CSC 225 - Laser Printer Components and The Printing Process (Module 9)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
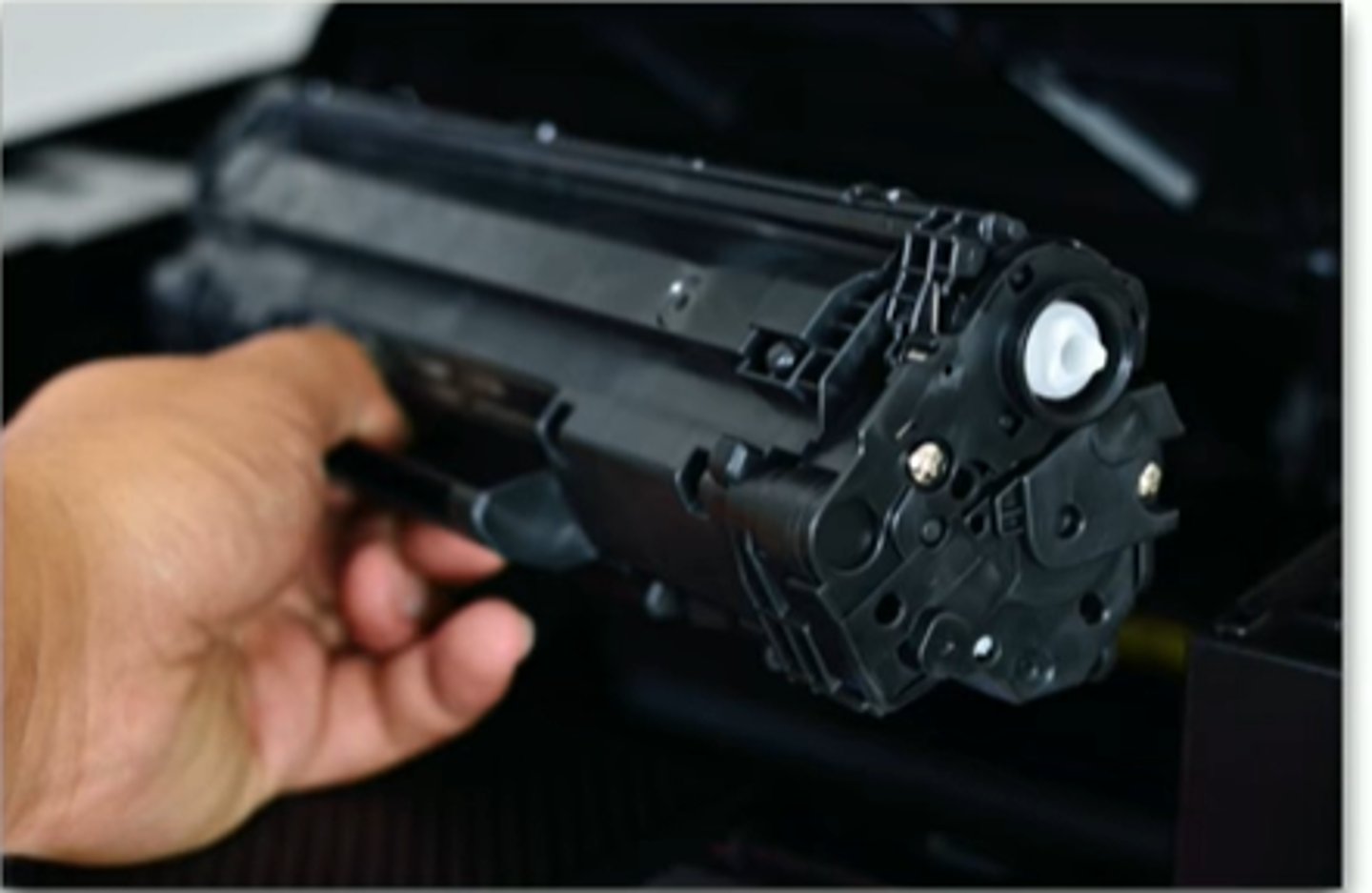
Toner cartridge
Component that supplies toner

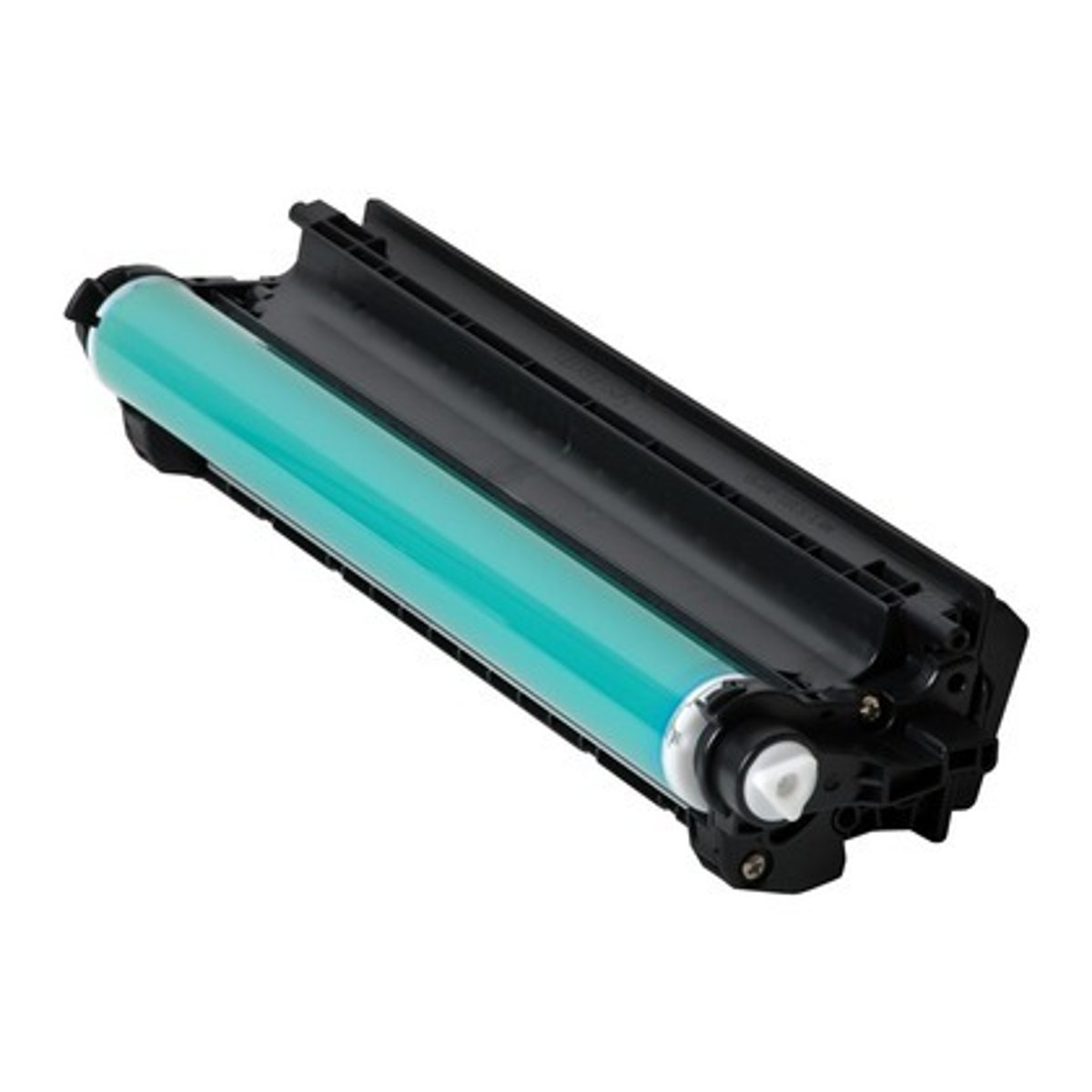
Imaging Drum (aka Photosensitive Drum)
An aluminum cylinder that is coated with photosensitive compound particles. Grounded to the power supply, Electrical charge is drained from the coating when light hits it.

Erase Lamp
Component inside laser printers that uses light to make the coating of the photosensitive drum conductive. Clears the previously printed image from the imaging drum.
Laser
The very precise writing mechanism used by laser printers. Strikes particles on the drum which creates the image
Transfer Corona
A thin, positively charged wire that attracts negatively charged toner particles off the drum and onto the paper. Requires extremely high voltages causing it to have a particularly dangerous power supply
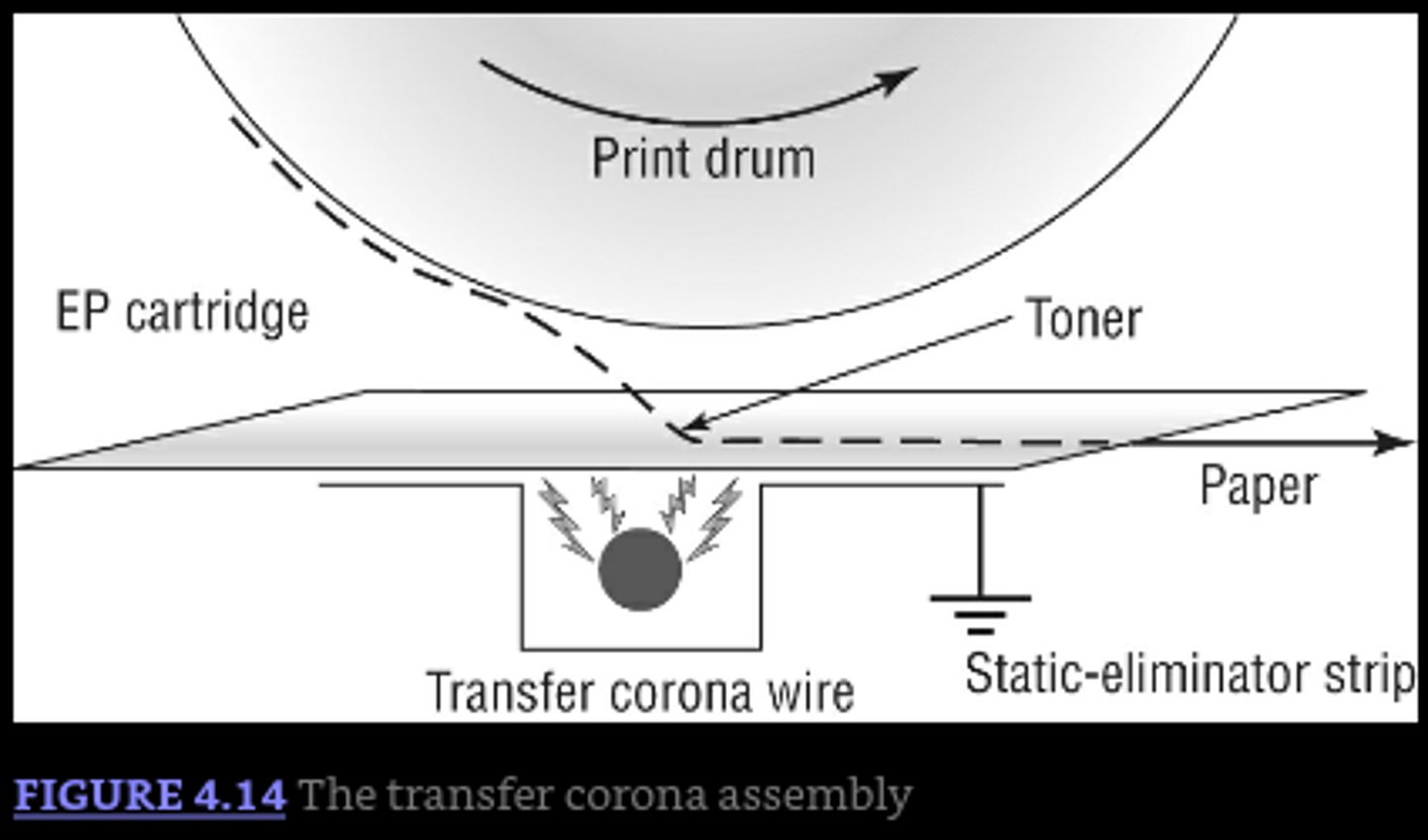
Static Charge Eliminator
Removes the electrical charge from the paper to prevent it from wrapping around the drum
Fuser Assembly
A component in laser printing that uses heat and pressure to fuse the toner to paper. Usually, two rollers, one heated and one for pressure, that the paper runs between
Gear Boxes
System or 2 or 3 gears that move the paper and components through the printer
System Board
Laser printers always have at least one. Contains the main processor, ROM (firmware), and RAM (memory storage)
Ozone Filter
A ventilation component that removes the ozone that is
generated inside printers during the printing process.
Print Spooler
Area of the printer memory that enables you to queue up multiple print jobs
Processing
Step 1
-Printer is not moving
-CPU processes the print request and builds the entire page in memory
-Windows sends the print job to the printer, a potential bottleneck
-Raster Images are Created
Sensors and Switches
Delicate components that detect printer conditions like paper jams, empty paper trays, toner levels, and more. Need to be cleaned or replaced occasionally
Charging
Step 2
-The primary corona applies a uniform negative charge to the entire surface of the imaging drum
-Charge is between 600V and 1000V
Exposing
Step 3
-A laser or LED is used to write an image to the surface of the imaging drum
-Particles that are hit by the laser become positively charged and attract to the negatively charged drum
Developing
Step 4
-Image is developed
Transferring
Step 5
-Image is transferred from the imaging drum to the paper
-Transfer corona and transfer rollers give the paper a positive charge to attract the negatively charged toner particles
Fusing
Step 6
-Heat and pressure are applied to the paper
-Toner is melted to the page
-Static charge eliminator removes the paper's positive charge
-Completed print is ejected
Cleaning
Step 7
- Imaging drum is physically and electrically wiped of excess toner particles by the erasing lamp before the next print
- Sometime the discarded toner is reused