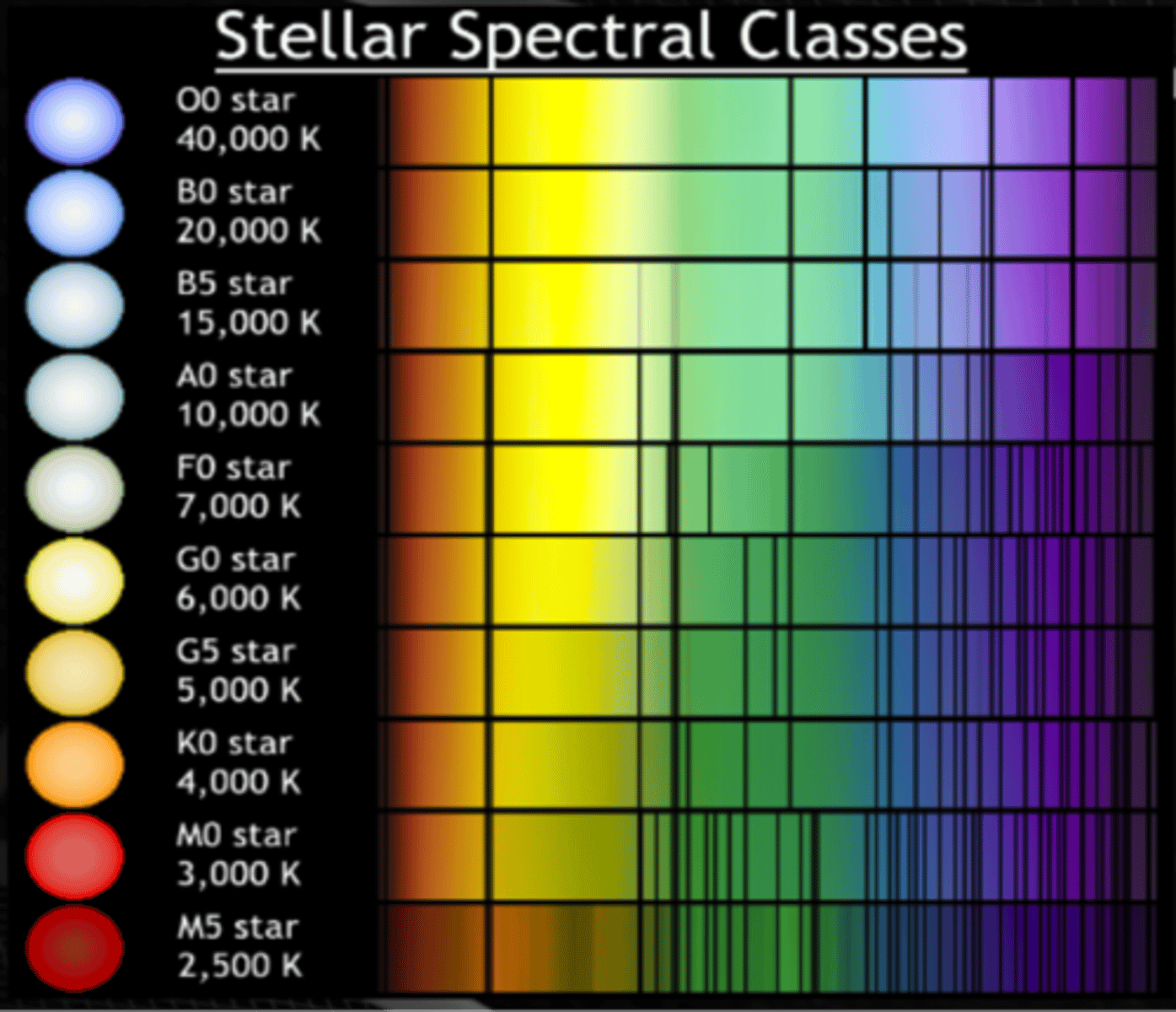
Spectral Class
a classification system for stars based on their colour
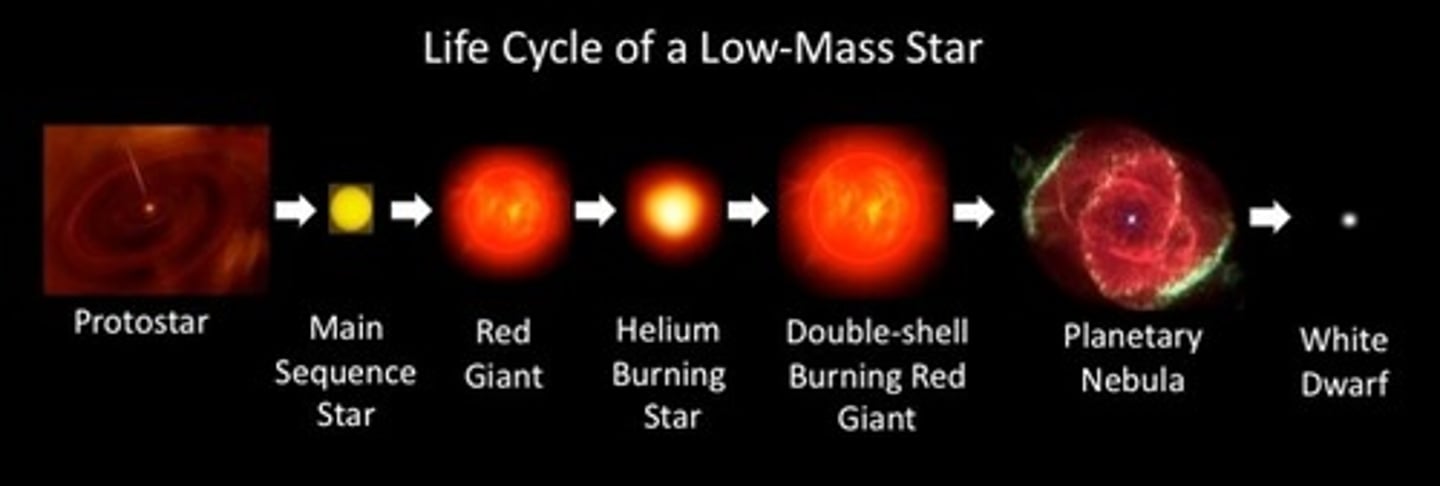
Life cycle of a low mass star
nebula, protostar, main sequence star, red giant, planetary nebula, white dwarf, black dwarf
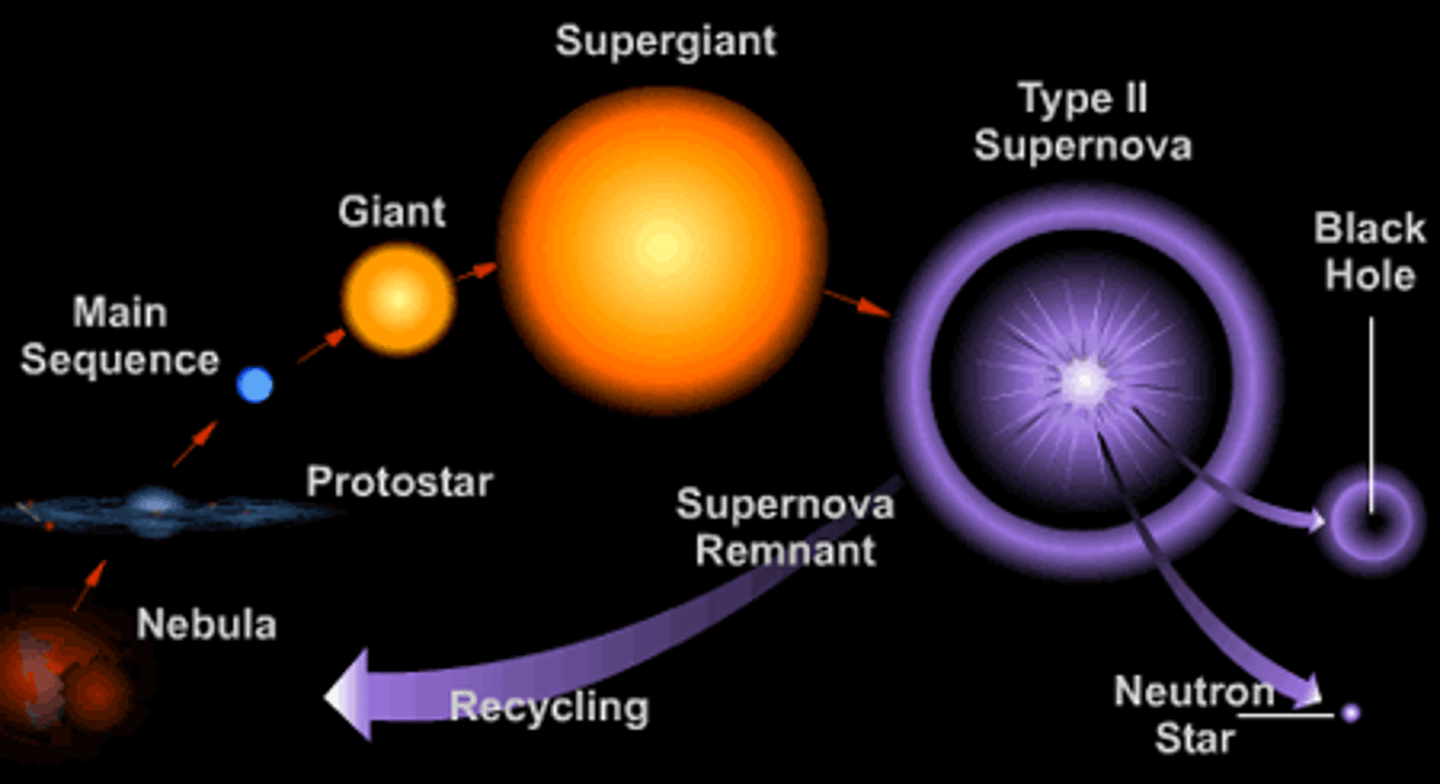
Life cycle of a high mass star
nebula --> protostar ---> main sequence ---> red supergiant ----> supernova ---> black hole ---> neutron star
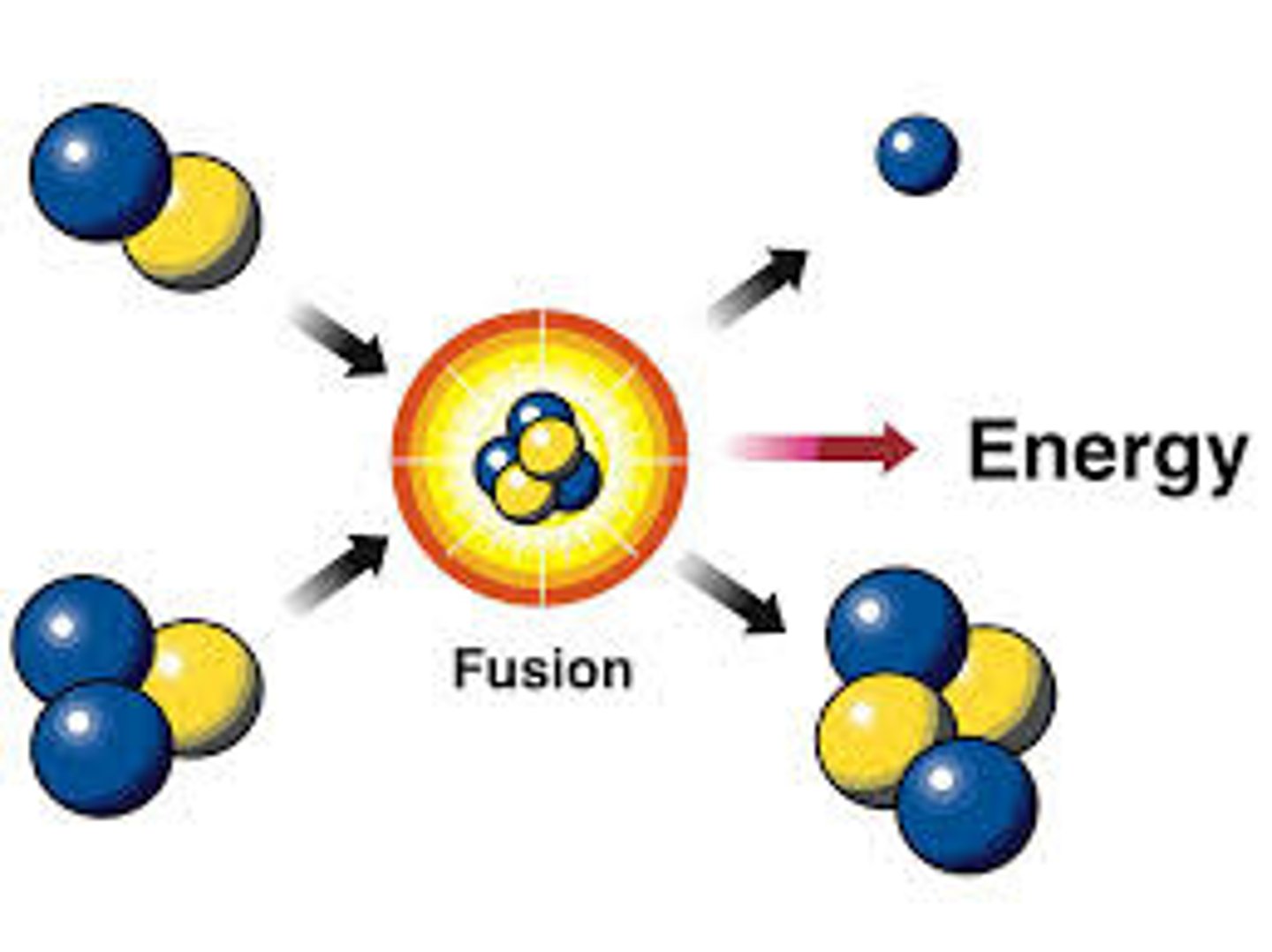
Fusion
Creation of energy by joining the nuclei of two hydrogen atoms to form helium.
Cosmology
the understanding of the nature of the universe

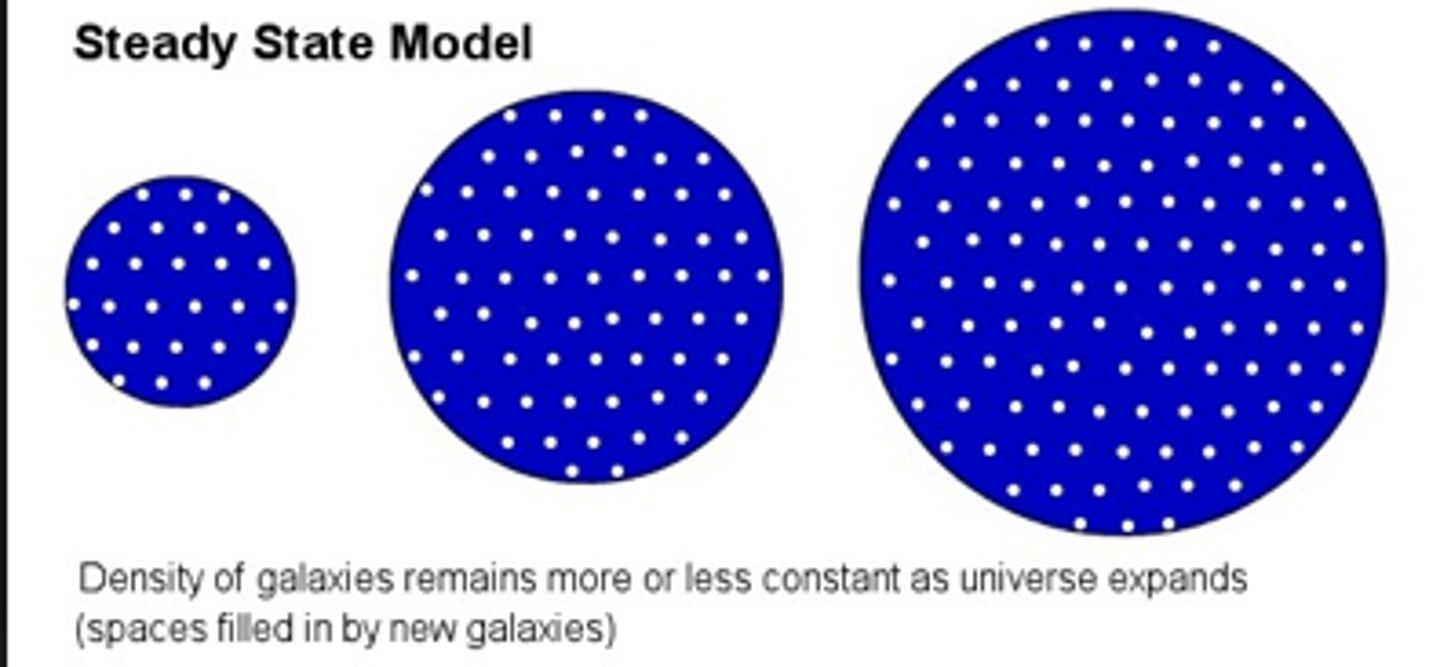
Steady State Theory
a theory which states that there was no beginning to the universe and that the universe does not change in appearance.
Big Bang Theory
The theory that the universe originated in a huge explosion that released all matter and energy.

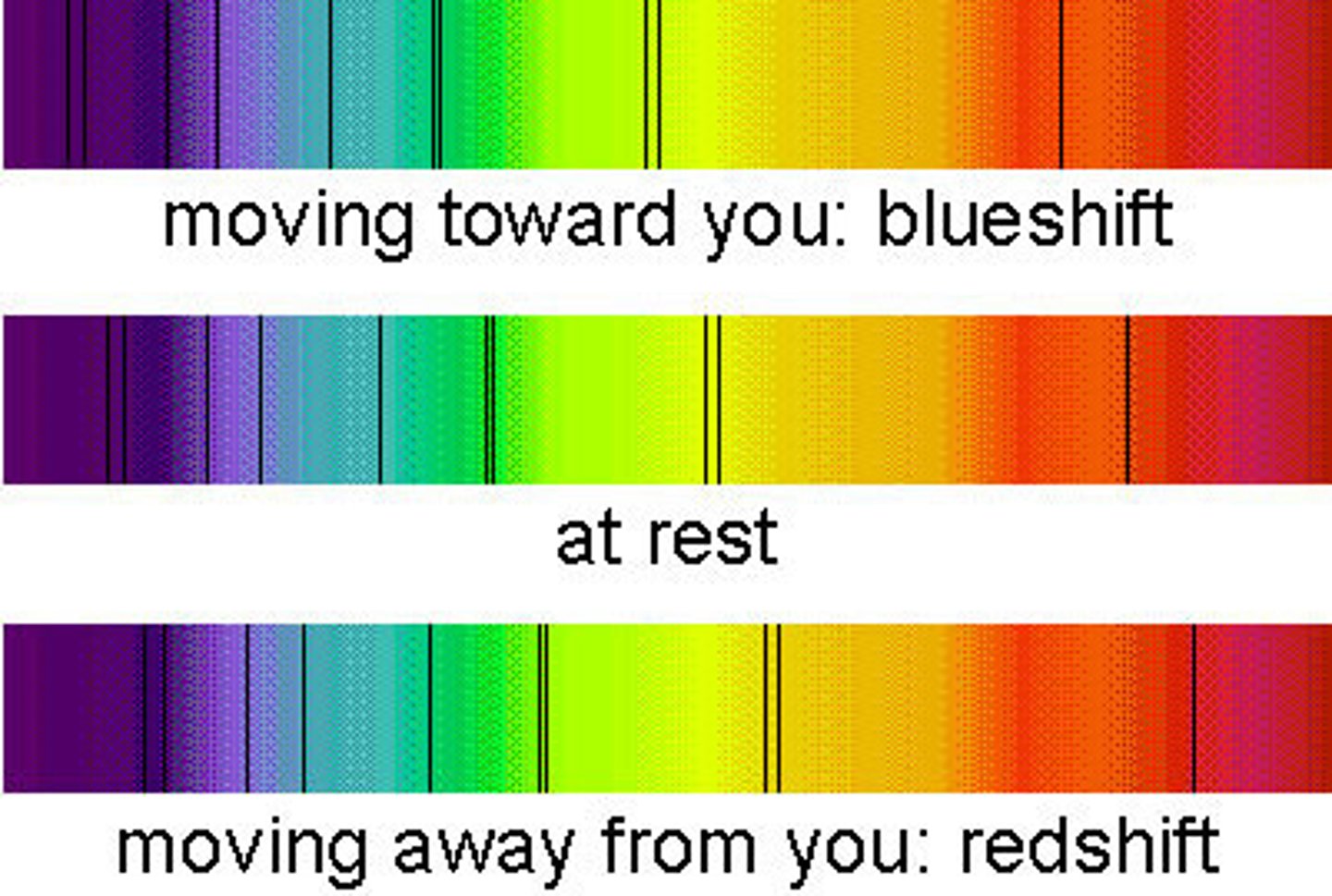
red shift and blue shift
Redshift and blueshift describe how light changes as objects in space (such as stars or galaxies) move closer or farther away from us. The concept is key to charting the universe's expansion.
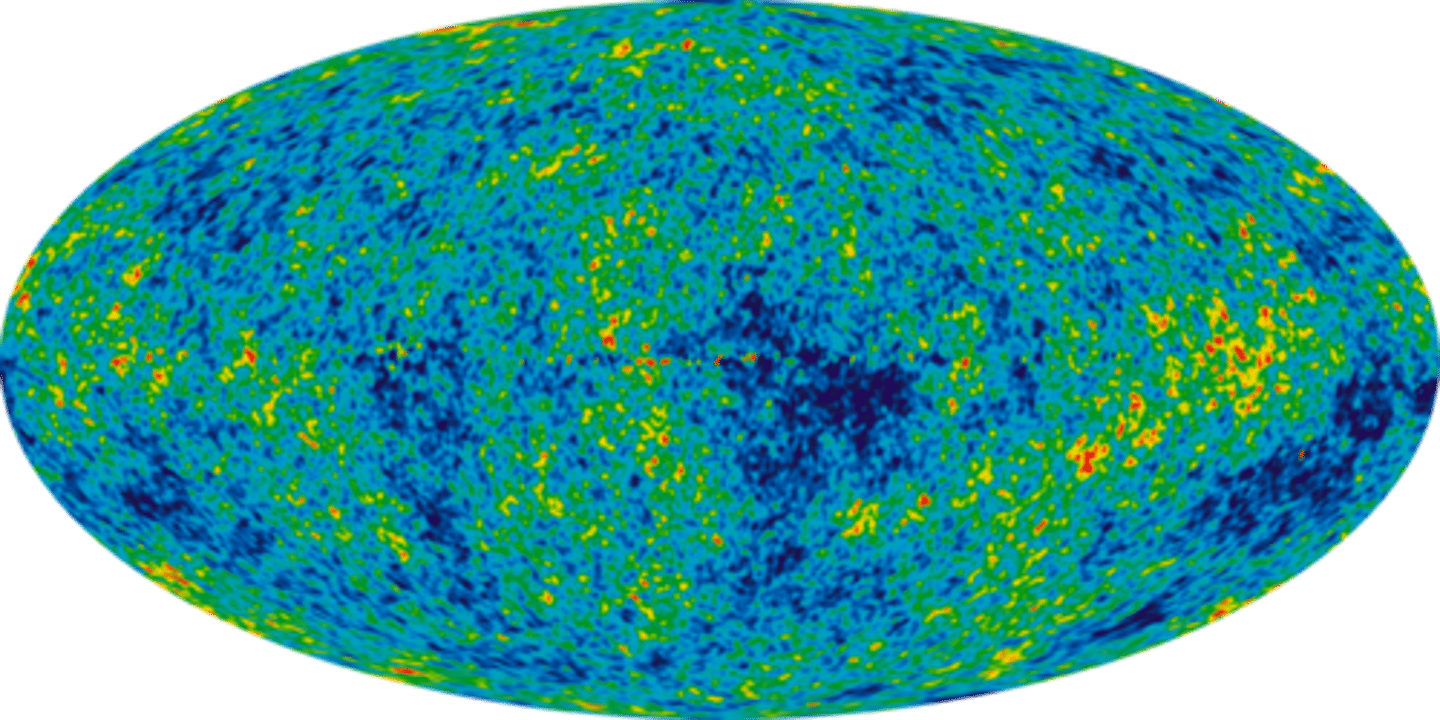
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
electromagnetic radiation that has been travelling through space ever since it was created shortly after the Big Bang
