BIOCHEM 410
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Metabolism
-the sum of all of the chemical reactions occurring in the cell
-the overall processes by which living things acquire and utilize free energy in the cell
-living organisms need a continuous influx of energy to battle entropy (disorder)
-Metabolism requires tightly coordinated cellular activity
Metabolism Pathways
-Enzymes are the basic units of metabolism
-The substrates of these enzymes are called metabolites
-A metabolic pathway is a series of connected enzymatic reactions that produces a specific product
-Metabolic pathway consist of sequential steps
4 Functions of Metabolism
-Obtain free energy for the cell
-Degrade macromolecules as required for biological function
-Convert nutrients into macromolecules
-Assemble macromolecules into cellular structures
Catabolism
Catabolism —> degradative pathways
produces free energy
Oxidative
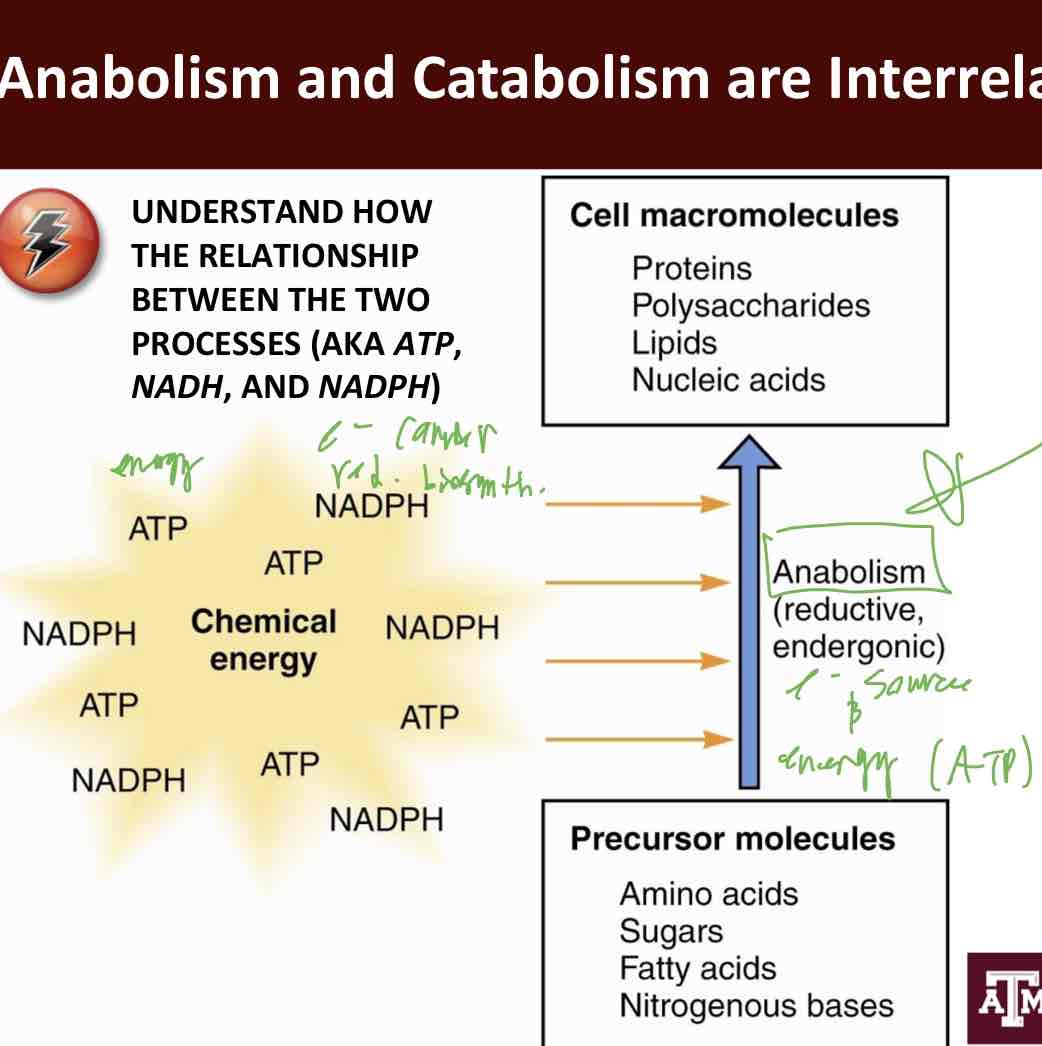
Anabolism
Metabolism—> biosynthetic pathway
consumes free energy
Reductive
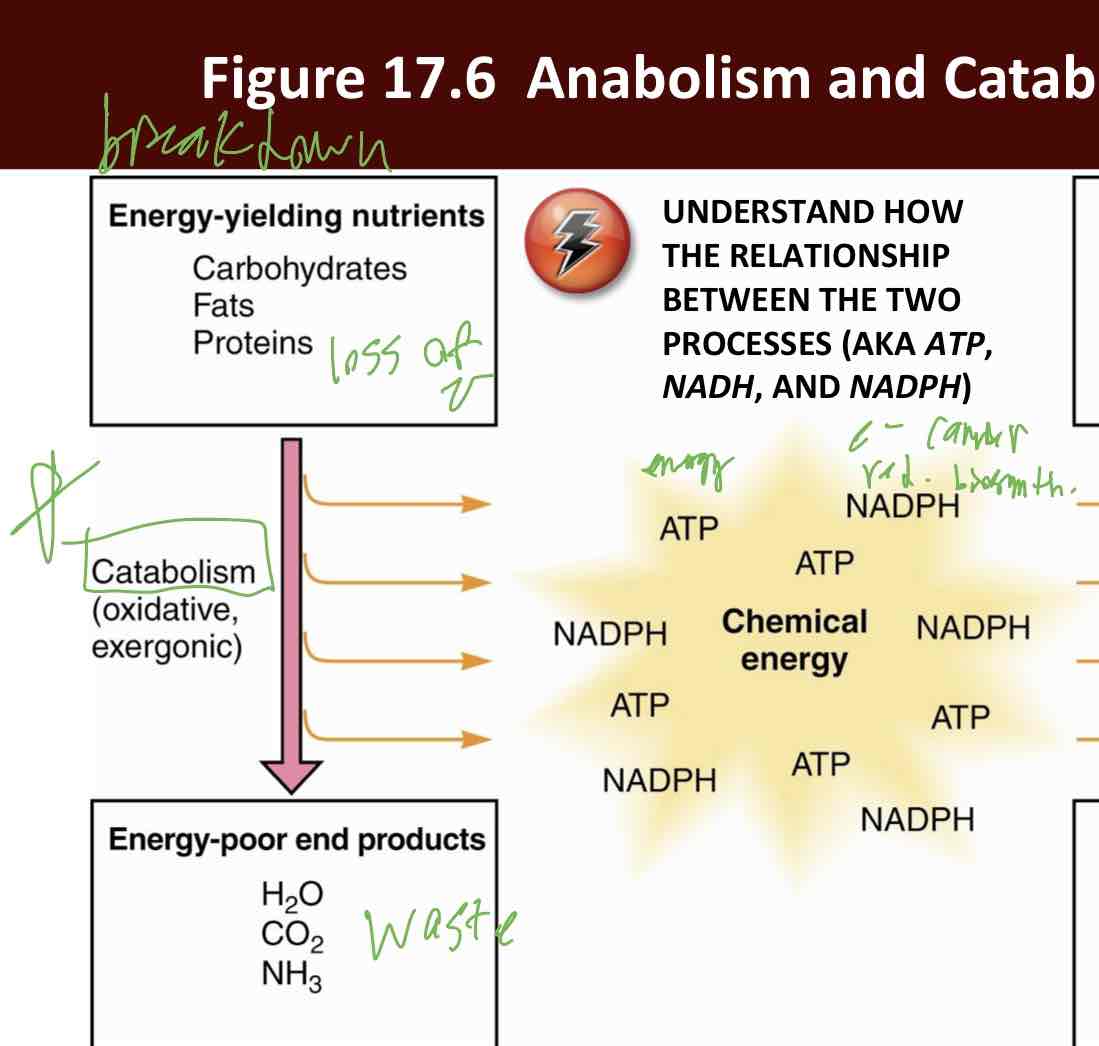
Energy-yielding nutrients
Carbohydrates
Fats
Proteins
Energy poor end products
H2O
CO2
NH3
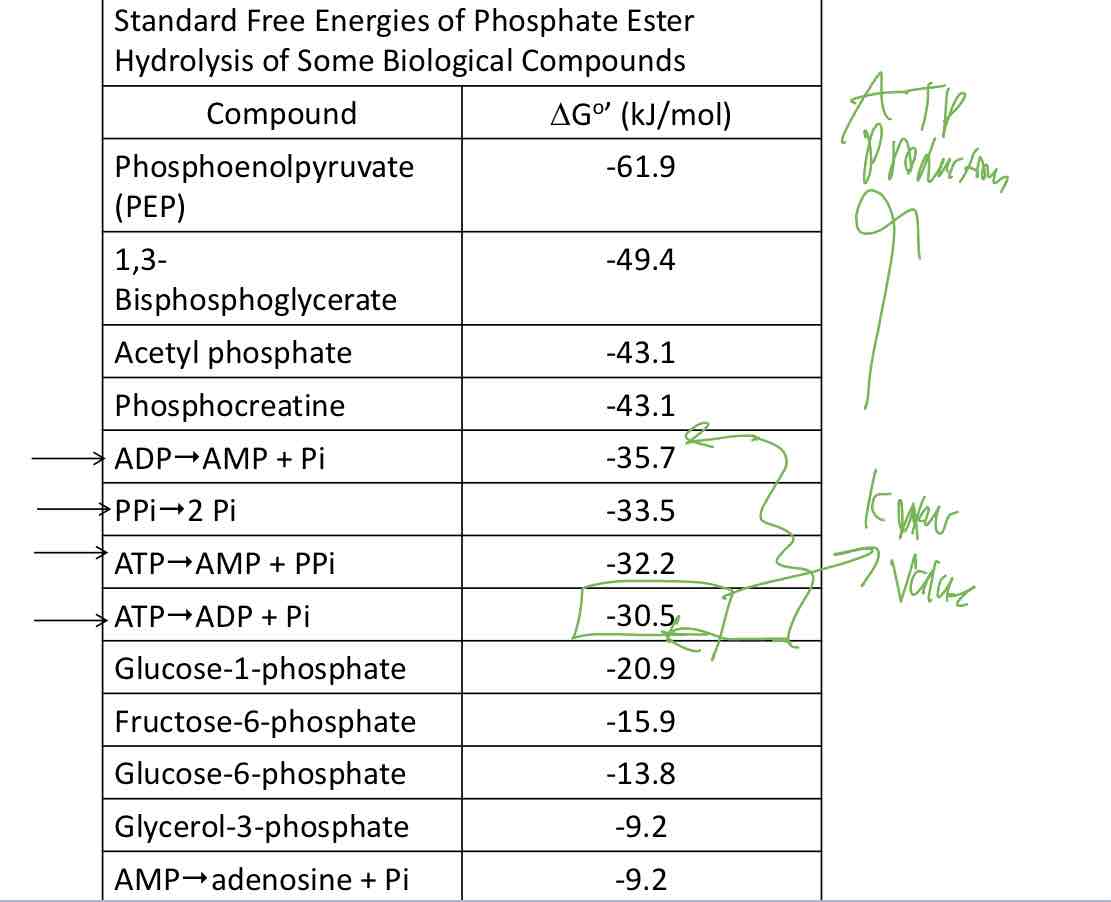
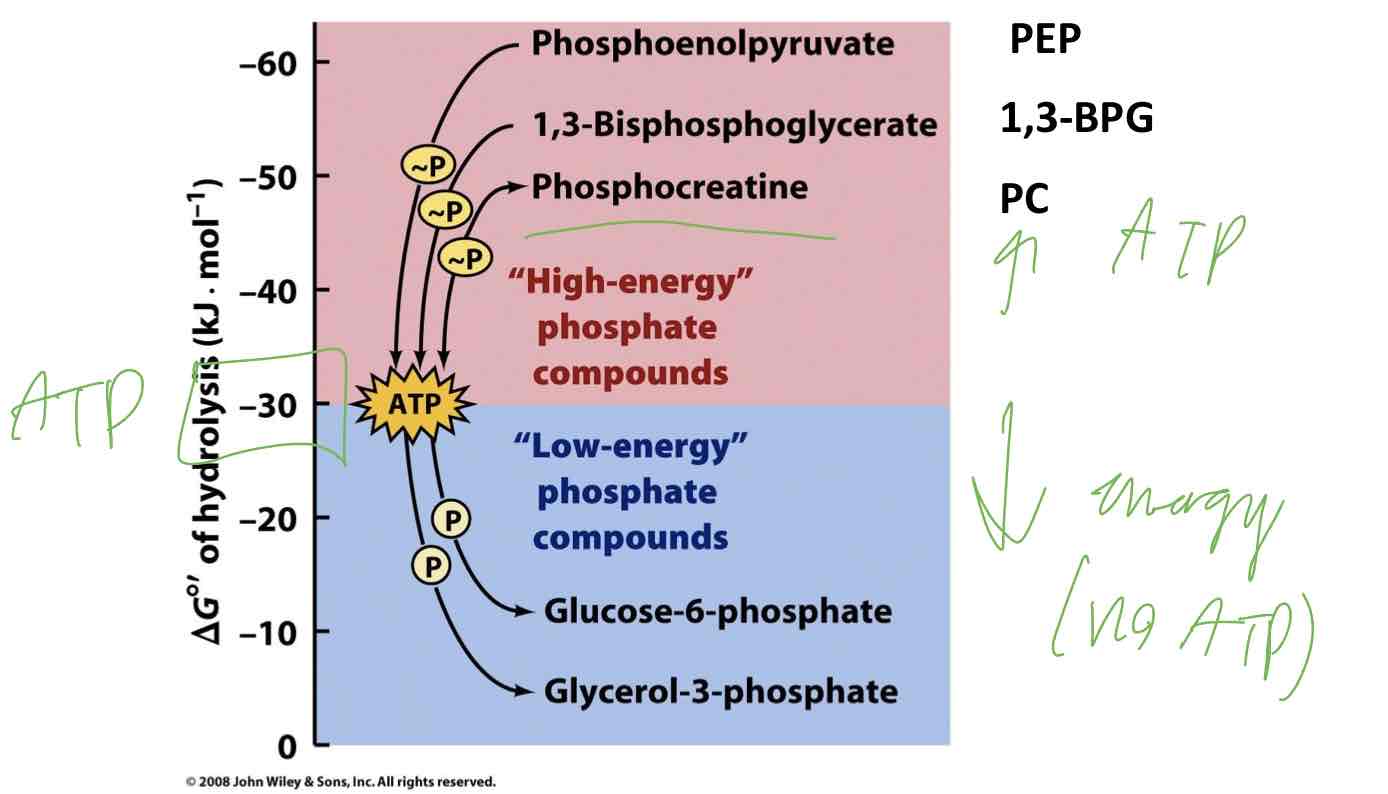
Free energy value of ATP
-30 — -35
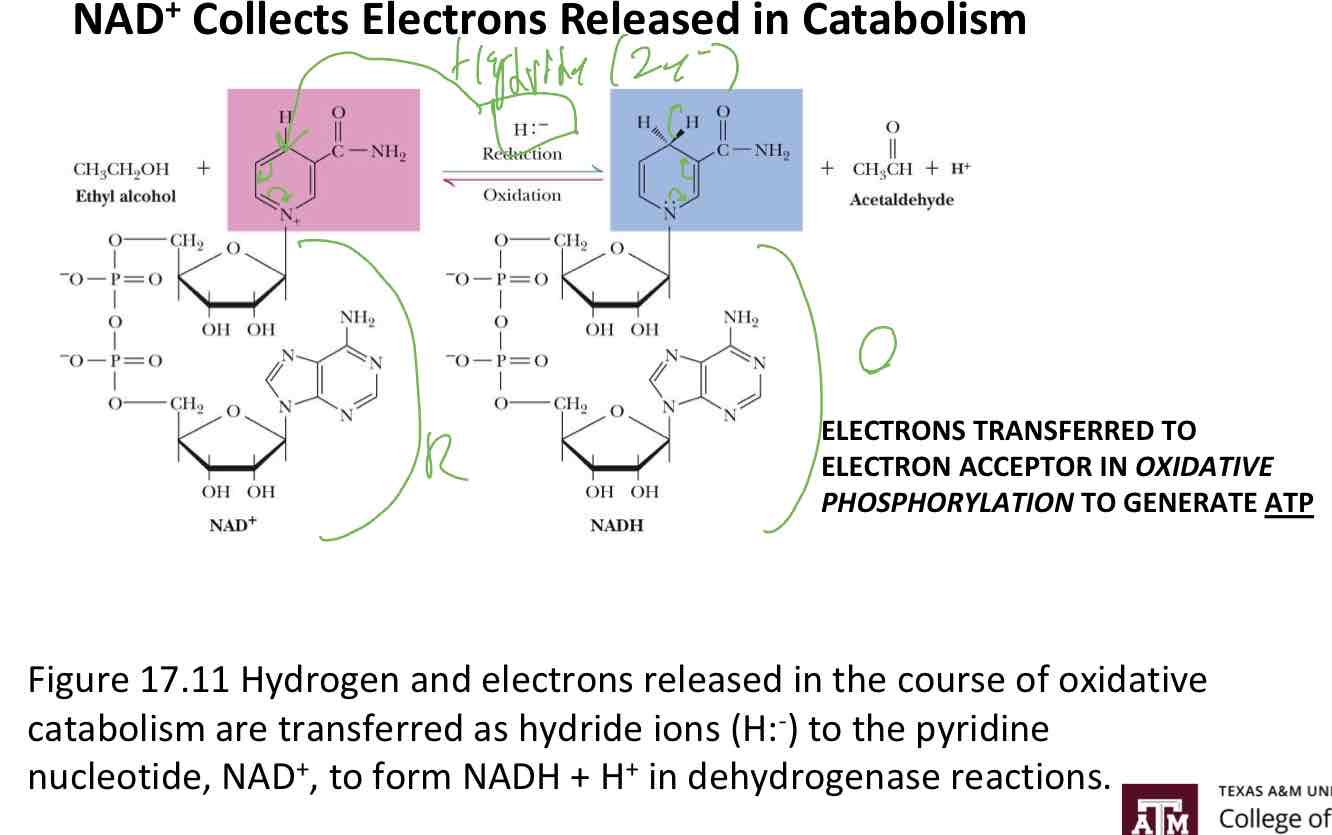
NAD+ Collects Electrons Released in Catabolism
Electrons transferred to electron acceptor in oxidative phosphorylation to generate ATP
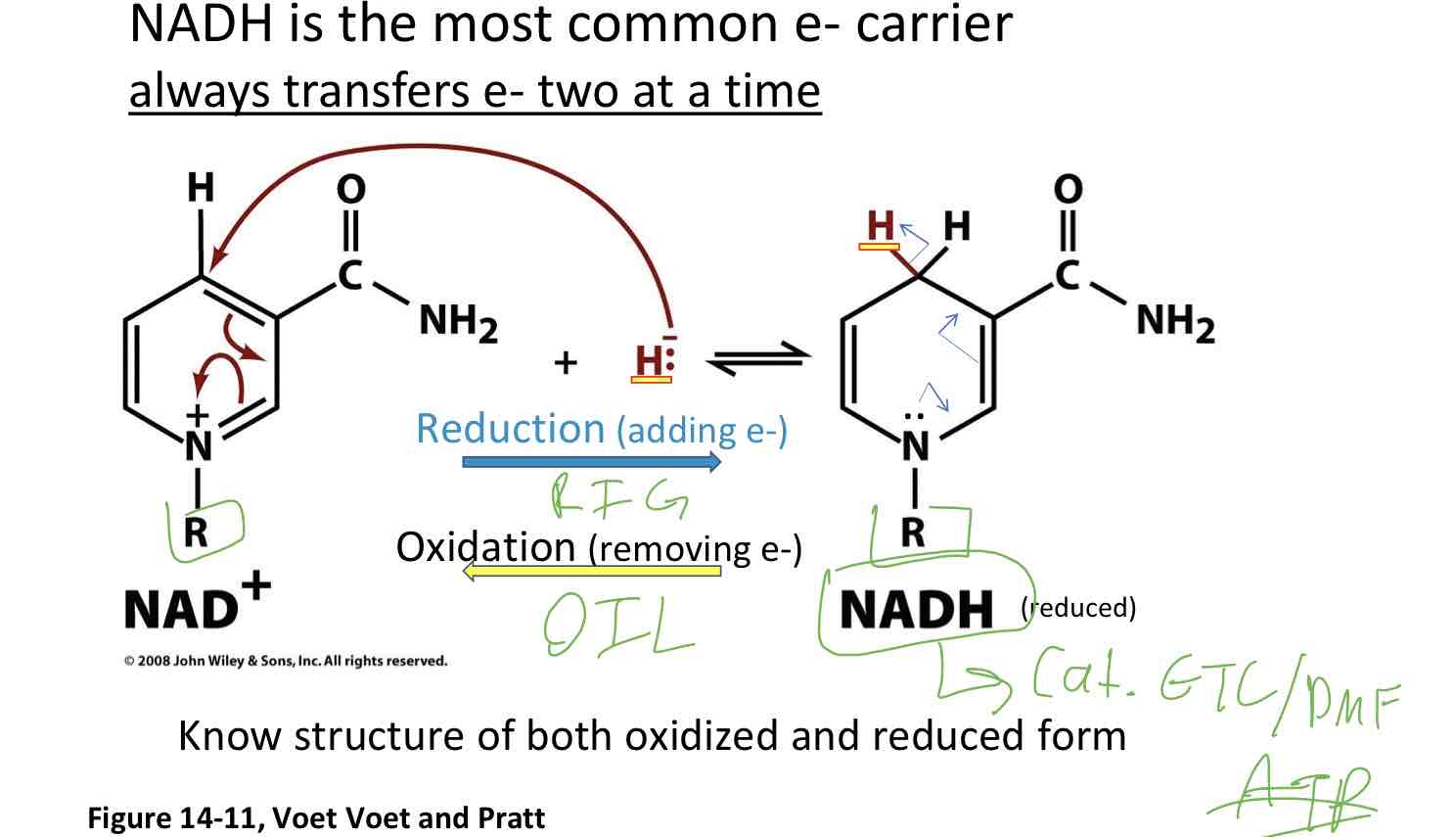
NADH is the most common e- carrier
Always transfers e- two at a time
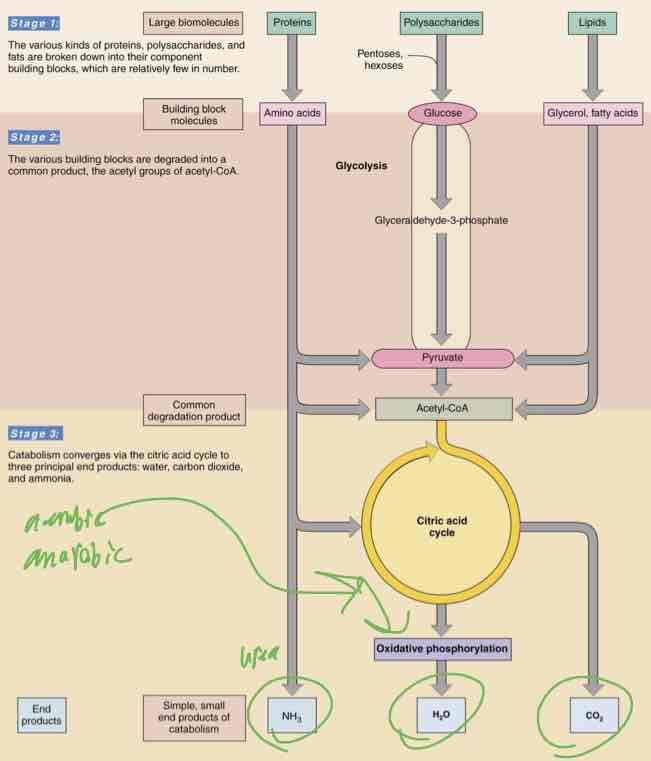
Two Ways to Manage Catabolism and Anabolism
Cell maintains tight and separate regulation of catabolism and anabolism so metabolic needs can be met
Metabolic pathways are localized within different cellular compartments (compartmentalization)
Comparing Pathways
Anabolic and catabolic pathways involving the same product are not the same
Some steps may be common to both (reversible enzymes)
Others must be different- to ensure that each pathway is spontaneous/aerodynamically favorable ( unique enzymes)
This also allows regulatory mechanisms to turn one pathway on and the other off ( activate/deactivate)
Biosynthetic enzymes
Operate as part of anabolic pathways (reductive biosynthesis)
Degradative enzymes
Operate as part of catabolic pathways (oxidative degradation)
Vitamins are organic molecules acquired through diet that assist metabolic reactions
Water-soluble vitamins- almost always con erred to coenzymes
Fat soluble vitamins- A, D, E, and K are stored for longer periods of time
Metabolic pathways are controlled by…
Thermodynamics
Compartmentalization
Metabolic flux
Metabolic pathways must collectively operate as a process of supply and demand
Metabolic Flux - regulation of key enzymes
Allosteric control- positive (R state) and negative regulators (T state), also known as allosteric effectors
Covalent modification- addition of a chemical group that enhances or diminishes enzyme function (ex. Phosphorylation)
Substrate cycles - control of flux through a pathway by enhancing rates while diminishing those rates in opposition
Genetic control- control of levels of enzyme biosynthesis (availability)
Important Molecules
Remember with the cell it is always about energy
ATP or equivalent molecules are used to power endergonic processes
ATP must be biosynthesized
Compounds that have high phosphoryl group transfer potentials are particularly important in the biosynthesis of ATP
These high-energy phosphate compounds are coupled to biosynthesis of ATP (ie. Thioester bonds)
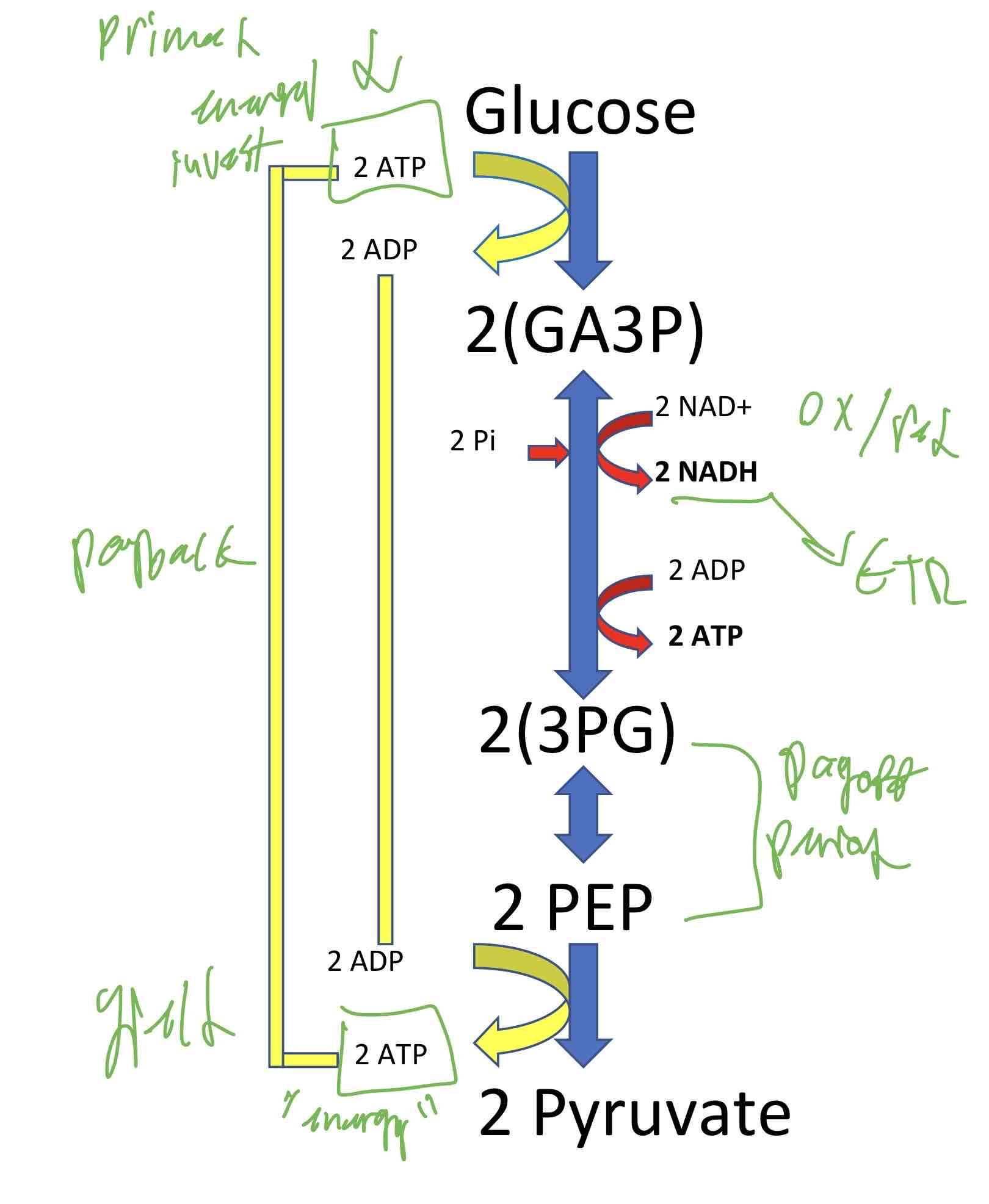
Glycolysis Phases
The first phase consumes 2 molecules of ATP (Investment)
The second phase produces 4 molecules of ATP ( 2 payback and 2 yield)
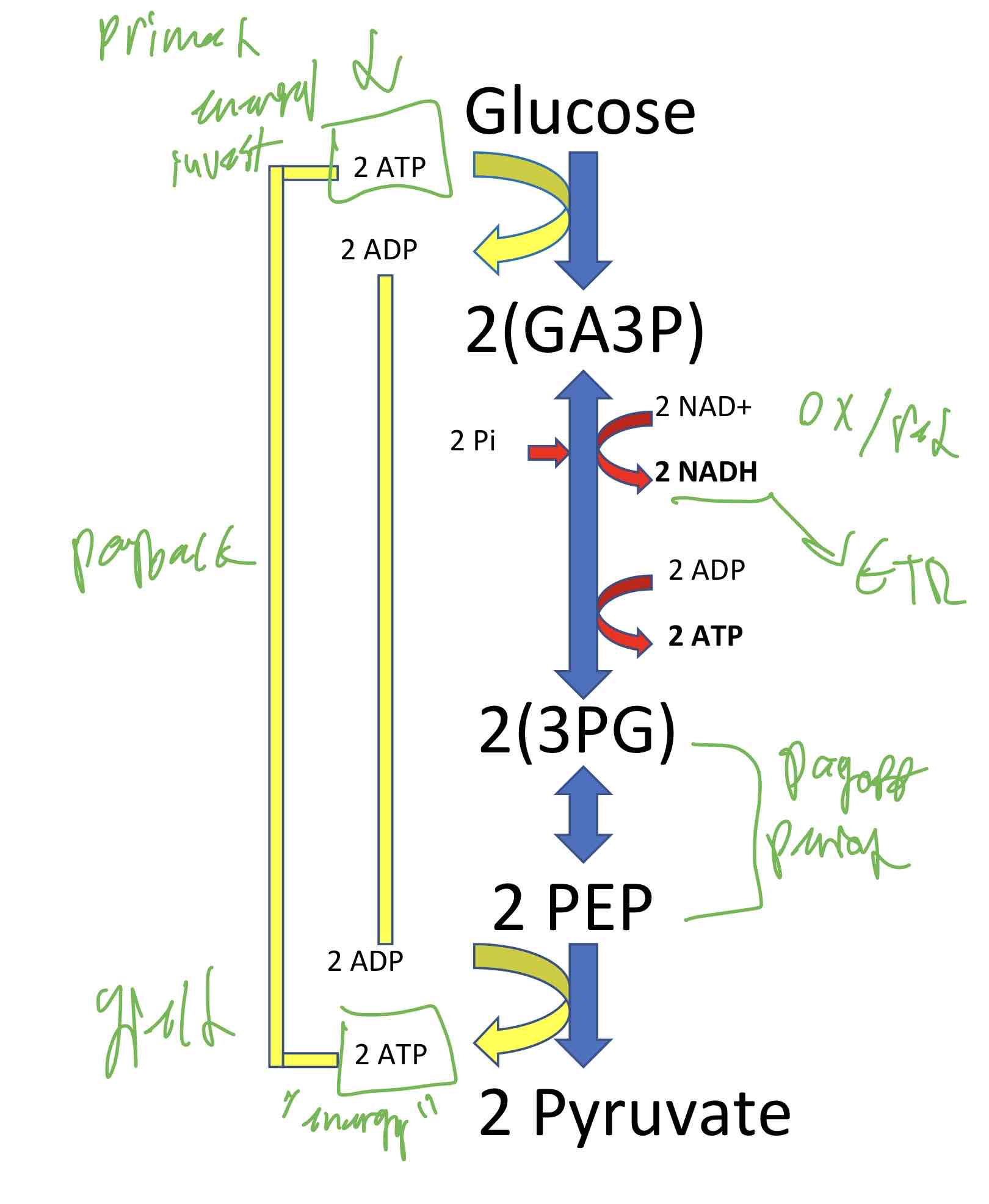
Glycolysis Overview

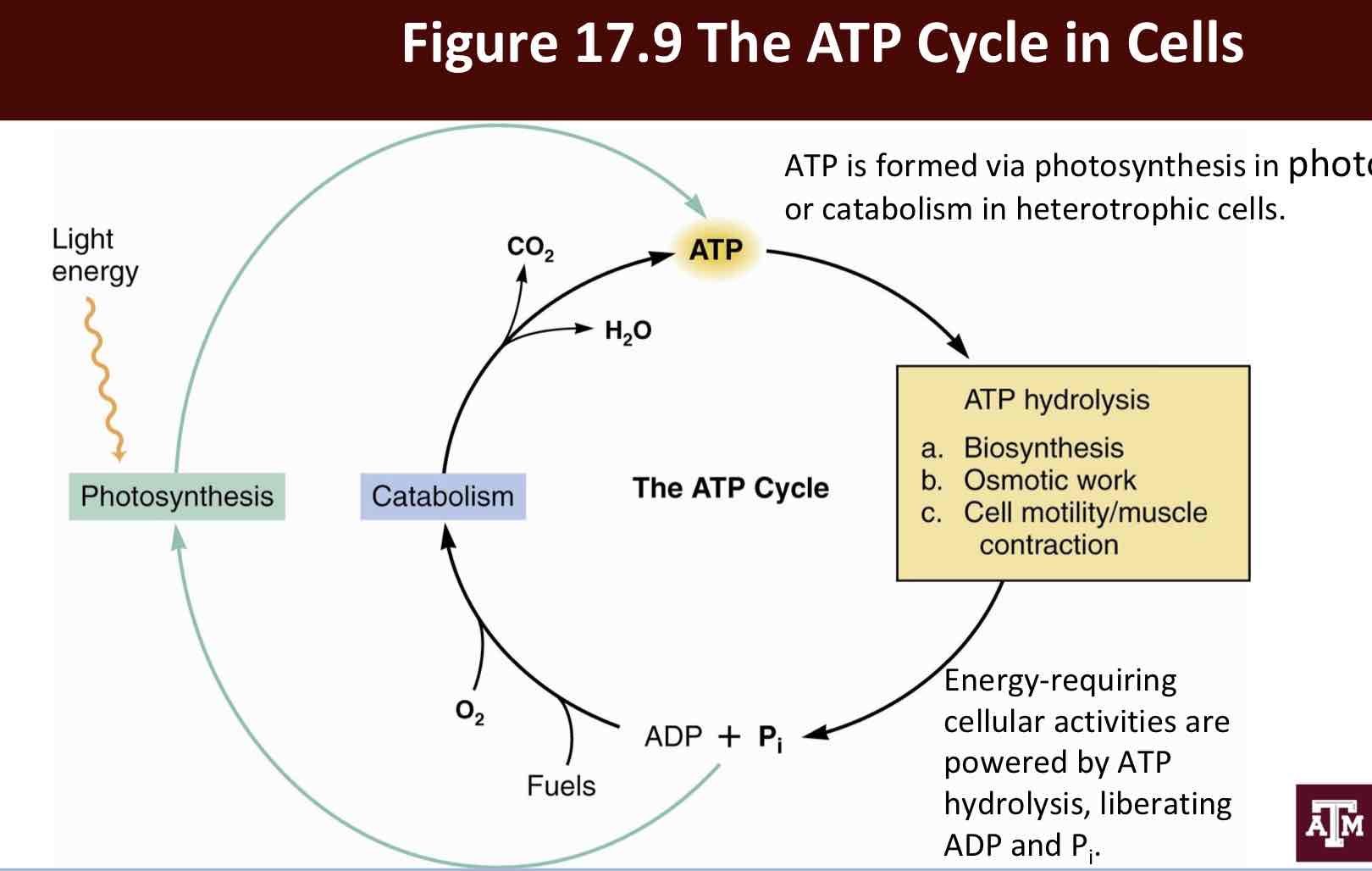
ATP Cycle
ATP Structure
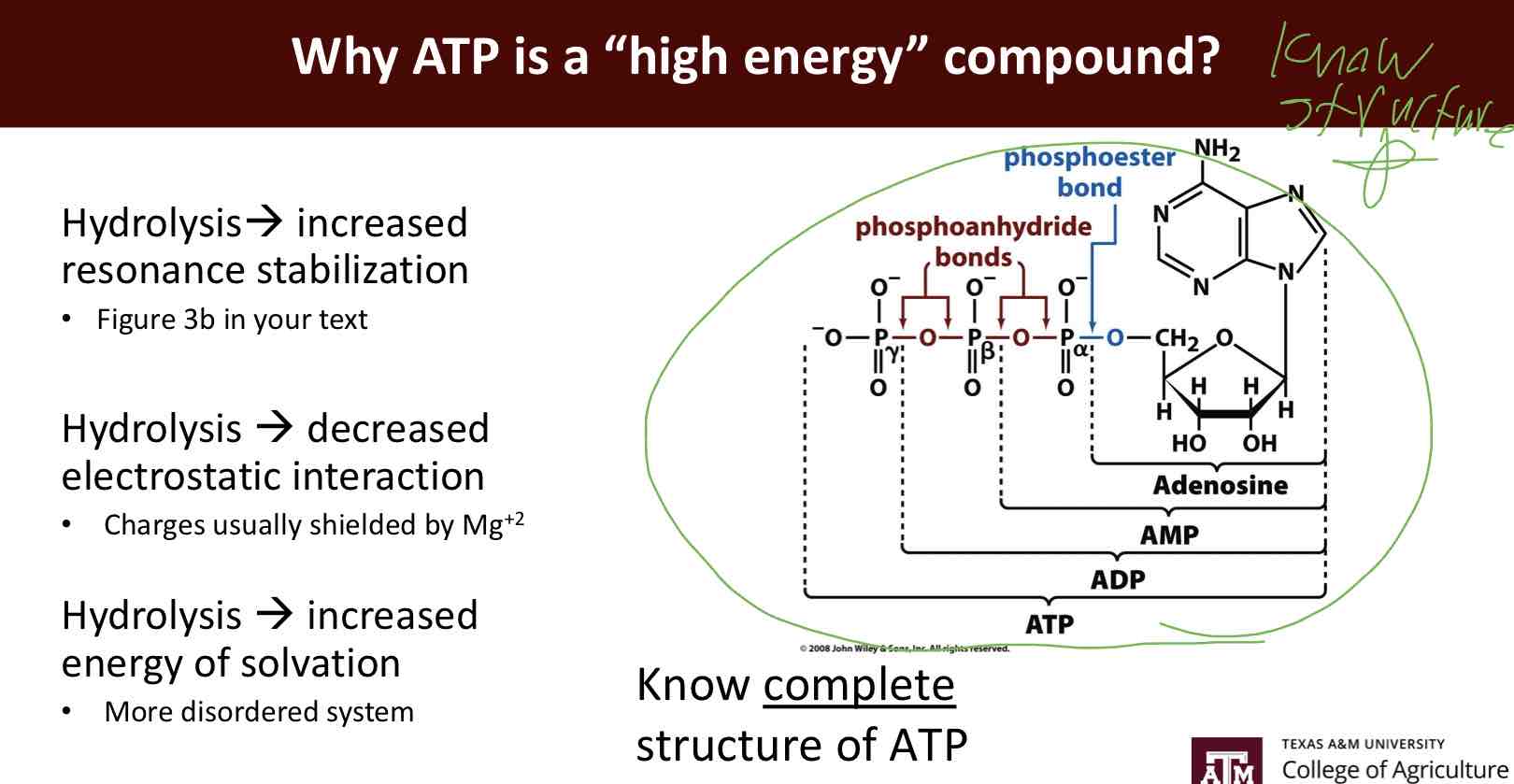
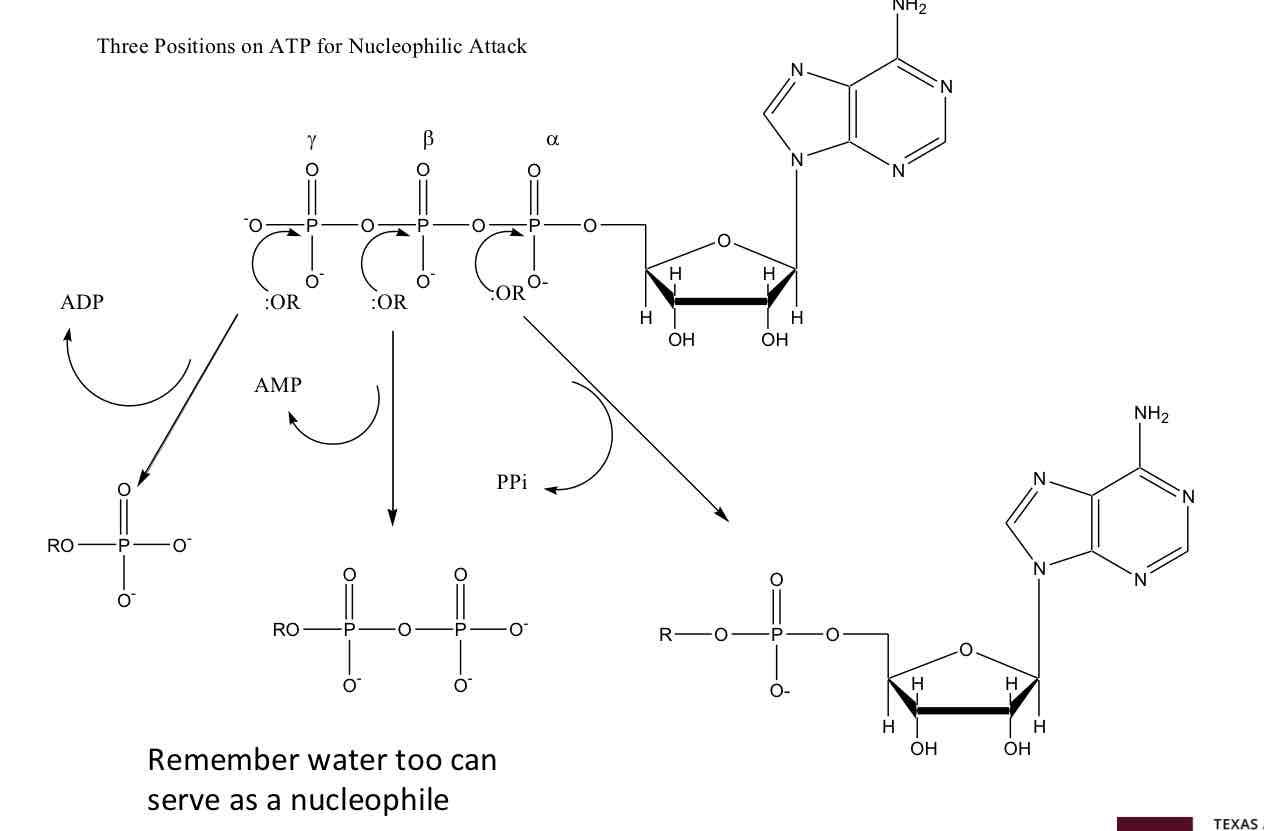
ATP with Nucleophilic attacks
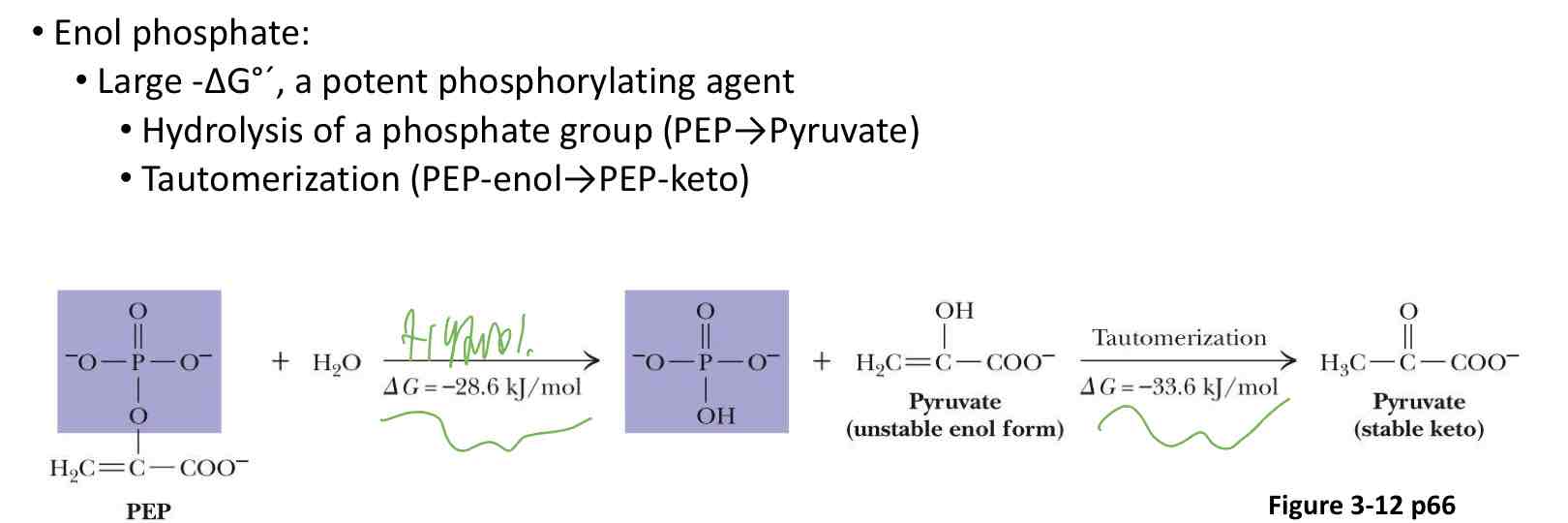
What PEP is such a high-energy intermediate
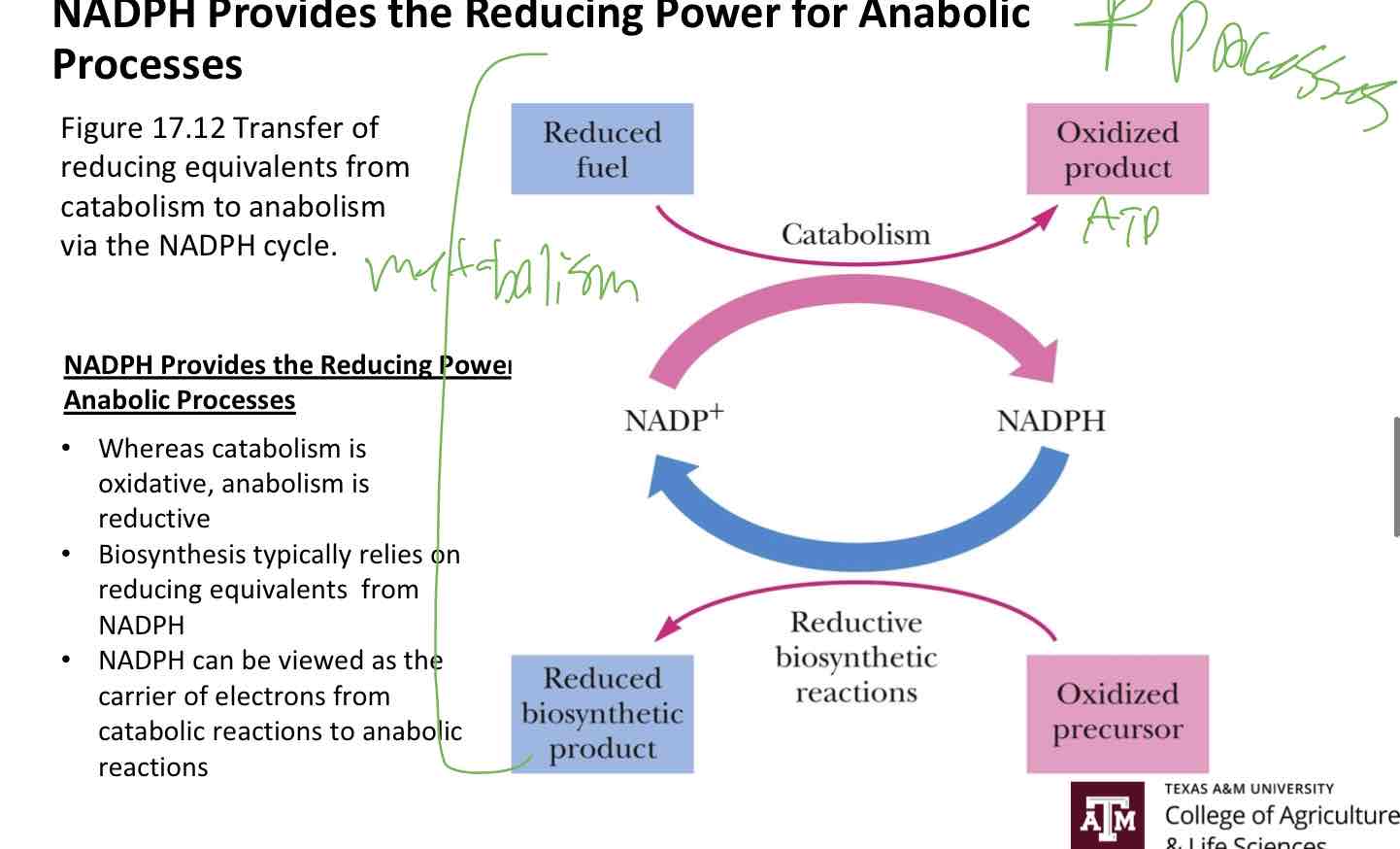
NADPH Processes
Free Energy of hydrolysis
High energy phosphate compounds = ATP
Low-energy phosphate compounds = No ATP