G&E MCQs
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
In a test cross examining two genes of interest, I obtained 3000 offspring.
Of these, 2850 were parental type and 150 were recombinant. What is the genetic distance between the two genes?
a. 0.2 centimorgans
b. 0.5 centimorgans
c. 2 centimorgans
d. 5 centimorgans
e. 20 centimorgans
D.
The genetic distance between two genes can be calculated using the formula: (Number of recombinant offspring / Total offspring) x 100. In this case, it would be (150 / 3000) x 100 = 5%.
Genetic distance is measured in map units or centimorgans (cM), where 1% recombination frequency equals 1 cM.
Given two genes that are 8cM apart, if I plant 2000 seeds, how many recombinant offspring do I expect to obtain?
a. 8
b. 16
c. 160
d. 250
e. 800
C.
Expected recombinant offspring = 8% of 2000 = 160.
Men have only one X chromosome, while women have two. We say that males are …………….. for the X chromosome. [fill in the blank]
a.Homozygous
b.Dominant
c.Heterozygous
d.Hemizygous
e.Recessive
d. hemizygous
In a test cross examining two genes of interest, I obtained 2000 offspring.
Of these, 1960 were parental type and 40 were recombinant.
What is the genetic distance between the two genes?
a.0.02 centimorgans
b.0.2 centimorgans
c.2 centimorgans
d.20 centimorgans
e.200 centimorgans
c.
(Number of recombinant offspring / Total offspring) x 100. In this case, it would be (40 / 2000) x 100 = 2%.
The mallorn tree has bark that may be either smooth and grey, or rough and brown. These traits are are affected by two linked genes on chromosome 7. The Lothlorien variety has smooth grey bark, while the Mirkwood variety has rough brown bark. I have set up a back cross experiment to measure the distance between the two genes concerned. Out of 3000 seedlings, I observed:
1555 with smooth grey bark
1385 with rough brown bark
35 with rough grey bark
25 with smooth brown bark
What is the genetic distance between the two genes?
a.1 centimorgan
b.2 centimorgans
c.5 centimorgans
d.8 centimorgans
e.30 centimorgans
c. (Number of recombinant offspring / Total offspring) x 100. In this case, it would be (60 / 3000) x 100 = 2%. The genetic distance is therefore 2%.
In a family where the father is colourblind, and the mother is a carrier for colourblindness, which of the following is true of their children?
a.On average, more boys will be colourblind than girls
b.All boys will be either carriers or affected
c.All boys will be colourblind
d.No girls will be colourblind
e.On average, 50% of all children will be colourblind regardless of sex
e.
Which of the following statements best explains why modification or change in an organ or tissue during the lifetime of an individual is not inherited?
a.Characteristics acquired during an organism's life are generally not passed on through genes.
b.Spontaneous mutations can result in the appearance of new traits.
c.Only favourable adaptations have survival value.
d.Disuse of an organ may lead to its eventual disappearance.
e.The question is misleading, since modification or change in an organ or tissue during lifetime can be inherited
a. Characteristics acquired during an organism's life are generally not passed on through genes.
DDT was once considered a "silver bullet" that would permanently eradicate insect pests. Instead, DDT is largely useless against many insects. Which of these would have prevented this evolution of DDT resistance in insect pests?
a.All habitats should have received applications of DDT at about the same time.
b.The frequency of DDT application should have been higher.
c.None of the insect pests would have genetic variations that resulted in DDT resistance.
d.DDT application should have been continual.
e.The concentration of DDT would have to be increased over time
c. None of the insect pests would have genetic variations that resulted in DDT resistance.
I have a female tortoiseshell cat with mackerel tabby stripes. Before she was neutered, she had a litter of four kittens as follows:
1 ginger male with classic tabby stripes
1 black male with no stripes (abyssinian pattern)
1 tortoiseshell female with mackerel tabby stripes
1 ginger female with no stripes (abyssinian pattern)
What colour was the father?
a.Black male with no stripes (abyssinian pattern)
b.Ginger male with classic tabby stripes
c.Black male with mackerel tabby stripes
d.Ginger male with no stripes (abyssinian pattern)
e.Tortoiseshell male with mackerel tabby stripes
d.
In Draenor womp-rats, fur coloration is affected by a gene with two alleles S and s. S is a dominant “spotty” allele that leads to the formation of white spots of unpigmented fur. S shows complete penetrance for spotting on the chest and back, and low penetrance for spotting on the legs. In an F1 cross between an S / s male and an S / s female, which of the following statements is FALSE?
a.Less than 75% of the offspring will have spotty legs
b.Both parents will have spotted chests
c.25% of the offspring will be completely unspotted
d.Some individuals may have spotty chests but non-spotty legs
e.Some individuals may have spotty legs but non-spotty chests
e.
Which of the following processes is an early step in the whole-genome shotgun approach to sequencing?
a.break genomic DNA at random sites
b.map the position of cloned DNA fragments
c.randomly select DNA primers and hybridise these to random positions of chromosomes in preparation for sequencing
d.run an agarose gel
e.add the nucleotide A
a.
In parts of India where malarial infection is common, the sickle-cell allele constitutes 10% of the β hemoglobin alleles in the human gene pool. If the sickle-cell allele is recessive, what proportion of the population should be susceptible to sickle-cell anemia under typical conditions?
a.0.01
b.0.10
c.0.18
d.0.36
e.0.81
a
If, on average, 42% of the loci in a species' gene pool are heterozygous, then the average homozygosity of the species should be
a.21%
b.100%
c.84%
d.58%
e.There is not enough information to calculate the average homozygosity
d
A large population of laboratory animals has been allowed to breed randomly for a number of generations. After several generations, 25% of the animals display a recessive trait (aa), the same percentage as at the beginning of the breeding program. The rest of the animals show the dominant phenotype, with heterozygotes indistinguishable from the homozygous dominants. What is the estimated frequency of allele A in the gene pool?
a.0.25
b.0.50
c.0.75
d.0.80
e.0.60
b
The estimated frequency of allele A in the gene pool can be calculated using the Hardy-Weinberg principle, where the frequency of the recessive phenotype (aa) is represented by q². Since 25% show the recessive trait, q² = 0.25, leading to q = 0.5. Therefore, p (frequency of allele A) is 1 - q = 0.5.
Considering the overall human population of the U.S. mainland at the time when the slave trade brought large numbers of people from equatorial Africa, what was primarily acting to change the frequency of the sickle-cell allele in the overall U.S. population?
a.natural selection
b.gene flow
c.genetic drift
d.founder effect
e.two of the responses are correct
b
Which of the following types of genes or gene families may be created by mutations that occur in one member of a gene pair that arose from gene duplication?
a.only a pseudogene
b.only a gene with a new function
c.only a gene family with two distinct but related members
d.a pseudogene, a gene with a new function, and a gene family with two distinct but related members
e.a pseudogene and a gene with a new function
d
In a Hardy-Weinberg population of a 1,000 individuals with two alleles, A and a, that are in equilibrium, the frequency of allele a is 0.1. What is the percentage of the population that is heterozygous for this allele?
a.0.2
b.2.0
c.4.0
d.18.0
e.36.0
d
2pq, where p is the frequency of allele A and q is the frequency of allele a.
Given that q is 0.1, then p would be 0.9.
Therefore, the percentage of heterozygous individuals is 2(0.9)(0.1) = 0.18, or 18% of the population.
Homeotic genes (HOX) contain a homeobox sequence that is highly conserved among very diverse species. The homeobox is the code for the domain of a protein that binds to DNA in a regulatory developmental process. Which of the following statements is therefore correct regarding homeotic genes?
a.Homeotic genes are selectively expressed as an organism develops.
b.Homeoboxes cannot be expressed in nonhomeotic genes.
c.Homeotic genes in apes and humans are very different.
d.All organisms must have homeotic genes.
e.Homeotic genes do not share a common ancestral gene
a. Homeotic genes are selectively expressed as an organism develops.
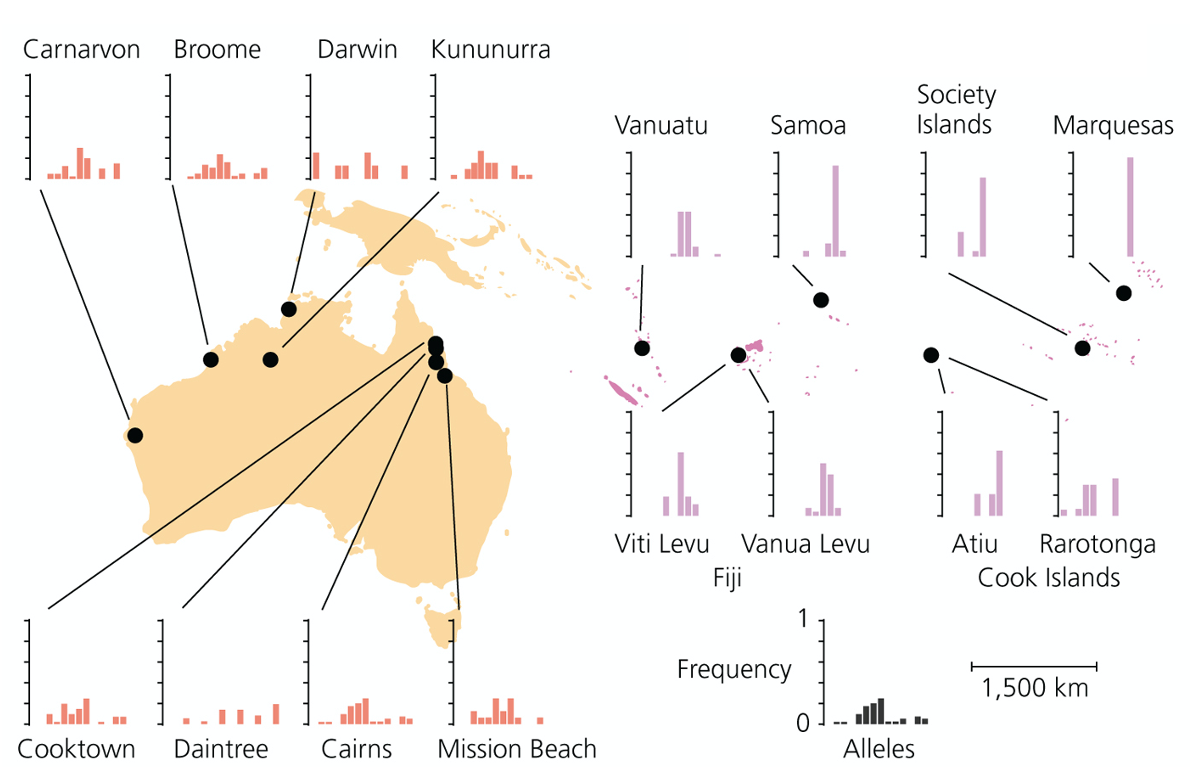
A group of researchers studied the genetic diversity of one single species of Pacific field crickets in Australia and Oceania. In the image below, the researchers plotted the frequency of alleles in a locus (graph) for each population (black dot). Populations in Australia are coloured in orange, while populations in Oceania in pink. The researchers know that the environmental conditions in all the islands in Oceania are very similar.
Looking at the graphs of the frequency of alleles in all islands, can you explain why they might have this distribution?
a.The distribution of allele frequencies in Australia is wider, while in Oceania all islands show a very narrow distribution. This can be explained by natural selection acting differently in each island of Oceania.
b.The distribution of allele frequencies in Australia is wider, while in Oceania all islands show a very narrow, but different distribution. This can be explained by founder effect, crickets could have travelled to each island independently.
c.Looking at the graphs we cannot tell the reason behind the distribution of frequencies.
d.The distribution of allele frequencies in Australia is wider, while in Oceania all islands show a very narrow distribution. This can be explained by bottleneck effect.
e.The allele frequencies are similar in all the populations, therefore, they all are in Hardy-Weinberg equilibium
b
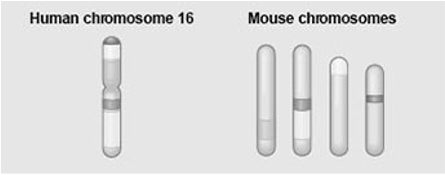
The figure shows a diagram of blocks of genes on human chromosome 16 in different shade os greys, and the locations of blocks of similar genes on four chromosomes of the mouse.
Which of the following statements describes the result of the movement of these blocks?
a.During evolutionary time, these sequences have separated and have returned to their original positions.
b.DNA sequences within these blocks have become increasingly divergent.
c.Sequences represented have duplicated at least three times.
d.Chromosomal rearrangements have moved blocks of sequences to other chromosomes.
e.Transposable elements have moved blocks of sequences to other chromosomes
d. Chromosomal rearrangements have moved blocks of sequences to other chromosomes.
Early biologists thought that the sperm contained a miniature human, which in turn contained even smaller humans inside it. What is this theory called?
a.Embryology
b.Pangenesis
c.Gemmule theory
d.Epigenesis
e.Preformation
e. Preformation
What is the Second Law of Mendelian genetics?
a.
Segregation: A zygote (fertilised embryo) has twice as many chromosomes as a gamete
b.
Independent Assortment: Males pass on some traits while females pass on different traits
c.
Dominance: When two homozygous organisms that differ in a given trait are crossed, the heterozygous offspring will display only the dominant trait
d.
Segregation: Each organism has two alleles of each gene, and one of these is passed on at random in each gamete
e.
Independent Assortment: Alleles for separate traits are inherited independently of one another
e
What is the First Law of Mendelian genetics?
a.
Segregation: Gametes have half as many chromosomes as a somatic cell from the same organism
b.
Dominance: Alleles passed on from the female parent are always recessive
c.
Dominance: When two homozygous organisms that differ in a given trait are crossed, the heterozygous offspring will display only the dominant trait
d.
Segregation: Each organism has two alleles of each gene, and one of these is passed on at random in each gamete
e.
Independent Assortment: Alleles for separate traits are inherited independently of one another
d
How did Louis Pasteur DISPROVE the theory of spontaneous generation?
a.
He showed that each parent only contributes half the genes necessary for the next generation.
b.
He showed that sterilised (boiled) media in a “swan neck” flask remained sterile until the flask was tilted to allow contaminants to enter it.
c.
He showed that transfusing blood from a white rabbit into a black rabbit does not change the colour of the black rabbit’s future offspring.
d.
He showed that incubating harmless bacteria with DNA from virulent (disease-causing) bacteria may cause the harmless bacteria to become virulent.
e.
He showed that organisms do not inherit traits acquired during their own lifetime.
b
What is the correct order of the stages of cell division?
a.
Anaphase, metaphase, telophase, prophase
b.
Telophase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase
c.
Metaphase, telophase, anaphase, prophase
d.
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
e.
Prophase, telophase, metaphase, anaphase
d
What are the key differences between meiosis and mitosis?
Question 26Select one:
a.Meiosis generates diversity and the resulting daughter cells are non-identical
b.Meiosis involves DNA damage repair while mitosis does not
c.Meiosis halves the chromosome number in the final product
d.(a) and (c) are both true
e.All of (a), (b) and (c) are true
d
Which of the following observations DISPROVES the “blending” model of inheritance?
a.
On average, offspring look similar to their parents
b.
Offspring sometimes show recessive traits (e.g. blue eyes in humans, wrinkling in peas) even if neither parent shows the trait
c.
Transfusing blood from a white rabbit into a black rabbit does not change the colour of the black rabbit’s future offspring
d.
Incubating harmless bacteria with DNA from virulent (disease-causing) bacteria will cause the harmless bacteria to become virulent
e.
Inbred animals are often less fertile than outbred animals
b
What was the importance of the Hershey/Chase experiment?
a.
It showed that DNA does not contain sulphur
b.
It showed that radioactively labelled bacteriophages are more virulent
c.
It showed that DNA contains phosphorus
d.
It showed that genes are made of both proteins and DNA
e.
It showed that bacteriophages transfer their DNA into bacteria during infection
e
Which best describes epistasis?
a.An allele that changes the genotype of another allele
b.An allele that alters the phenotypic effect of another allele at the same locus
c.A gene that alters the phenotypic effect of another gene at a different locus
d.A gene that changes the genotype of another gene
e.An allele that interacts with the environment to generate a phenotype
c
Which of the events of meiosis I is the molecular basis for Mendel’s law of independent assortment?
a.
synapsis of homologous chromosomes.
b.
polygenic inheritance of traits with multiple causative genes.
c.
random alignment of homologous chromosome pairs on the metaphase plate.
d.
the division of cells at telophase.
e.
DNA synthesis during S phase.
c