Musical terms
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What are the elements of music
Duration, dynamics, expressive devices, pitch, structure, texture and tone
effect of dynamics: increasing or decreasing volume
A sudden increase in volume can create excitement or tension, while a decrease can evoke sadness or calm.
Effect of tempo: speed of music
Fast tempos can increase feelings of energy, excitement, or urgency, whereas slow tempos can create feelings of relaxation, sadness, or solemnity.
Effect of timbre: tone color or quality of
A "bright" timbre can sound joyous, while a "dark" or "heavy" timbre can create a sense of sadness or myste
Effect of timbre
Staccato notes (short and detached) can create a playful feel, while legato (smooth and connected) can create a flowing, lyrical effect.
effect of melody and harmony: A sequence of single notes (melody) and combinations of notes played together (harmony)
Minor key harmonies are often associated with feelings of sadness or introspection, while more complex progressions can build suspense.
glissando
sliding effect between two notes
tempo markings:

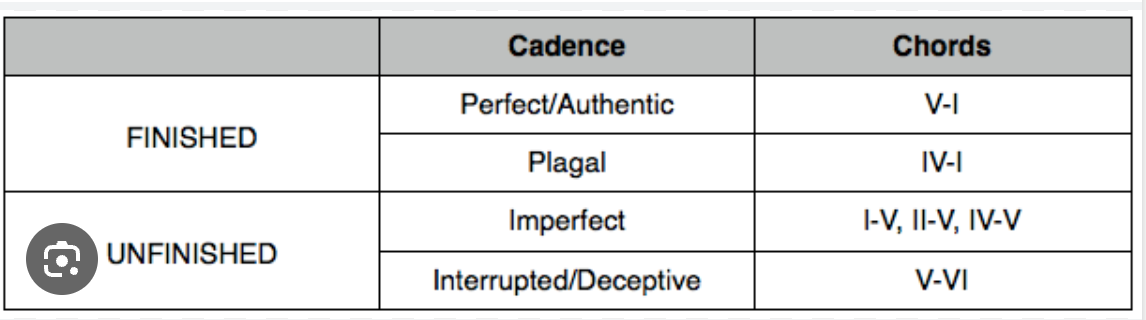
Cadences
Perfect (or Authentic) Cadence: Provides a strong sense of completion.
Half Cadence: Ends on a dominant (V) chord, creating a feeling of anticipation for what's next.
Plagal Cadence: Often called the "Amen" cadence, providing a feeling of gentle finality.
Deceptive Cadence: Ends on an unexpected chord instead of the expected resolution, which can delay the ending or lead to a new section.
ostinato
An ostinato creates musical effects by establishing a repeated musical phrase (melodic or rhythmic) that provides structure, continuity, and character to a piece. Its persistent repetition can generate drive, momentum, and tension, acting as a musical hook or a stable foundation for other elements to develop. In film, ostinatos can build suspense or emotional intensity, while in popular music, they form the memorable riff or bassline that defines a song
melisma
singing multiple notes on a single syllable
adds emotional depth, expressiveness, and ornamentation to a vocal performance by extending a single syllable across multiple musical notes, creating a smooth, flowing, and often dramatic effect. Melisma is a challenging technique that can heighten the emotional impact of lyrics, enhance the melodic contour, and demonstrate the singer's vocal agility and control, although it can sometimes be overused or feel like mere "showing off
glissando
creates a dramatic, fluid effect by smoothly sliding between notes, adding flair, emotion, and a sense of continuity or momentum to a piece of music. Depending on the context, a glissando can convey intensity and excitement, provide a lyrical or vocal quality, or create a sense of mystery, making the music more expressive and engaging
arpeggio
adds movement and melodic contour to a static chord, creating a flowing, cascading sound that can fill a song with texture, depth, and harmonic richness. It functions as a rhythmic accompaniment, a melodic line, a bridge between harmony and melody, and a tool to emphasize harmony in a more interesting, multidimensional way.
ritatando
gradually slowing down tempo
mono, homo and poly
Monophonic Texture:
Definition: Features a single, unaccompanied melodic line.
Effect: Creates a simple, exposed texture where the melody stands alone.
Homophonic Texture:
Definition:
A single melody that is supported by chordal accompaniment or a harmonic background.
Effect:
Provides a richer, fuller sound than monophony by adding harmony to the melody
Polyphonic Texture:
Definition:
Involves two or more independent melodic lines woven together simultaneously.
Effect:
Creates a complex, interwoven texture with multiple distinct melodies interacting with each othe
sycopation
creates interest, a sense of groove, and emotional expression in music by shifting emphasis away from expected strong beats to weaker beats or off-beats, which creates a feeling of rhythmic tension, bounce, and unpredictability. This disrupts the listener's expectations, leading to increased cognitive engagement and a more dynamic, less "robotic" musical experience. Effects include creating a feeling of "forward drive," enhancing the emotional valence of a piece, and providing a tool for composers to add variety and dramatic effect.
tremolo
creates a “trembling” or “quivering” sound by rapidly and repeatedly playing a single note or by rapidly alternating between two different notes.
trill
enhance musical texture, can fill gaps in melodies, express taste, imitate nature, or add a sense of "vibrato
modulation
Key Change:
Modulation is essentially a key change, which changes the fundamental scale and collection of chords around which a piece of music is organized.
Tonal Center:
The term refers to the shift from one tonal center (or tonic) to a new one.
Effects and Purpose
Variety:
Modulation introduces novelty and prevents the music from becoming monotonous, especially in longer compositions.
Emotional Impact:
A shift in key can alter the mood of the music, making it more uplifting, sad, or intense.
Contrast:
It creates contrast between different musical sections or themes, making the overall structure of the piece more interesting.
Storytelling:
In larger forms, returning to the home key after a modulation provides a sense of closure, unity, and completion, akin to a musical story with a beginning, middle, and end.
Highlighting Sections:
Modulation can emphasize the importance of a new theme or idea by placing it in a new key.
legato
indicates that musical notes are played or sung smoothly, such that the transition from note to note is made with no intervening silence.