topic 6 flash cards
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
what are the branches of the nervous system
CNS - brain and spinal cord
PNS - somatic
PNS - autonomic - sympathetic - parasympathetic
define reflex
where the body responds to a stimulus without making a conscious decision
define stimulus
something that can detected by an organism
define receptor
an organ or specialised cell that can detect the change causing the stimulus
define taxis
a response that involves movement in a specific direction
what is a positive and negative taxis
positive - where the organism moves towards the stimulus
negative - where an organism moves away from a stimulus
what is an example of taxis
gravitaxis - gravity
define kinesis
a response that involves movement but in random direction, the speed and frequency of direction change increase
what is an example of kinesis
a woodlouse in a dry area speeds up and changes direction more frequently to find a damper area
define tropism
a growth response controlled by a direction stimulus
explain photo tropism in the shoots
IAA moves to the shaded side of the shoot causing the shoot to elongate and bend towards the light as the plants shoots are POSITIVLY PHOTOTROPIC
explain photo tropism in the roots
IAA moves to the shaded side growth is inhibited and the root beds away from the light as roots are NEGATIVLY PHOTOTROPIC
explain gravitropism in the shoot
IAA moves to the low side of the shoots causing the cell to elongate and grow upwards as they are NEGATIVLY GRAVITROPIC
explain gravitropism in the roots
IAA increases in the lower side causing growth to be inhibited and the root to grows downwards
what are Pacinian corpuscles
mechanoreceptors which detect pressure in the skin
what is the first step in the Pacinian corpuscle creating a generator potential
there are stretch-mediated sodium ion channels in the membrane
what is the second step in the Pacinian corpuscle creating a generator potential
lamellae deforms
what is the third step in the Pacinian corpuscle creating a generator potential
sodium ion channels open
what is the fourth step in the Pacinian corpuscle creating a generator potential
sodium ions diffuse in
what is the fifth step in the Pacinian corpuscle creating a generator potential
sodium ions cause depolarisation which creates a generator potential
what does myogenic mean
the ability to initiate its own contraction
describe the process of control of regular heart beat
the SA node initiates a rhythm by releasing a electrical impulse through the atrial walls causing both atria to contract at the same time
the AV node relays the electrical impulse after a short delay to make sure all the blood has left the atria
the impulse is then conducted down the bundle of HIS to the Purkinjee fibres in the ventricle walls
this causes the ventricles to contract from the bottom up
how should you answer a question on receptors to increase heart rate
give same answer as pe - give an example - chemo or baroreceptors
explain how the sodium potassium pump maintains resting potential
the sodium potassium pump using ATP to transport 3 sodium ions out of the cell and 2 potassium ions into the cell
this leads to the inside of the cell being more negatively charged
the outside is more positively charged as some potassium ions are released through the potassium ion channels
what is the first step in forming an action potential
depolarisation - a stimulus causes sodium ion channels to open causing sodium ions to move into the cell down the concentration gradient making the inside of the neurone more positive
what is the second step in forming an action potential
if the potential reaches the threshold more sodium ion channels open and more sodium ions diffuses into the neurone
what is the third step in forming an action potential
repolarisation - sodium ion channels close and potassium ion channels open causing potassium ions to diffuse out of the neurone
what is the fourth step in forming an action potential
hyperpolarisation - potassium ion channels are slow to close causing too many potassium ions to diffuse out leading to the neurone becoming more negative than resting potential
what is the fifth step in forming an action potential
resting potential - sodium potassium pump returns the neurone to resting potential
what is a refractory period and when does it occur
ion channels are recovering and cant be opened
occurs between hyperpolarisation and resting potential
describe the all or nothing law
An action potential is only generated when threshold is reached and will fire with same voltage no matter the size of the stimulus
describe how myelination occurs
saltatory conduction can occur where the neurones cytoplasm conducts enough electrical charge to depolarise the next next so the impulse jumps from node to node
how does an impulse travel along a non myelinated axon
depolarisation occurs along the whole axon making it slower than saltatory conduction
how does axon diameter effect the speed of an action potential
the bigger the diameter the less resistance so depolarisation occurs quicker in each part of the neurone
how does temperature affect the speed of an action potential
if temperature is increased the ions diffuse more rapidly until around 40 degrees where proteins begin to denature and decreases speed
what is the 1st step in synaptic transmission of ach across of cholinergic synapse and what does it cause
an action potential arrives at the synaptic knob and depolarises the pre synaptic membrane.
this causes voltage gated calcium ion channels to open causing calcium ions to diffuse into the synaptic knob
what is the 2nd step in synaptic transmission of ach across of cholinergic synapse and what does it cause
the influx of calcium ions cause the vesicles to fuse with the presynaptic membrane
this causes the vesicles to release acetylcholine into the synaptic cleft
what is the 3rd step in synaptic transmission of ach across of cholinergic synapse and what does it cause
acetylcholine diffuses across the synapse and bind to the complimentary receptors on the post synaptic membrane
this causes sodium ion channels to open on the post synaptic membrane causing an influx of sodium ions
what is the 4th step in synaptic transmission of ach across of cholinergic synapse and what does it cause
the influx of sodium ions causes depolarisation of the post synaptic membrane
this causes an action potential to be generated in the post synaptic membrane if the threshold is met
what is the 5th step in synaptic transmission of ach across of cholinergic synapse
the enzyme acetylcholinesterase hydrolyses the remaining acetylcholine into products which are reabsorbed into the pre synaptic membrane
what effect occurs when drugs are the same shape as a neurotransmitter
they mimic neurotransmitter causing more receptors to be activated
what effect occurs when drugs block the receptors
receptors cant be activated or only a few so muscle cells cant be stimulated causing paralysis
what effect occurs a drug inhibits an enzyme that breaks down a neurotransmitter
the causes more neurotransmitter to bind to the receptors
what is the function of tendons
non elastic tissue that connects muscle to bone
what is the function of ligaments
elastic tissue that connects bone to bone
what happens in an antagonistic muscle pair
one muscle relaxes while the other contracts
what is the structure of muscles myofibrils
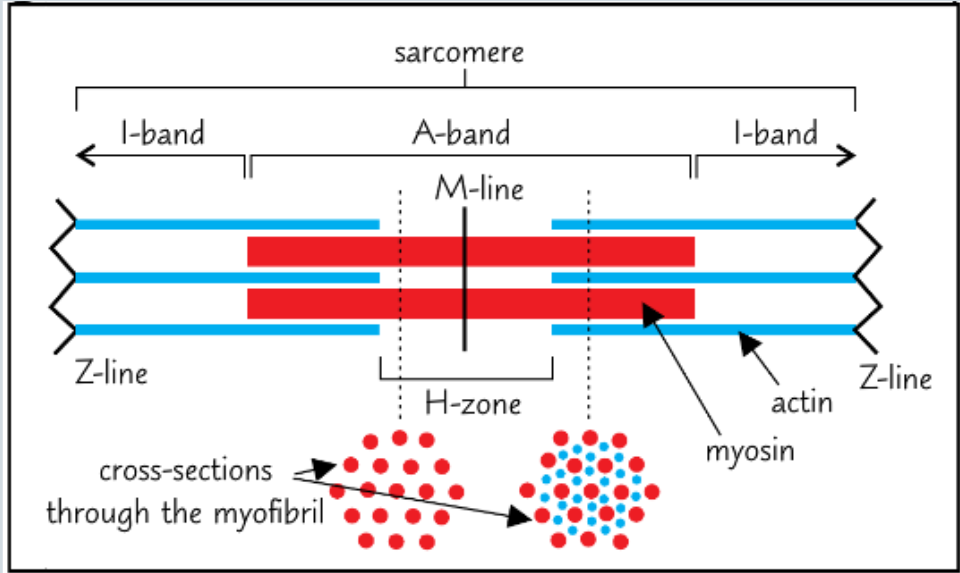
are A band light or dark
dArk
are I band light or dark
lIght
what are the 3 difference between a neuromuscular junction and cholinergic synapse
Post synaptic membrane has clefts which store acetylcholinesterase
Post synaptic membrane has more receptors.
acetylcholine is always excitatory so a motor neurone action potential will result in a response in the muscle
what is the 1st step of muscle contraction
an action potential depolarises the sarcolemma and down the T-tubules
this cause a release of calcium ions
what is the 2nd step of muscle contraction
calcium ions cause tropomyosin to change shape
this exposes the myosin binding site
what is the 3rd step of muscle contraction
the myosin head binds to the actin filament forming a cross bridge