PSYC102: CH3 - Biological Psychology
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Neuron
Nerve cells specialized for communication
85 billion of them in the brain with 160 trillion connects
Obey the “all or none” law: They either fire or they don’t
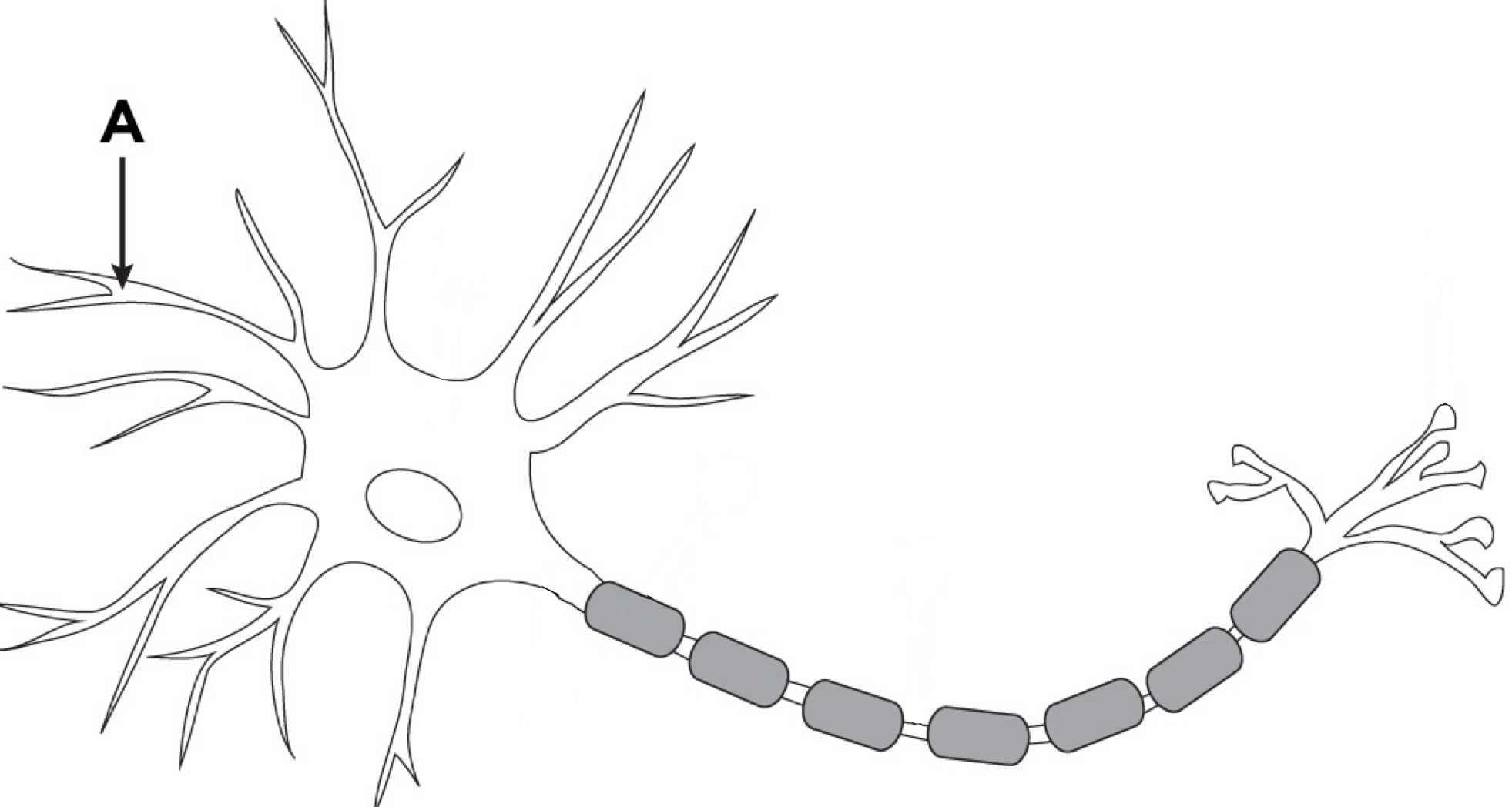
Dendrites
Portion of neuron that receives signals from other neurons and pass them on to the cell body
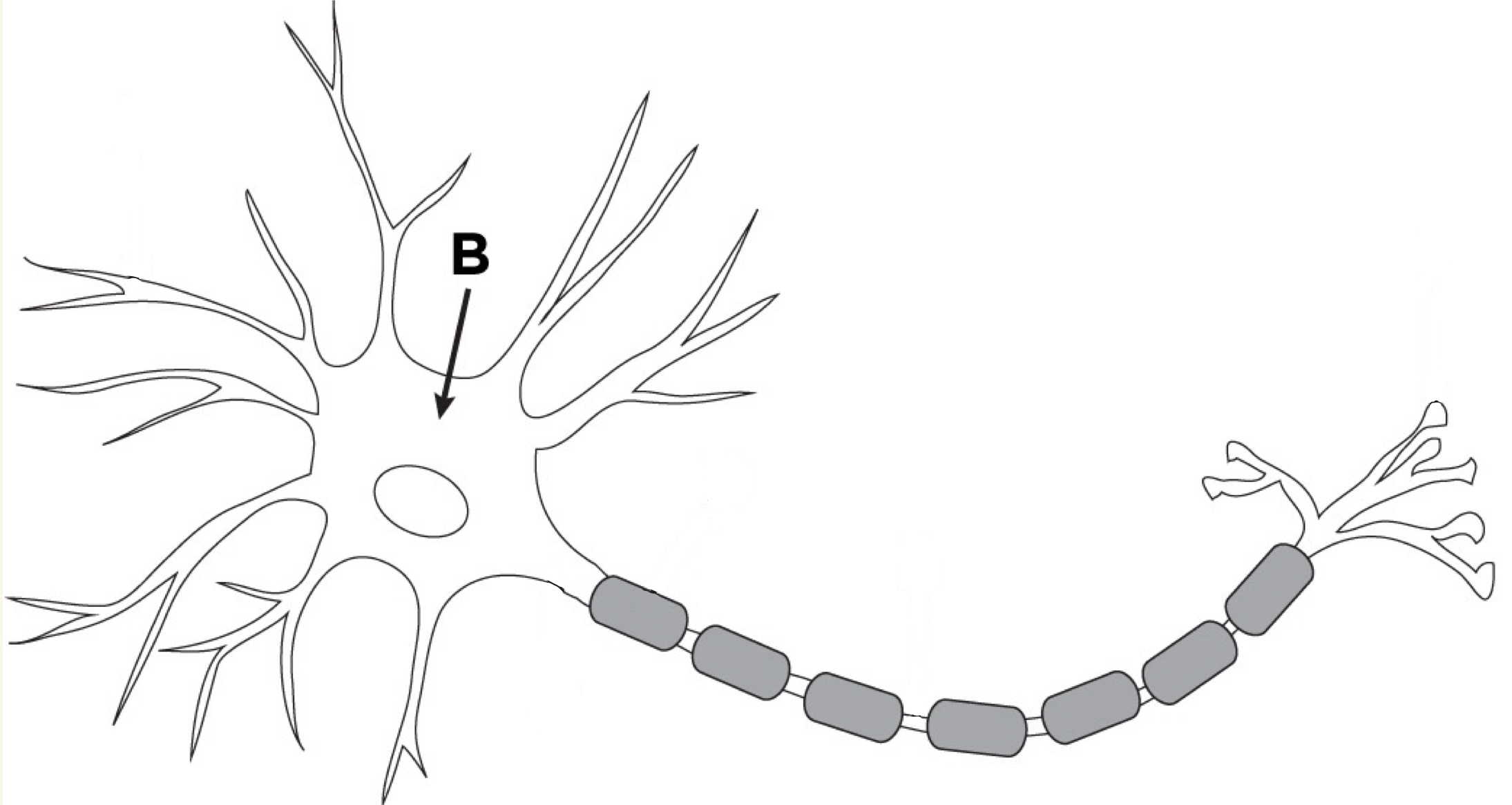
Cell Body/Soma
Manufactures new cell components and materials needed by the neuron. Contains nucleus and genetic material
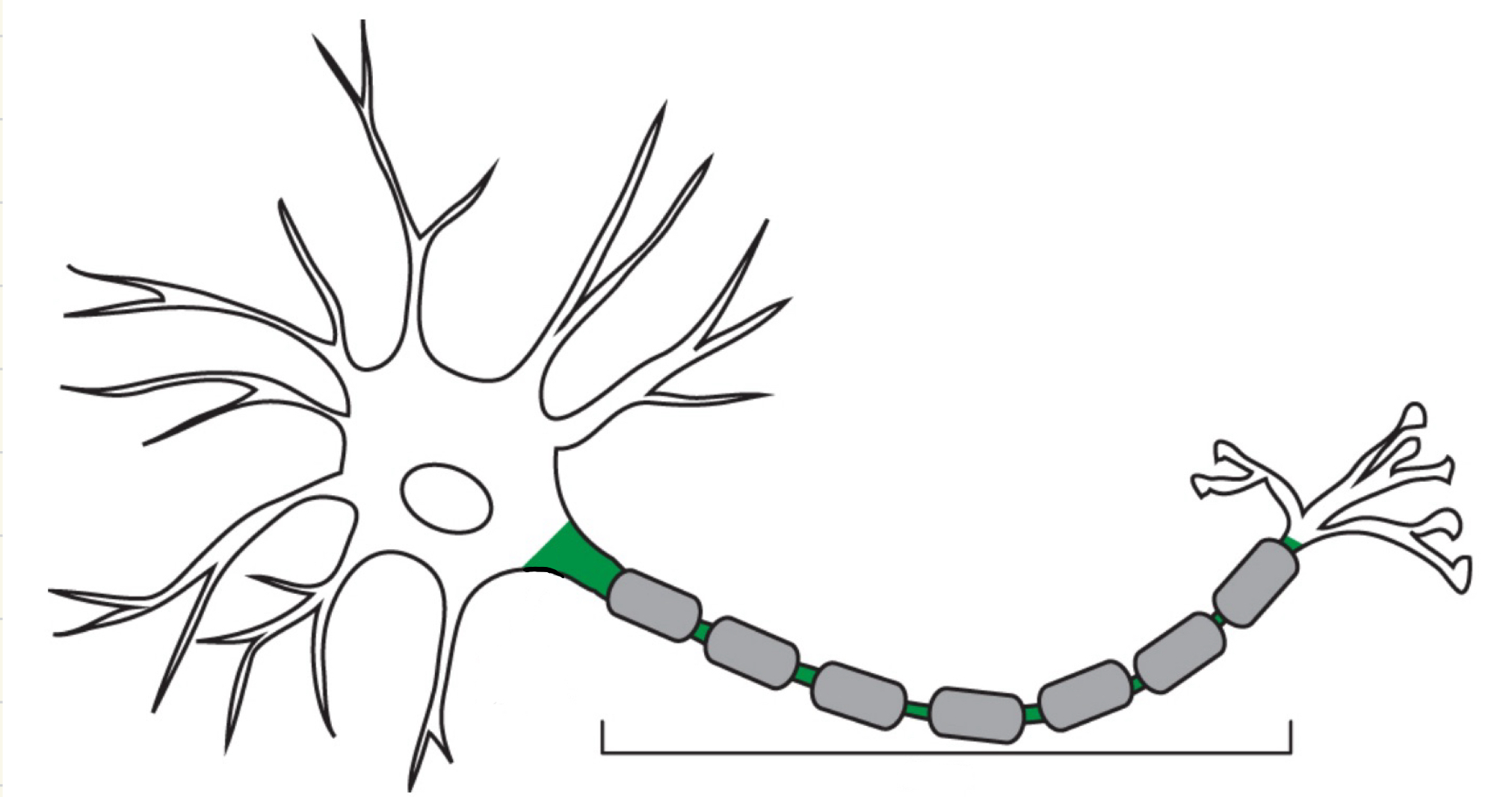
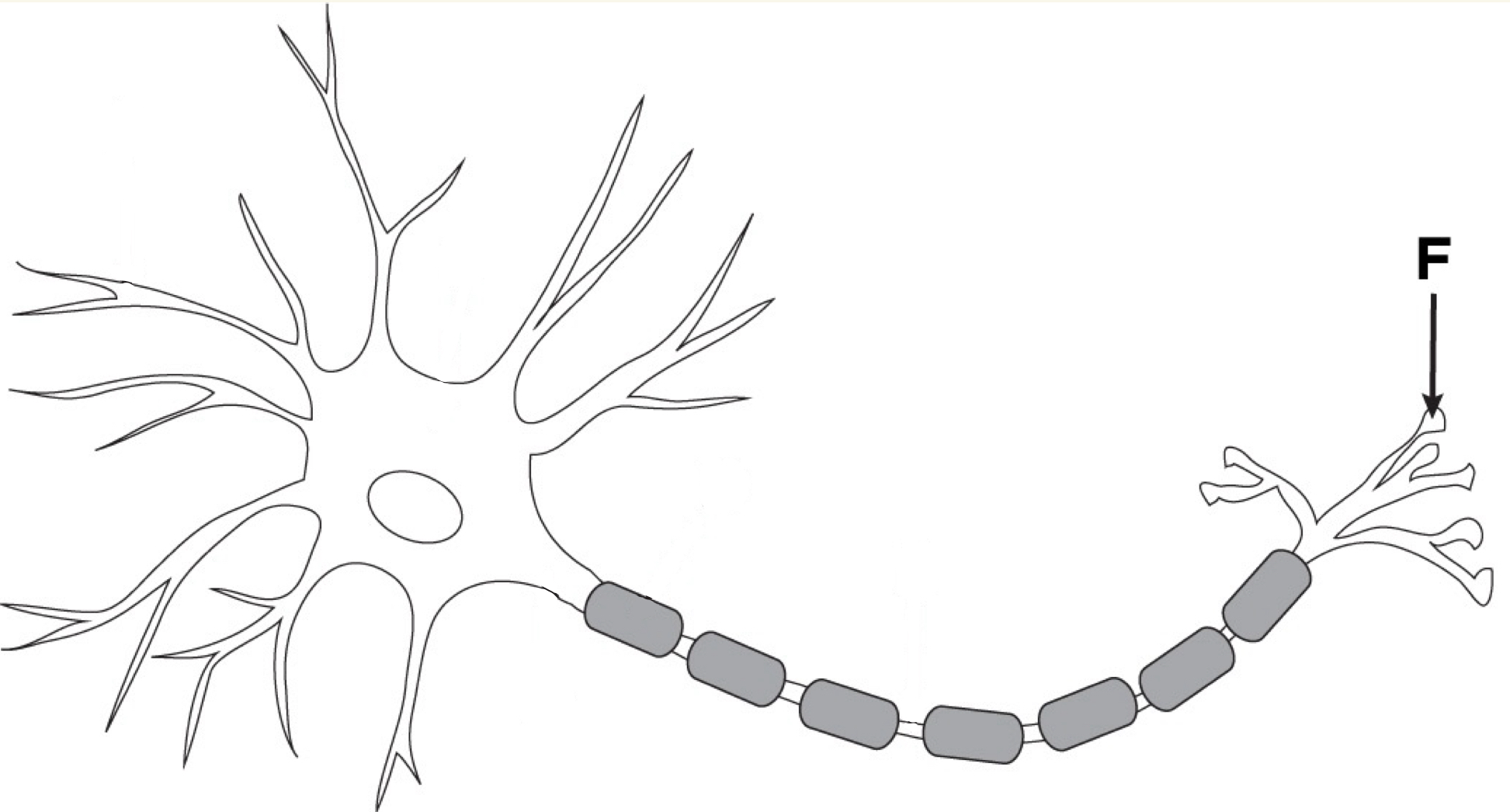
Axon
Portion of the neuron that sends signals
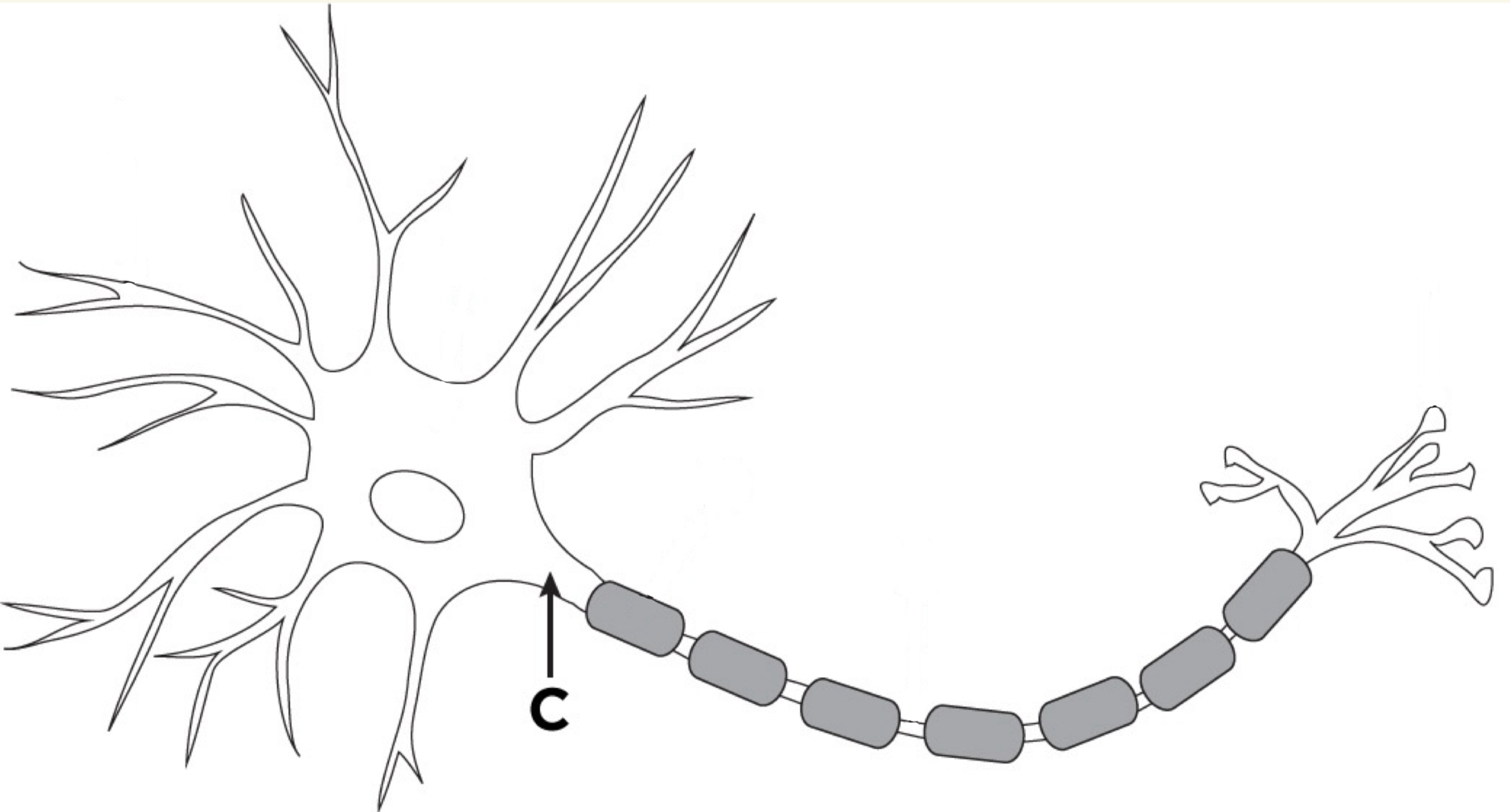
Axon Hillock
Part of the neuron where the cell body connects to the axon; it integrates incoming signals and is the point where an action potential is generated if the signal is strong enough.
Axon Terminal/Terminal Button
Where the electrical message is changed to a chemical signal using neurotransmitters to communicate with another neuron or target cell. It sends them signals by releasing neurotransmitters into the synapse.
Acts as the “messenger” delivering the signal across the synapse.
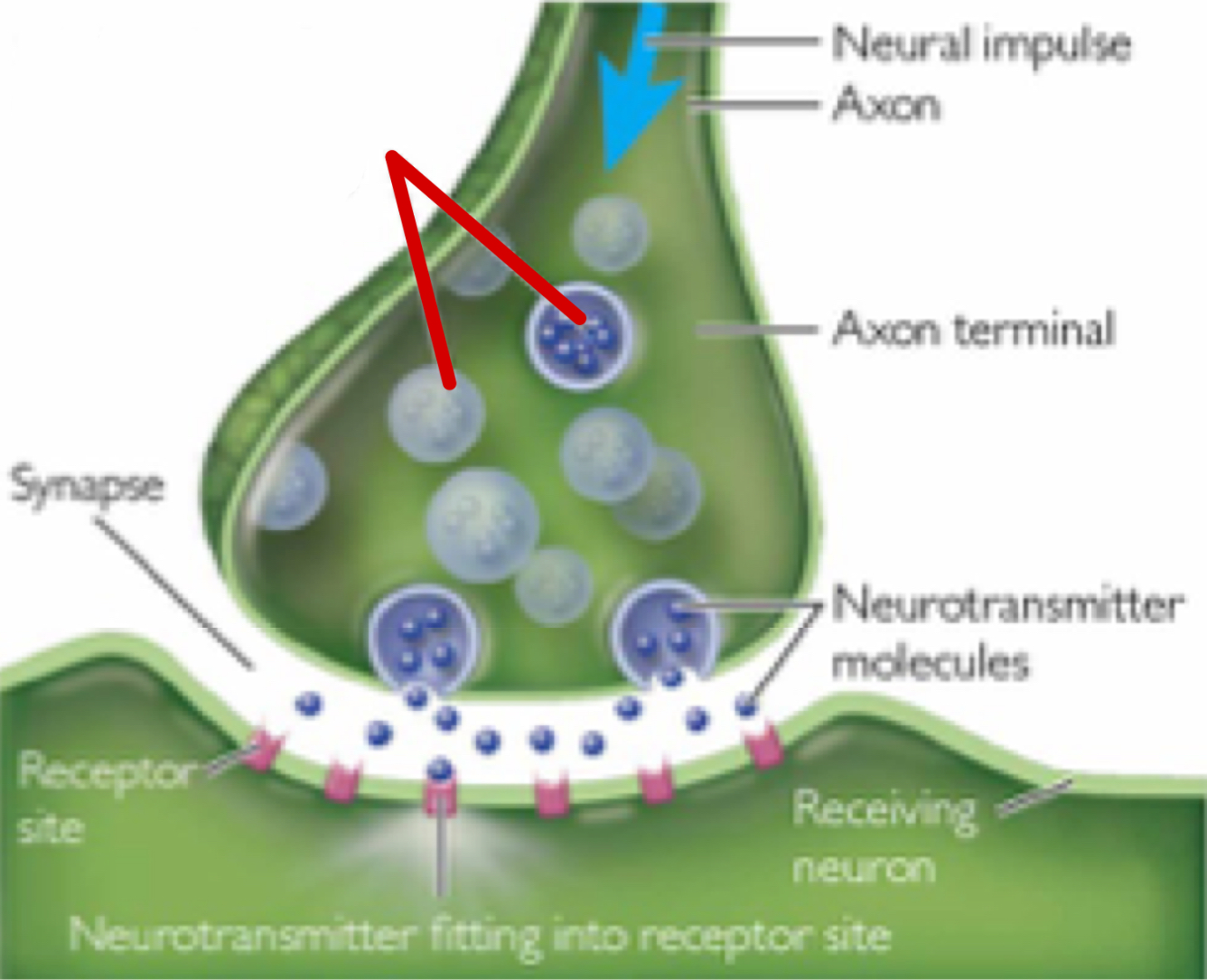
Synaptic Vesicle
Spherical sac containing neurotransmitters that travel the full length of the axon to the axon terminal, where it bursts, releasing the neurotransmitters
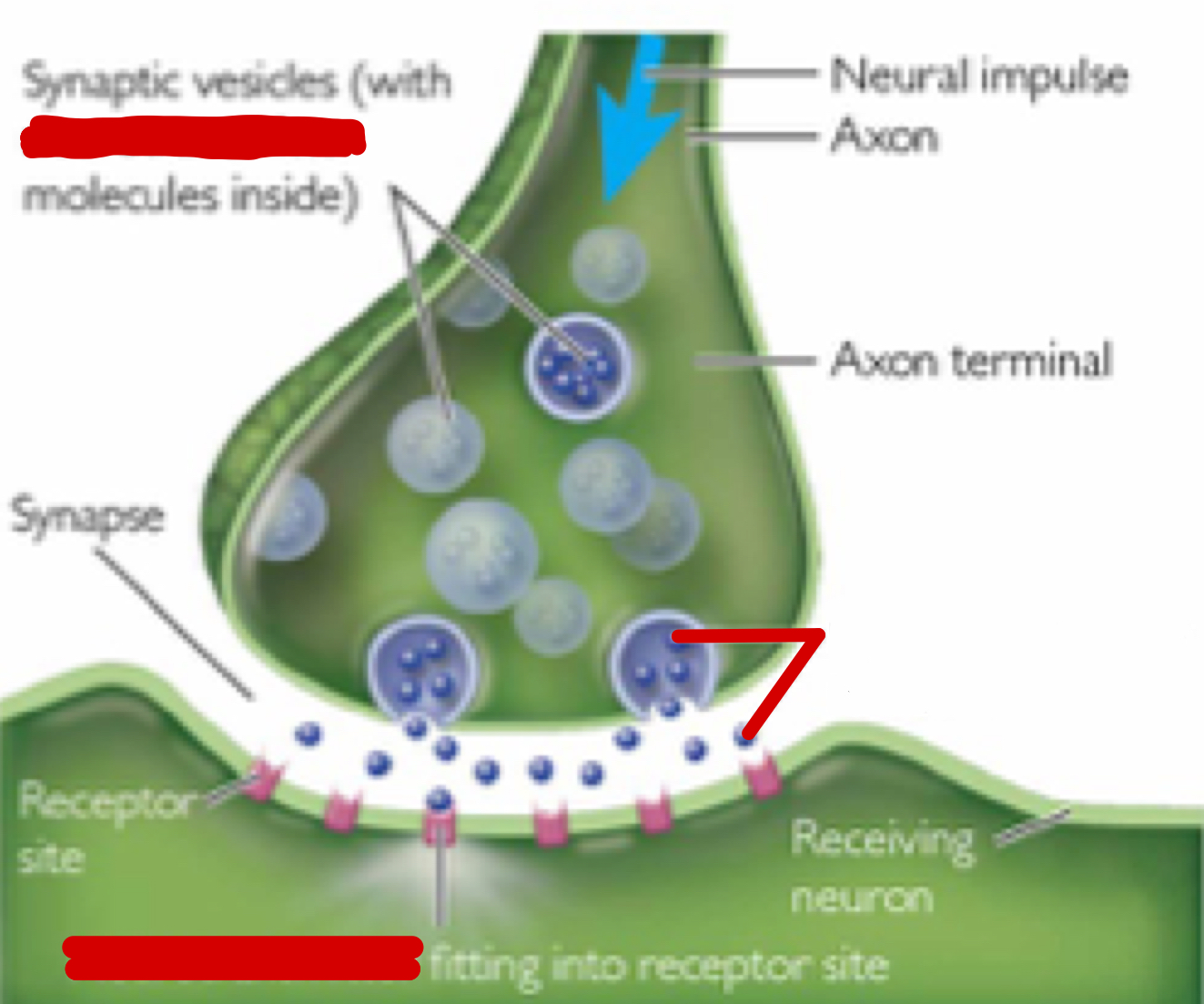
Neurotransmitter
Chemical messengers that allow neurons to communicate
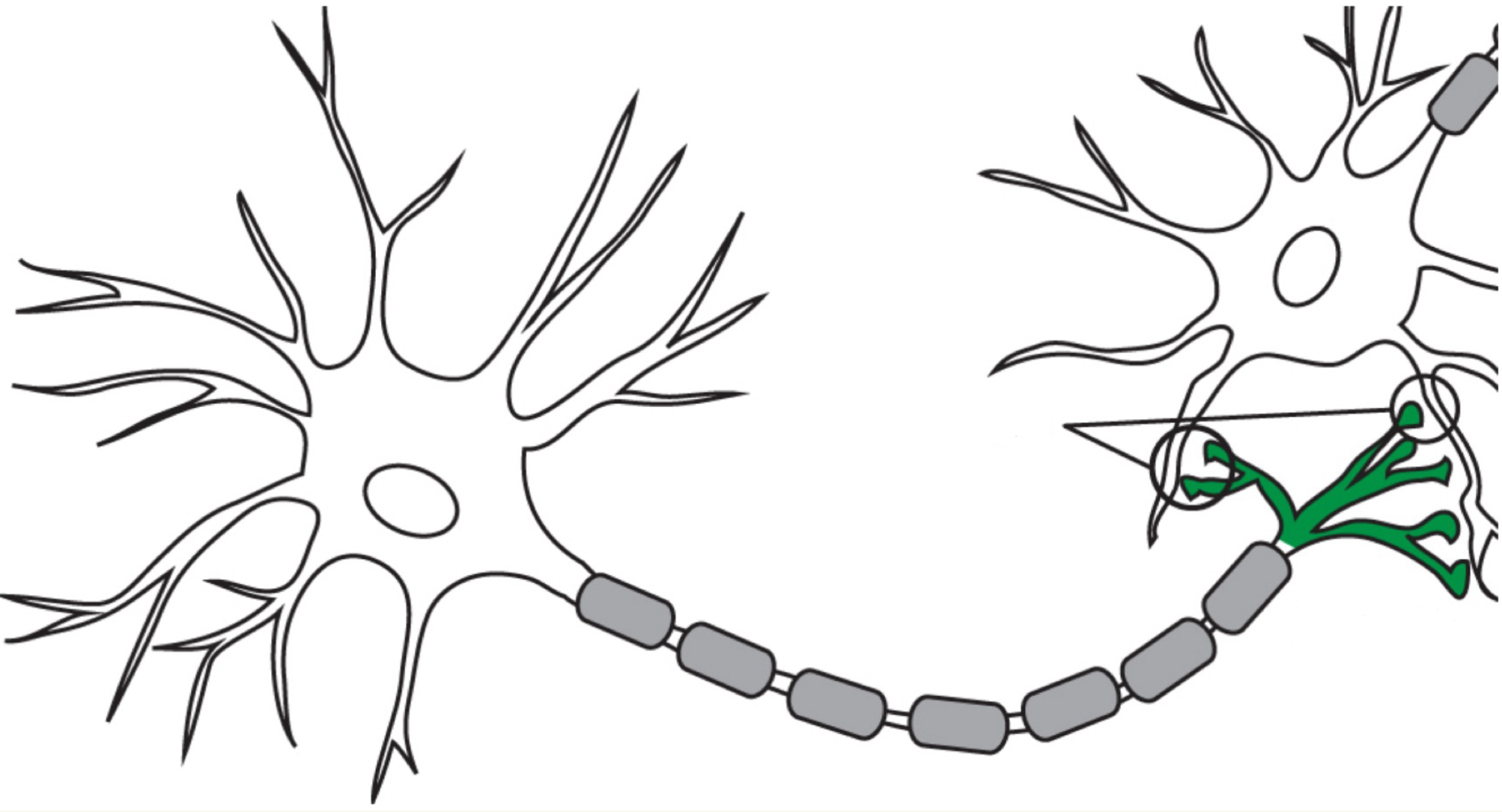
Synapse
Space between two connecting neurons (terminal buttons of one dendritic spines of another) through which messages are transmitted chemically
Neurons communicate across it using neurotransmitters, which are released by the action potential reaching the terminal button
Synaptic Cleft
A gap into which neurotransmitters are released from the axon terminal
Glial Cell
Cell in the central nervous system that plays a role in:
the formation of myelin for neurons (oligodendrocytes) and
the blood-brain barrier (astrocytes),
clean away debris after injury (microglial cells)
Maybe enhances learning and memory?
Ratio to Neurons: 1:1
Myelin Sheath
Glial cells wrapped around axons that act as insulators of the neuron’s signal so they don’t become scrambled
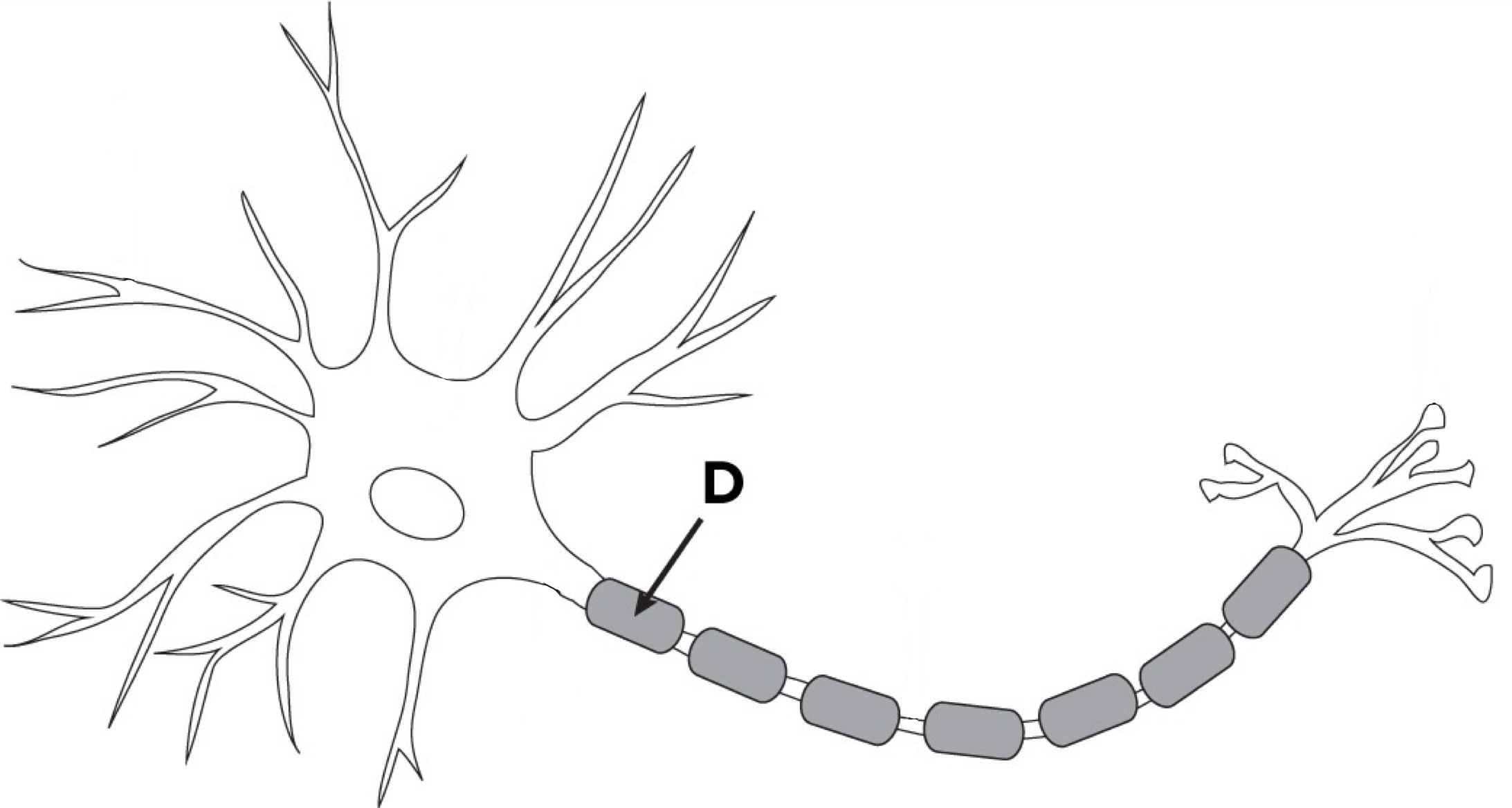
Nodes of Ranvier
Small gaps between segments of the myelin sheath on a neuron’s axon that help speed up the transmission of nerve impulses by allowing the electrical impulses to leap and go faster (preventing info loss)
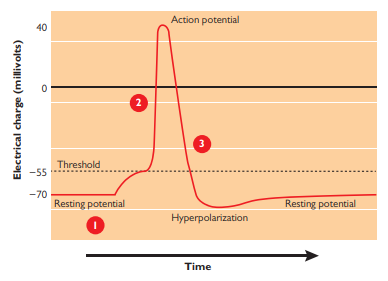
Resting Potential
Electrical charge difference (-60 millivolts) across the neuronal membrane when the neuron is not being stimulated or inhibited
When there are no neurotransmitters acting on the neuron
Baseline state: neuron isnt doing much of anything, there are more negative particles inside than outside
While at rest, particles of both types are flowing in and out of the membrane.
Threshold
Membrane potential necessary to trigger an action potential
When the electrical charge inside the neuron reaches a high enough level relative to the outside, called the _______, an electrical impulse called an action potential is triggered
Action potential
How neurons communicate, abrupt waves of electrical discharge triggered by a massive change in charge inside the axon. When this occurs, the neuron fires.
Positively charged particles flow rapidly into the axon then flow out just as rapidly, causing a dramatic and sudden spoke in positive charge followed by a dramatic and sudden decrease in charge, with the inside charge ending up at a slightly more more negative than its original resting value. These radical shifts produce a release of electricity. Which then reaches the axon terminal.
Electrical impulse that travels down the axon triggering the release of neurotransmitters
Does not vary in strength, but does vary in frequency
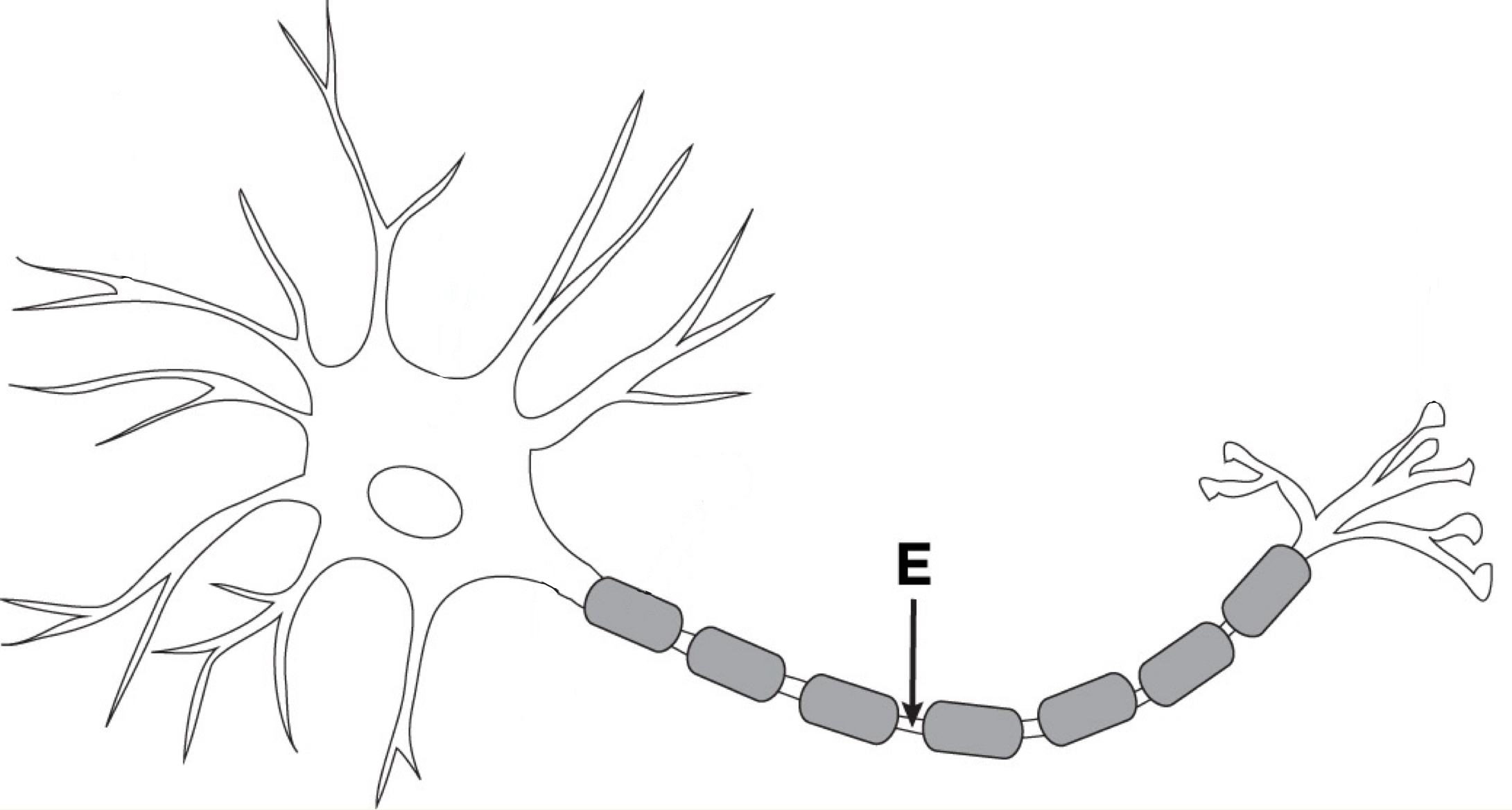
Absolute refractory period
Time during which another action potential is impossible; limits the maximal firing rate
Receptor site
Location along dendrites that uniquely recognizes a neurotransmitter
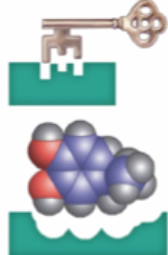
Reuptake
Means recycling of neurotransmitters. They are released from receptors and go back into the axon terminal, a continually occurring process by which the synaptic vesicle reabsorbs the neurotransmitter.
Ex. Like letting some liquid drip out of the bottom of a straw and then sucking it back up again.
Plasticity
The ability of the nervous system to change, an axon can break connection and connect to another set of dendrites
Neurogenesis
Creation of new neurons in the adult brain
Stem cell
A cell, often originating in embryos, having the capacity to differentiate into a more specialized cell
Central Nervous System
Part of nervous system containing the brain and spinal cord that controls the mind and behaviour
Command center; integrates information (deals with a lot of sensory info)
Peripheral Nervous System
Nerves in the body that extend outside the CNS
Cerebral cortex
Outmost part of the forebrain, responsible for analyzing sensory processing and higher brain functions
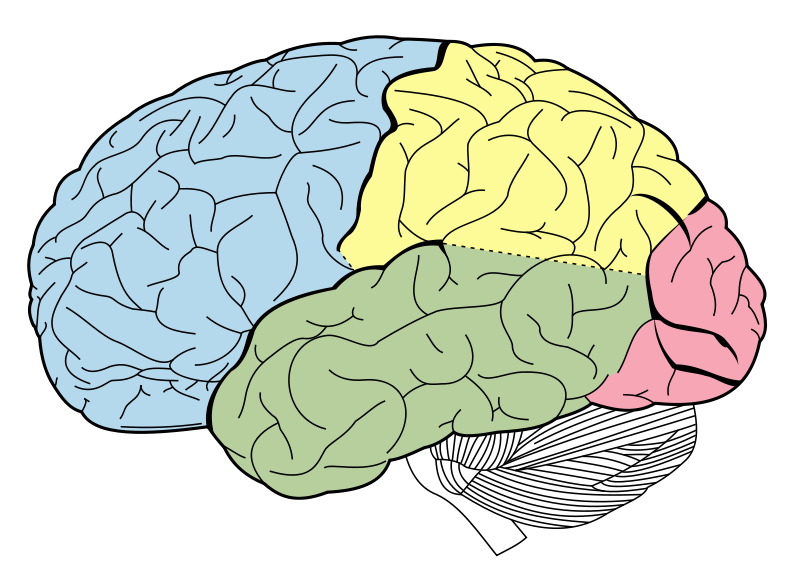
The Cerebrum/Forebrain
Forward part of the brain that allows advanced intellectual abilities
Most highly developed area of the human brain
Consists of 2 hemispheres, which communicate and cooperate
Includes most of the limbic system, basal ganglia, olfactory bulb, and cerebral cortex
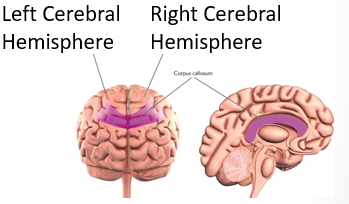
Cerebral Hemispheres
Two halves of the cerebral cortex, each of which serve distinct yet highly integrated functions
Corpus Callosum
Large band of fibers connecting the two cerebral left and right hemispheres
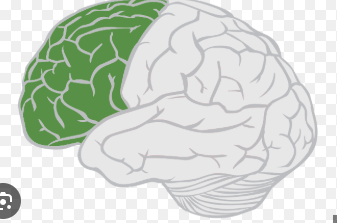
Frontal lobes
Forward part of cerebral cortex responsible for motor function (movement), language, memory, and planning
Oversee and organizes most other brain functions (a process called executive functioning)
Motor Cortex
Part of frontal lobe responsible for body movement
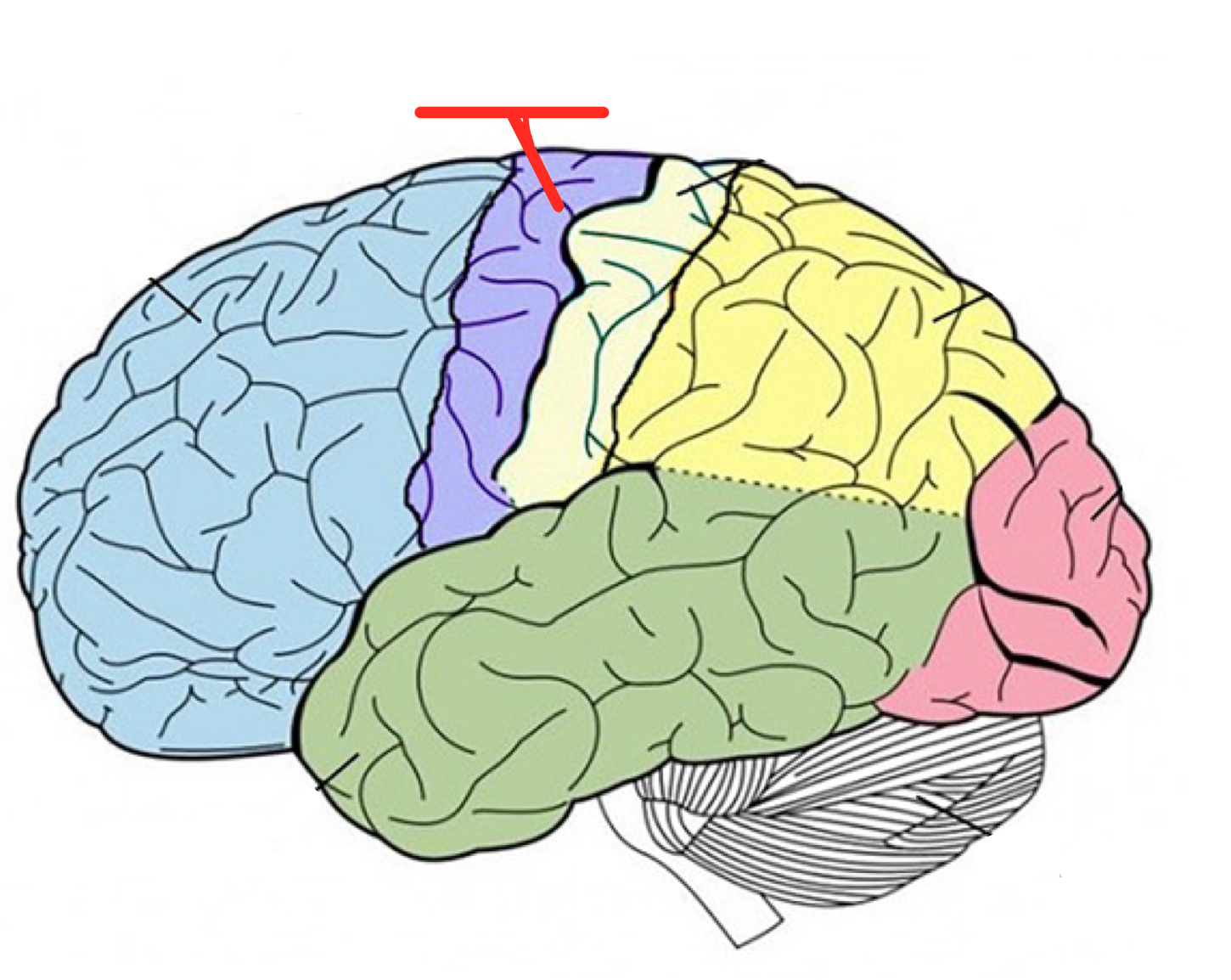
Prefrontal Cortex
Part of frontal lobe responsible for thinking, planning, personality, mood, self-awareness, decision making, executive functions, and language
In front of the motor cortex
Damage to this region often boosts people’s risk for impulsive or even criminal behaviours
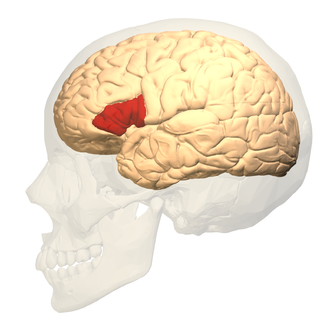
Broca’s area
Language area in the prefrontal cortex that helps to control speech/language production
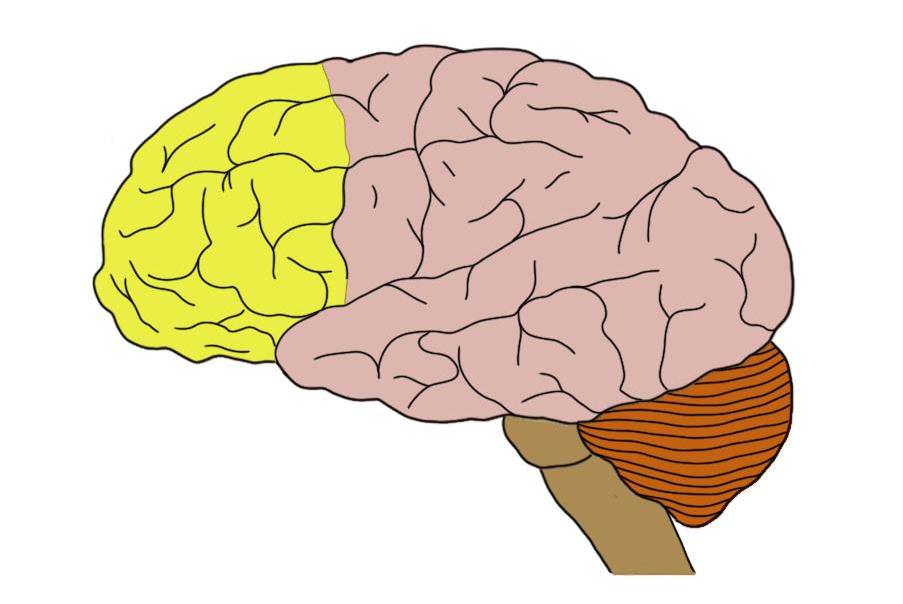
Parietal Lobe
Upper middle part of the cerebral cortex lying behind the frontal lobe that’s specialized for touch and perception
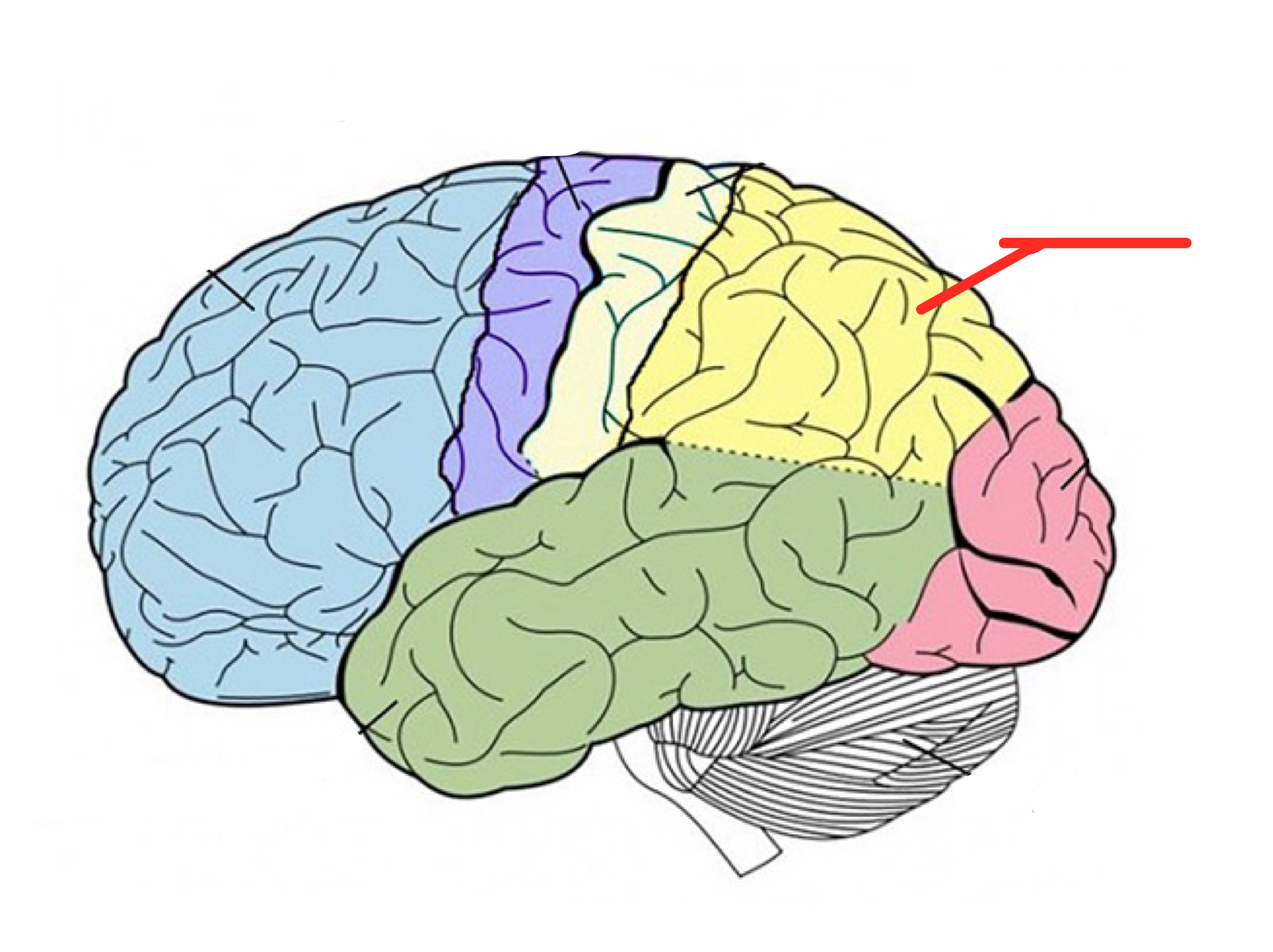
Temporal lobe
Lower part of cerebral cortex that plays roles in hearing, understanding language, and memory
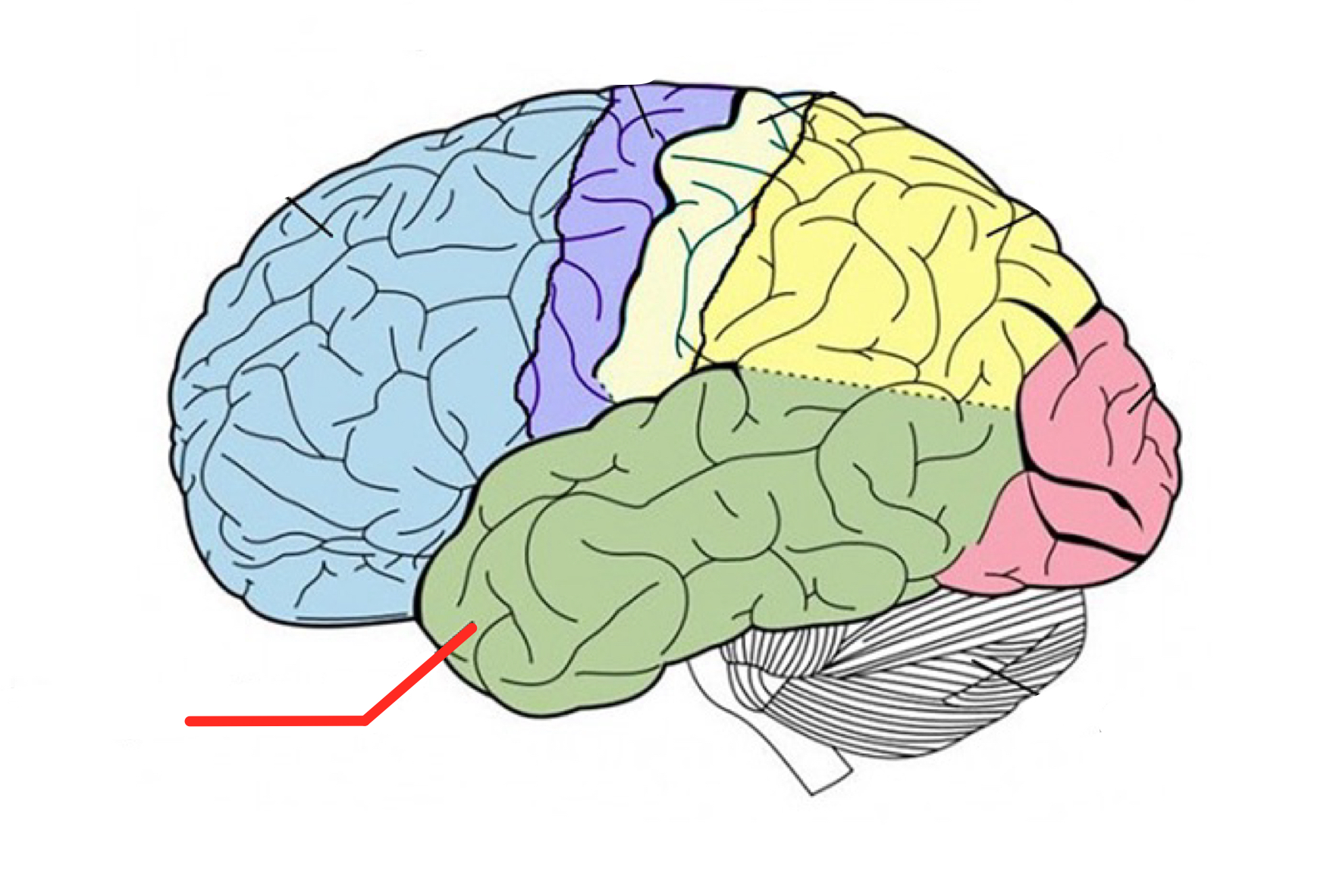
Wernicke’s area
Part of the temporal love involved in understanding speech and language
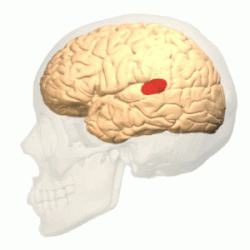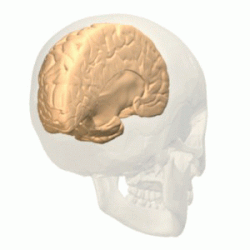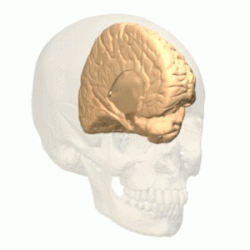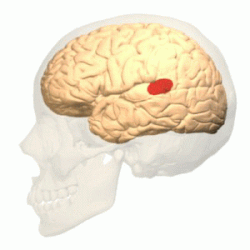
Occipital lobe
Back part of cerebral cortex specialized for vision
Primary sensory cortex
Regions of the cerebral cortex that integrate simpler functions to perform more complex functions
Basal Ganglia
Structures in the forebrain that help to control movement and motor planning
Damage results in Parkinson’s: lack of control over movement and uncontrollable tremors. Tourette’s
Complex structures, much unknown
Activates before voluntary movement: action selection, motor preparation, timing, task switching
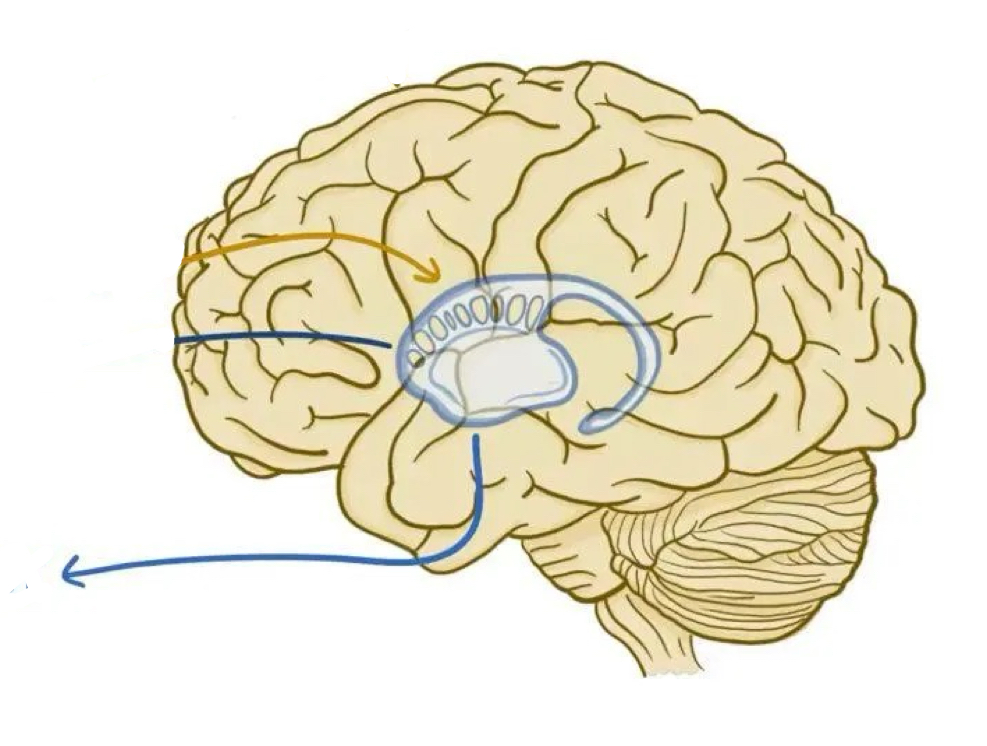
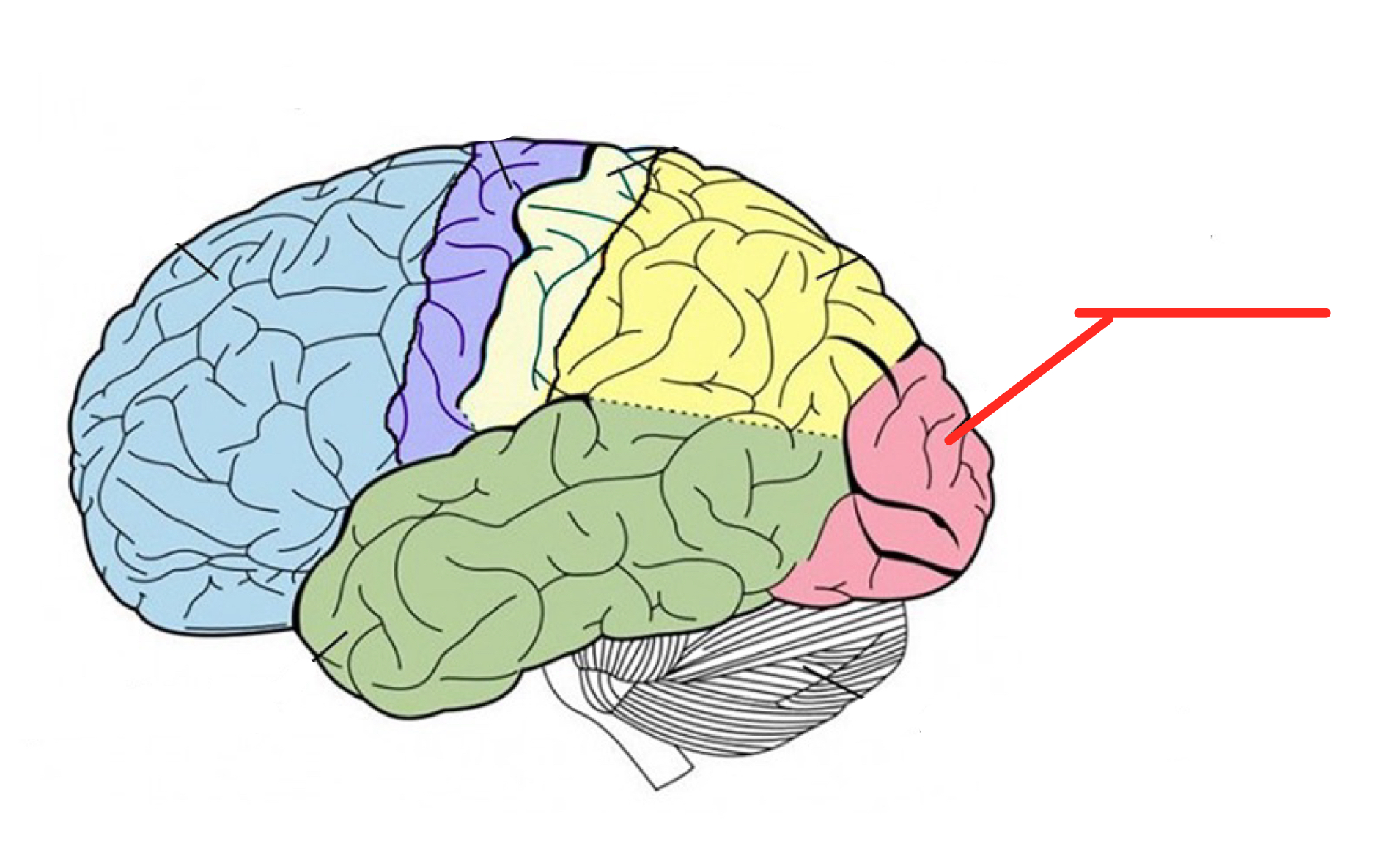
Limbic system
Emotional center of brain that also plays roles in smell, motivation, and memory
Processes information about our internal states such as BP, Heart, Respiration, perspiration
Thalamus
Gateway from the sense organs to the primary sensory cortex, conveys sensory information to cortex
Contains many areas, each of which connects to a specific region of the cerebral cortex
The “sensory relay station,” it passes through it, goes through initial processing, before traveling to the cortex.
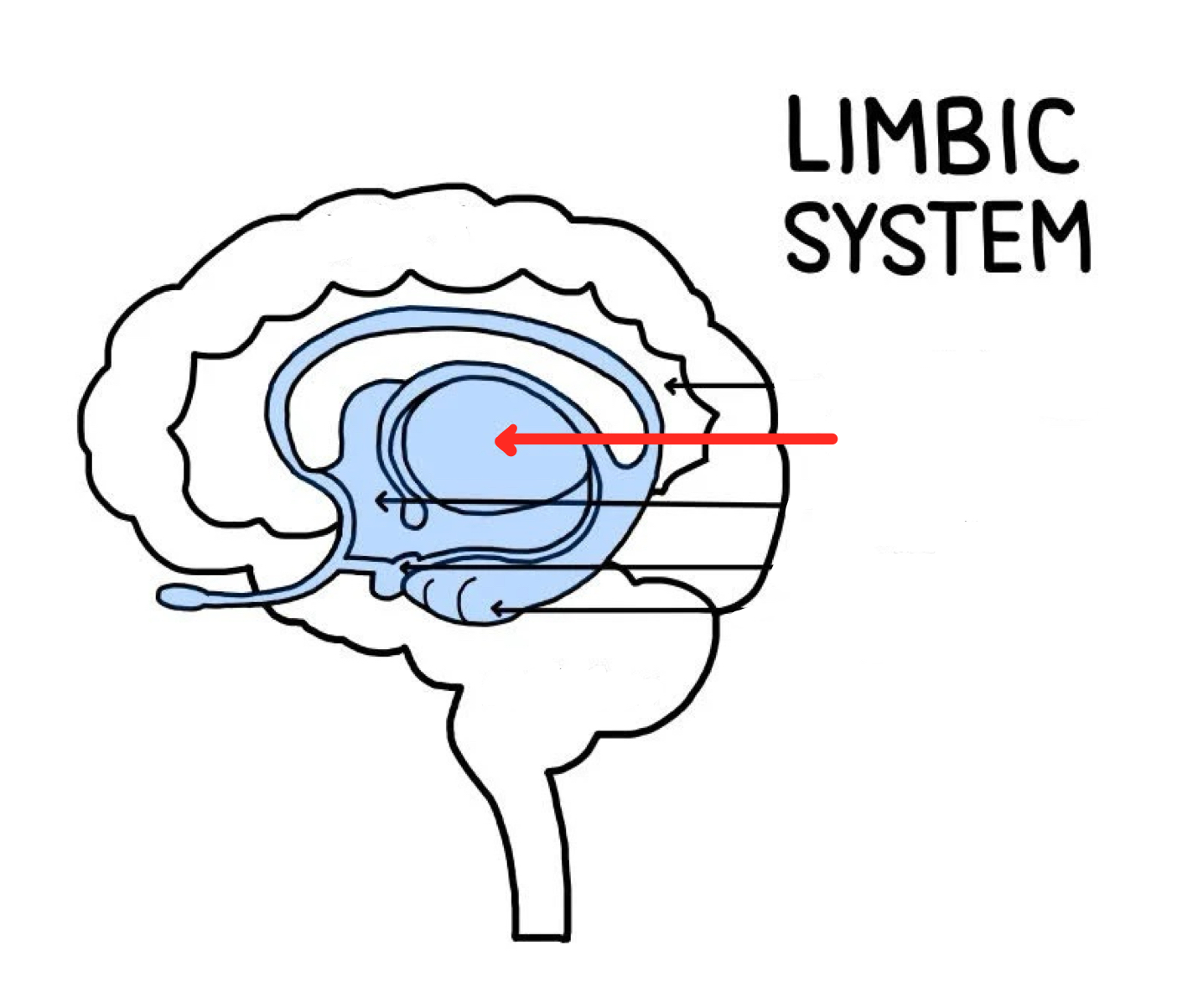
Hypothalamus
Part of the brain responsible for maintaining a constant internal bodily state
Oversees endocrine and autonomic nervous system
Key psychological drivers, regulating hunger, thirst, sexual motivation, temperature, other emotional behaviors
“The Four F’s: feeding, fighting, fleeing, sexual activity
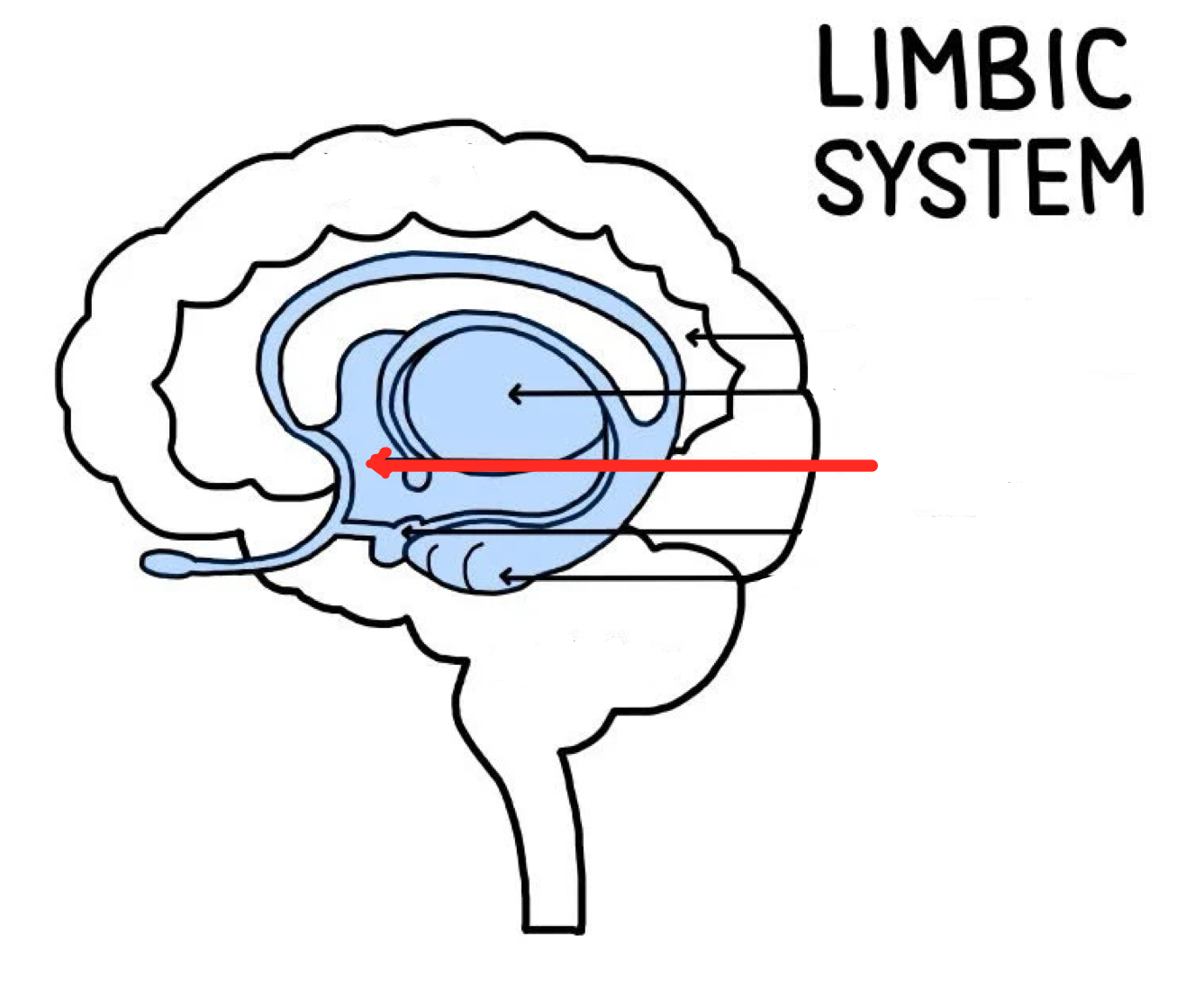
Amygdala
Part of limbic system that plays key roles in fear, excitement, and arousal
Also plays role in fear conditioning, predicting when something scary is about to happen
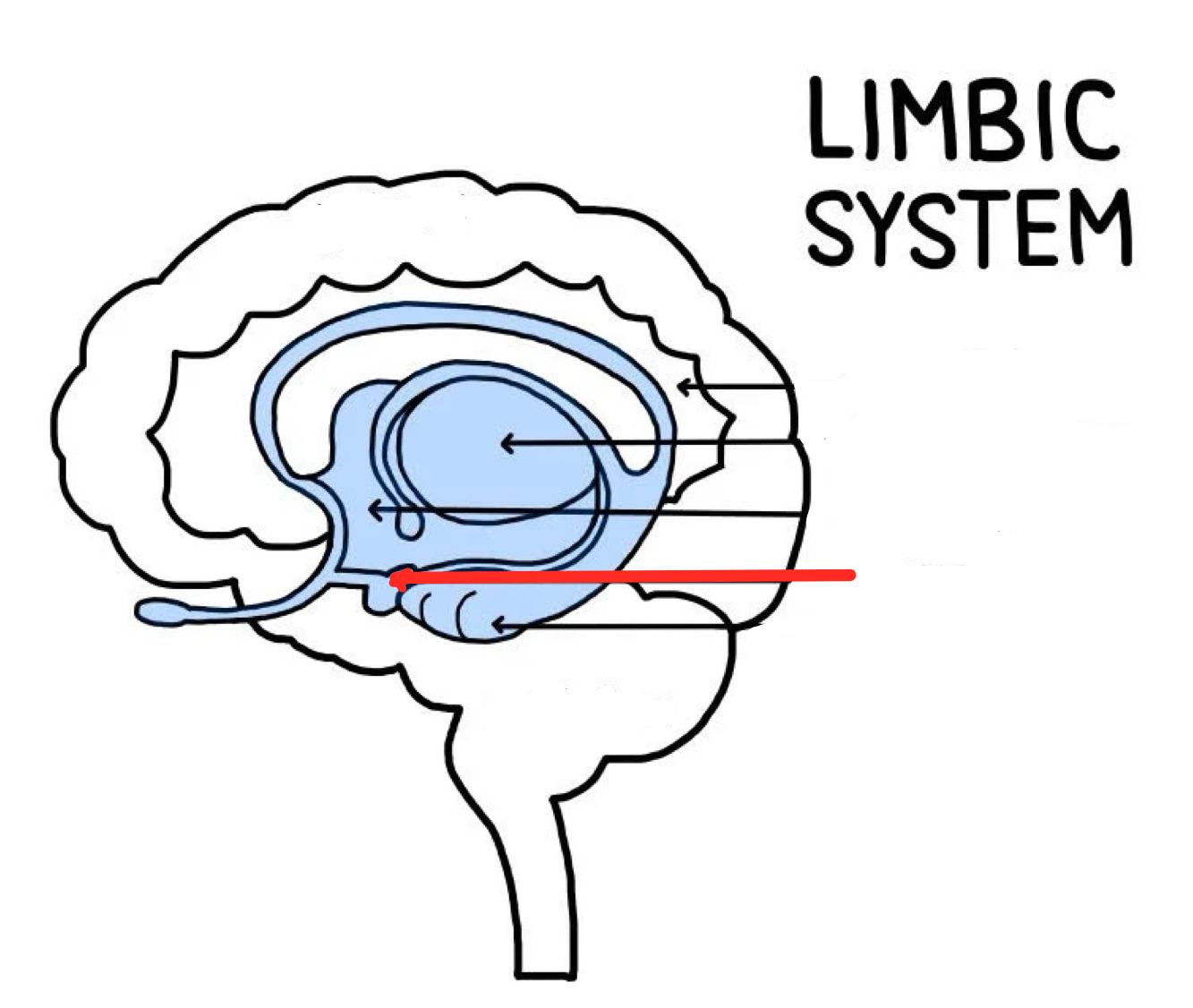
Hippocampus
Part of the brain that plays a role in memory, especially spatial memory— the memory of the physical layout of things in our environment
When we make a mental map of how to get from one place to another
Damage leads to problems forming new memories, but leaves old ones in tact
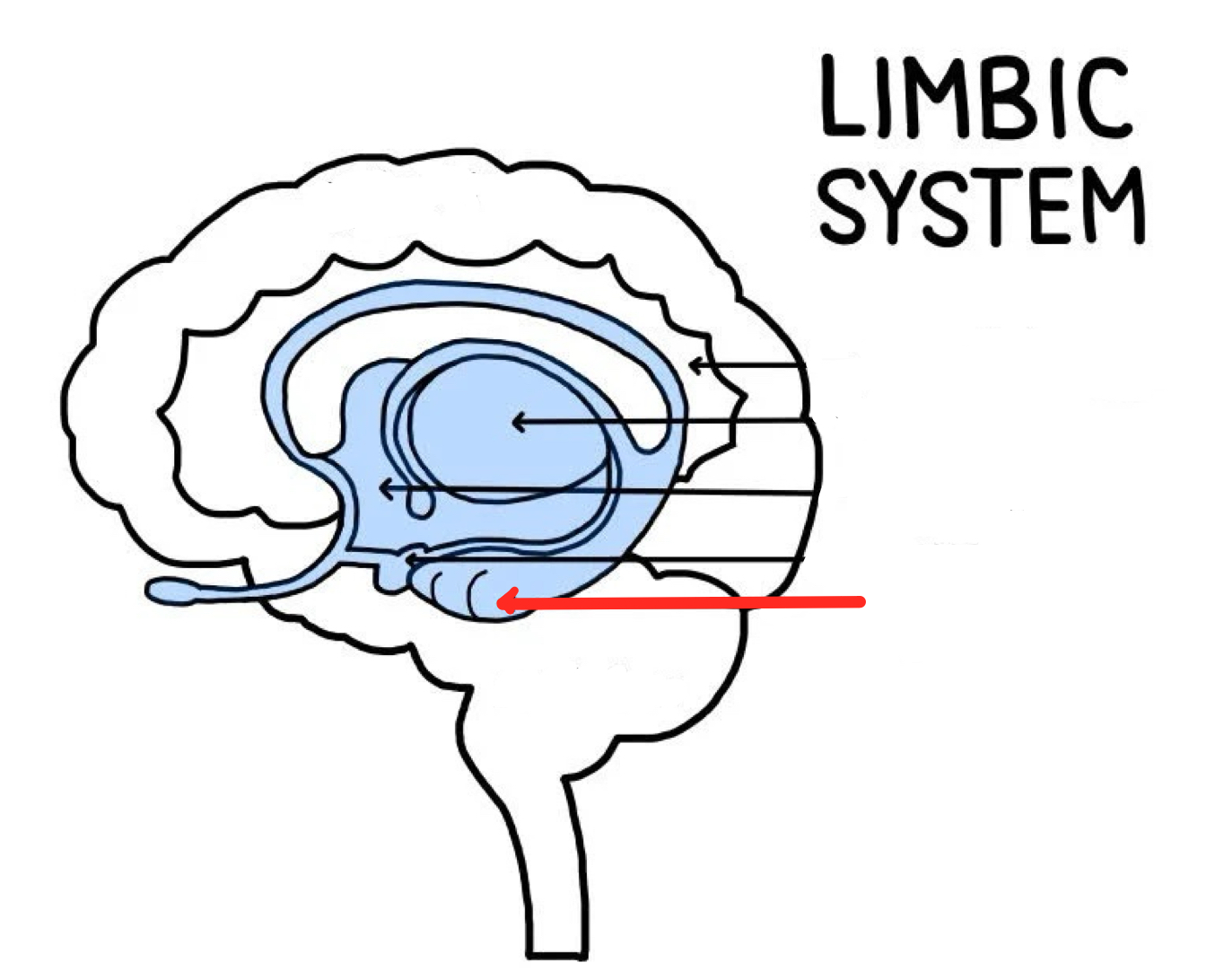
Cerebellum
Brain structure responsible for our sense of balance
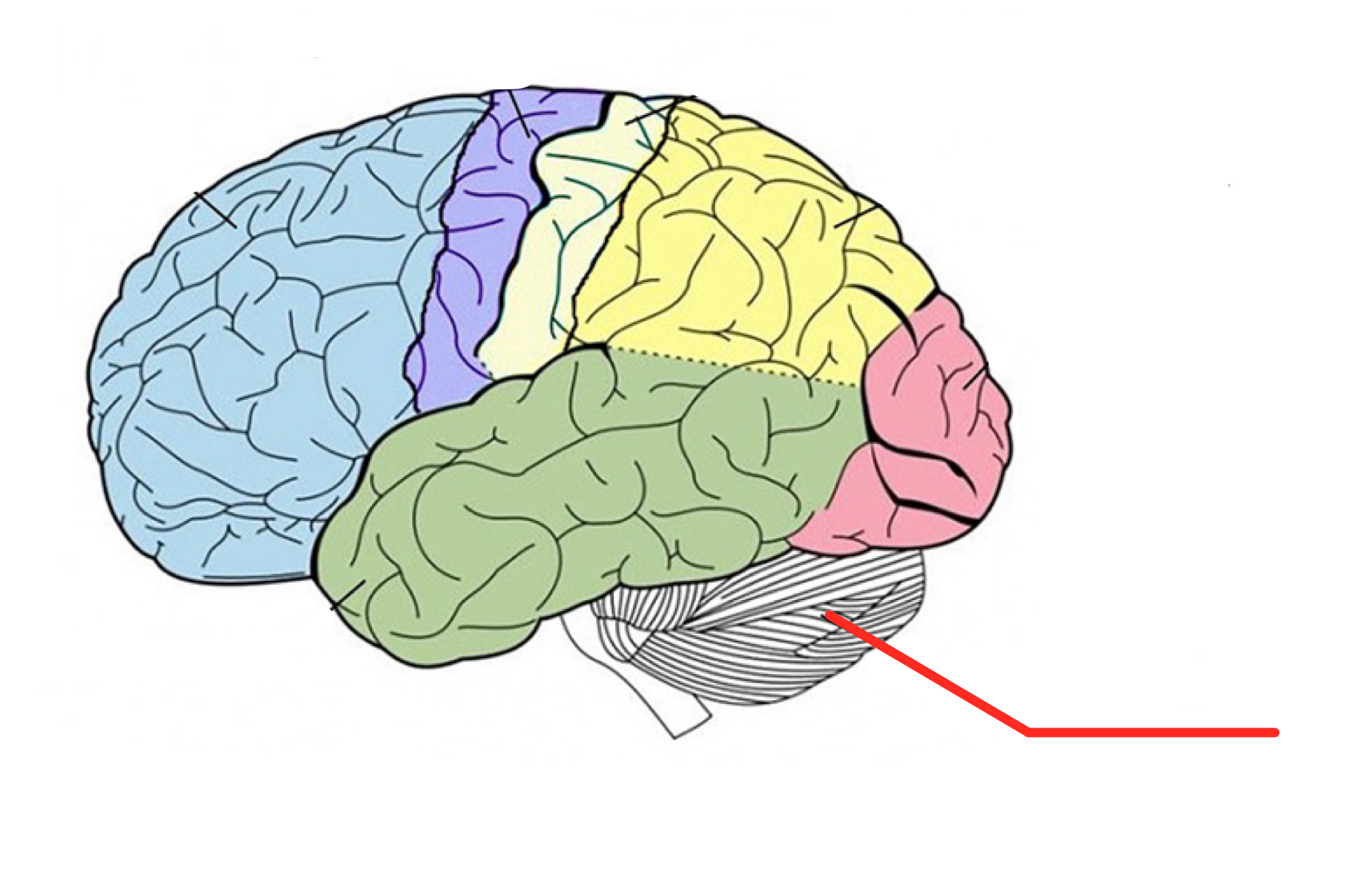
Brain stem
Part of the brain between the spinal cord and cerebral cortex that contains the:
midbrain: tracks visual stimuli and reflexes triggered by sounds, contributes to movement
pons: conveys sensory information between the cortex and cerebellum
and medulla: regulates breathing and heartbeats
Midbrain
Part of the brain stem that contributes to movement, tracking of visual stimuli, and reflexes triggered by sound
Spinal Cord
Thick bundle of nerves that conveys information between the brain and the rest of the body
Interneuron
Neuron that sends messages to other neurons nearby
Reflex
An automatic motor response to a sensory stimulus
The Somatic Nervous System
Part of the nervous system that conveys information between the central nervous system and the body, controlling and coordinating voluntary movement
Walking, reaching, grasping
The Autonomic Nervous System
Part of the nervous system controlling the involuntary actions of our internal organs and glands, which (along with the limbic system) participates in emotion regulation
Sympathetic Nervous System
Division of the autonomic nervous system engaged during a emotional arousal and crisis or after actions requiring fight or flight
Neurons fire together (“in sympathy’)
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Division of the autonomic nervous system that controls rest, slows heart rate, and digestion
Works in opposition to sympathetic to maintain homeostasis
electroencephalograph (EEG)
recording of brain’s electrical activity at the surface of the skull
Computerized Tomography
a scanning technique using multiple X-rays to construct three-dimensional images
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
technique that uses magnetic fields to indirectly visualize brain structure
Measures distribution of hydrogen atoms, which are released because of the magnetic field
Positron Emission Tomography
imaging technique that measures consumption of glucose-like molecules, yielding a picture of neural actiXity in different reIions of tJe brain
Isotope that attaches to glucose
Poor Temporal resolution: relies on blood
Good Spatial resolution
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging
technique that uses magnetic fields to visualize brain activity using changes in blood oxygen level
Good spatial resolution
Good temporal resolution
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
technique that applies strong and quickly changing magnetic fields to the surface of the skull that can either enhance or interrupt brain function
Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
technique that measures brain activity by detecting tiny magnetic fields generated by the brain
high temporal resolution
Glutamate & GABA
Main excitatory neurotransmitter
Function: Increases likelihood that neurons will fire
Role in: Learning and memory
Main inhibitory neurotransmitter
Function: Dampens neural activity
Role in: Learning, memory, sleep
Acetylcholine
Functions: Arousal, selective attention, memory, sleep
Monoamines (contain 1 amino acid)
Dopamine
Pleasure, reward, goal-seeking
Activated by: Food, sex, humour, gambling
Norepinephrine, Serotonin
Regulate arousal and response to stimuli
Anandamide
Binds to same receptors as THC v
Eating, motivation, memory, sleep
Neuropeptides
Short chains of amino acids; act like neurotransmitters but are more specialized
Endorphins: Chemical in the brain that plays a specialized role in pain reduction
Other neuropeptides: Regulate hunger, satiety, learning, and memory.