Patho Exam #2 pt. 1
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
Shift of fluid from vascular space to interstitial space.
This fluid is cannot be used by the body and manifests into edema.
Third Spacing
Extracellular Fluid (ECF) deficits due to decreased vascular volume, & interstitial volume is called
(Removal of sodium-containing fluid from the body)
Fluid Volume Deficets
Fluid Volume Deficits Etiology
-Vomiting
-Diarrhea
-Polyuria
-Third spacing
-Burns
Fluid Volume Deficits Manifestations
-Decreased skin turgor
-Sunken Eyes
-Dizziness
-Syncopy
Extracellular Fluid (ECF) increases due to an increase in plasma volume & interstitial volume is called
Fluid Volume Overload
Fluid Volume Overload Etiology
Heart Failure
Fluid Volume Overload Manifestations
-Sudden weight gain
-Bounding pulse
-Distended neck veins
-Orthopnea
Electrolyte that is the highest concentration in the intracellular fluid
Potassium
Hyponatremia Manifestations
-Cerebral Edema
-Lethargy/fatigue
Hypernatremia Manifestations
-Concentrated Urine
-Decreased muscle reflexes
Hypokalemia etiology
-GI losses
-Diuretics, Steroids, Insulin
Hypokalemia manifestations
-Arrhythmias (ECG changes)
-Skeletal muscles weakness
Hyperkalemia etiology
-Kidney Failure
-Deficient aldosterone
-Large trauma injuries
Hyperkalemia manifestations
-Arrhythmias (widened QRS complex)
-Non-specific vague muscle weakness
Hypocalcemia etiology
-Hypoparathyroidism & neck surgery (decreased PTH levels)
Hypocalcemia manifestations
-Tetany (increased nerve membrane excitability)
-Hyperreflexia
-Laryngeal spasms
Hypercalcemia etiology
-Hyperparathyroidism (make to much PTH)
-Malignancies (multiple myeloma, lymphoma, lung cancer)
-Breakdown of bones
Hypercalcemia manifestations
-Muscle weakness
-Decreased reflexes
-Confusion, lethargy, coma
Blood pulling in the saphenous vein due to incompetent valves that do not prevent back flow
Varicose Veins
Varicose Veins manifestations
-Distended & palpable veins
-Syncope
What is the main complication for DVT
Pulmonary Embolism
Thrombus VS Embolism
Thrombus- Blood clot that remains attached to the vessel wall
Embolism- Bolus of matter circulating in the blood stream
Abnormal thickening and hardening of vessel walls
Atherosclerosis
The initial stage of atherosclerosis is due to the accumulation of
LDL in the endothelium
Hypertension is characterized by what systolic & diastolic numbers
Systolic- Above 130 mm Hg
Diastolic- Above 80 mm Hg
Measured multiple times
Urgent Hypertension is characterized by what systolic & diastolic numbers
Systolic- Above 180 mm Hg
Diastolic- Above 120 mm Hg
Measured multiple times
Hypertension is connected to what system
RAAS stress response which increases vasoconstriction
Hypertension leads to what
Chronic damage to the heart, kidney, brain, eyes.
Cardiovascular disease leads to what
Left Ventricular Hypertrophy → Heart failure
Local dilation or outpouching of an artery vessel wall is called
Aneurysm
What is the etiology of an aneurysm
Atherosclerosis & Hypertension
Aneurysm are a key part of what syndrome
Marfan Syndrome
Clinical manifestations of an aneurysms
-Stroke
-Sudden severe pain radiating to abdomen or back
LDL
-LDL we want low because it is bad cholesterol
-High level of LDL increases risk for atherosclerosis
HDL
-HDL we want high because it is good cholesterol
-High levels of HDL protects against atherosclerosis
How to increase HDL
-Increase exercise
-Decreases with smoking, alcohol, diabetes.
Episodic vasospasm in arteries and arterioles of fingers, which changes skin color.
Goes from cyanotic → red
Raynauds Disease
Raynauds Disease is considered
Secondary to autoimmune disorders (SLE)
When does Raynaud’s disease flare up
Initiated by cold and emotional distress → So avoid cold and smoking
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) is caused by what
Atherosclerosis of arteries
Acute arterial occlusion is due to
A thrombus or emboli lodged in arterial circulation
Acute arterial occlusion can lead to
Necrosis & possible amputation
Decrease in systolic and diastolic BP upon standing
Orthostatic Hypotension
Orthostatic Hypotension etiology
Hypovolemia
Impaired blood flow to coronary arteries that leads to acute insufficient delivery of oxygenated blood to myocardium
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Chest pain that occurs with activity and is relived by rest
Stable angina
Chest pain that is not relived by rest
Unstable angina
Physiology of angina
Reduced O2 supply goes from aerobic metabolism to anaerobic metabolism.
Leads to lactic acid build up → pain
Clinical manifestations of angina are
-10/10 chest pain
-Pain radiating down left arm & jaw
-Feeling of impending doom
Large plaque build up in vessels that leads to a spontaneous rupture that blocks blood supply leading to ischemia.
Occurs with physical exertion
(Shoveling snow, moving furniture)
Myocardial Infarction (MI)
Increased levels of troponin indicate
Myocardial Infarction
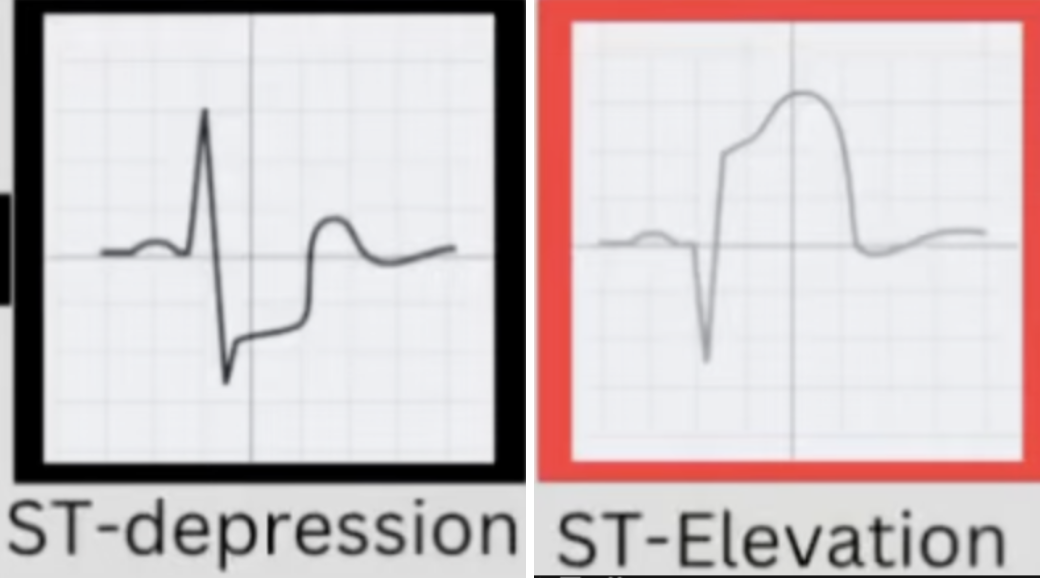
NSTEMI VS STEMI
NSTEMI- Partial blockage of the coronary artery. ST wave depression.
STEMI- Complete blockage of the coronary artery.
ST wave elevation.
Inability of the heart to maintain sufficient cardiac output to meet metabolic demands of tissues/organs due reduced myocardial contraction which leads to progressive back up of systemic circulation
Heart Failure
Clinical manifestations of heart failure
Composed of backwards effects (pulmonary edema, SOB, less than 40% ejection fraction) & forward effects (Tachycardia & fatigue)
Acute Pericarditis Vs Constructive Pericarditis
Acute- Inflammation of the pericardium
Constructive- Chronic, healed stage of acute pericarditis
Acute Pericarditis Vs Constructive Pericarditis Manifestations
Acute manifestations- fever, chest pain, malaise, tachycardia, leukocytosis, friction rub
Constructive manifestations- Exercise intolerance, fatigue, heart failure.
Pericardial Effusion
Accumulation of fluid in between pericardial membranes
Large effusions can lead to external compression of the heart chambers which impairs filling of the heart.
Cardiac Tamponade
Cardiac Tamponade manifestation
-Muffled Heart sound
-Hypotension
-Tachycardia
Increased left atrial pressure is an indication of what
Mitral Valve Stenosis
Complications of Mitral Valve Stenosis
-RV Hypertrophy
-A Fib
-Chronic pulmonary HTN
Mitral valve prolapses (falls back into LA) which leads to back flow of blood from LV to LA during ventricle systole
Mitral Regurgitation
Mitral Regurgation manifestations
LA & LV hypertrophy
Accumulation of calcifications related to aging which obstructs the flow out of LV during systole
Aortic Stenosis
Infectious inflammation of the endocardium
Endocarditis
What factors lead to endocarditis
-Staph aureus
-IV drug use
-Implantable devices
-Immunodeficiencies
Endocarditis manifestatons
-Joint Pain
-Weight loss
-Night sweats
Cardiovascular system fails to perfuse tissues adequately which leads to widespread impairment of cellular metabolism
SEVERE HYPOTENSION
Shock
Shock manifestations
-Sluggish cap refill
-Cool skin
-Decreased urine ouput
Shock manifested by capillary leak, third spacing
Burn shock
Shock due to brain stem injury or spinal cord injury
Neurogenic Shock
Shock due to MI, heart failure, “pump failure”
Cardiogenic shock
Shock due to loss of fluid volume like dehydration or hemorrhages
Hypovolemic shock
Dysrhythmias etiolgy
-Hypoxia
-Potassium (electrolyte imbalance)
-MI
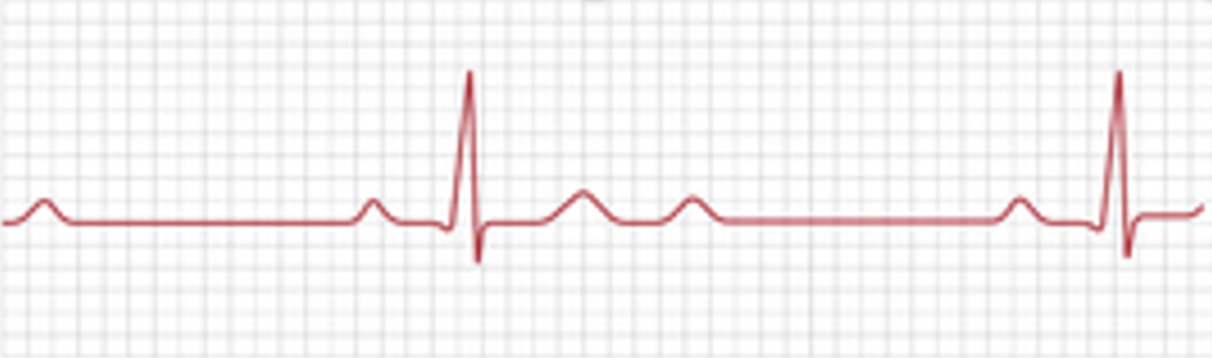
“-”
Heart Block
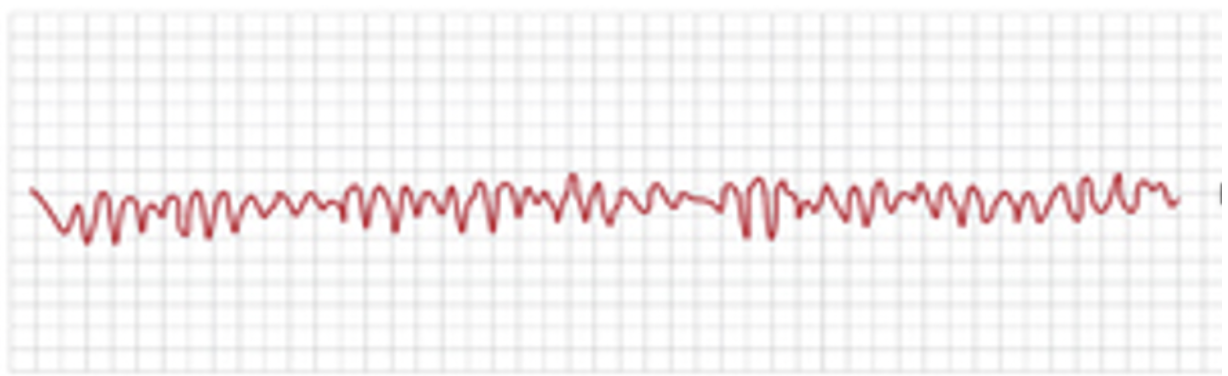
“bunch of nonsense”
V Fib
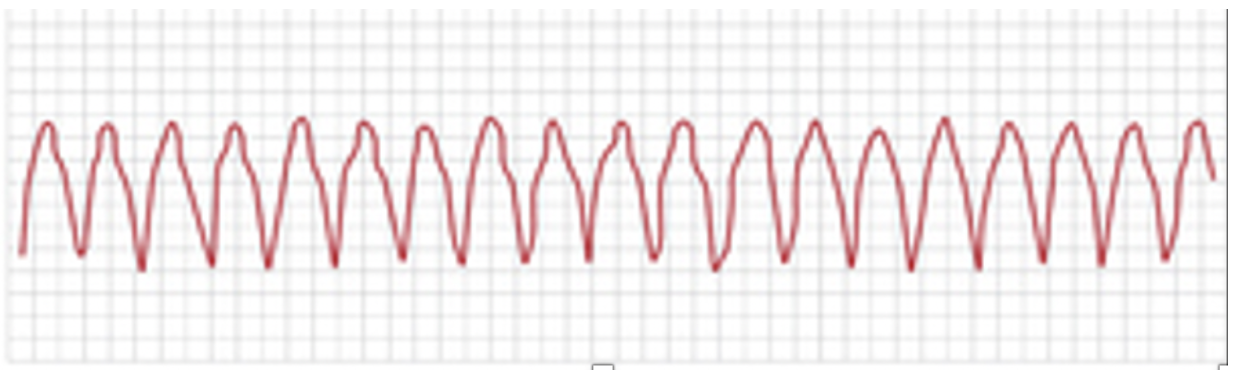
“shark teeth”
V Tach
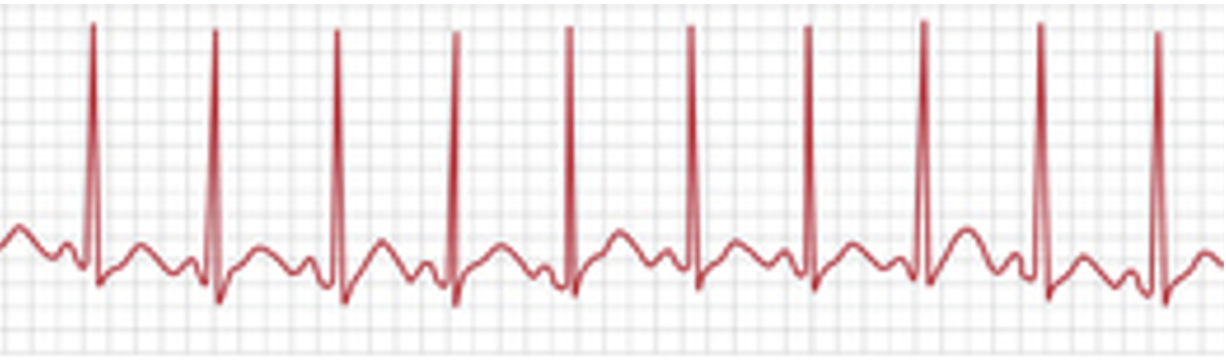
“sinus spikey”
Sinus Tachycardia

“sinus slow”
Sinus Bradycardia
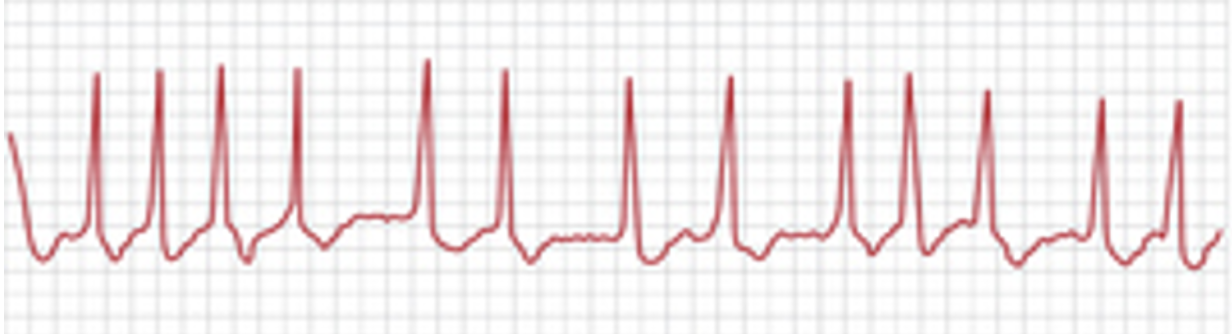
“mirror U’s”
A Fib
Associated- Embolic Stroke

“flap, flap, flap”
A Flutter
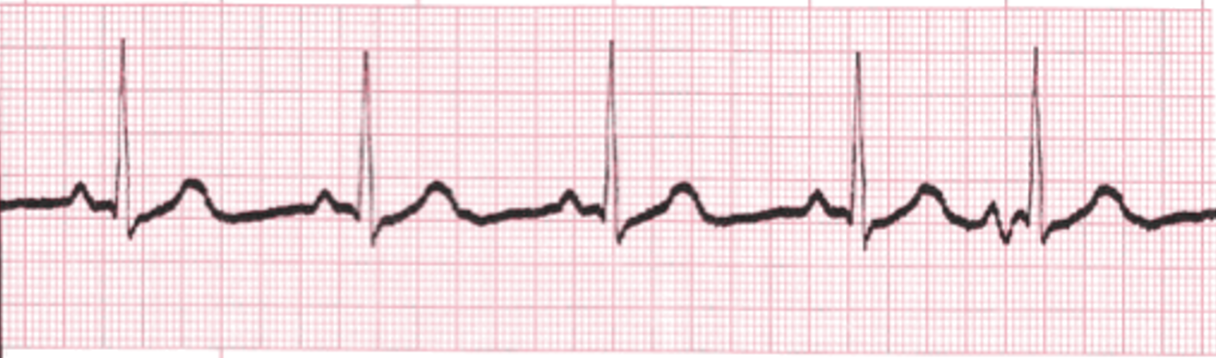
“-”
Normal Sinus
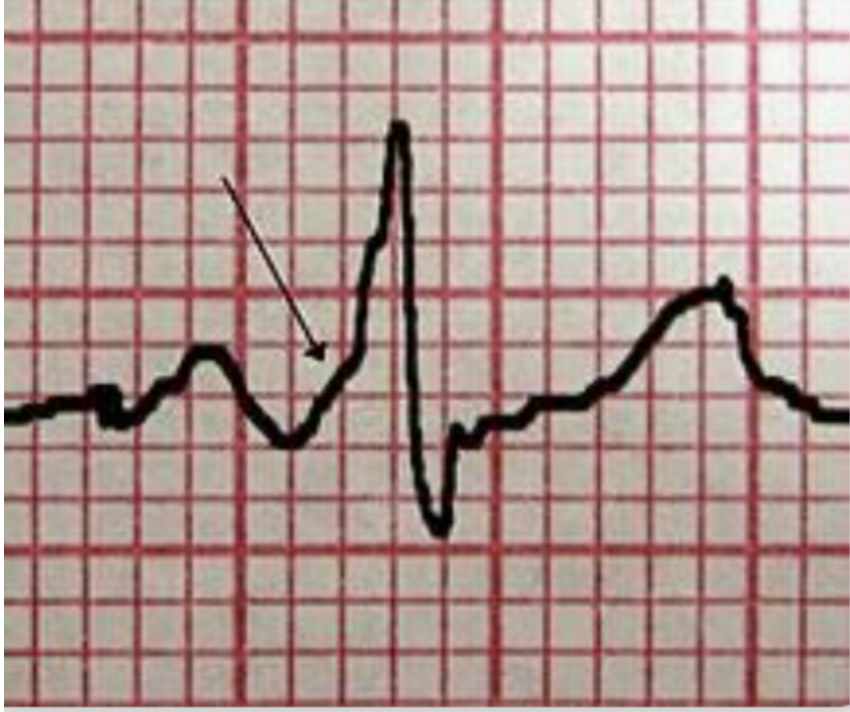
“Delta Wave”
WPW
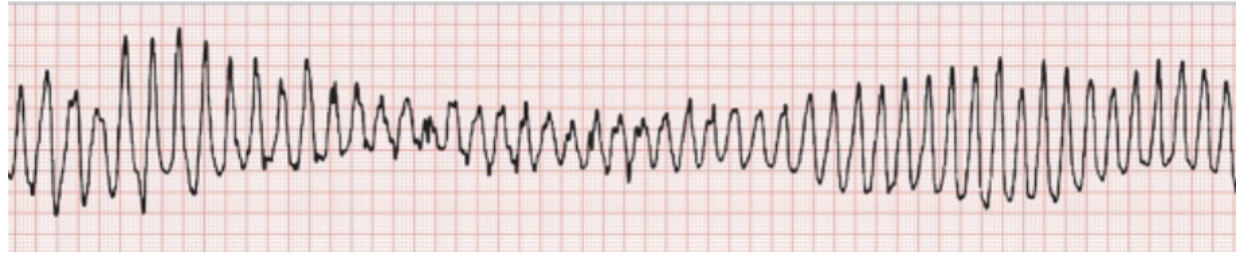
“-”
Torsades
Associated- Hypomagnesium
What is the human average blood pH level
7.35-7.45
Metabolic acidosis ph & bicarbonate levels
Low pH (more acidic)
Low bicarbonate
Metabolic acidosis etiology
DKA & kidney failure
Metabolic acidosis compensatory response
Hyperventilation (excreting CO2)
Metabolic alkalosis ph & bicarbonate
High pH (less acidic)
High bicarbonate
Metabolic alkalosis etiology
NG suctioning
Metabolic alkalosis compensatory response
Hypoventilation (retaining CO2)
Respiratory Acidosis pH & CO2
Low pH (more acidic)
High CO2
Respiratory acidosis etiology
Lung diseases such as COPD → Hypoventalation
Respiratory acidosis compensatory response
Retain bicarbonate
Excrete acid
Respiratory alkalosis pH & CO2
High pH (less acidic)
Low CO2
Respiratory alkalosis etiology
Pain & Panic attack → Hyperventilation
Respiratory alkalosis compensatory response
Excrete bicarbonate
Retain acid