1. ethanol metabolism
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
ethanol metabolism
the process by which the body break down ethanol or alcohol into other compounds that are easier to process
the liver is th eprimary site of ethanol metabolism
but the sotmach also plays a role
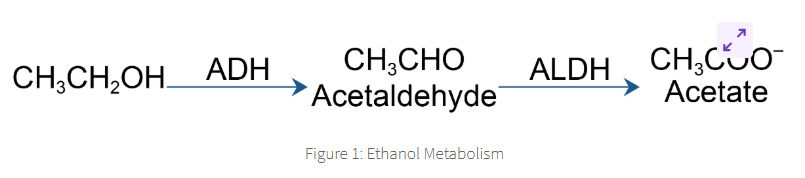
the main way ethanol is metabolised in the body onvolvles theee distinct steps
alcohol dehydrogenase
aldehyde dehydrogenase
carbon dioxide + water
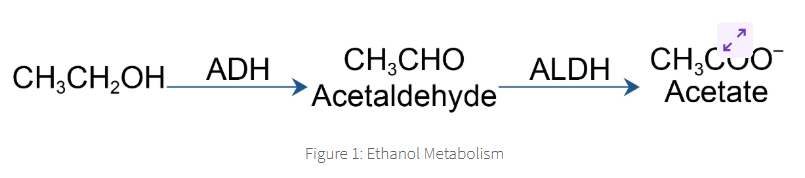
alcholol dehydrogenase ADH
ADH metabolises ethanold into acetaldehyde and toxic compounds that can damage tissue and potentially contribute to addiction
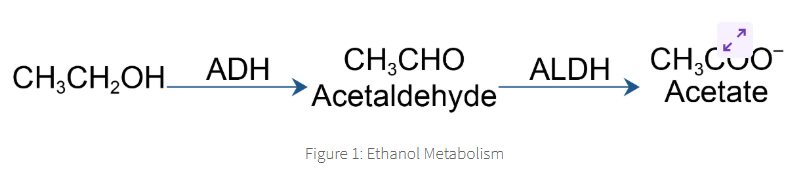
aldehyde dehydrogenase ALDH
ALDH breaks down acetaldehyde into acetate, a less toxic compound
carbon dioxide and water
acetate is broken down into carbon dioxide and water mainlin in tissue outside of the lvier
at high levels of ethanol cocnsumption
cytochrome P450 2E1 (CYP2E1) becomes invovled in metabolising ethanol to acetaldehyde
small amounts of alcohol are removed by interacting with fatty acids
to form fatty acid ethly esters FAEEs
FAEEs contribute to damage
to the liver and pancrease
the rate at which ethanol is metabolised
depends on the activity levels of the enzyems invovled
different variants od ADH and ALDH have different levels of activity
which can affect how a erson repsonds to ethanol and ther risk of alcohol dependence
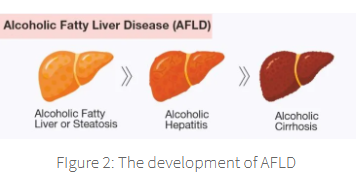
the body also uses hydrogen atoms released during these reactions
to create reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide NADH
NADH + acetate → fatty acids
fatty acids → fatty liver disease if consumed in large amounts over time
majority of ethanol metabolised in the body
a small percentage of ethanol is eliminated through the lungs skin and kidneys
