study guide unit 1
1/189
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
190 Terms
Hydroxyl Group
A functional group with the formula -OH, found in carbohydrates and alcohols; polar and can form hydrogen bonds.
Carbonyl Group
A functional group containing a carbon double-bonded to an oxygen (C=O), commonly found in lipids and proteins; can be an aldehyde or a ketone.
Carboxyl Group
A functional group containing a carbon double-bonded to an oxygen and single-bonded to a hydroxyl group (-COOH); polar, acidic, and forms ions.
Amino Group
A functional group containing a nitrogen bonded to two hydrogens (-NH2); basic and can form hydrogen bonds, important in amino acids.
Phosphate Group
A functional group containing a phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms (-PO4); negatively charged and holds a lot of energy, found in DNA and ATP.
Isomers
Molecules that have the same molecular formula but differ in the arrangement of their atoms, leading to different properties.
Chemical Reaction
A process that involves the rearrangement of atoms and molecules to form new substances; reactants are converted into products.
Chemical Equilibrium
A state where the rate of forward and reverse reactions are equal, resulting in no net change in the concentrations of reactants and products.
Dehydration Reaction
A chemical reaction that removes water to build larger molecules from smaller ones (also known as a condensation reaction).
Hydrolysis Reaction
A chemical reaction that adds water to break down large molecules into smaller ones.
Ketone
A carbonyl group where the carbon double bonded to oxygen is bonded to two other carbon atoms.
Aldehyde
A carbonyl group bonded to at least one hydrogen atom; highly reactive in biochemical reactions.
Functional Groups
Specific small molecules that contribute specific properties when attached to larger molecules.
Sulfhydryl Group
A functional group containing a sulfur bonded to a hydrogen (-SH); exhibits low polarity, van der Waals forces; stabilizes proteins.
Methyl Group
A functional group containing a carbon bonded to three hydrogens (-CH3); nonpolar and affects molecule shape.
Hydrocarbons
Organic molecules that are composed of only carbon and hydrogen atoms.
Reactants
The starting materials in a chemical reaction.
Products
The substances that are formed as a result of a chemical reaction.
Macromolecules
Large molecules that are typically formed by the polymerization of smaller subunits (monomers).
Equilibrium
The state in a reversible reaction where the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction, resulting in no net change in concentrations over time.
Hydroxyl Group
A functional group consisting of an oxygen atom bonded to a hydrogen atom (-OH).
Monomers
Small, repeating units that are linked together to form a polymer or macromolecule.

What functional group is this?
Hydroxyl Group: A polar functional group that can form hydrogen bonds. It is found in carbohydrates and alcohols.
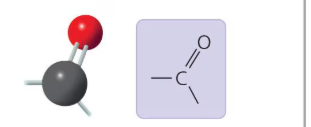
What functional group is this?
Carbonyl Group: A functional group found in lipids and proteins; can be an aldehyde or a ketone.
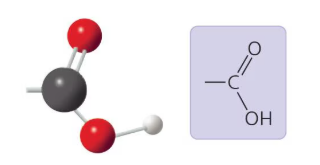
What functional group is this?
Carboxyl Group: A polar and acidic functional group that can form ions.
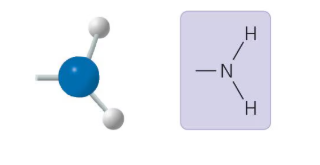
What functional group is this?
Amino Group: A basic functional group that can form hydrogen bonds, important in amino acids.
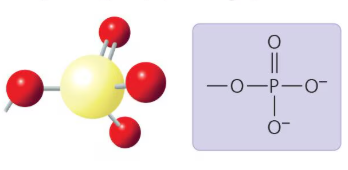
What functional group is this?
Phosphate Group: A negatively charged functional group that holds a lot of energy, found in DNA and ATP.
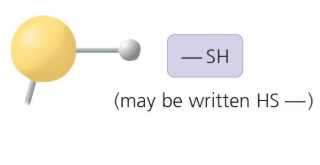
What functional group is this?
Sulfhydryl Group: A functional group that contains a sulfur atom bonded to a hydrogen atom, important in protein structure.
Characteristics of living things
Living things share characteristics such as organization, metabolism, responsiveness, growth, development, reproduction, and adaptation.
Homeostasis
The maintenance of a stable internal environment.
Prokaryotic cells
No membrane-enclosed organelles, circular DNA, small cell size.
Eukaryotic cells
Cells containing a nucleus and other complex organelles.
Domains of life
Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya. Eukarya includes Kingdoms such as Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia.
Scientific method
Observation, hypothesis, experimentation, data analysis, and conclusion.
Statistics
Used to analyze data and determine the significance of results.
Hypothesis vs. Theory
A proposed explanation for a phenomenon, a well-substantiated explanation acquired through the scientific method and repeatedly tested and confirmed through observation and experimentation.
Matter
Anything that has mass and takes up space.
Atom
The smallest unit of matter that retains the chemical properties of an element.
Element
A substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means.
Compound
A substance consisting of two or more different elements combined in a fixed ratio.
Molecule
Two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds.
Four elements comprising 96% of living matter
Oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen.
Atomic nucleus
The central core of an atom, containing protons and neutrons.
Atomic number
Number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
Atomic weight
The total mass of an atom, approximately equal to the number of protons plus the number of neutrons.
Mass number (atomic mass)
The sum of the number of protons and neutrons in an atom's nucleus.
Isotope
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons.
Electron (e-)
Negative charge, negligible mass, located in electron shells around the nucleus.
Proton (p+)
Positive charge, mass of 1 Dalton, located in the nucleus.
Neutron (n0)
No charge, mass of 1 Dalton, located in the nucleus.
Dalton/AMU
A unit of mass for atoms and subatomic particles.
Energy shell
Also known as Electron Shell, An energy level representing the distance of an electron from the nucleus.
Orbital
The three-dimensional space where an electron is found 90% of the time.
Electronegativity
The tendency of an atom to attract electrons towards itself in a chemical bond.
Polarity (polar)
A molecule with an uneven distribution of charge, resulting in positive and negative sides.
Non-polar
A molecule with an even distribution of charge.
Chemical bonds
The force that holds atoms together.
Ion
Are charged atoms or molecules.
Anion
A negatively charged ion.
Cation
A positively charged ion.
Ionic bond
A chemical bond resulting from the attraction between oppositely charged ions.
Covalent bond
A chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms.
Double covalent bond
A covalent bond in which two pairs of electrons are shared between two atoms.
Triple covalent bond
A covalent bond in which three pairs of electrons are shared between two atoms.
Polar covalent bond
A covalent bond in which the electrons are shared unequally between atoms.
Non-polar covalent bond
A covalent bond in which the electrons are shared equally between atoms.
Hydrogen bond
A weak bond between two molecules resulting from an electrostatic attraction between a proton in one molecule and an electronegative atom in the other.
Van der Waals interaction
Weak, short-range attraction between atoms caused by temporary fluctuations in electron distribution
Acid
A substance that increases the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution.
Base
A substance that reduces the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution.
Neutral
A pH of 7; an acid/base neutralize each other forming salt and water often
Equilibrium
The state in which the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction.
pH
A measure of the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution.
[H+]
Hydrogen ion concentration
[OH-]
Hydroxide ion concentration
Organic molecules
Study of compounds that contain carbon.
Dehydration reaction
A chemical reaction in which two molecules are bonded together with the removal of a water molecule.
Hydrolysis reaction
A chemical reaction that breaks apart molecules by the addition of water.
Roadrunner Body Temperature Regulation
Roadrunners maintain a body temperature of 104˚F even when external temperatures are above 120˚F, demonstrating a property of life related to internal regulation and homeostasis.
Four Elements of Life
The four elements that make up 96% of life are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Domain Archaea Habitat
Members of the Domain Archaea are most likely to be found in extreme environments such as boiling mud.
Electronegativity
Electronegativity determines whether electrons will be shared equally in bonding. The more electronegative an atom is, the more desperately it wants to form a bond
Non-Polar Covalent Bond
A non-polar covalent bond occurs when two atoms share electrons evenly/equally, with an electronegativity difference of less than 0.5.
Polar Covalent Bond
A polar covalent bond occurs when two atoms share electrons unevenly/unequally, with an electronegativity difference of >=0.5.
Non-Polarity of Carbon Tetrafluoride (CF4)
Carbon tetrafluoride (CF4) is non-polar because the symmetrical arrangement of the four polar C-F bonds results in the fluorines pulling in opposite directions with equal force, leading to no net movement of electrons.
Hydrogen Bond
A hydrogen bond is a chemical interaction formed through the attraction between a hydrogen atom in one molecule and a small atom of high electronegativity in another molecule, typically between molecules with polar covalent bonds; an intermolecular bond.
Water's Polarity
Four properties of water caused by its polarity are its solvent capabilities, high specific heat, high heat of vaporization, and high cohesive strength.
Solvent
A solvent is a liquid in which a substance (solute) is dissolved to form a solution. Water is an excellent solvent due to its polarity.
Dissociate
Dissociate is the process where water breaks molecules apart into ions.
Dissolve
Dissolve is the process where water separates molecules from one another, keeping the molecules intact.
Cohesion
Cohesion is the capacity of water molecules to resist coming apart from each other when under tension; bonding to other water molecules, means that water has a high surface tension.
Adhesion
the capacity of water molecules to bond to other molecules besides themselves.
Structural Isomers
Structural isomers have the same molecular formula, but differ in the covalent arrangements of their atoms
Dehydration Reaction Requirements
For a dehydration reaction to occur, the reactants must be monomers, water must be generated, and the monomers must each have a free hydroxy group.
pH Scale
[H+] = concentration of hydrogen ions; pH = -log[H+]; [OH-] = concentration of hydroxide ions; pOH= -log[OH-]
Water Molecules in Macromolecule Formation
In the formation of a macromolecule 18 monomers long, 17 water molecules are generated.
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis is the chemical breakdown of a compound due to reaction with water.
Hydroxyl Group
A hydroxyl group is a functional group consisting of a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to an oxygen atom (-OH).
Carbonyl Group
A carbonyl group (C=O) is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom.
Carboxyl Group
A carboxyl group (-COOH) is a functional group consisting of carbonyl (C=O) and a hydroxyl (O-H) bonded to the same carbon atom.