NSC 308 Chapter 15
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Remodeling is vital for bone health because it:
permits calcium and phosphorous to be withdrawn from bone.
allows bones to grow normally.
allows bones to repair and replace damaged areas.
______ are bone-building cells the help form healthy bone.
Osteoblasts
______ are biochemically active cells embedded in bone matrix. They can take up calcium from the bone and release it back into the blood, as well as help bone become more dense.
Osteocytes
______ are cells on the bone surface that dissolve bone by releasing acid and enzymes.
Osteoclasts
The process of bone resorption is dependent on:
osteoclast activity.
vitamin D.
What is bone remodeling?
The process of removing and replacing bone
How do osteoblasts form healthy bone?
They produce collagen and add minerals.
Ostecytes take up calcium from the ______ and release it into the ______.
blood; blood
The activity of osteoclasts is stimulated by ______.
parathyroid hormone
Which of the following is considered to be calcium's major function(s) in the body?
Developing and maintaining bones
Bone ______ is the process in which osteoclasts break down bone and release minerals.
resorption
Which of the following foods are good sources of calcium?
Kale
Broccoli
Cheese
Increased bone health, protection from colorectal cancer, and reduced formation of kidney stones are all benefits associated with the consumption of foods rich in which mineral?
calcium
Which mineral plays a significant role in developing and maintaining bones, blood clotting, the transmission of nerve impulses, muscle contractions, and cell metabolism?
Calcium
The form of vitamin D that is synthesized by skin cells after exposure to UV light is a prohormone or ______.
precursor of an active hormone
Which behaviors have resulted in low blood levels of Vitamin D in the U.S. population?
Low intakes of vitamin D
Use of sunscreen
More time spent indoors
Milk, collards, and almonds are all good sources of which mineral?
Calcium
Aside from bone health, what are some additional benefits associated with dietary calcium consumption?
Decreased blood pressure
Reduced formation of kidney stones
Name the two forms of vitamin D.
Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol).
Vitamin D is unique because in the presence of sunlight, skin cells can synthesize a sufficient supply of vitamin D, which is why it is also correctly classified as a(n):
prohormone.
conditional vitamin.
In the U.S. population, low blood levels of vitamin D that may be linked with a risk of vitamin D deficiency have ______ over several decades.
remained constant
The signs of rickets include:
deformed pelvis.
enlarged head.
bowed legs.
Which form of vitamin D occurs naturally in foods and is used in supplements?
Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol)
______ also contributes to antioxidant defenses. More than one answer may be correct.
Copper
Manganese
Zinc
Unstable compounds with 1 or more unpaired electrons that produce chain reactions stopped by antioxidants are called ______ _______.
free radicals
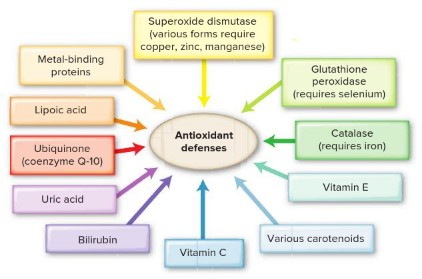
Enzyme systems that function as part of our body's antioxidant defense system include:
superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase.
Members of both the tocopherol and tocotrienol families are labeled according to the ______ alphabet.
Greek
Rickets is the deficiency disease caused by the lack of vitamin ______.
D
Nutrients that are important parts of the body's antioxidant network include Blank______. More than one answer may be correct.
vitamin E
selenium
beta-carotene
vitamin C
Antioxidants help maintain the integrity of cells by ______.
stopping chain reactions caused by free radicals
The fat-soluble antioxidant vitamin responsible for protecting cell membranes by helping to stop damage by free radicals is ______.
vitamin E
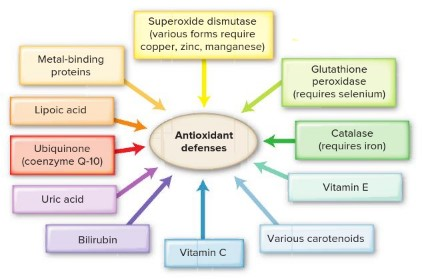
Nutrients and metabolites that provide antioxidant protection to our body include:
uric acid.
bilirubin.
lipoic acid.
The vitamin E content of food depends on which of the following?
Storage
Processing
Harvesting
Which two compound classes form part of the eight naturally occurring compounds that make up the vitamin E family?
Tocopherols and tocotrienols.
A deficiency of vitamin E may result in ______.
hemolytic anemia
Vitamin C performs a variety of cell functions by donating electrons in ______ reactions.
oxidation-reduction
______ also contributes to antioxidant defenses. More than one answer may be correct.
Copper
Zinc
Manganese
Vitamin E protects cell membrane integrity by ______.
neutralizing lipid peroxyl radicals
preventing lipid peroxidation
Which of the following provide the richest sources of vitamin C? More than one answer may be correct.
red peppers
citrus fruits
The vitamin E content of a food may be affected by:
exposure to sunlight.
exposure to oxygen.
deep-fat frying.
Vitamin E deficiencies are ______ in humans.
rare
Although the results of some studies are positive, vitamin C has not been shown to conclusively prevent:
cancer.
heart disease.
As an electron donor, vitamin C:
has antioxidant defense functions.
has a cofactor role for several metalloenzymes.
Selenium acts as an antioxidant as part of what group of enzymes?
glutathione peroxidase
Which of the food groups provide the highest levels of vitamin C to the body?
Fruits and vegetables
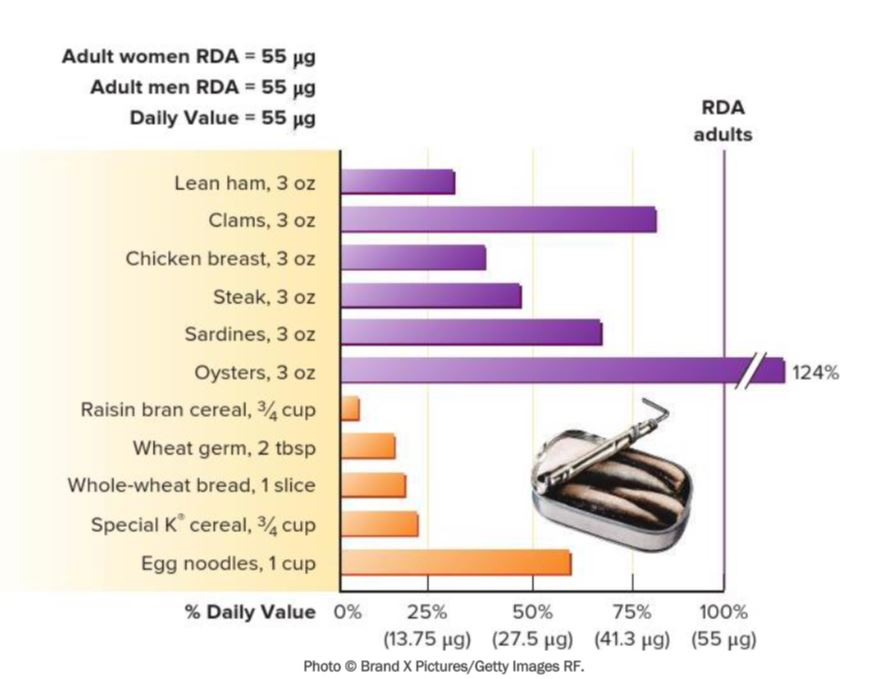
Select the food source that provides the most selenium per serving.
Oysters, 3 oz
Foods that are good sources of vitamin E include:
nuts.
plant oils.
wheat germ.
The American Heart Association has concluded that antioxidant supplements like vitamin C ______ prevent heart disease.
do not
Keshan disease, which is associated with a deficiency of selenium, is characterized by ______ .
insufficient cardiac function
What is a function of selenium?
Antioxidant
The biologically active forms of vitamin A collectively are called ______.
retinoids
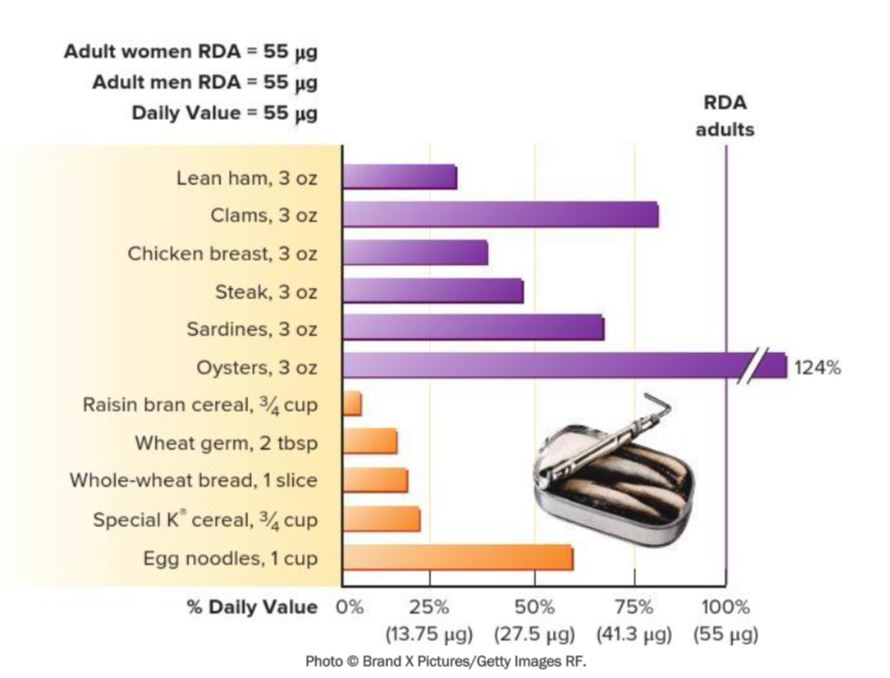
Select the food source that has the least amount of selenium per serving.
Raisin bran cereal
Which carotenoids can be converted to biologically active forms of vitamin A?
Beta-cryptoxanthin
Beta-carotene
Alpha-carotene
A deficiency of selenium is associated with:
changes in thyroid hormone metabolism.
an increased risk of certain cancers.
______ help protect the body through their roles in the immune system and maintenance of the epithelium.
Retinoids
Retinoids exist in which 3 forms?
Retinol
Retinal
Retinoic acid
Vitamin A supports immune function most likely because vitamin A helps maintain the ______.
epithelium
In many regions of the world where vitamin A deficiency is common, vitamin A supplements have been shown to reduce the severity of some infections such as:
measles and diarrhea
Yellow-orange pigmented materials in fruits and vegetables that can be converted into vitamin A are called _____.
carotenoids or provitamins
Retinoids are critical to:
cell differentiation.
growth and development.
vision.
Studies have indicated that ______ deficient individuals have greater susceptibility to illness and infection.
vitamin A
A lack of which vitamin during fetal development is linked to fetal mortality?
A
Vitamin A deficiency maintains the epithelium, whose role is to ______.
form a barrier that protects the body against disease pathogens
Vitamin A is important for the production, structure, and normal function of epithelial cells in which organs? More than one answer may be correct.
lungs
skin
trachea
Vitamin A is important in maintaining normal differentiation in cells related to the structural components of the eyes, including the:
cornea and retina
The vitamin that is needed in the retina of the eye to turn visual light into nerve signals to the brain is vitamin _____.
A
Sources of retinoids, the preformed source of vitamin A, include ______. More than one answer may be correct.
eggs
fortified milk
Vitamin A is involved in the development of:
eyes.
the cardiovascular system.
the nervous system.
limbs.
Which vitamin is necessary for the production, structure, and normal function of epithelial cells?
Vitamin A
Vitamin A affects ______ expression, which directs cell differentiation.
gene or genetic
Sources of provitamin A carotenoids include ______. More than one answer may be correct.
carrots
broccoli
sweet potatoes
Vitamin A (as retinal) is needed for vision in the retina of the eye which is composed of structures called:
rods and cones.
______ is an early sign of vitamin A deficiency.
Night blindness
Fish and fish oils and liver are natural sources of ______.
preformed vitamin A
The consumption of vitamin A in excess of the Upper Level results in a condition called ______.
hypervitaminosis A
In chronic toxicity of vitamin A, infants and _____ show a wide range of signs and symptoms.
adults
Using Accutane during pregnancy can produce ______ side effects.
teratogenic
Dark green and yellow-orange vegetables are sources of ______.
carotenoids
Consuming large doses of carotenoids in foods ______ result in toxicity.
does not
When the retinol in the blood is insufficient to replace the retinal lost during the visual cycle, ______.
the rods in the retina regenerate rhodopsin more slowly
Why is there an Upper Level for retinoids, but not for the carotenoids?
Toxicity occurs after excess intake of retinoids but not carotenoids.
A possible side effect of high intake levels of vitamin A is ______.
liver damage
Hypervitaminosis A can lead to which of the following in pregnant women?
Spontaneous abortions
Birth defects
Possible side effects of high intake levels of vitamin A-yielding carotenoids include ______.
skin that becomes yellow-orange in color