animal and plant cells
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
cell membrane
Surrounds the cell and holds the cell together, bi-layered
cell wall
Supports & protects plant cell, Provides rigidity (plants dont have a skeleton), Made of cellulose
cytosol
Jelly-like material that fills the cytoplasm, Holds organelles in place, Gives shape to the cell
nucleus
Controls Cellular Activities, Contains DNA, The “control centre” of the cell
nucleolus
primary site of ribosome synthesis and rRNA production
mitochondria
Produces Chemical Energy: The “powerhouse” of the cell
chloroplast
Where photosynthesis occurs, Use energy of the sunlight co2 and h2o to produce glucose and oxygen, Contains chlorophyll
ribosome
makes protien
endoplasmic rectillium
smooth ER transports lipids, rough ER transports ribosomes
golgi appratus
packages materials to transport out of cell
vacuole
Storage centre for fluids, nutrients & waste, Many vacuoles in animal cells, 1 large vacuole in plant cells
lysosome
breaks down and removes waste, exclusive to animal cells
making protiens
The nucleus stores DNA, which provides instructions for protein synthesis. Proteins are made in two steps: transcription, where RNA is copied from DNA, and translation, where ribosomes use RNA to assemble amino acids into proteins.
exporting protiens
Proteins for export are made by ribosomes on the rough ER, folded, then sent to the Golgi apparatus for modification and packaging. Vesicles transport these proteins to the cell membrane for release.
photosynthesis
occurs in chloroplasts, sunlight, h2o and co2 is converted to glucose and o2
cellular respiration
occurs in the mitochondria, conversion of glucose and oxygen to (ATP- adenosine triphosphate) energy
stomata
opens and closes to let gases in and out of leaves
fungal cells
Cell Wall Made from chitin, Do not have chloroplast
prokaryote
smaller and Simpler, single-celled organisms without a nucleus. Their DNA floats freely in the cytoplasm, and they lack membrane-bound organelles.
eukaryote
more Complex larger cells with a nucleus to store DNA and membrane-bound organelles that perform specialized functions. Found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists.
specialised cells
A cell with unique structures to perform certain functions
red blood cells
Flattened disc shape, Large surface area, Efficient gas exchange, Contain haemoglobin which attaches to oxygen, no nucleus
neuron
Long, branch like structures called drendites recieve signals from other neurons, they Carry electrical impulses, through a long axon, gaps called synapses to pass signals
guard cells
open and close stomata, Contains vacuole and chloroplast, Thick inner wall
root hair cells
absorbs water and nutrients from soil by maximising surface area
Intestinal Epithelial Cells
A cell with finger-like structures to maximise surface area that help it absorb water and nutrients from food
Myocytes
muscle cells that contract and relax to control muscle movements A long, thin cell
cytoskeleton
holds organelles in place
centrioles
exclusive to animal cells; aids in cell division/ mitosis, organises spindle fibres from the cytoskeleton
cilia and flagella
created by the centrioles, enables cell movement/ movement across the cell surface
smooth muscle cells
are involuntary and are in organs like the intestine and stomach
skeletal cell
long, cylindrical cells, strong and rigid
cardiac cells
involuntary and striated,
organ
A body part that performs a specific function
tissue
A group of similar cells that work together
shape, and size, number of and type of organelles to suit function
specialised cells vary in..
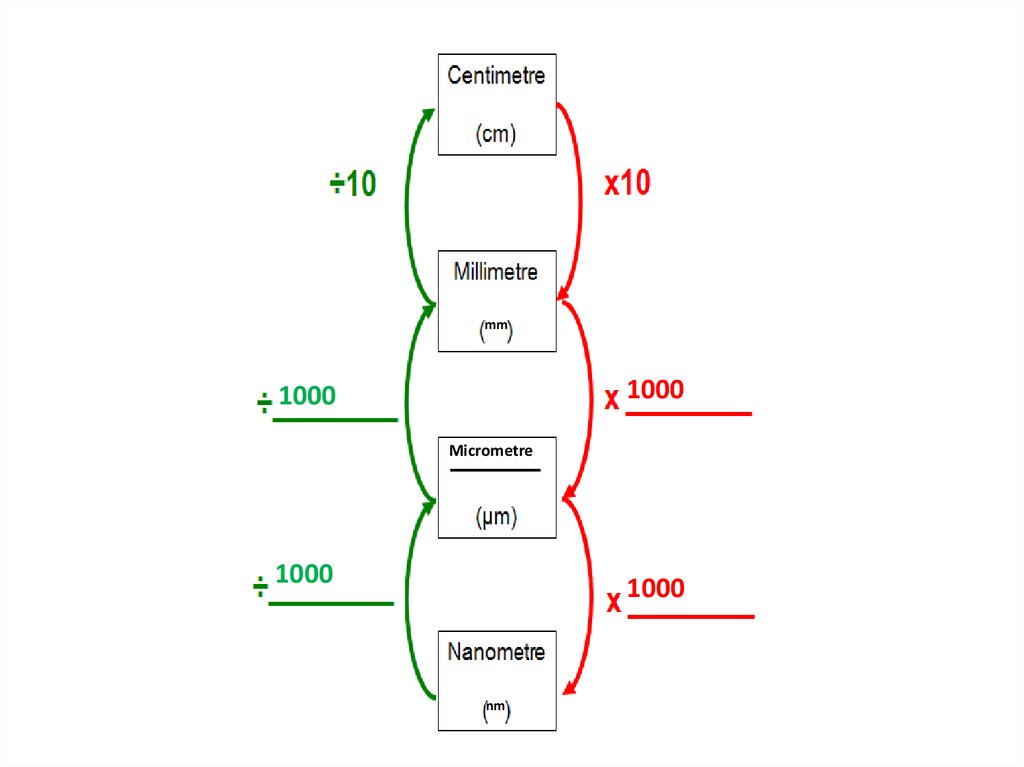
1000
micrometers in a millimeter