Unit 2: Hematopoiesis Review
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What is hematopoiesis?
RBC production, differentiation, and development
All blood cells come from what kind of cell in what location?
pluripotent stem cells
bone marrow
Pluripotent cells differentiate into what 2 kinds of cells?
lymphoid progenitor cells
myeloid progenitor cells
(Lymphoid/Myeloid) progenitor cells mature into platelets, RBCs, monocytes, and granulocytes.
myeloid
(Lymphoid/Myeloid) progenitor cells mature into T cells, NK cells, and B cells
lymphoid
Most immature group of hematopoietic cells capable of self-renewal:
mature cells
primitive, multipotential cells
precursors
intermediate cells
primitive, multipotential cells
Consist of committed progenitor cells destined to develop into distinct cell lines:
mature cells
primitive, multipotential cells
precursors
intermediate cells
intermediate cells
Give rise to mature cells and are distinguished in the bone marrow and peripheral circulation:
mature cells
primitive, multipotential cells
precursors
intermediate cells
precursors
Most developed group with specific physiologic funtions:
mature cells
primitive, multipotential cells
precursors
intermediate cells
mature cells
Erythropoiesis occurs on distinct sites called erythropoietic _________.
islands
What protrude through the cell wall to deliver platelets into the blood?
megakaryocytes
What cell induces intracellular signaling to the target cell for survival, proliferation, or differentiation as a means of regulating cell production?
cytokines
What are the 3 types of cytokines?
interleukins
colony-stimulating factors
interferons
What type of cytokine are primary messengers of the immune system and act independently or in conjunction with other interleukins to encourage hematopoietic growth?
interleukins
Chromosome 7 encodes for what growth factor?
EPO
Chromosome 17 encodes for what growth factor?
G-CSF
What 2 growth factors affect myeloid cells?
G-CSF
GM-CSF
What growth factor stimulates T and B lymphocytes?
IL-7
What growth factor stimulates NK cells?
IL-12
T lymphocytes mature in the ________ and B lymphocytes mature in the _____________.
thymus
bone marrow
CD4+ cells are T (helper/cytotoxic) cells.
helper
CD8+ cells are T (helper/cytotoxic) cells.
cytotoxic
T helper cells bind to antigens on _________ sites and T cytotoxic cells bind to antigens on __________ sites.
MHC class II
MHC class I
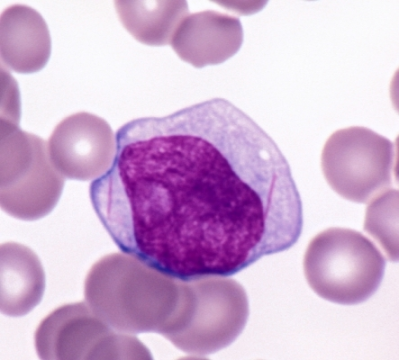
Reactive lymphocytes are indicative of:
infectious mononucleosis
An child presents with elevated lymphocytes and decreased neutrophils. What is this indicative of?
nothing; children have more lymphocytes that neutrophils compared to adults
What is the most reliable indicator of cell age?
chromatin density
less dense = immature
more dense = mature
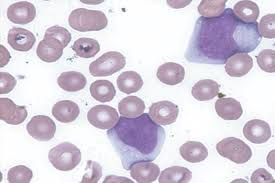
What cell is this?
myeloblast (blue nongranular cytoplasm, large nucleus, nucleoli visible)
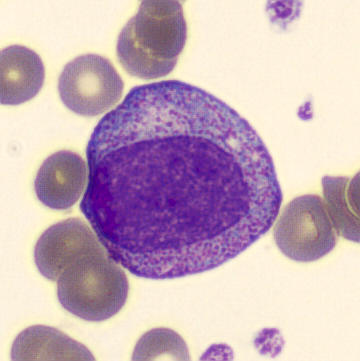
What cell is this?
promyelocyte (presence of large dark primary granules,
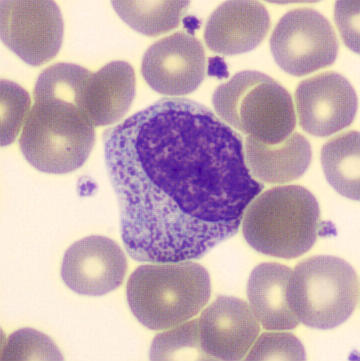
What cell is this?
myelocyte (eccentric nucleus, secondary smaller and lighter granules appear, lighter cytoplasm, no nucleoli)
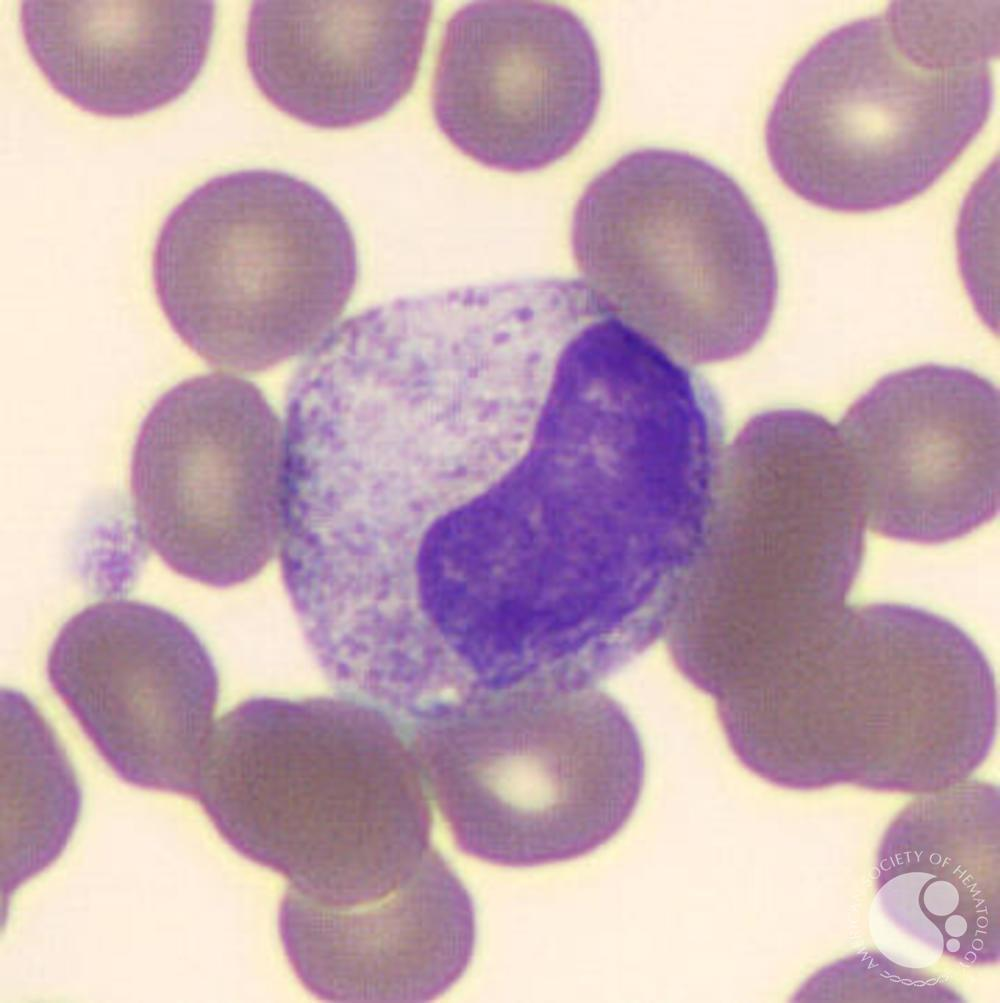
What cell is this?
metamylocyte (kidney-bean shaped, many secondary granules, eccentric nulceus)
A “left shift” seen during bacterial infections is characterized by and increase in what type of WBC?
banded neutrophil (less mature of the 2 types; released early from bone marrow to fight infection)
What cell is the most mature of the myelocytic series?
segmented neutrophils
Monocytes mature into:
tissue macrophages
What are the 3 steps of platelet maturation?
megakaryoblast
megacaryocyte
platelet
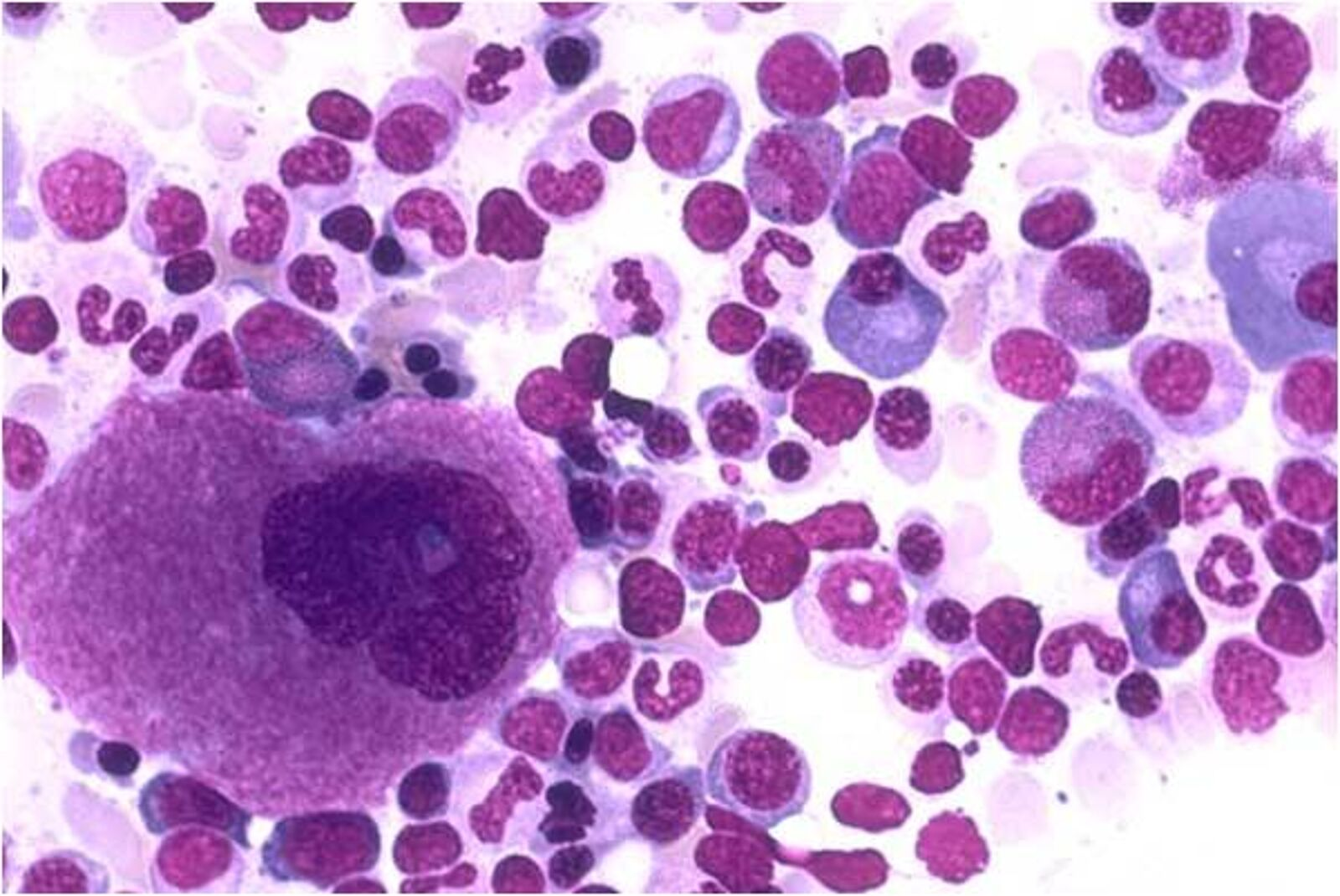
What is the large cell and what does it mature into?
megakaryocyte
matures into platelets
What 2 sites are samples collected from for bone marrow examination?
sternum
iliac crest of pelvis
What is the normal myeloid:eryhtroid ratio in healthy patients?
4:1
What percentage of bone cavity in adults are filled by fatty tissue:
10%
20%
50%
75%
50%
Which of the following blood cells does NOT mature in the bone marrow in the normal adult:
erythrocyte
lymphocyte
monocyte
thrombocyte
lymphocyte
As most cells mature:
nuclear chromatin is less condensed
N:C ratio decreases
nucleoli become more prominent
basophilia of cytoplasm increases
N:C ratio decreases
The most mature cell that can undergo mitosis is the:
myeloblast
myelocyte
promyelocyte
metamyelocyte
myelocyte
Which of the following features is most characteristic of the promyelocyte:
fine nuclear chromatin
basophilic cytoplasm
nucleoli
primary granules
primary granules
Production of primary granules ceases and production of secondary granules commences with what cell stage:
myeloblast
myelocyte
promyelocyte
metamyelocyte
myelocyte
An increased amount of cytoplasmic basophilia in a blood cell indicates:
increased cytoplasmic maturation
decreased cytoplasmic maturation
reduction in size of the cell
decreased nuclear maturation
decreased cytoplasmic maturation
What percentage of neutrophils in the peripheral blood are considered the circulating pool:
5%
10%
50%
100%
50%
Metamyelocytes are characterized by:
appearance of specific granules
color of cytoplasm
absence of nucleoli
indentation of nucleus
indentation of nucleus
Plasma cells develop from which cell line:
neutrophil
lymphocyte
monocyte
erythrocyte
lymphocyte
The attachment of neutrophils to the blood vessel walls is referred to as:
diapedesis
opsonization
phagocytosis
margination
margination
The two stem cells that can originate from the pluripotent stem cells are:
thromboid & erythroid
myeloid & erythroid
myeloid & lymphoid
erythroid & lymphoid
myeloid & lymphoid
What is the largest normal cell in the bone marrow:
myeloblast
lymphoblast
monoblast
megakaryocyte
megakaryocyte
If a cell displays characteristics of 2 stages of development, how should it be named:
as the less mature stage
as the more mature stage
as a skipocyte
None of the above
as the more mature stage
Basophila in the cytoplasm is due to:
DNA
RNA
Hemoglobin
All of the above
RNA
When does a metamyelocyte become a band neutrophil:
when the nuclear indentation is greater than ½ the diameter of the nucleus
when the nuclear indentation is greater than ¾ the diameter of the nucleus
when the nuclear indentation is greater than ¼ the diameter of the nucleus
when secondary granules appear
when the nuclear indentation is greater than ½ the diameter of the nucleus
When does a band become a seg:
when the nuclear indentation is greater than ½ the diameter of the nucleus
when the nuclear indentation is greater than 3/4 the diameter of the nucleus
when secondary granules appear
when a thread of chromatin connects nuclear lobes
when the nuclear indentation is greater than 3/4 the diameter of the nucleus
Primary granules are:
specific
nonspecific
produced after secondary granules
prominent in myelocytes
nonspecific