ch 11 Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Their Properties
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
Organic chemistry
Study of carbon-containing compounds
Inorganic chemistry
Study of the elements and all noncarbon compounds
Inorganic compound
Characterized by the presence of ionic bonding
Covalent bonding
Bonding within molecules in organic compounds
Ionic bonding
Bonding within molecules in inorganic compounds
Flammability of organic compounds
Usually flammable
Flammability of inorganic compounds
Usually non-flammable
Normal physical state of organic compounds
Gases, liquids, or low-melting-point solids
Normal physical state of inorganic compounds
Usually high-melting-point solids
Conductivity of organic compounds
Non-conductor
Conductivity of inorganic compounds
Conductor
Rate of chemical reactions in organic compounds
Usually slow
Rate of chemical reactions in inorganic compounds
Usually fast
sp3 hybrid orbitals
Orbital produced from the combination of two or more nonequivalent orbitals of an atom
Shape of sp3 orbital
Two-lobed shape, similar to the shape of a p orbital but with different-sized lobes

Sigma (σ) bond
Created by sharing of two electrons in the overlap region of a C (sp3) and an H (1s) orbital
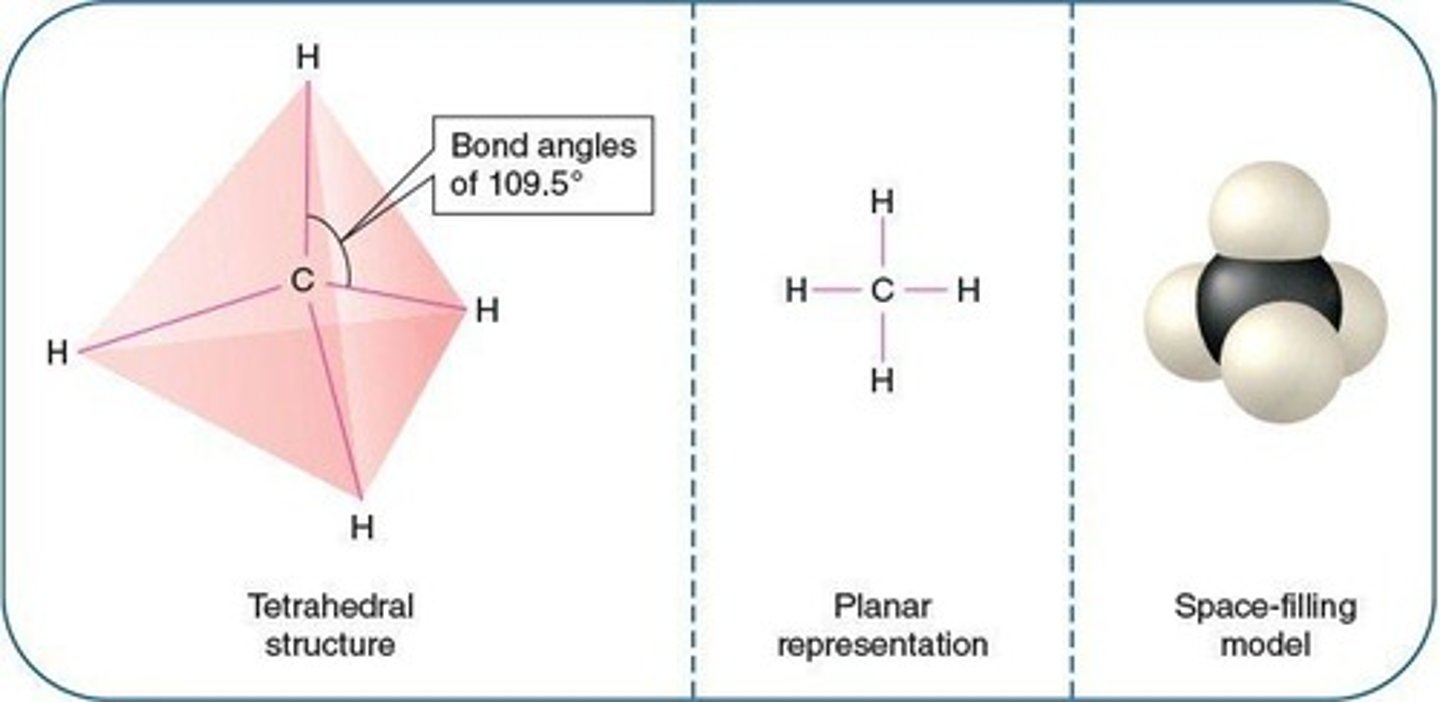
Tetrahedral configuration
Resultant shape when carbon is joined to four substituents (i.e., CH4)
Isomers
Compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas
Condensed structural formulas
A way to represent the structure of a compound in a simplified form
Expanded structural formulas
A detailed representation of the structure of a compound showing all bonds
IUPAC naming
Systematic method for naming organic chemical compounds
Geometric isomers
Isomers that have the same molecular formula but differ in the spatial arrangement of atoms

Carbon bonding
Carbon can bond to other carbon atoms.
Covalent bonding limit
There is no limit to the number of carbon atoms that can bond covalently.
Multiple bonds
May share more than one pair of electrons to form multiple bonds.
Organic molecules
Organic molecules range from simple molecules like methane (CH4) to very complicated molecules containing over a million carbon atoms.
Isomerism
Property in which two or more compounds have the same molecular formula but different arrangements of atoms.
Structural isomer
Isomerism in which the atoms bond in different patterns.
Example of structural isomer
Isomers of C2H6O.
Ethyl alcohol
Ethyl alcohol is a liquid at room temperature and completely soluble in water.

Dimethyl ether
Dimethyl ether is a gas at room temperature and only partially soluble in water.
Functional group
Unique reactive combinations of atoms that differentiate molecules of organic compounds of one class from those of another.
Functional group characteristics
Except for alkanes, each functional group contains a multiple bond or at least one oxygen or nitrogen atom.
Expanded structural formula
Shows all the covalent bonds.
Condensed structural formula
Shows the general arrangement of atoms but without showing all the covalent bonds.
Example of condensed structural formula
CH3CH2CH2CH3 or CH3(CH2)2CH3.
Hydrocarbon
Organic compound that contains only carbon and hydrogen.
Hydrocarbon properties
Helps to understand the chemical properties of more complex biomolecules.
Hydrocarbon uses
Used as a primary source of energy and as an important source of raw materials for the manufacture of plastics, synthetic fibers, drugs, and other compounds used daily.
Alkanes general formula
Represented by the general formula CnH2n+2.
n in alkanes
n - Number of carbon atoms in the molecule.
Methane
Methane (CH4) is the simplest alkane, which is the primary compound in natural gas.

Ethane
Ethane (C2H6) is a minor component of natural gas.
Propane
Propane (C3H8) is used as an industrial fuel and for heating homes.
Normal alkane
All carbon atoms are aligned in a continuous chain.
Branched alkane
At least one carbon atom is not a part of a continuous chain.
Normal vs Branched molecule
Branched molecule will have at least one carbon atom bonded to three or more other carbon atoms; normal molecule will not have any carbon atoms bonded to more than two other carbon atoms.
C6H14 isomers
C6H14 has 5 possible structural isomers.
Conformations
Different arrangements of atoms in space achieved by rotation about single bonds.
Structural Isomers
Different conformations do not represent different structural isomers.
IUPAC
International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry.
Methane
1 carbon atom, molecular formula CH4.
Ethane
2 carbon atoms, molecular formula C2H6.

Propane
3 carbon atoms, molecular formula C3H8.
Butane
4 carbon atoms, molecular formula C4H10.
Pentane
5 carbon atoms, molecular formula C5H12.
Hexane
6 carbon atoms, molecular formula C6H14.
Heptane
7 carbon atoms, molecular formula C7H16.
Octane
8 carbon atoms, molecular formula C8H18.
Nonane
9 carbon atoms, molecular formula C9H20.
Decane
10 carbon atoms, molecular formula C10H22.
Alkane Nomenclature Step 1
Identify and name the longest carbon chain.
Alkane Nomenclature Step 2
Number the longest carbon chain to give the lowest number to any carbon to which a group is attached.
Alkane Nomenclature Step 3
Locate and name the attached alkyl groups.
Alkane Nomenclature Step 4
Combine the longest chain and the branches into the name.
Alkane Nomenclature Step 5
For multiple branches, show the location of each branch with numbers.
4-isopropyl-2,3-dimethylheptane
An example of a complex alkane name following IUPAC rules.
di-, tri-, sec-, and t- prefixes
Can be ignored when listing multiple branches alphabetically.
2,2,4-trimethylpentane
A branched-chain alkane with the molecular formula C8H18.
3-isopropylhexane
An alkane with a six-carbon chain and an isopropyl group attached to the third carbon.
3-ethyl-2,4-dimethylheptane
An alkane with a seven-carbon chain, an ethyl group on the third carbon, and two methyl groups on the second and fourth carbons.
Cycloalkanes
Alkanes in which carbon atoms form rings.
Cyclo-
Prefix used before the alkane name to indicate a ring structure.
Substituted cycloalkanes
Cycloalkanes that have one or more groups attached to the ring.
Geometric isomers
Molecules with restricted rotation around C—C bonds that differ in the three-dimensional arrangements of their atoms.
Cis-
Isomers with substituents on the same side of a double bond or ring.
Trans-
Isomers with substituents on opposite sides of a double bond or ring.
Hydrophobic
Molecules or parts of molecules that are insoluble in water.
Homologous series
Group of compounds with the same functional class that differ by a —CH2— group.
Physical properties of alkanes
Odorless compounds that are non-polar with weak intermolecular forces.
Methane
The simplest alkane with the formula CH4, melting point -182.5°C and boiling point -164.0°C.
Ethane
An alkane with the formula CH3CH3, melting point -183.2°C and boiling point -88.6°C.
Propane
An alkane with the formula CH3CH2CH3, melting point -189.7°C and boiling point -42.1°C.
Butane
An alkane with the formula CH3CH2CH2CH3, melting point -133.4°C and boiling point -0.5°C.
Pentane
An alkane with the formula CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3, melting point -129.7°C and boiling point 36.1°C.
Hexane
An alkane with the formula CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3, melting point -95.3°C and boiling point 68.9°C.
Heptane
An alkane with the formula CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3, melting point -90.6°C and boiling point 98.4°C.
Octane
An alkane with the formula CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3, melting point -56.8°C and boiling point 125.7°C.
Nonane
An alkane with the formula CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3, melting point -53.5°C and boiling point 150.8°C.
Decane
An alkane with the formula CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3, melting point -29.7°C and boiling point 174.1°C.
Combustion
A significant reaction of alkanes involving rapid oxidation, producing CO2 and H2O.
Incomplete combustion
A reaction that occurs when there is not enough oxygen available, producing CO and H2O.