Chpt. 4 Notes
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/108
Last updated 2:25 AM on 10/18/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
1
New cards
Body membranes
covers surfaces, line body cavities, and form protective sheets around organs
2
New cards
body membranes groups
epithelial and connective tissue
3
New cards
epithelial membranes
cutaneous, mucous, serous
4
New cards
connective tissue membrane
synovial
5
New cards
cutaneous membrane
skin; keratinizing stratified squamous epithelium and dense connective tissue (dermis); dry membrane
6
New cards
mucous membrane
epithelium tissue on loose connective tissue; lines cavities open to exterior; refers to only location of membrane not cellular make-up; either stratified squamous or simple columnar; wet membrane to protect and lubricate
7
New cards
serous membrane (serosa)
Thin, double-layered membranes; covers ventral body cavity and organs; simple squamous on areolar; lines closed body cavities; occur in pairs of parietal layer and visceral layer; separated by serous fluid; names depend on location
8
New cards
parietal layer
lines a specific portion of the wall of the ventral body cavity for serous membrane
9
New cards
visceral layer
covers the outside of the organs in that cavity for serous membrane
10
New cards
serous fluid
allows organs to slide easily without friction
11
New cards
peritoneum serous membrane
lining of the abdominal cavity/organs
12
New cards
pleura serous membrane
lines the lungs
13
New cards
pericardium serous membrane
lines the heart
14
New cards
synovial membrane
soft areolar tissue; lines fibrous capsules around joints,, bursae, and tendon sheaths; provides smooth surface and secretes lubrication and cushions organs during activity
15
New cards
integumentary system
includes skin and derivatives to make up a complex set of organs that have served many functions but mainly protection
16
New cards
Skin
tough and pliable allowing it to take constant punishment; keeps water/molecules in or out of body
17
New cards
skin functions
insulates/cushions, protects from damage/radiation/desiccation, heat loss regulation, mini-excretory system, Vitamin D synthesis, and cutaneous sensory receptors.
18
New cards
skin structure
epidermis (outer) and dermis (inner) layers connected by basement membrane
19
New cards
epidermis
outer layer, stratified squamous epithelium, can become keratinized
20
New cards
dermis
underlying layer of dense connective tissue
21
New cards
subcutaneous layer
deep to dermis, adipose, anchor of skin; functions as shock absorber and insolation from extreme temps
22
New cards
4 cells types of epidermis
keratinocytes, melanocytes, merkel cells, langerhans cells
23
New cards
keratinocytes
majority of cells in epidermis; produces keratin; areas of great friction have increased cell and keratin production; persistent friction causes epidermis thickening
24
New cards
keratin
fibrous protein that gives epidermis protective properties
25
New cards
melanocytes
spider-shaped epithelial cells; produce melanin; melanin granules form on sunny side of cell to protect nucleus
26
New cards
langerhans cells
star shaped cells arises from bone marrow; called epidermal dendritic cells; are macrophages aiding in activating immune system; 1st line of defense after pathogens enter the skin
27
New cards
merkel cells
present at epidermal/dermal junction; spiky shaped hemisphere; works closely with disk-like sensory ending; combination known as a merkel disk and functions as sensory receptor for touch
28
New cards
layers of epidermis
varies in thickness; stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosom, stratum lucidum, stratum corneum
29
New cards
thick epidermis
covers palms, feet soles, and finger tips
30
New cards
thin epidermis
covers rest of body; stratum lucid is absent and other stratum are thinner
31
New cards
stratum basale
deepest epidermal layer; closest to dermis and cells get nutrients from dermis diffusion; single row of cells represents youngest keratinocytes; also known as stratum germinativum bc it's constantly doing cell division
32
New cards
stratum spinosum
several layers thick, keratinocytes flatten and appear irregular in shape causing it to be named prickle cells; langerhans cells are most abundant; aids in activating immune system to protect basal layer
33
New cards
stratum granulosum
keratinocytes change drastically, flattening and begin to disintegrate; accumulate lamellate granules; keratinocytes toughen up with plasma membranes thickening and lipids coat external surface
34
New cards
lamellate granules
contain waterproofing glycolipid and major factor in slowing water loss across epidermis
35
New cards
why do keratinocytes toughen up?
it makes them more resistant to destruction making the outer strata the strongest skin region
36
New cards
stratum lucidum
only occurs where skin is hairless and extra thick; cells are dead because of constant accumulation of water repellant keratin and is unable to get nutrients and o2 as they move farther from dermis/blood supply
37
New cards
stratum corneum
outermost layer (20-30 cell layer thick); shingle like cell remnants of layer completely filled with keratin; often called horny cells; abundance of keratin allows durable body overcoat
38
New cards
durable body overcoat
protect deeper cells from hostile external environment (air), from water-loss, and helps body resist from bio/chem/physical assaults.
39
New cards
melanin
pigment that ranges in color from yellow to brown to black; produced by melanocytes in stratum basale; exposure to sunlight stimulates melanin production; stratum basale cells phagocytize the pigment as it accumulates within the cells forming protective umbrella around nucleus to keep away UV rays
40
New cards
Dermis
your "hide" (corresponds to animal hides), strong stretch envelope (weird way to say covering but ok...) that helps hold body together, varies in thickness, sages and wrinkles with age bc of decrease in fibers
41
New cards
thick dermis
palms of hands, soles of feet, fingertips
42
New cards
thinest dermis
eyelids
43
New cards
major 2 layers of dermis
papillary and reticular
44
New cards
papillary layer
upper dermal region, uneven with dermal papillae which indent epidermis
45
New cards
dermal papillae
fingerlike projections of dermis, may contain capillary loops to furnish nutrients to epidermis, has pain and touch receptors, functions on thick areas to increase friction and enhance gripping. Creates our fingerprint.
46
New cards
Reticular layer
deepest skin layer (80%), contains blood vessels, sweat/oil glands, and deep pressure receptors, numerous phagocytes found in layer to prevent bacteria going deeper into the body
47
New cards
3 functions of the dermis
toughness, hydration and elasticity
48
New cards
skin color is determined by
amount/kind of melanin, amount of carotene in stratumcorneum/subcutaneous tissue, and amount of 02 going to hemoglobin
49
New cards
carotene
orange-yellow pigment found in carrots and other leafy green/orange-yellow veggies
50
New cards
hemoglobin
pigment found in RBC in dermal blood vessels
51
New cards
cyanosis
bluish color of skin due to poor 02 in blood
52
New cards
redness/erythema
indicators of embarrassment, fever, hypertension, or allergy reaction
53
New cards
Pallor (blanching)
certain emotional stress can cause paleness, or signify anemia, low BP, or impaired blood flow to area
54
New cards
Jaundice (yellow cast)
abnormal yellow skin tone caused by liver disorder where yellow bile pigments build up in blood and goes into the tissue
55
New cards
Bruises
reveals sights where blood has escaped circulation and clotted in tissue spaces, clotted masses known as hematomas
56
New cards
4 appendages of skin
sweat glands, oil glands, hair and fair follicles, nails
57
New cards
cutaneous glands
all exocrine, found in dermis
58
New cards
2 types of cutaneous glands
oil glands (sebaceous) and sweat glands (sudoriferous)
59
New cards
sebaceous (oil) glands
found everywhere except for palms and soles, secretes sebum substance
60
New cards
sebum (oil)
a mix of oil and cell fragments
61
New cards
sebum functions
soften/lubricates hair and skin, prevents brittle hair, impedes water loss from skin, acts as bacteria killing agent.
62
New cards
Sweat (sudoriferous) glands
everywhere on skin except for nipples and some external genitalia parts, over 2.5 million sweat glands per person
63
New cards
2 types of sweat glands
eccrine and apocrine
64
New cards
eccrine glands
produce sweat, which is 99% water and the rest are salts, vitamin c, metabolic wastes, and lactic acid, found all over the body, helps with body heat regulation, and secretes sweat when in a hot environment or internal temp it high
65
New cards
appocrine glands
mostly in axillary and genital areas, larger than eccrine glands and empty into hair follicles, secrete true sweat, fatty acids and proteins. Secretion is odorless until skin bacteria decomposes protein and fatty acids causing BO (stinky odor)
66
New cards
hair and hair follicles minor protective functions
prevents head trauma, eyelashes shields eyes, nose hair keeps dust/particles out of upper respiratory tract
67
New cards
structure of hair
flexible, produced by hair follicles with hard, fused keratinized epithelial cells
68
New cards
2 regions of hair
shaft and root
69
New cards
hair shaft
projects from skin
70
New cards
hair root
impeded in skin
71
New cards
Hair bulb matrix
well nourished epithelial cells where mitosis occurs allowing hair growth
72
New cards
hair color/pigment
comes from hair melanocytes and varies from different melanin types to create hair color
73
New cards
hair texture
determined by hair shaft shape
74
New cards
flat and ribbon like hair shaft
kinky hair
75
New cards
oval hair shaft
wavy hair
76
New cards
perfectly round hair shaft
straight hair
77
New cards
hair follicle layer
inner epidermal sheath and outer dermal sheath
78
New cards
hair follicles
2 distinct layers, papillae gives blood to matrix, is slanted
79
New cards
arrector pili muscle
small, smooth muscle cells that connect hair follicle to dermal issue, when contracted it pulls follicle into upright position, dimpling skin and creates goosebumps
80
New cards
Distribution/growth of hair
scattered everywhere but lips, nipples, parts of external genitalia, and thick skin area
81
New cards
nails
Scale like modifications of the epidermis, provides clear and protective covering on distal parts of fingers/toes, appears pink because of rich capillary beds in dermis
82
New cards
]free edge, body, root, nail folds, eponychium (cuticle), root
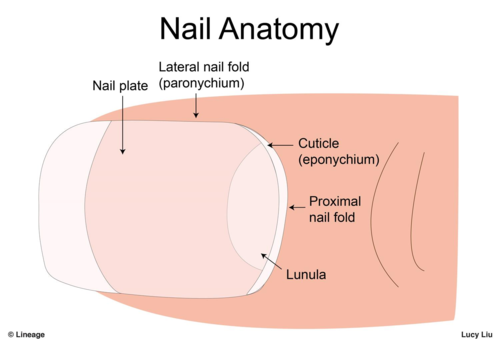
83
New cards
Homeostatic Imbalances of Skin
most common come from allergies, bacteria, viral or fungal infections, less common and more damaging are burns and skin cancer
84
New cards
athlete's foot (tinea pedis)
itchy, red, peeling condition of the skin between the toes, resulting from fungal infection
85
New cards
boils and carbuncles
inflammation of hair follicles and sebaceous glands on neck
86
New cards
cold sores (fever blisters)
Fluid filled blisters that itch and sting caused by herpes simplex infection, localized in cutaneous nerve and is dormant until activation by upset, fever, or UV radiation, occurs around lips and in mouth
87
New cards
contact dermatitis
itching, redness, and swelling of skin leading to blisters, caused by skin exposure to chemicals provoking allergic responses
88
New cards
impetigo
pink, water-filled, raised lesions that develop a yellow crust and eventually rupture, caused by highly contagious staph infection
89
New cards
psoriasis
chronic condition characterized by reddened epidermal lesions covered with dry, silvery scales, cause is unknown
90
New cards
burns
tissue damage and cell death caused by heat, electricity, UV radiation, or chemicals
91
New cards
2 life threatening problems with burns
1. loss of body fluids (dehydration)
2. microbial infections
2. microbial infections
92
New cards
Dehydration
leads to electrolyte imbalance causing shutdown of kidneys and circulatory sock
93
New cards
microbial infections
bacteria and fungi multiply rapidly on dead tissues and immune system becomes depressed within 1-2 days after severe burn
94
New cards
1st degree burn
only epidermis is damaged, area is red and swollen, heals within 2-3 days, ex. sunburn (classified as partial-thickness burns)
95
New cards
2nd degree burn
epidermis and upper dermis is damaged, skin is red, painful and has blisters, epithelium can regrow (classified as partial-thickness burns)
96
New cards
3rd degree burn
entire thickness of the skin is damaged, burned areas is blanched or blackened, not painful due to nerve endings being destroyed, regeneration isn't possible and requires skin grafts. (classified as full-thickness burns)
97
New cards
burns considered critical if
- Over 25% of body has 2nd degree burns
- Over 10% of body has 3rd degree burns
- There are 3rd degree burns on face, hands or feet
- Over 10% of body has 3rd degree burns
- There are 3rd degree burns on face, hands or feet
98
New cards
Facial burns are extremely dangerous because
Respiratory passages could swell cause breathing problems
99
New cards
rules of nines
indirectly estimated volume of fluid loss by determining total body surface burned
100
New cards
skin cancer
most skin tumors are benign and don't spread, some are malignant and do spread, is the most common type of cancer in humans, cause is unknown but risk factor is overexposure to UV rays.