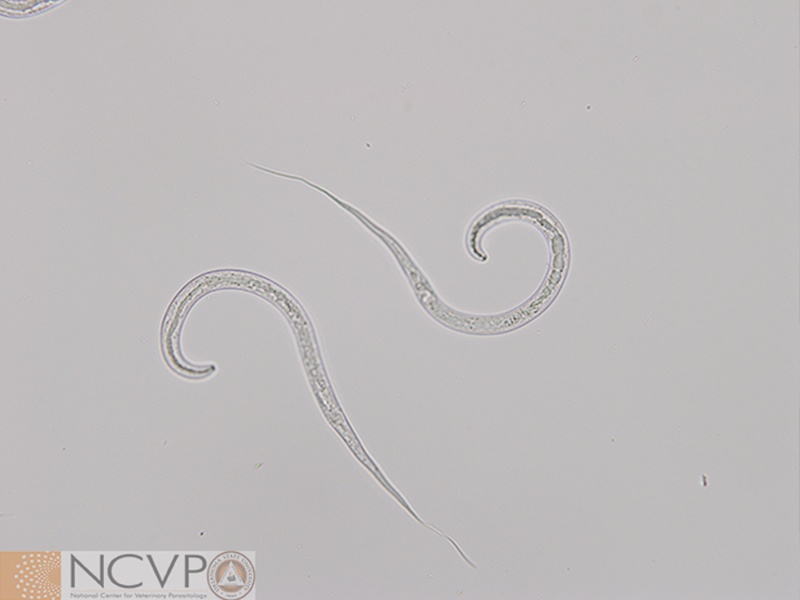
Filariasis and Guinea Worm
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
filariasis
tropical disease caused by parasitic thread-like worms transmitted through mosquito bites, primarily affecting the lymphatic system
types of filariasis
lymphatic, cutaneous, nonpathogenic
lymphatic filariasis is caused by—
Wucheria bancrofti and Brugia malayi
cutaneous filariasis is caused by—
Loa loa and Onchocerca volvulus
nonpathogenic filariasis is caused by—
Mansonella spp.
sheathed
enclosed in a protective coating
microfilariae
embryo stage of filarial parasite, usually in blood or tissue of humans and can be ingested by intermediate host where the microfilariae will develop into its infective stage
clinical features of filariasis
adult filariae live in lymphatic vessels and cause them to over time become thickened and destroyed
lymph is pooled and endothelial and connective tissue proliferate
total lymphatic obstruction
elephantiasis is the end result
lab diagnosis of filariasis
thick blood smears, micropore filtration
repeating over the course of 24 hours to catch periodicity (nocturnal)
circulating filarial antigen detection is commercially available
eosinophilia is marked in all forms
Brugia malayi morphology
sheathed
nuclei densely packed in single row to tip but separated
tapered tail to poimt
Wuchereria bancrofti morphology
sheathed
tapered tail to point
nuclei singly do not extend to tip\
individually visible nuclei
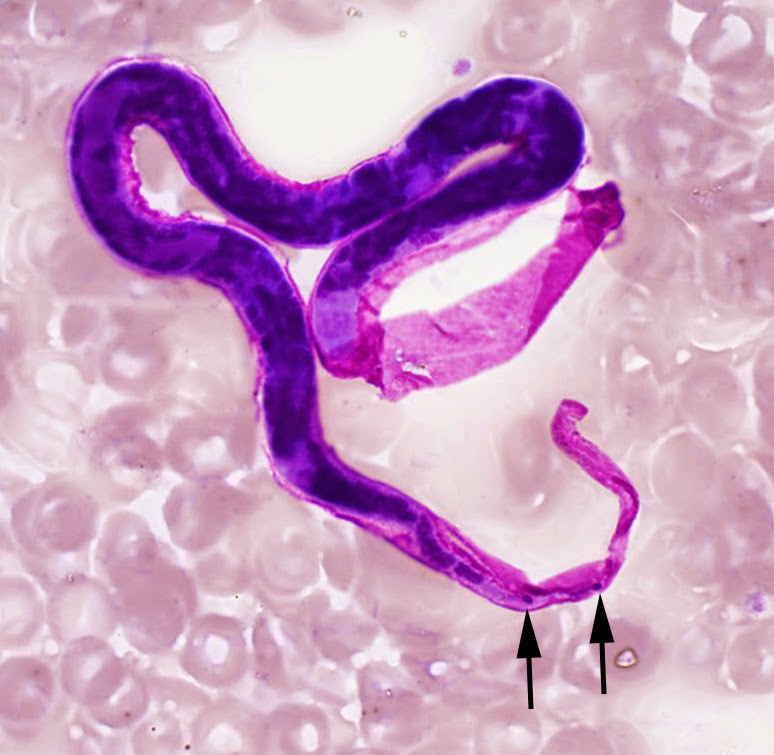
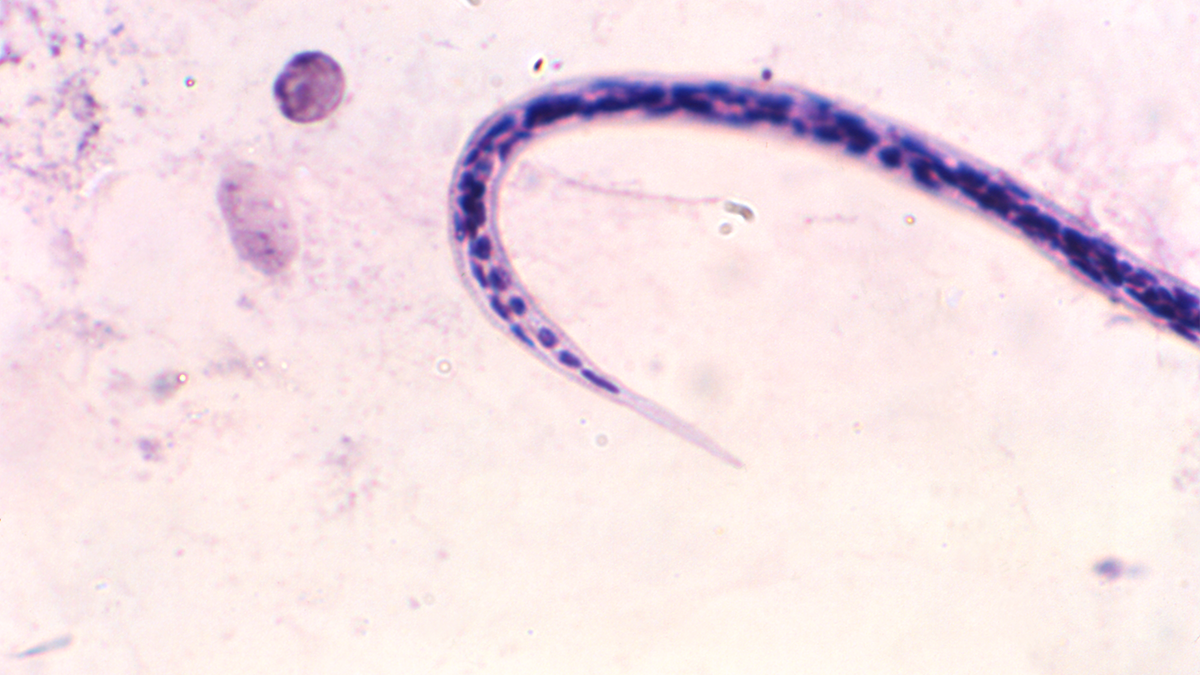
Loa loa morphology
sheathed
tapered, often coiled
nuclei to tip
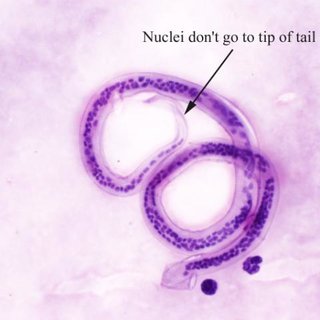
Onchocerca volvulus morphology
not sheathed
tail tapered toa point, sharp angle at end
Loa loa is known colloquially as the—
African eye worm
the vector of Loa loa is —
mango fly or deerfly (Chrysops spp.)
clinical features of Loa loa
calabar swellings, nodules mostly on extremities
localized pain, itching, urticaria
microfilaremia usually asymptomatic
diurnal
lab diagnosis of Loa loa
thick blood smear for microfilariae
removal of cutaneous worm
microscopy
onchocerca volvulus is known colloquially as causing—
river blindness
Onchocerca volvulus is predominant in —
equatorial Africa, central and south America
the vector of Onchocerca volvulus is —
blackflies (Simulium spp.)
clinical features of Onchocerca volvulus
chronic dermatitis (leopard sin), subcutaneous nodules or masses, ocular lesions with or without lymphadenitis
skin lesions early focal or generalized itching, redness, diffuse papules and scabbing to chronic edema, hypopigmentation and lichenification because of scratching
eye lesions early punctate keratitis, corneal fibrosis, glaucoma, optic atrophy
lab diagnosis of Onchocerca volvulus
skin snip, scleral punch
Americas - gluteus and calf skin
Africa - deltoid and scapular
UA following small DEC dose to mobilize microfilariae into urine
immunochromatographic test for specific antigens
clinical features of Dracunculus medinensis
itchy blister and ulceration
secondary bacterial infection leading to abscess
lab diagnosis of Dracunculus medinensis
clinical diagnosis is sufficient
therapy of Dracunculus medinensis
slow removal of female worm by winding on a stick a few inches per day
prevent breaking the worm and killing it
metronidazole
Dracunculus medinensis is known colloquially as —
Guinea worm
Dracunculus medinensis morphology
fishhook shape
sharp thin tapered tail
unsheathed
similar to filarids