Water and Carbon cycles
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Hydrology
Study of water
Hydrosphere
Includes all liquid and frozen waters, groundwater held in soil and rock and atmosphere
Cryosphere
Water locked up as ice (surface)
Atmosphere
Water in atmosphere (in clouds and rain etc.) as mainly water vapour and ice crystals
Oceanic
Water in oceans and seas, not inland seas
Terrestrial
Consists of groundwater, soil moisture, lakes, wetlands and rivers
Water cycle
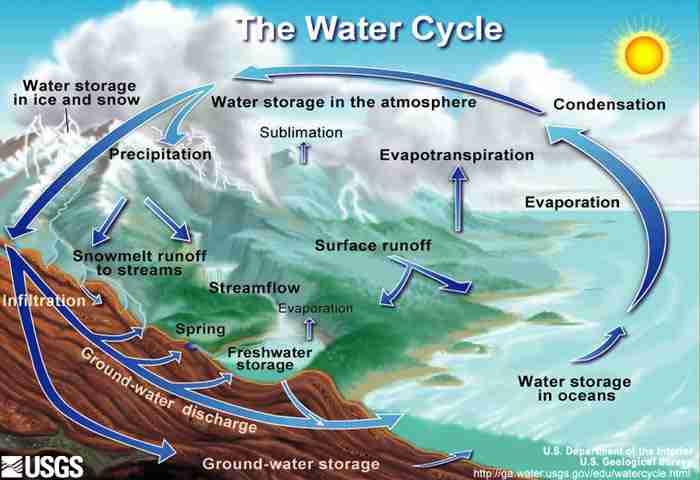
Aquifer
Storage of water below rocks
Why is the North West Sahara aquifer system so important?
It wasn’t always a desert and could be drilled into to supply water
Total global water
Oceans 97%
Freshwater 2.5%
Other saline water <1%
Total freshwater
Glaciers, ice sheets/caps 69%
Groundwater 30%
Surface/other freshwater 1%
Total surface water and other freshwater
Ground ice and permafrost 69%
Lakes 21%
Atmosphere 3%
Living things <1%
Rivers, marshes, soil water 7%
Flow/transfer
A form of linkage between one store and another, involves movement energy or mass
Input
The addition of matter and/or energy into a system
Store/component
A part of the system where energy/mass is stored or transformed
System
A set of interrelated components working together towards some kind of process
Isolated systems
No input or output
No interactions outside boundaries
Only in Labs
Closed systems
Transfers energy into and beyond boundaries
Not matter
Open system
Energy and matter can be transferred across boundary into surroundings
Dynamic equilibrium
Balance between inputs and outputs
Positive feedback
System increases or amplifys
Negative feedback
System decreases or slows
Drainage basin
An area of land that is drained by a river system and is characterised by a series of inputs, flows and outputs
The water budget
Length of channel ÷ drainage area
Fine drainage
More tributaries
Coarse drainage
Few tributaries
Trellis drainage basin
Bulb shape morphology
Linear drainage basin
Rectangular shaped morphology
Water table
Top of groundwater
Field capacity
The water not available for plant use
Soil moisture utilisation
Spring and summer, vegetation grows and uses moisture
Soil moisture surplus
Reached saturation point and more rainfall will lead to flooding
Soil moisture deficit
Reached wilting point and there is no water available for plants
Soil moisture recharge
Late autumn/winter to spring, rainfall replaces water lost from summer
Hydrograph key terms
●Discharge= level of river
●Peak rainfall=most rainfall within an hour
●peak discharge=river reaches highest point after rainfall
●lag time=rivers response time to rainfall event
●base flow=river level being fed by groundwater
●bankfall=channel is full and any more water over the line signals a flood
Subdued hydrograph
Long lag time/ slow reponse
Flashy hydrograph
Short lag time/quick response
Hydrograph
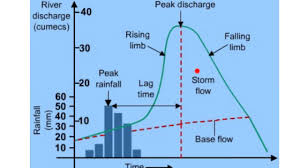
Factors affecting hydrographs
Physical
Human
Antecedent conditions
Factors affecting changes in the water cycle
Deforestation
Soil drainage
Water abstraction
Anthropogenic
CO2 made by human activity
Biosphere
Total sum of all living matter
Carbon sequestration
The capture of CO2 from either the atmosphere or anthropogenic sources before it gets released
Greenhouse gases
Any gaseous compound in the atmosphere that absorbs infrared radiation, thereby trapping heat
Important compounds of carbon
CO2
Methane CH4
Calcium carbonate
Hydrocarbons
Bio-molecules
Primary source of carbon
Earth's mantle when it was formed
Origins of carbon
●Escapes through tectonic plates and volcanic activity
●Most CO2 derives from the metamorphosism of carbonate rock that subducts with the ocean crust
●carbon is removed from long-term storage by the burial of sedimentary rock
The carbon cycle

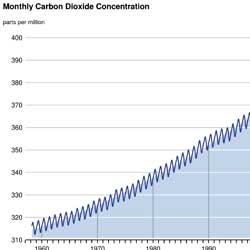
The Keeling curve
Net carbon sink
If more carbon enters something than out
Net carbon source
If more carbon leaves something than enters
Movements of carbon
Geological
Photosynthesis
Respiration
Decomposition
Evapotranspiration
Physical carbon pump
Warm tropical water goes to poles and absorbs CO2 then gets dragged along the ocean bed to equator and releases CO2
Biological carbon pump
Carbon is incorporated into Marine life as organic matter or as structural CaC - Skeletons
Dies - goes onto ocean floor - layers of carbon rich sediment
After Millions of years, you get sedimentary rocks