Wk Four - ECG basics | Sinus Rhythms | History taking
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
All of the ECG intervals:
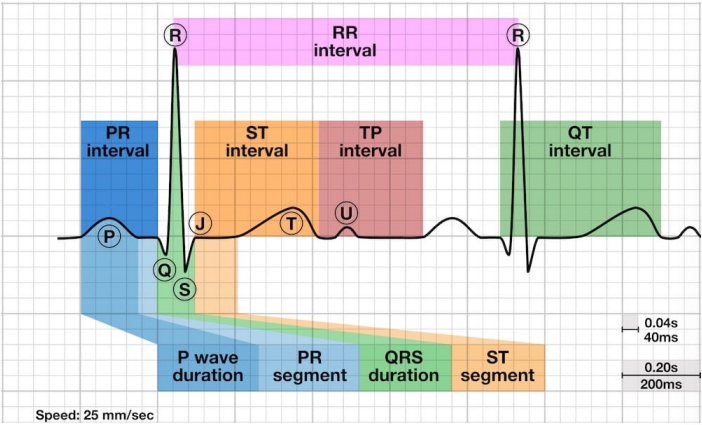
What is the normal presentation of a P wave?
It should be the first positive deflection on the ECG. It represents atrial depolarisation, and should be <0.12s (3 small squares). It will look smooth and rounded upright in Lead 2.
What is the normal presentation of a PR interval?
It is the time from the onset of the P wave to the start of the QRS, reflecting conduction through the AV node. It should be between 120-200ms, or 3-5 small squares.
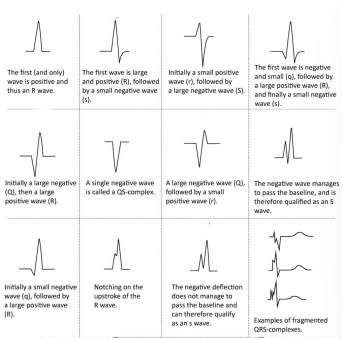
Types of QRS complex
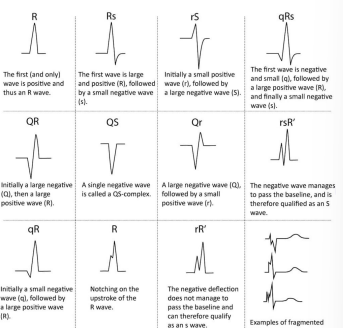
What is the normal presentation of a QRS complex?
It represents ventricular depolarisation. Q = first negative, R = first positive, S = first negative after R. Should be 0.06-0.12s (1.5-3 small squares)
What is the normal presentation of a Q wave?
Any negative wave that comes before an R wave - represents normal left to right depolarisation of the interventricular septum.. Should be 40ms or 1mm wide, 2mm deep & 25% of the QRS. NOT SEEN in V1-3.
What is the J point?
Marks the transition of the QRS complex to the ST segment - it determines ST elevation.
What is the normal presentation of a ST segment?
The flat, isoelectric section between the end of the S (J point) and the start of the T wave. It is the interval between ventricular depolarisation and repolarisation. It is often elevated due to myocardial ischemia or infarction.
What is the normal presentation of a T wave?
T wave is a positive deflection after the QRS complex. It represents ventricular depolarisation. It should be upright in all leads but aVr & V1, and last 0.1 - 0.25 seconds.
T wave size in males & females
5mm in limb leads and 10mm in precordial leads. 10mm in males, 8mm in females.
What is the normal presentation of a QT interval?
It is the time from the start of the Q to the end of the T. Time taken for ventricular depolarisation & repolarisation. QT should be 440ms in men or 460ms in women. ABNORMALLY SHORT = 350ms.
How does HR affect the QT inteval?
Faster = shorter QT
Slower = longer QT
What is the normal presentation of a RR interval?
Time between two ventricular depolarisations, gives you the rate, should be regular.
What is the normal presentation of a TP interval?
Time between two PQRST complexes - no activity, baseline/ioselectic line.
What is the cardiac axis?
represents the sum of depolarisation vectors generated by individual cardiac myocytes
Cardiac Axies
Normal Axis = QRS axis between -30° and +90°
Left Axis Deviation = QRS axis less than - 30°.
Right Axis Deviation = QRS axis greater than +90°.
Extreme Axis Deviation = QRS axis between -90° and 180° (AKA “Northwest Axis”).
What should the RR interval be? (rhtymn)
more than 0.08 (2 boxes) between the shortest & longest RR, or more than a 10% difference is abnormal.
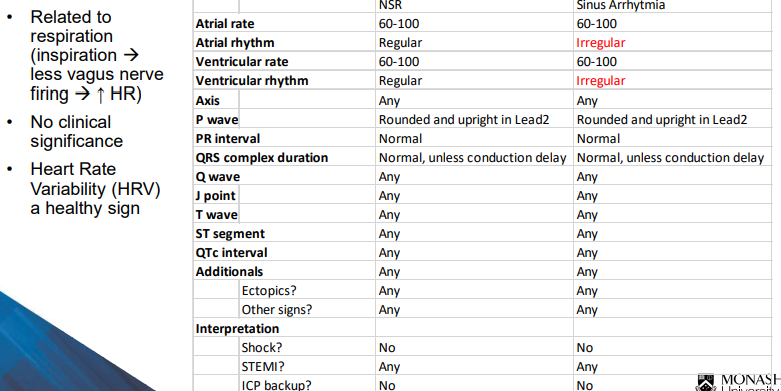
What defines normal sinus rhythm?
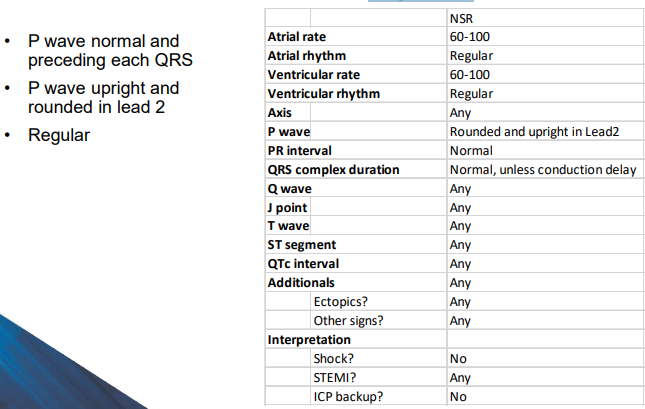
What defines sinus arrhythmia?
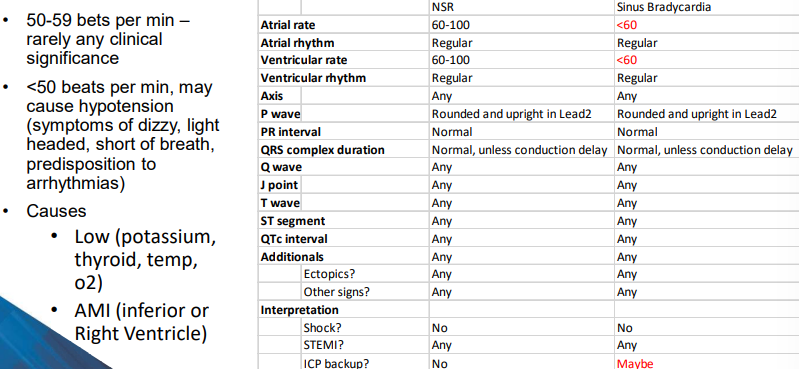
What defines sinus bradycardia?
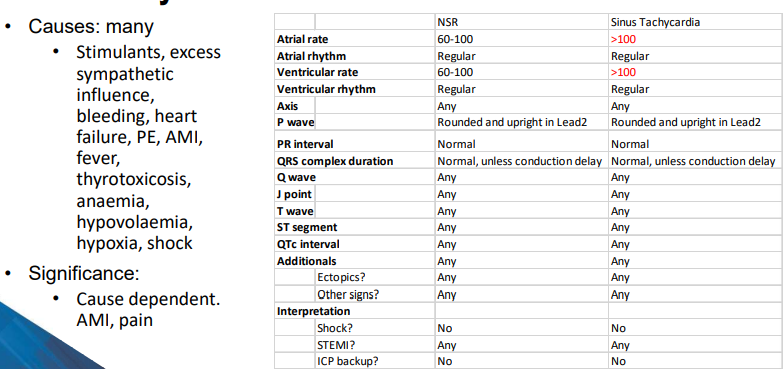
What defines sinus tachycardia?
Why is history taking important?
80% of disease can be determined by Hx alone. It’s a cheap way of assessing a patient, and helps improve paramedic-patient relationship.
What is a prodrome?
A symptom that may precede an ACS event, can occur hours to weeks beforehand.
Prodromal cardiac symptom examples
Chest pain, tiredness, sleep disturbance, anxiety, arm weakness or ache, heart racing, indigestion, tingling, pain in neck or throat, vision problems etc..
What is a risk factor?
increase the likelihood of a person developing a disease or health disorder
2 kinds of risk factor?
Modifiable & Non-Modifable
Non-modifiable RF
Age (>55), Sex (male), Family Hx (CHD or stroke before 55M or 65F), Ethnicity (Indian, Sri Lankan, Indigienous)
Modifiable RF
Behavioural: Smoking, not enough movement, diet, alcohol consumption, drug abuse
Biomedical: Hypertension, High Cholestrol, Overwieght, Recent Covid 19, Depression, Previous AMI
Shift work and ACS?
shift work puts you at higher risk of ACS by 23&.
Expected reporting for ACS in DOLOR
D - heavy, tight, squeezing, dull
O - gradual, sudden, excerise induced or at rest
L - poorly localised, chest to back to jaw,
O - SOB, sweaty, palpitations
R - relieved with nitrates, poor relief with position or NSAIDS