Understanding Mood Disorders, Substance Abuse, Psychosis and Their Treatments
1/600
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
601 Terms
Depression
A mood disorder characterized by persistent sadness.
Mania
An elevated mood state often seen in bipolar disorder.
DSM-5-TR
Diagnostic manual for mental health disorders.
Unipolar Depression
Depression without manic episodes, affecting mood only.
Bipolar Disorder
Mood disorder with alternating episodes of mania and depression.
Cultural Challenges
Difficulties in comparing depression and anxiety across cultures.
Risk Factors for Suicide
Age and gender significantly influence suicide risk.
Unipolar
Mood disorder with only depression or mania.
Mixed features
Simultaneous manic and depressive symptoms present.
Emotion
Affect with physiological, cognitive, and behavioral components.
Mood
Prolonged emotion influencing perceptions and behavior.
Mood disorder
Prolonged, abnormal mood affecting daily functioning.
Major depressive disorder
Depression without manic or hypomanic episodes.
Recurrent MDD
Multiple depressive episodes separated by two months.
Major depressive episode
Severe depression lasting at least two weeks.
Anhedonia
Loss of pleasure in previously enjoyed activities.
Cultural influences
Variations in symptom expression across cultures.
Children's symptoms
Physical complaints and irritability due to emotion misunderstanding.
Elderly symptoms
Depression linked to physical complaints and isolation.
Severity continuum
Symptoms range from mild to severe, affecting impairment.
Psychotic features
Delusions or hallucinations accompanying severe depression.
Delusions
Fixed false beliefs, often related to guilt or persecution.
Hallucinations
Sensory experiences without external stimuli, often auditory.
Mood congruent
Delusions matching the individual's depressed mood.
Mood incongruent
Delusions not aligning with depressive symptoms.
Persistent depressive disorder
Chronic depression lasting at least two years.
Double depression
MDD episodes occurring on top of PDD.
Impairment
Reduced functioning due to mood disorder symptoms.
Comorbidity
Presence of multiple disorders simultaneously.
Treatment responsiveness
Effectiveness of treatment varies by disorder type.
Chronicity
Duration of symptoms crucial for diagnosing depression.
Specifiers
Criteria that further define mood disorders.
Psychotic features
Presence of hallucinations and delusions in mood disorders.
Somatic delusions
Physical sensations believed to be caused by illness.
Peripartum onset
Depression occurring before or after childbirth.
Seasonal pattern
Episodes occurring during specific seasons, like winter.
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)
Depression linked to seasonal changes, often winter.
Excessive sleep
Common symptom in seasonal affective disorder.
Acute grief
Intense grief that evolves into integrated grief.
Integrated grief
Adjustment to loss after initial acute grief.
Suicidal thoughts
Increased risk when grief persists beyond a year.
Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD)
Severe emotional reactions before menstruation.
Controversial diagnosis
PMDD's classification may lead to stigma.
Prevalence of PMDD
Affects 2 to 5% of women.
Clinical description of PMDD
At least 5 symptoms before menses, improving after.
Affective lability
Mood swings and sensitivity to rejection.
Marked irritability
Increased anger and interpersonal conflicts.
Depressed mood
Feelings of hopelessness or self-deprecation.
Anxiety and tension
Feelings of being on edge or keyed up.
Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder
Diagnosis for children with severe mood swings.
Broader diagnostic criteria
Used for diagnosing bipolar disorder in youth.
Chronic Irritability
Persistent irritability leading to aggression and tantrums.
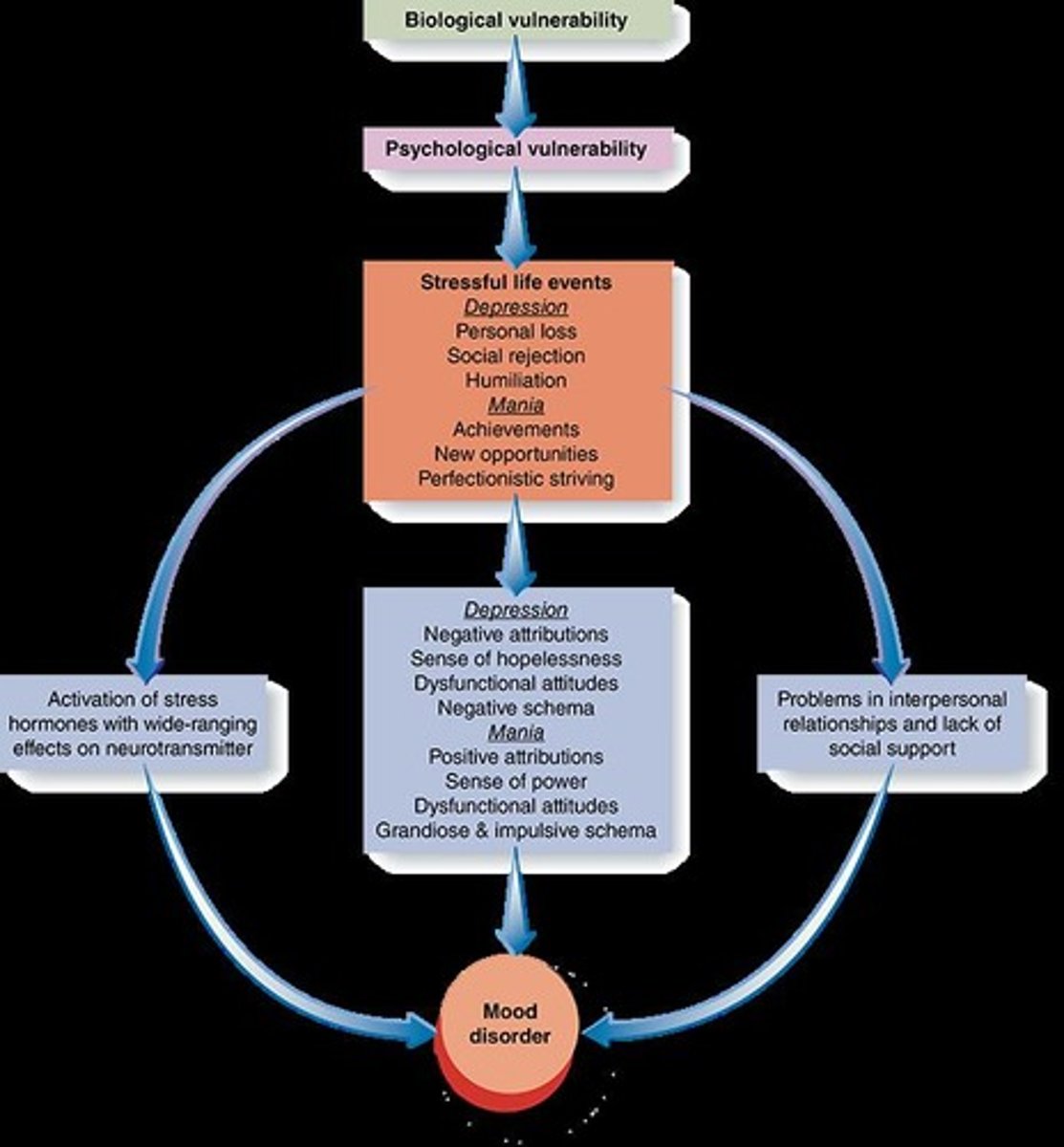
Mood Disorders
Psychological disorders affecting emotional states.
Lifetime Prevalence
4-12% in adults, 2.5% in children.
Adolescent Prevalence
8.3% of adolescents experience mood disorders.
Gender Risk
Girls are twice as likely to be affected.
Subclinical Symptoms
25% of girls and 10% of boys show mild symptoms.
Age of Onset
Average onset age is 25 years.
Interpersonal Factors
Social exits often trigger mood episodes.
Suicide Risk
Increased risk of suicide among affected individuals.
Occupational Dysfunction
Impairment in work due to mood disorders.
Episode Duration
First episode lasts 2 to 9 months.
Remission Rate
40% remit within 3 months, 90% within 12 months.
Biological Contributors
Genetic and neurological factors influencing mood disorders.
Heritability
32-37% heritability in mood disorders.
Neurological Correlates
Brain regions associated with mood regulation.
Prefrontal Cortex
Decreased thickness linked to affect regulation.
Hippocampus Size
9-13% smaller in women with MDD.
Neurotransmitter Dysregulation
Imbalance of serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine.
Monamine Theory
Balance of neurotransmitters is crucial for mood.
HPA Dysregulation
Chronic stress elevates HPA activation.
Biological Treatments
Medications like TCAs and SSRIs for mood disorders.
Tricyclics
Increase serotonin and epinephrine, block reuptake.
MAO-inhibitors
Prevent breakdown of neurotransmitters in synapse.
SSRIs
First choice antidepressants with fewer side effects.
Ketamine Infusions
Promote neural growth, short-term effects.
Electroshock Therapy (EST)
Effective for treatment-resistant depression.
Transmagnetic Stimulation
Non-invasive procedure targeting specific brain areas.
Social Contributors
Stressful life events often precede depressive episodes.
Interpersonal interactions
Social exchanges between individuals affecting relationships.
Romantic partner selection
Choosing a partner based on personal preferences.
Marital discord
Conflict or disagreement within a marriage.
Intergenerational transmission of depression
Passing depressive traits from parents to children.
Depressed mother effects on daughter
Daughters may develop similar depressive symptoms.
Dysfunctional relationships within daughters
Unhealthy relationship patterns observed in daughters.
Marrying alcoholics
Daughters more likely to choose partners with alcoholism.
Increased likelihood of depression
Daughters at higher risk for developing depression.
Interpersonal Psychotherapy (IPT)
Therapy focusing on current interpersonal issues.
Structured therapy sessions
IPT typically involves 15-20 weekly sessions.
Role disputes
Conflicts arising from differing roles in relationships.
Relationship loss
Emotional impact of losing a significant relationship.
Relationship initiation
Beginning new romantic or social relationships.
Deficient social skills
Lack of abilities to effectively interact socially.
Resolution of disputes
Actions taken to resolve interpersonal conflicts.
Negotiation stage
Partners actively try to resolve their disputes.
Impasse stage
Dispute unresolved, leading to underlying resentment.
Resolution stage
Partners take decisive actions like separation.
Cognitive Processes (AT Beck)
Cognitive therapy focusing on thought patterns.
Cognitive content
Thoughts involving self-criticism and comparisons.