SI&LI- Special Topics
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
What is the MC emergency general surgical disease that affects the abdomen?
acute appendicitis
One of the more common complications of acute appendicitis is what?
perforation
A pt presents with abd pain in the epigastric/periumbilical region that started about 12 hrs ago. She also has anorexia, N/V, fever, and a change in bowel habits. Upon PE you note abd tenderness (RLQ pain) and + rebound tenderness-- what is the likely dx?
acute appendicitis
What is the diagnostic tool for acute appendicitis
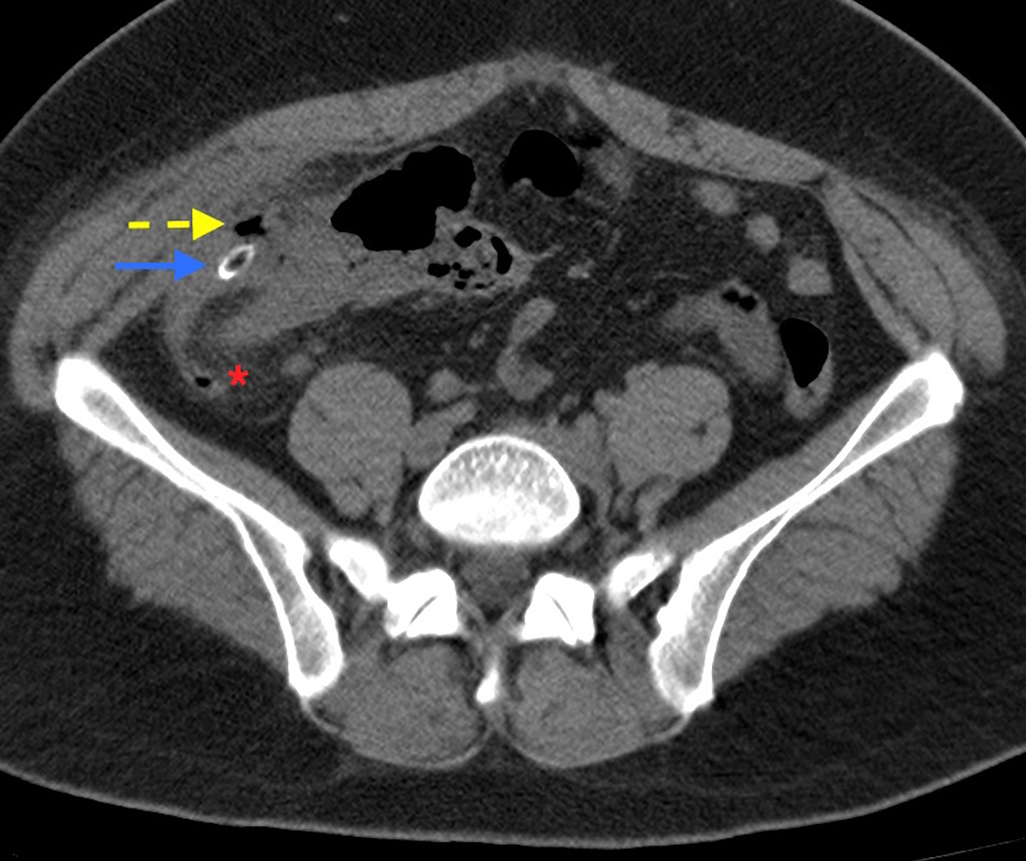
CT scan- dilation >6mm with wall thickening, lumen that does not fill with contrast, or fatty tissue stranding
WBC- mildly elevated
What is the treatment for acute appendicitis?
definitive- surgery (laparoscopic appendectomy)
What occurs due to persistent portion of the embryonic vitteline duct (yolk sac) still present, rule of 2's?
meckel's diverticulum
A pt presents with painless rectal bleeding and + Pain in the periumbilical region. A meckels scan is preformed to look for ectopic gastric tissue in the ileal region--- what is the likely dx?
meckel's diverticulum
What is the diagnostic tool for meckel's diverticulum?
meckels scan
What is the tx for meckel's diverticulum?
surgical resection in any peds pt
surgery only if symptomatic in adults
What occurs when the splanchnic perfusion fails to meet demands of the intestine leading to ischemic tissue injury?
visceral artery insufficiency
what are the four classifications of visceral artery insufficiency (based on their etiology)?
acute mesenteric ischemia
nonocclusive mesenteric ischemia
chronic mesenteric ischemia
ischemic colitis
What visceral artery insufficiency occurs due to:
occlusive arterial disease - embolic or thrombosis
acute mesenteric ischemia
What visceral artery insufficiency occurs due to:
low flow due to heart failure, sepsis, hypotension
nonocclusive mesenteric ischemia
What visceral artery insufficiency occurs due to:
“angina”, demand not met during feeding (abd pain worse after meals)
chronic mesenteric ischemia
A pt presents with complaints of abd pain that worsens after meals (intestinal angina). Upon PE you note bruit. You order a CT and see reduced BF to the small bowl due to atherosclerotic narrowing of 2 major splanchnic vessels. --- What is the likely dx?
chronic mesenteric ischemia
What visceral artery insufficiency occurs due to:
variant, inferior mesenteric artery- ischemia and sloughing (sudden and transient reduction in BF)
ischemic colitis
A pt presents with a complaint of rapid onset mild crampy abd pain over the LLQ. You find out he had bloody diarrhea that started about 24 hrs ago and the abd pain proceeded. You order a CT and see segmental bowel thickening adn edema in a nonsegmental pattern. -- what is the likely dx?
ischemic colitis
What vascular insufficiency occurs due to extensive collateralization between major mesenteric trunks and branches of the mesenteric arcades?
mesenteric vascular insufficiency
What is the MC location for colonic ischemia?
griffith's point and sudecks point
A pt presents with N/V, diffuse abd pain, worsening distension without focal pain. PE if strikingly out of proportion to symptoms. -- what is the likely dx?
acute mesenteric vascular insufficiency
A pt presents with intestinal angina, WL, and chronic diarrhea. Upon PE you notice malnourishment and an abd bruit-- what is the likely dx?
chronic mesenteric vascular insufficiency
What is the diagnostic testing for mesenteric vascular insufficiency?
- CBC, CMP, Coagulation profile, ABG, Amylase and lipase , Lactic acid, Blood type and cross, Cardiac enzymes
- EKG, echocardiogram, abdominal radiographs
- CT and mesenteric angiography (highlights where blood is going)
Do not delay surgery if indicated with imaging if surgery is indicated!
What is the treatment for mesenteric vascular insufficiency?
admit to ICU, IVF, BS ABX, oxygen, surgery
What presents with Post prandial pain + hypercoagulable state and has a spiral CT angiography as diagnostic tool?
acute mesenteric vein occlusion
What is the diagnostic tool for acute mesenteric vein occlusion?
spiral CT angiography
What is the tx for acute mesenteric vein occlusion?
anticoagulation, bowel rest
- surgery for infarction
What is the term for abnormal outpouchings in the intestinal wall of the colon?
diverticulosis
What is the term for inflammation/infection of the diverticula?
diverticulitis
What type of diverticula is a saclike herniation through the entire bowel wall?
true
What type of diverticula Involves only protrusion of mucosa and submucosa through the muscularis propria - most commonly affecting the colon?
false/pseudo
What is always spared in diverticular disease?
rectum
A pt presents with chronic constipation, abd pain with fluctuating bowel habits. Upon PE it seems normal with mild LLQ tenderness and palpable sigmoid/descending colon--- what is the likely dx?
diverticulosis
A pt presents with complaints of hematochezia. They also have a hx of HTN-- what is the likely dx?
diverticular disease
What is the MCC of hematochezia in patients >50?
diverticular disease
What are the diagnostic tools for diverticular disease?
Colonoscopy/anoscopy/sigmoidoscopy
CTA- reserved for pts with MASSIVE BLEEDING
Nuclear medicine tagged red cell scan
Angiography - shows pt of bleeding
How are you treating an unstable pt with diverticular disease?
emergent surgery
What is the tx for a stable pt with diverticular disease?
IR management, angiography
colonoscopy- epi injection, cautery
elective surgery
A pt presents with fever, N/V, and obstipation. Upon PE you note LLQ pain and tenderness with a palpable mass. KUB shows air fluid level and ileus. --- what is the dx?
diverticulitis
What presents like a left-sided appendicitis? (think all the sx of appendicitis but on the LEFT!)
diverticulitis
What are the diagnostic tools for diverticulitis?
- CBC: leukocytosis
- KUB: air-fluid level, ileus or LBO possible
- CT scan
- Colonoscopy – do not do until at least 6 weeks after diverticulitis
When can you do a colonoscopy on a diverticulitis pt?
not until at least 6 wks after
What is the treatment for a symptomatic pt with diverticulitis?
lifestyle changes
What is the outpt treatment for a symptomatic uncomplicated diverticular disease pt?
clear liquids x 3 days, Augmentin BID x 7-10 days if abscess < 3-4cm
What is the inpt treatment for a symptomatic uncomplicated diverticular disease pt?
NPO, NG tube, IVF, abx
- cefoxitin (2nd gen)
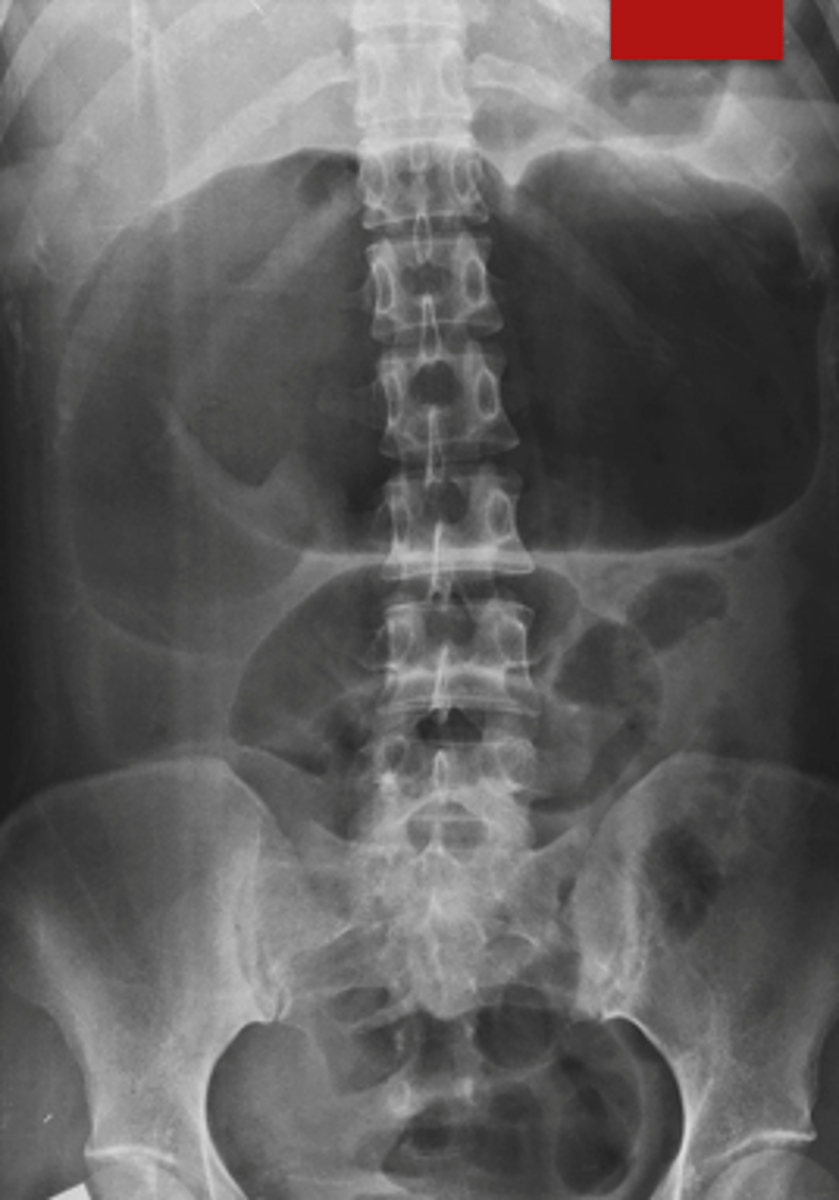
What occurs due to non-obstructive, severe colon dilation >6cm with UC and CD as #1 causes?
toxic megacolon
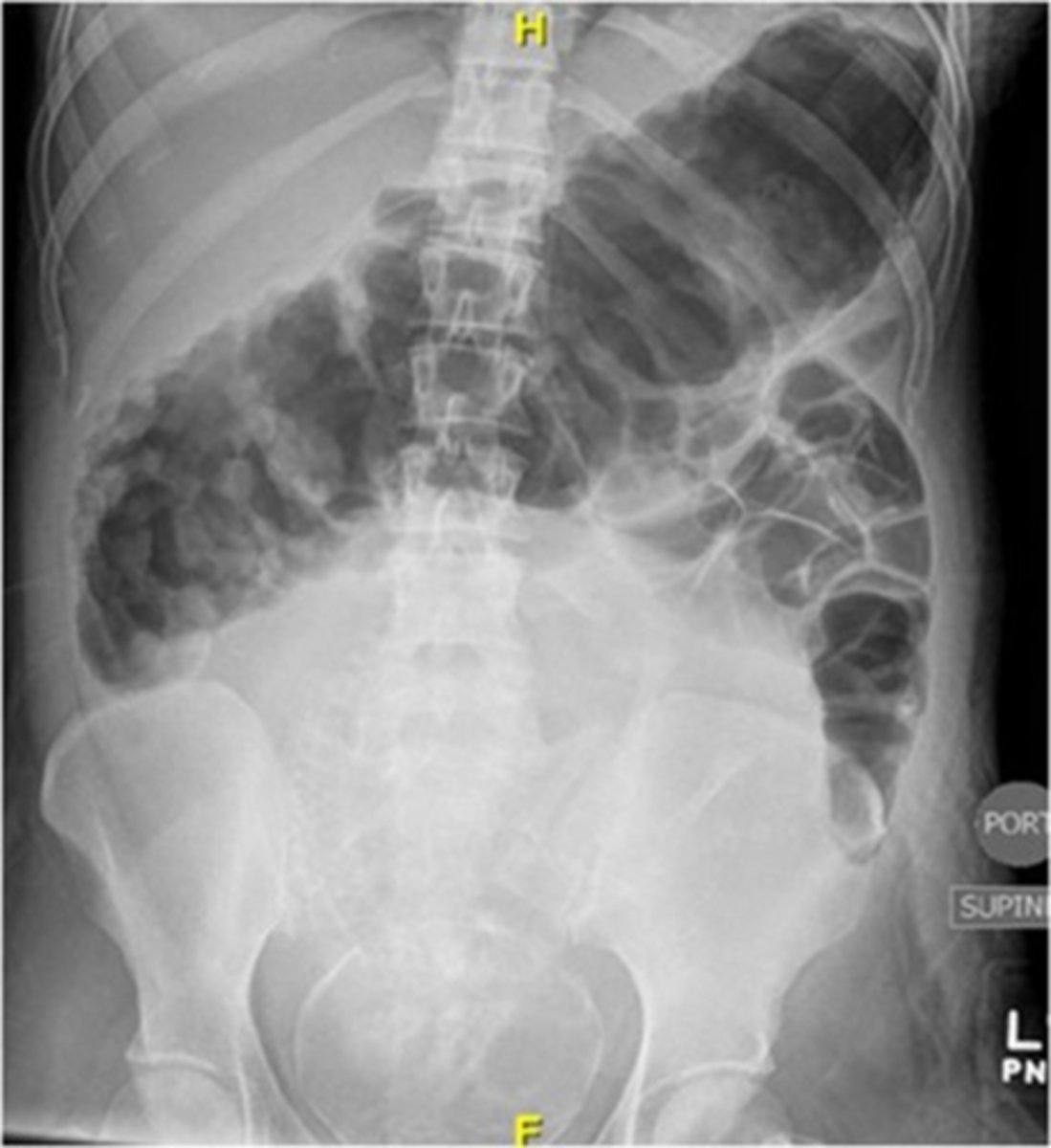
A pt presents with abd pain, N/V/D, rectal bleeding (sometimes with tenesmus, fever, and electrolyte derangements). Upon PE you note abd distention, fever, tachycardia, and dehydration. On the KUB you see a large colon >6mm-- waht is the likely dx?
toxic megacolon
What is a congenital aganglionic colon (neurogenic bowel obstruction) that is seen with toxic megacolon?
Hirschsprung
What is the diagnostic tool for toxic megacolon?
KUB
What is the tx for toxic megacolon?
decompression- bowel rest, NGT
BX ABX
What are 2 major types of IBD?
UC and CD
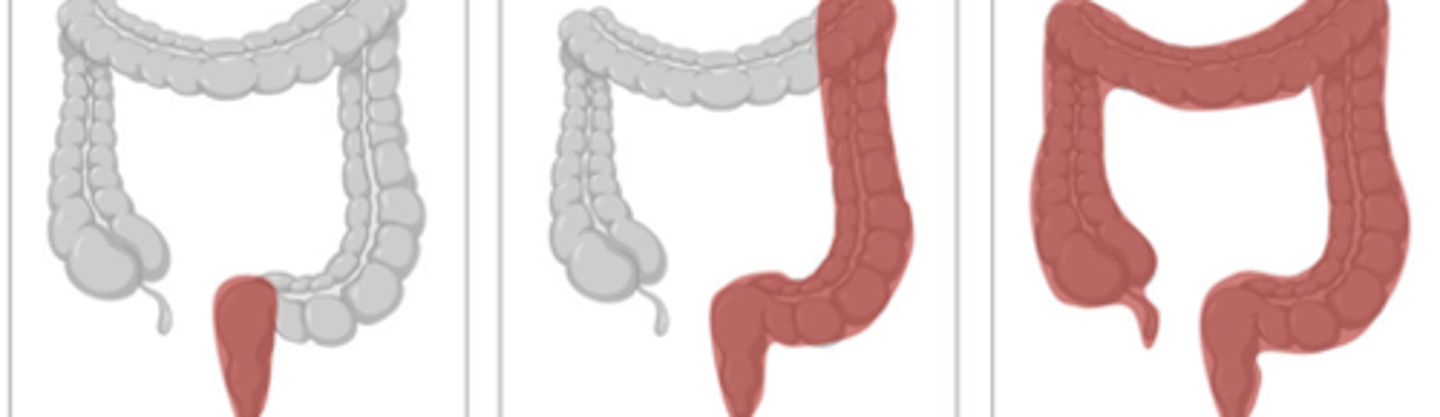
UC or CD
UC
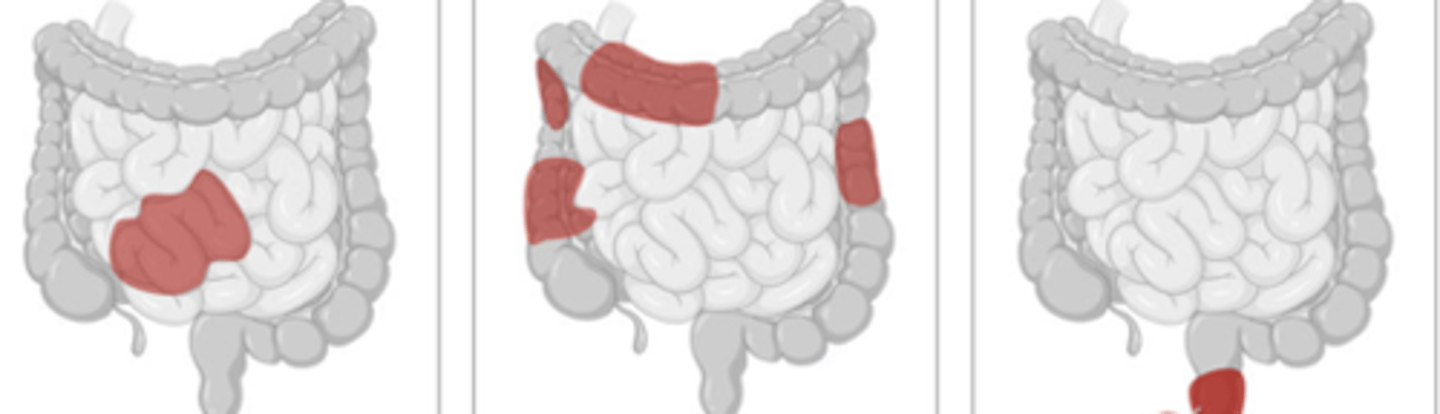
UC or CD
CD
What occurs mouth to anus with the rectum usually being sparred (40%), transmural, and is segmental with skipped areas?
crohn's disease
What is the microscopic features of CD?
noncaseating granulomas
What are the gross pathology features of CD?
cobblestone (disfigured corn on the cob 🥲)
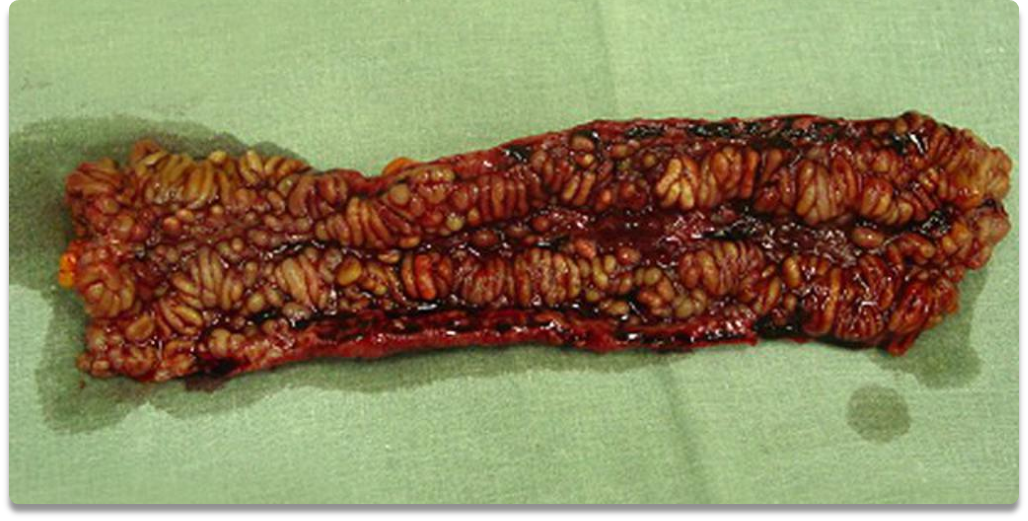
A pt presents with Abd pain, diarrhea (±/- gross bleeding), fatigue and WL. -- these are the hallmarks of what disease?
CD
What type of crohn’s disease presents as:
recurrent colicky RLQ pain relieved by defecation, diarrhea
ileocolitis
What type of crohn’s disease presents as:
crampy abd pain, hematochezia, and fecal urgency
colitis
What type of chrons disease presents with:
fecal incontinence, large hemorrhoidal tags, anal strictures, anorectal fistulae, and perirectal abscesses
perianal disease
What are the serological markers for CD?
+ ASCA, - p-ANCA
What does endoscopy for CD show?
Rectal sparing, aphthoid/linear/stellate ulcerations, fistulas and skip lesions
what are the typical imaging findings of crohn’s disease on recon CT?
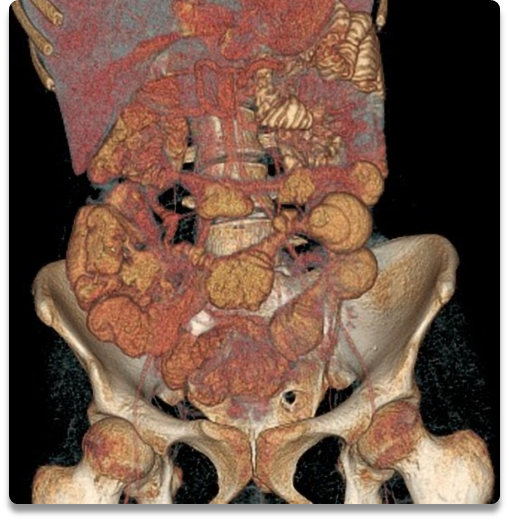
Multiple strictures and hyper-vasculature
what are the typical imaging findings of crohn’s disease on x-rays?

thumbprinting
What are some complications of CD?
fistula formation: rectovaginal, abd, enterovesicle
perianal disease
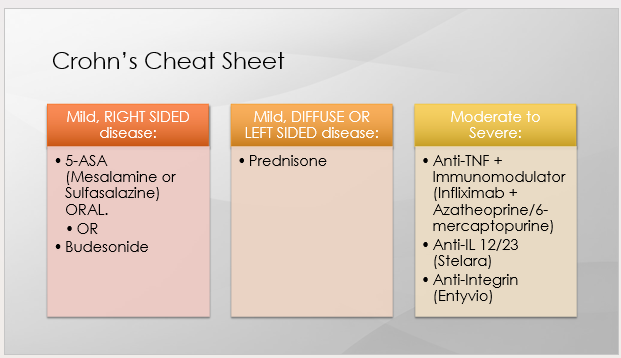
what is the treatment for CD
VERY PT SPECIFIC
Mild disease: balanced diet, smaller but more frequent meals, hydration, dairy restriction
- Loperamide (2-4mg) up to QID for diarrhea
Severe disease: low roughage diet (no raw fruit or vegetables, nuts), B12 and Vit D, low fat diet, Loperamide
What is the tx for mild, R sided CD?
5-ASA (mesalamine or sulfasalazine) PO
or
Budesonide
What is the tx for mild, R sided CD → specifically, ileocolonic disease?
Mesalamine 2.4g PO daily
What is the tx for mild, R sided CD → specifically, mild colonic disease only?
Sulfasalazine1.5-3g PO daily
What are the characteristics of MILD crohn’s disease?
Normal to mild increases in CRP/fecal calprotectin
Dx > 30 years of age
Limited distribution
Superficial ulceration
Lack of perianal complications
No resections
No fistulas
What is the tx for mild, Diffuse or L sided CD?
prednisone
What are the characteristics of MOD TO SEVERE crohn’s disease?
● Diagnosis at a younger age (<30 years)
●History of active or recent tobacco use
●Elevated C-reactive protein and/or fecal calprotectin levels
●Deep ulcers on colonoscopy
●Long segments of small and/or large bowel involvement
●Perianal disease
●Extra-intestinal manifestations
●History of bowel resections
What is the tx for moderate to severe CD?
Combo of Biologic (Anti-TNF) + Immunomodulator medications for induction (esp of disease with fistula)
Infliximab (Remicade) + Azatheoprine (Imuran) or 6-Mercaptopurine (Purinethol)
Adalimumab (Humira) + Azatheoprine or 6-Mercaptopurine
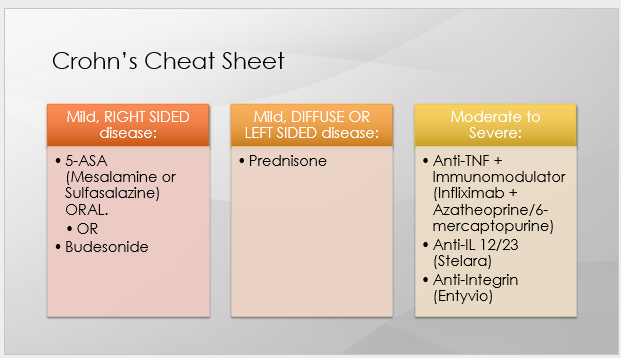
For patient’s with mod to severe CD, when should the immunomodulator be dropped for higher risk patients due to risk of hepatosplenic T-Cell Lymphoma and bone marrow suppression?
by 1-2 years
What involves 100% of the rectum and has some submucosal involvement?
UC
What are the microscopic features of UC?
- Crypt architecture of the colon is distorted
- Basal plasma cells and multiple basal lymphoid aggregates
A pt presents with diarrhea, tenesmus, passage of mucus, and crampy abd pain. Upon the PE you note tender anal canal, abd tenderness, signs of BV loss, and peritoneal signs. The P-ANCA was positive-- what is the likely dx?
UC
What are the serological marker findings for suspected UC?
- ASCA, + p-ANCA
How to differentiate between mild, mod, and severe UC?
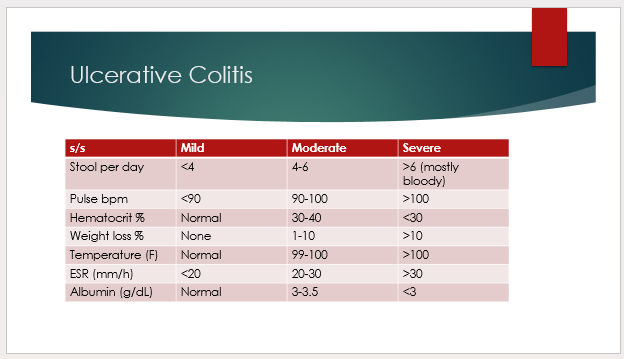
Does pseudopolyp formation occur in UC or CD?
UC
What is the treatment for Mild/moderate UC that affects the rectum and rectosigmoid region? **(check slide 100)
mesalamine Suppository or Enema

What is the tx mild/moderate UC that affects proximal to the sigmoid region?
combo oral (mesalamine) and rectal (5-ASA)

What is the tx for severe UC?
similar to chrons
Prednisone + Infliximab or mesalamine
or infliximab + thiopurine
- surgery!

What are some possible complications for UC?
toxic megacolon, stricture, malignancy
What are some extraintestinal symptoms of IBD?
- Erythema nodosum*
- Peripheral arthritis* most common
- Pyoderma gangrenosum*
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis
What is a functional bowel disorder characterized by abdominal pain or discomfort along with altered bowel habits for at least 3 months in the absence of detectable structural abnormalities?
IBS
What is the rome IV criteria that is associated with IBS?
recurrent abd pain at least 1d per week in the last 3 mos with 2 or more of the following:
1. related to defecation
2. associated with frequency of stool
3. associated with change in stool
A pt presents with complaints of abd pain that is episodic and crampy and is relieved by defecating--- what is the likely dx?
IBS
What are the expected work-up findings of IBS?
CBC: screen for anemia
Fecal calprotectin level (>50 mcg/g-> endoscopy)
+ Anti-endomysial IgA Ab & transglutaminase-2 Ab (IgA TG2)
What is the treatment for IBS?
Lifestyle changes
Stool bulking agents
Antispasmodics
Antidiarrheals
anticonstipation
A 60 year old patient with a history of pan-gastritis on chronic PPI therapy presents complaining of distention, bloating, diarrhea, and weight loss. There is no endoscopic evidence of malignancy or significant ulceration. Labs demonstrate low iron, folate and vit D. What condition do you suspect?
A. Crohn’s disease
B. Ulcerative colitis
C. SIBO
D. Short bowel syndrome
E. Irritable bowel syndrome
C!
The diagnosis of tropical sprue requires which of the following?
A. Anti-Ts antibodies
B. Exclusion of Celiac Disease
C. Single negative O&P
D. Amelioration of symptoms with gluten free diet
B!
A patient is s/p large ileal resection. Which of the following nutrient deficiencies should be monitored for? (multiple)
A. B12
B. ADEK vitamins
C. Carbohydrate
D. Proteins
A, B
Which of the following conditions does not typically result in weight loss or malnutrition? (multiple)
A. SIBO
B. Whipple’s
C. Celiac
D. Lactose intolerance
E. IBS
D, E
A patient is s/p anterior lumbar instrumentation and fusion. POD 1 the patient develops abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting and distention. His vitals are stable. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Sepsis
B. SBO
C. LBO
D. Ileus
E. Perforated viscus
D!
Which regimen could be used to induce remission in severe Crohn’s AND UC?
A. Infliximab + Thiopurine
B. Sulfasalazine + Prednisone
C. Budesonide alone
D. Mesalamine alone
A!
35 year old female presents with a 4 month history of abdominal pain, bloating and diarrhea. She also states that she gets moderate to severe cramping prior to her BM. She denies weight loss or bloody stools. She has a history of anxiety and depression. No significant family history. Exam shows mild lower abdominal tenderness, no masses, negative FOBT. Labs: negative anti-endomysial antibodies, negative fecal calprotectin, hydrogen breath test is negative. What is the most likely diagnosis
IBS