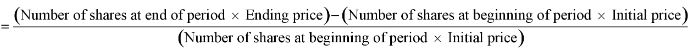Ch. 12 - Mutual Funds and ETFS
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Mutual Fund
A type of financial services organization that receives money from a group of investors and then uses those funds to purchase a portfolio of securities
Investors own a share of the fund proportionate to the amount of the investment
Actively Managed Fund
Manager’s goals is to identify and invest in securities that will achieve superior performance
Passively Managed Fund
Managers make no attempt to select a portfolio that will outperform a benchmark
Designed to mimic the performance of particular benchmark or stock index
Mutual Fund Ownership Benefits
Portfolio diversification
Full time professional management
Ability to invest small amounts
Service
Automatic reinvesting of dividends & capital gains
Exchange privileges
Convenience
Mutual Fund Ownership Drawbacks
Transaction costs
Spotty performance record
Mutual Fund Operations:
Management Company
Run the fund’s daily operations
Mutual Fund Operations:
Investment Advisor
Buys and sells securities and oversees portfolio
Includes participants such as: money manager, securities analysts, traders
Mutual Fund Operations:
Distributor
Sells the fund shares
Directly to public or through dealers
Mutual Fund Operations:
Custodian
Physically safeguards the securities
Mutual Fund Operations:
Transfer Agent
Keeps track of purchase and redemption requests from shareholders
Load Fund
Mutual fund that charges a commission when investors buy shares
No-Load Fund
Fund that levies no sales charges
12(b)-1 Fee (“hidden loads”)
Fee charged by some mutual funds to cover management and other operating costs
Amounts to as much as 1% of the average net assets
Low-Load Funds
Fund that offers discounts for large investments
Back-End Load
Fund that levies commissions when shares are sold
Open-End Funds
Mutual fund that regularly receives cash from investors and use that money to purchase more securities
Investors buy/sell shares directly with mutual fund company without a secondary market
Funds can issue unlimited number of shares
Greater liquidity
Net Asset Value (NAV)
The total market value of securities held in the fund dividend by the fund’s outstanding shares
Closed-End Funds
Operate with a fixed number of shares outstanding
Do not regularly issue new shares
Sell shares in the fund only at the initial offering
Subsequent trades done in a secondary market
Price of fund shares determined by supply & demand
Sell at a premium or discount to NAV
Brokerage commissions apply
Types of Mutual Funds:
Growth Fund
Objective is capital appreciation
Types of Mutual Funds:
Value Funds
Buy stocks with low prices relative to some measure of intrinsic value like earnings or dividends
Types of Mutual Funds:
Equity-Income Funds
Purchase stocks with high dividend yields
Types of Mutual Funds:
Balanced Funds
Tend to hold a balanced portfolio of both stocks and bonds for the purpose of generating a balanced return of both current income and long-term capital gains
Types of Mutual Funds:
Bond Funds
Invest exclusively in various types and grades of bonds, with income as the primary investment objective
Types of Mutual Funds:
International Funds
Funds that invest primarily in foreign securities
Types of Mutual Funds:
Sector Funds
Investments are restricted to a particular sector or industry
Types of Mutual Funds:
Asset Allocation Funds
Funds that spread investors’ money across different types of asset classes: stocks, bonds, and money market securities
Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF)
Type of open-end fund that trades as a listed security on one of the stock exchanges
Created when a portfolio of securities is purchased and placed in a trust, and then shares are issued that represent claims against the trust.
Low management expenses
Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT)
A type of close-end investment company that invests money in mortgages and various types of real estate investments
Investors receive both the capital appreciation ¤t income from real estate ownership without having to deal with property management
3 Types: Property/Equity, Mortgage, Hybrid
Hedge Funds
Pooled investment fund that accepts investors’ money and invests those funds on a collective basis
Not mutual funds
Not regulated by mutual fund regulations
Private limited partnerships
Only sold to “accredited investors”
Measuring Performance:
Dividend Income
Derived from the dividend and interest income earned on the security holdings of the mutual fund
Measuring Performance:
Capital Gains Distributions
Payments derived from the capital gains earned by the fund
Measuring Performance:
Unrealized Capital Gain (paper profits)
Change in the fund’s price (or NAV)
Capital gain that has not been realized since fund’s holding have not been sold.
For closed-end companies:
Changes in the price discounts/premiums are important
Measuring Performance:
Holding Period Return (HPR)
Include distributions of dividends/capital gains, or NAV appreciation