chemistry exam
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
concepts, definitions, pictures - look through the book and practice problems
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
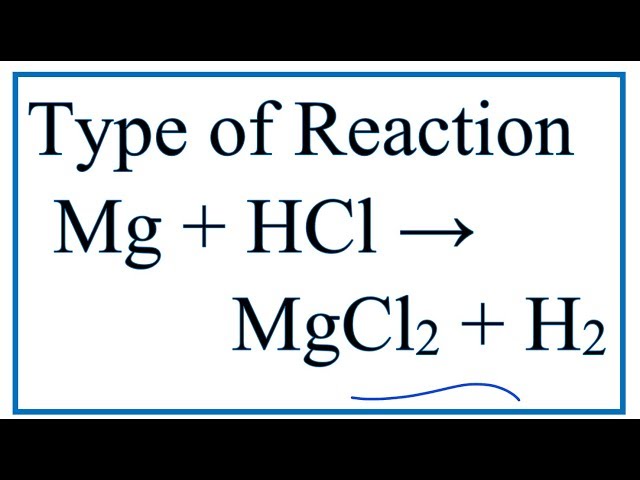
chemical reactions
rearrange atoms to produce chemicals different from those that were originally present
ex, Mg + 2HCl —> MgCl2 + h2
word equation
a way a saying a chemical reaction using words
ex. magnesium metal is reacted with aqueous (solution) hydrochloric acid to produce aqueous magnesium chloride and hydrogen gas
formula equation
a way of showing a chemical reaction using the actual elements in the equation with one side being reactants and another being products
visualization
showing chemical equations using pictures to represent the atoms and the amount and also using different colors to differentiate between the elements
reactants
the part of the chemical equation, the original chemcals that are acting together
products
the right side of the arrow that is the new chemicals produced
s, g, l, a
solid, gas, liquid, and aqueous, are used to indicate the state of matter in a equation, sometimes this will be given to you and others will not have enough information to identify it
writing word equations to formulas
take the elements and look for key words in the equation to figure out which goes on left and right, then make sure the equation is balanced
balancing equations
to change the equation so the amount of each element is the same. to abide by the law of conservation of mass which states that matter cannot be created or destroyed
classifying chemical reactions
double replacement, single replacement, combustion, synthesis, decompostition
double replacement
when the reactants switch spots with each in the products
ab +cd = ad +bc
single replacement
works with equations with three elements, where only one reactant switches places,
ab + c = ac +b
synthesis
where the reactants come together in the products
a +b = ab
decompositions
when the react separate in the product
ab = a +b
combsution
has to have oxygen in the reactant and water and carbon dioxide in the products
__ + o2 = co2 + h2o
neutralization
has to have water and ionic compound in the products
mole
a unit of measurement to help figure out what we can’t see
avogadros number
6.02 × 10²³
atomic mass
the mass put on the bottom of the element box on the periodic table thats specific to the element and it is equal to 1 mole of that element
molar mass
the mass of the entire compound
molar volume
22.4 L = 1 mole
percent composition
the percent of each element in a compound, finding the entire mass, then find the mass of each atom individually
practice mole conversion
mass, gas, liters , molecules ( atoms, formula units)
Stoichiometry
the process of calculating amounts of reactants and products in a reaction iusing the mole ratio from a balanced equation
percent yield
a calculation of a reactions efficiency by comparing the amount of product actually generated to what is theortically possible
calculatinjg actual yield v theoretical yield
actual yield/ theoretical yield
actual
collected, generated
theoretical
calculated, expected
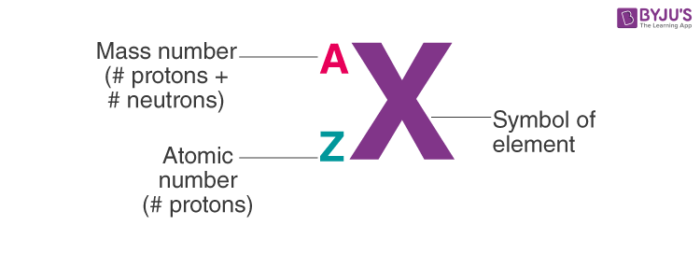
atomic number
number used to determine the element also the amount of protons
mass number
p + n
atomic mass
the weight of one mole of the element
john dalton
proposed the atomic theory, atoms are indivisible and indestructible, all atoms are identical in. mass (proved wrong bc of subatomic particles and isotopes), solid sphere model
based on law of conservation mass and the law of constant compostion
jj thompson
identified a negative entity within atoms (subatomic particles), cathode ray tube experiment, plum pudding model
cathode ray
deflected by negative charge, ray of light traveling in a vacuum
ernest rutherford
positive charge and mass are in a confined small area, gold foil experiment, atom is mostly empty space, nuclear model
gold foil experiment
positive charged alpha particles fired at atoms, mostly pass through undeflected, but once in a great while are deflected at great angles
niels bohr
electrons exist at specific energy levels, light emission spectra, and mathematic calculations, electrons have specific possible and energy amounts, planetary model
light emissions spectra
light patterns caused by electrons can generally be explained by mathematical computations
protons
postive, in the nucleus, mass and charge
electrons
negative, electron cloud, charge
neutrons
neutral, nucleus, mass
atom
the smallest piece of matter that has the chemical properties of the element
nuclear symbol
dmitri mendeleev
organizing the periodic table and left hols for new elements
period
horizontal on the periodic table
group
vertical on the periodic table
anion
negative ion
cation
postive ion
isotope
atoms of the same element with a different number of neutrons/different mass numbers
average atomic mass
find the sums of the isotopes and multiply the percent then add them together to the element
valence electrons
electrons on the outermost energy levels
different subshells
s, p, d ,f
s
2 e, 1 o
p
6 e, 3 o
d
10 e, 5 o
f
14 e , 7 o
s subshell endings
akali, and akaline
p subshell endings
the far right of the periodic tables
d subshell endings
transition metals
f subshell endings
lathan, actina
orbitals
where the electrons will mostly be located
aufbau
spectroscopic, electrons fill sub shells so that the total energy of atom is the minimum
hund’s rule
box and arrows, when filling the subshell, place electrons in unoccupied orbitals before pairing them up
pauli exclusion principle
two electrons that occupy the same orbital must have different spins, opposite spins
noble gas notation
the previous noble gas is used to represent the beginning configuration followed by the rest of the electrons
principle energy level
the shell or orbital in which the electron is located relative to the atom's nucleus
where the valence electrons are
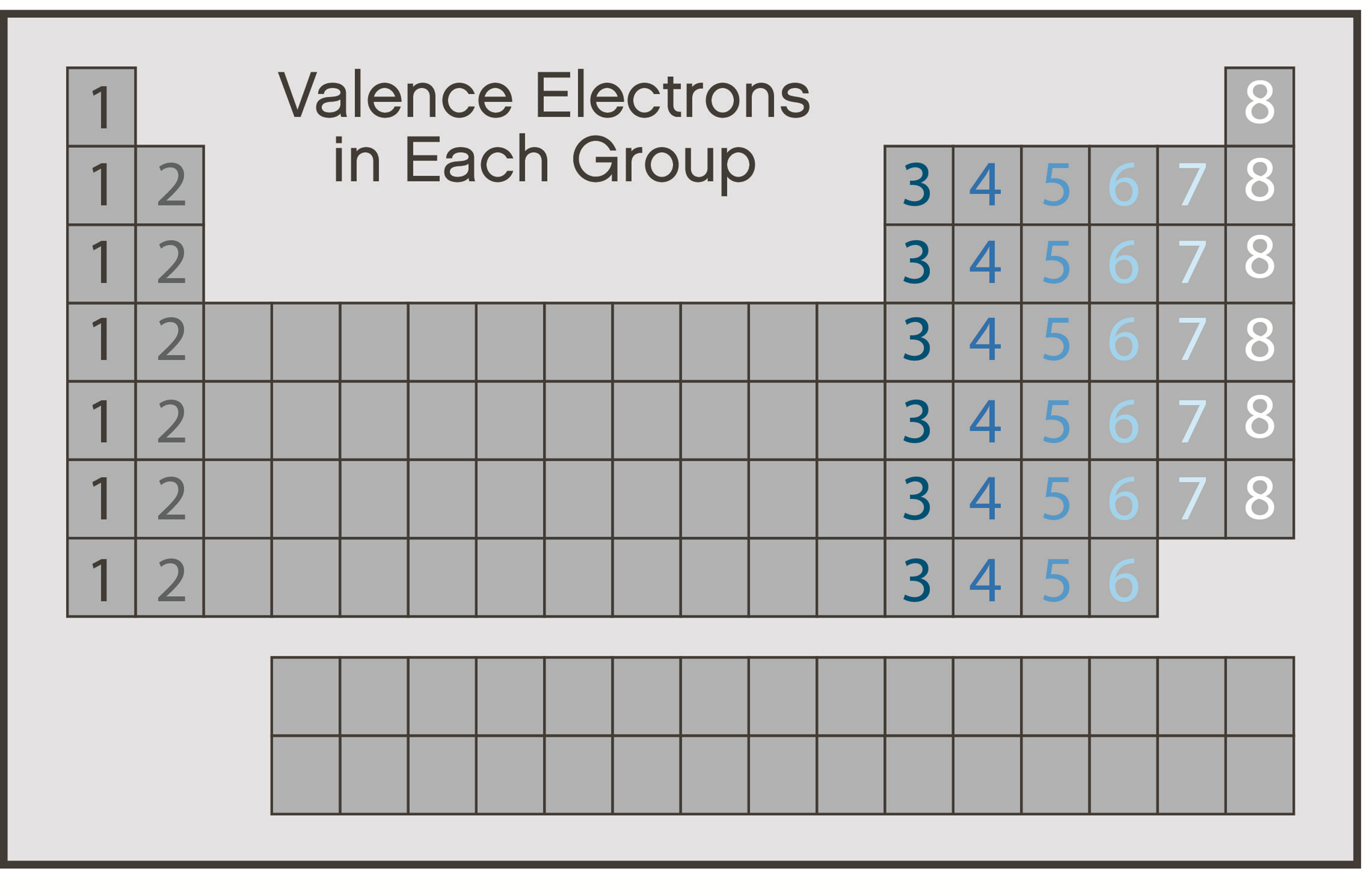
octet rule
all the elements have to equal 8 using dots and bonds
single bond
2
doublebond
4
triple bond
6
lewis dot structure
drawing molecule using dots and bonds to figure out where the elements should go
ionic compound
metal + non metal
covalent compound
non metal + non metal
shared pair
two dots together on one side of an element
lone pair
one dot on one side of the element
NH4
exception
ch3cl
ionic and covalent
ionic bond
cluster of + and - , transfers electrons, overcomes ionic bonds, soluble, free-floating ions, can conduct, high stp
non polar
nonmetal - nonmetal, evenly shared electrons, insoluble, intermolecular forces, cannot conduct, very low stp
polar
non metal - non metal, share electrons unevenly, overcome intermolecular forces, soluble, cant conduct, medium/low stp
metallic
metal + metal, pool of electrons, not bonded to specific atoms, insoluble, can conduct, med/varies stp