PCR Crash Course Part I
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What is PCR?
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Polymerase is an enzyme that facilitates the synthesis of a variety of polymers, specifically DNA or RNA.
Analysis of PCR
Multiple ways to analyze PCR, both qualitative and quantitative.
DNA Replication Steps
Unzipping: separating nucleic acid pairs, usually facilitated by helicases (enzymes/motor proteins)
DNA polymerase gathers nucleic acid base pairs to synthesize new DNA
The final product: two (hopefully) identical DNA strands
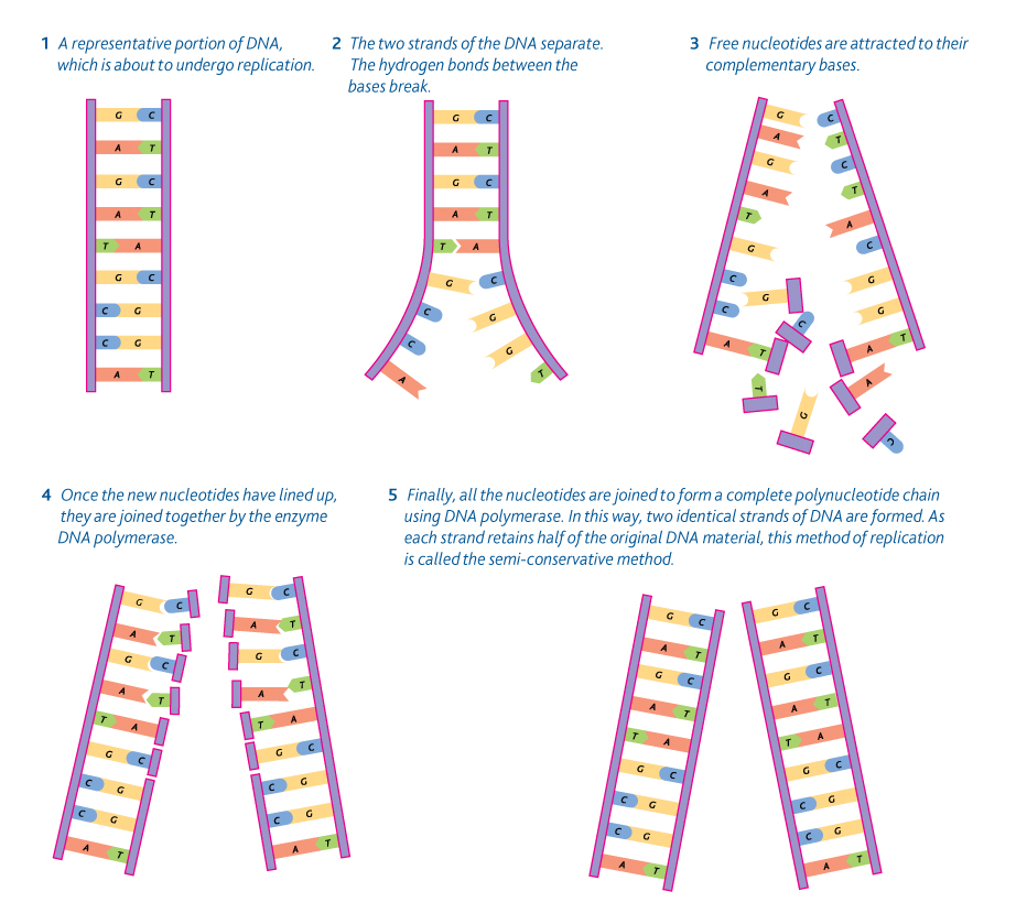
Performing PCR
The 4 main ingredients for PCR:
polymerase
nucleotides
template DNA
PCR Primers
Polymerase
enzyme that facilitates DNA synthesis
Nucleotides
base monomers of DNA
Template DNA
the sample DNA strand that contains a target sequence (the thing you want to replicate)
PCR Primers
short sequence of nucleotides (20 bp in length see “oglionucleotide”)
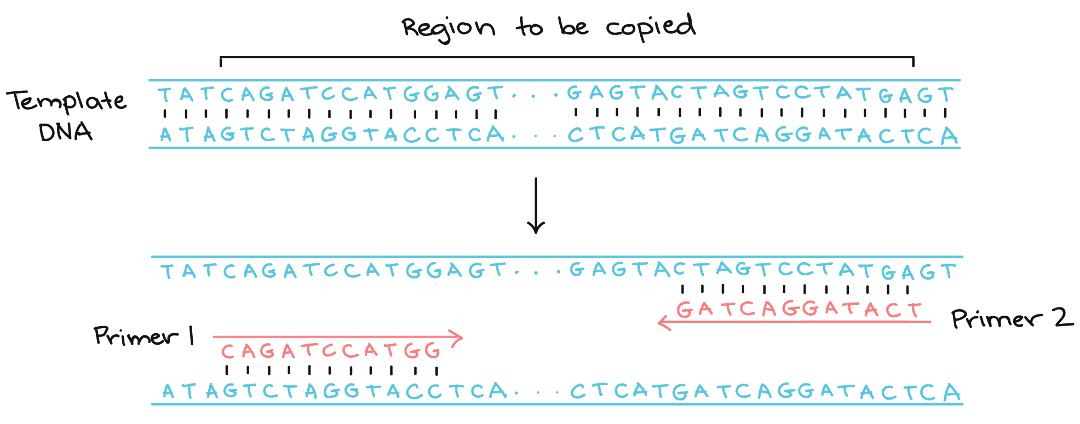
Performing PCR Primers: What do they do?
PCR Primers bind to template DNA and define the region that will be replicated and amplified
Where do they come from?
Primers are designed specifically for thetarget region of the tem
Why are they called primers?
Primers by definition, initiate actions. In this case, PCR primers are required to initiate PCR.
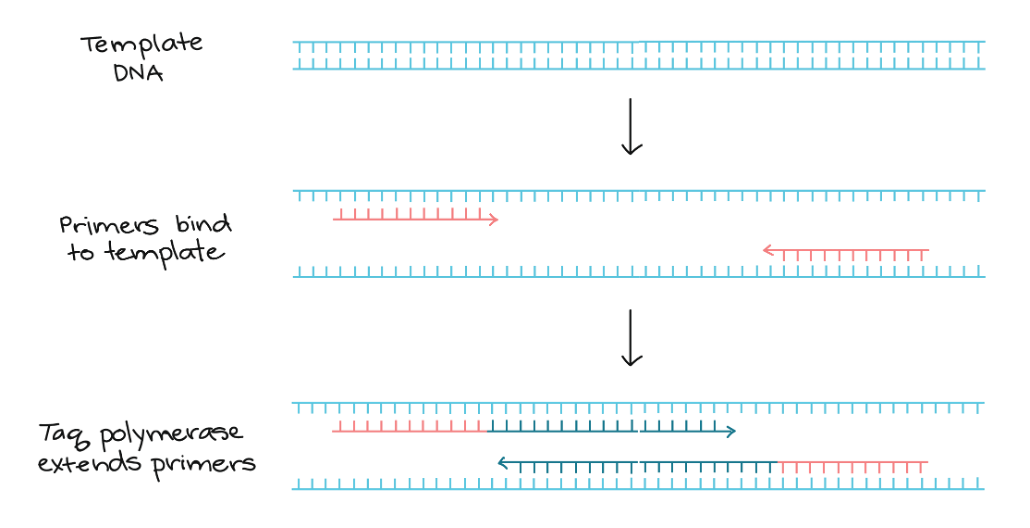
3 Main steps of PCR
Denaturation
Annealing
Extension
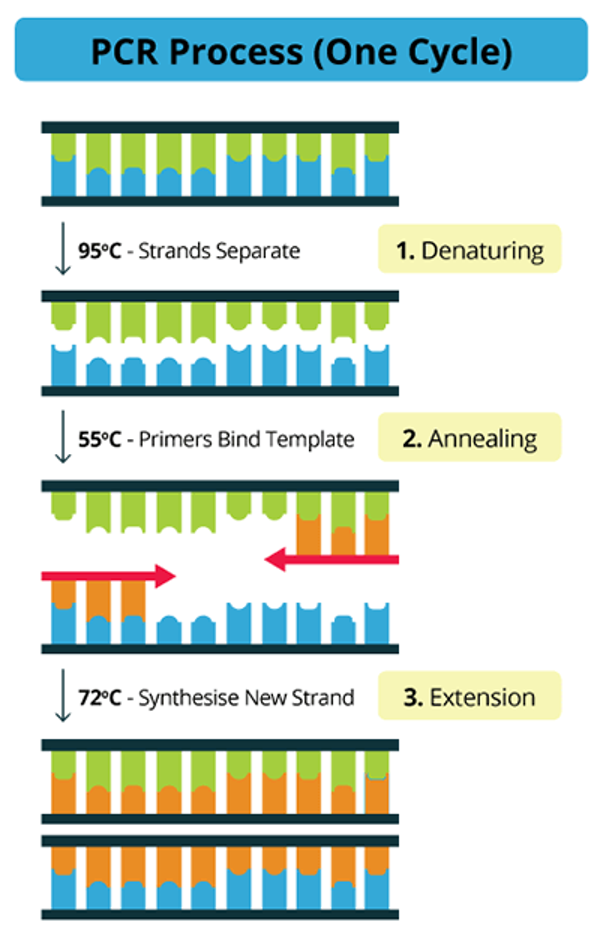
Denaturation
process by which hydrogen bonds are broken between nucleotide base pairs of double stranded DNA (dsDNA) to create two single strands (95C)
Annealing
Primers bind to the target region of the template DNA (See amplicon) (55)
Extension
DNA polymerase extends primers by binding free nuceltoide base pairs (72)
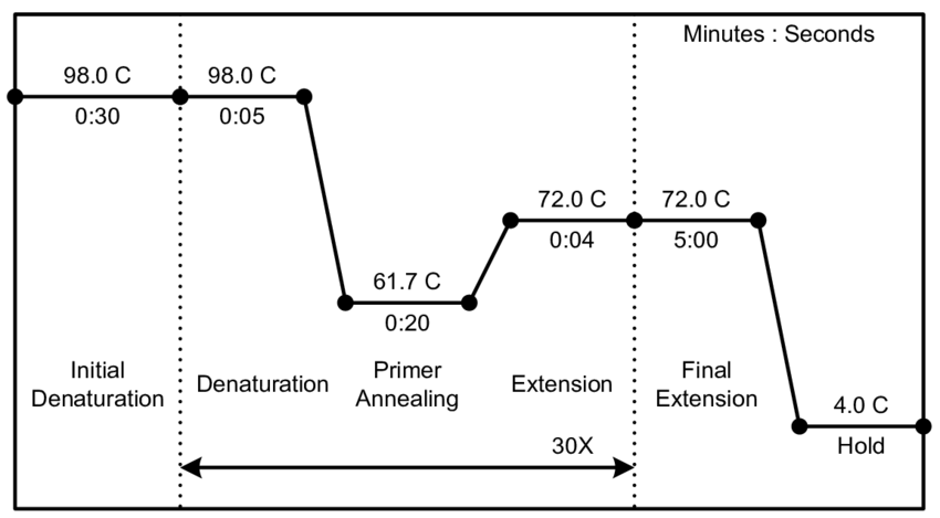
PCR chart
initial denaturation (98C)
denaturation (98C)
primer annealing (61.7C)
extension (72C
final extension (72C)
hold (4C)
Gel electrophoresis
technique in which fragments of DNA are pulled through a gel matrix by an electric current, seperating the fragments by size/weight/bp#.
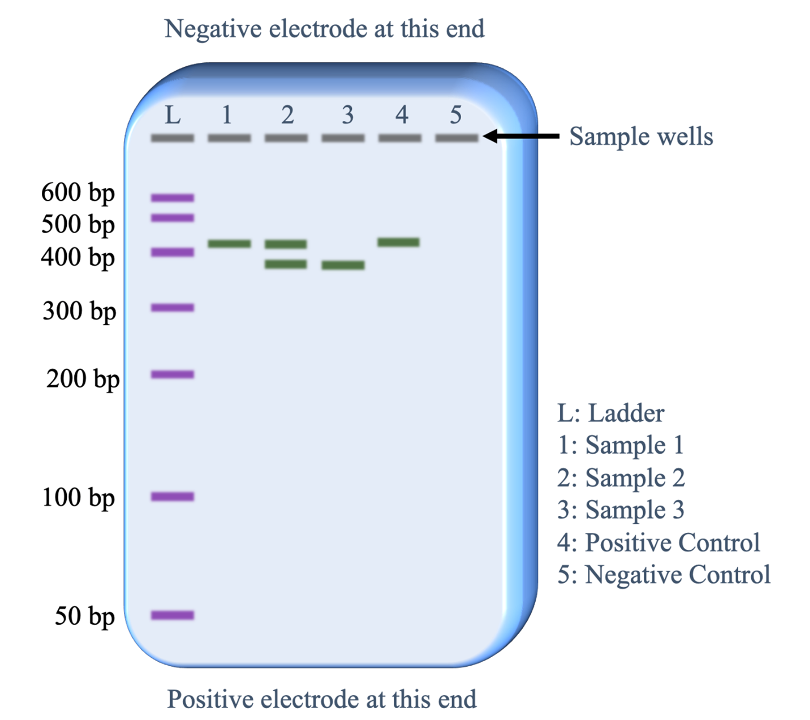
DNA ladder
is used as reference for comparison of band locations of tested samples
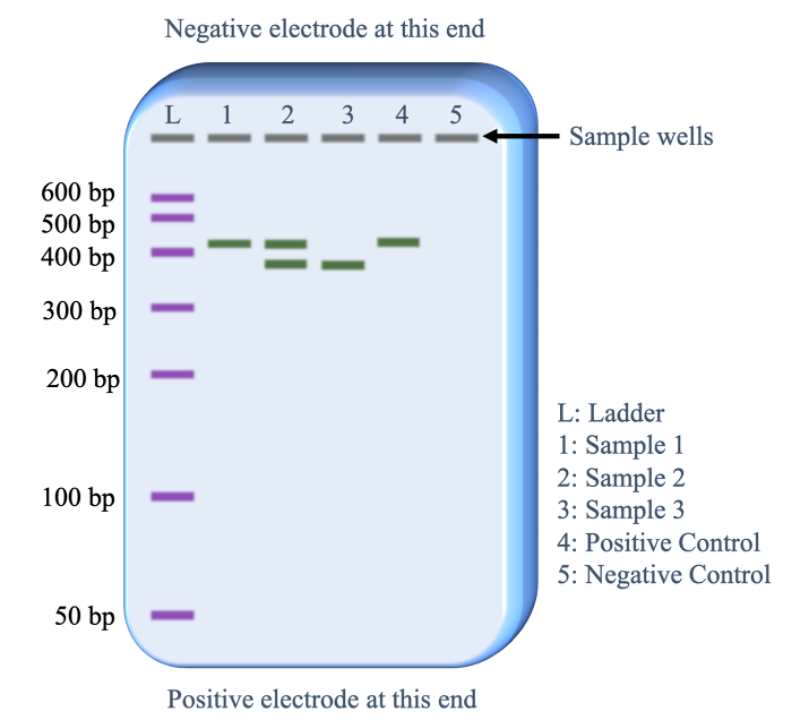
In the case of the figure, which one matches with the control?
Sample 1 would be considered “positive” for the target DNA, as it matches with the positive control.
Is analysis of PCR gel electrophoresis qualitative or quantitative?
Qualitative
Quantitative PCR (qPCR) vs PCR
The main difference between PCR and qPCR is that qPCR is a real-time method.
In other words, you can monitor DNA amplification as it is happening.
Quantifying amplification requires the addition of fluorescent dyes or probes that bind to target DNA.
During amplification, these dyes or probes emit energy at different wavelengths when they are excited by a laser.
What is probe?
Probes are another type of oligonucleotide with reporter dye and a quencher
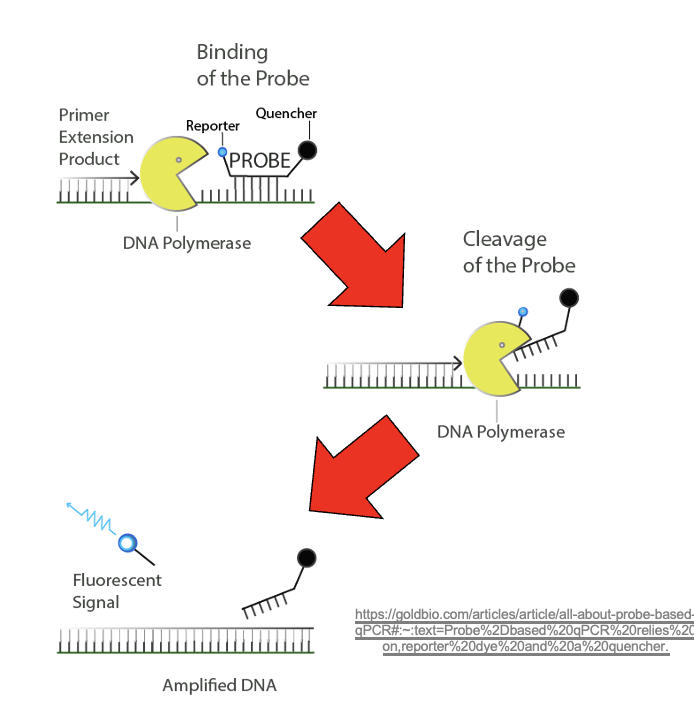
What is a quencher?
absorbs flouresnce given off by the reporter dye before the probe is degraded
What is a reporter dye?
gives off fluorescence to be detected adter the probe is degraded (fluorophore)
Extension phase of qPCR
DNA polymerase cleav
After probe is cleaved in qPCR
light fluorescent signal is emitted by the reporter and is detected by qPCR instrument
In qPCR how is amplification quantified?
By fluorescence output from cleaved probes
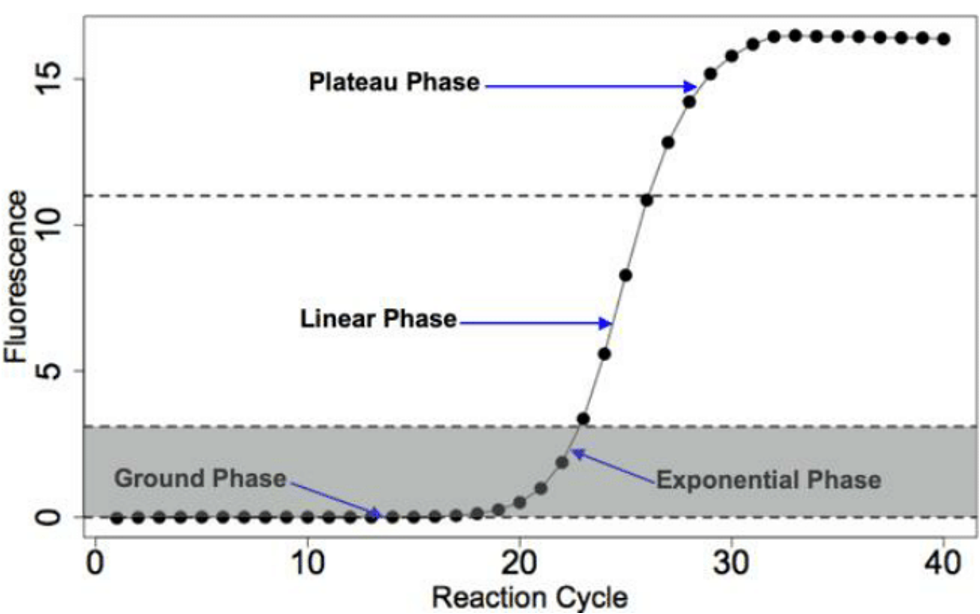
As amplification continues, fluoresence output increase
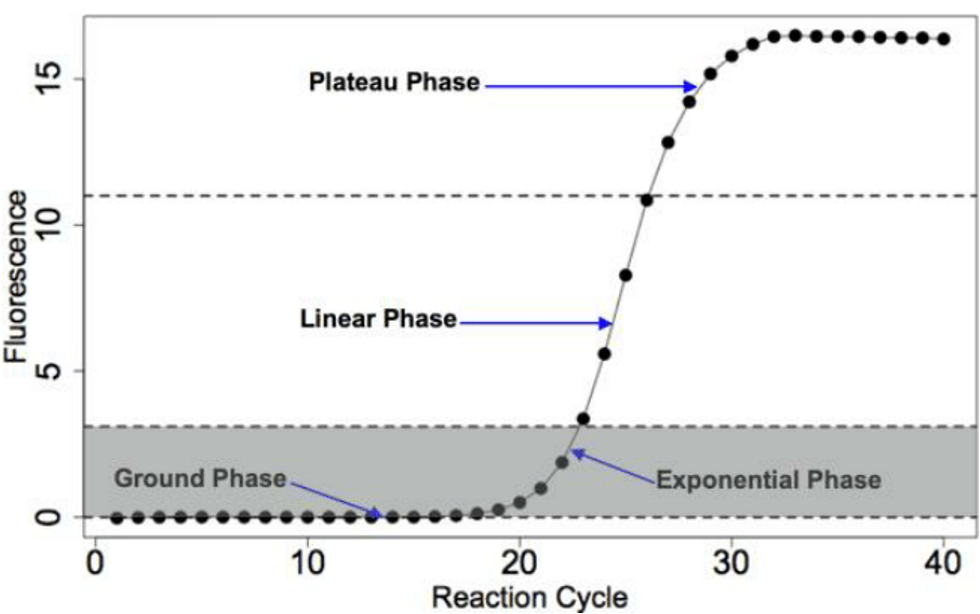
4 main phases of amplication
lag
exponential
linear
plateau phases
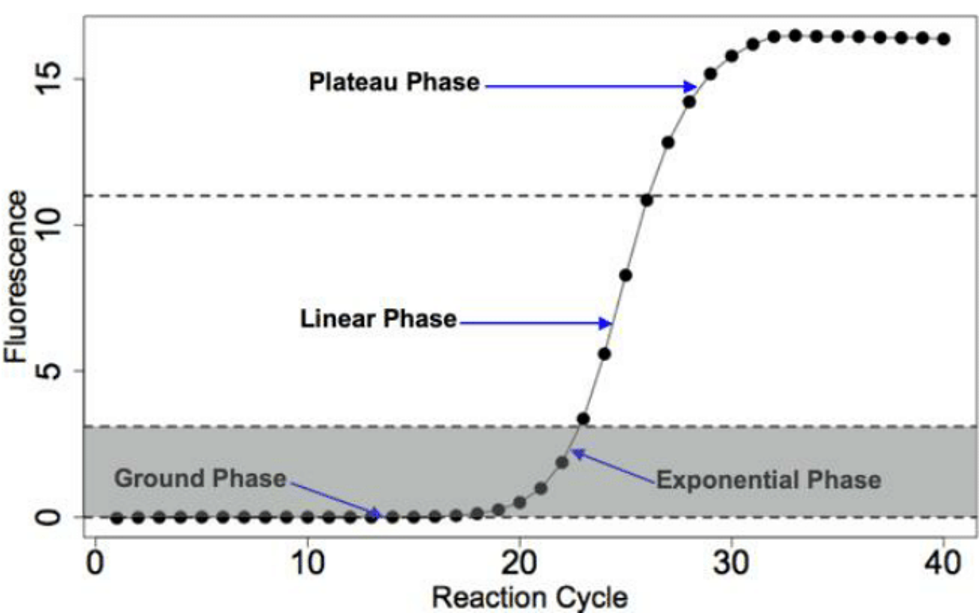
Ct or Cq
The value by which detection begins is called the cycle quantification
in qPCR, fluorescence is measured against the number of amplification cycles required for detection.
Can be PCR be used to detect DNA?
No