Cells P1
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What does the Turret do?
Rotates to bring the objectives lenses into place
Name some specialised cells
Sperm, Nerve cells
What is the function of Sperm?
To get the male DNA to the Female DNA
What is the adaption of sperm
Streamlined Head, long tail, lots if mitochondria to provide energy
What are infectious diseases caused by?
Micro-organisms
What is the equation of total magnification used?
Total Magnification Used = Eyepiece magnification x Objective lens magnification
How do you calculate magnification?
Size of image / Size of real object
What is the stage
Where the microscope slide is placed
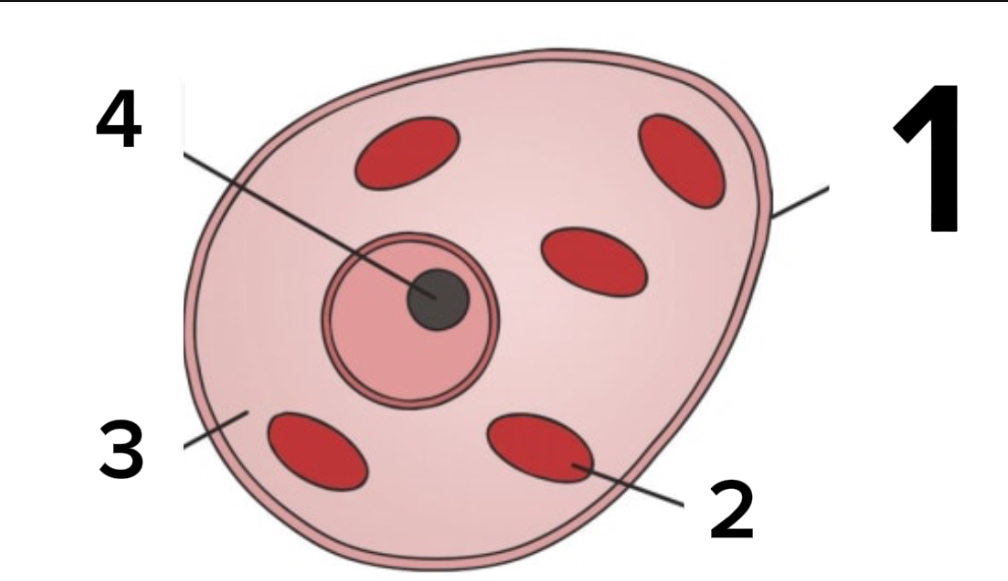
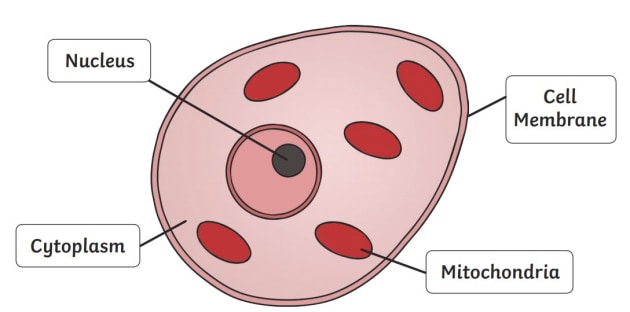
Label this diagram
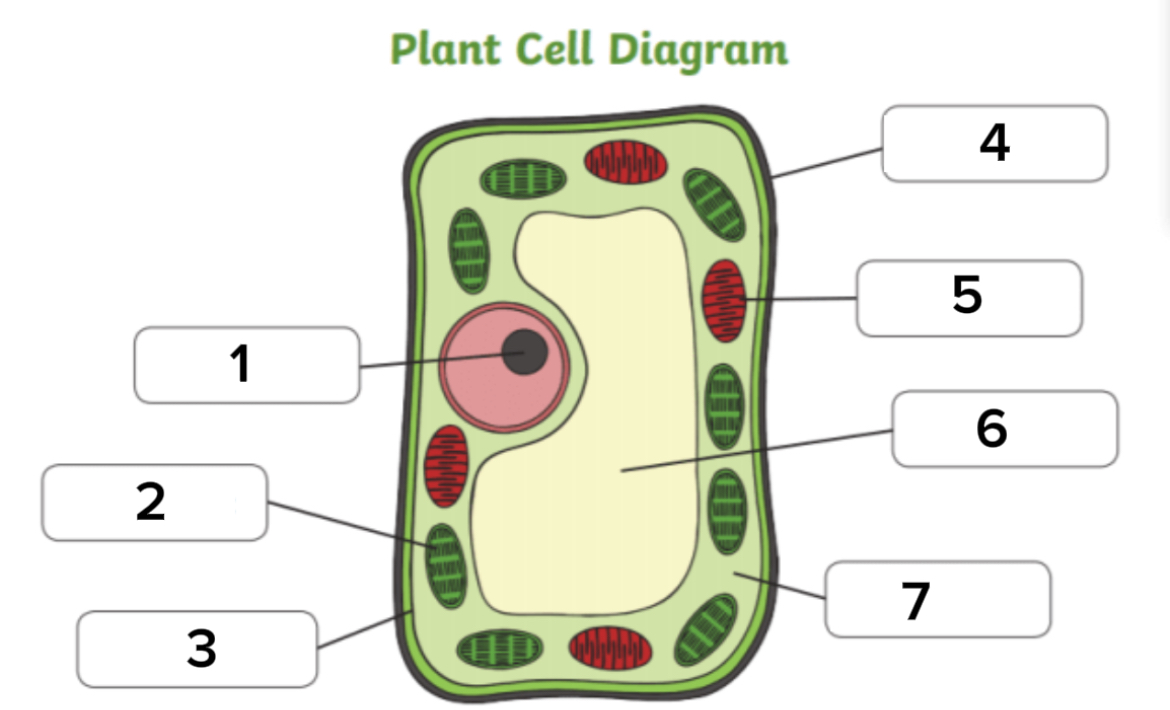
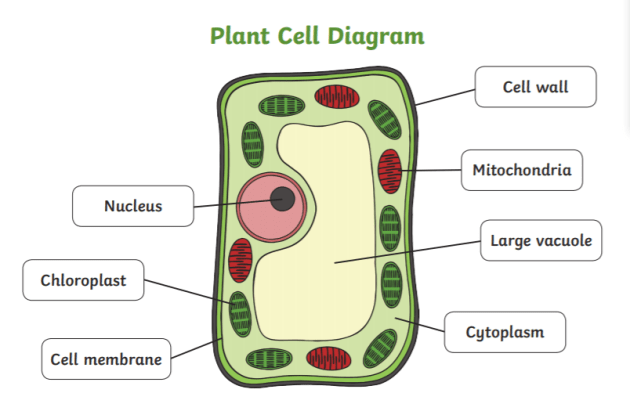
Label this diagram
What is magnification?
The number of times larger an image appears compared to the actual size.
Which lenses are the magnified image produced by?
The eyepiece lens and the objective lens
What is resolution?
The ability to distinguish 2 seperate points as distinct from eachother
Which beam and is the wavelength longer or shorter than an electron microscope in a light microscope
It has beams of light, and its wavelength is longer
Which microscope requires training?
Electron microscope
Which microscope shows colour?
Light microscope
Which microscope has a greater resolution and magnification
An electron microscope
What is an eukaryote
Any organism consisting of one or more cells that contain DNA in a membrane-bound nucleus, separate from the cytoplasm
Which cells contain a large number of organelles?
Eukaryotic cells
How do humans grow bigger?
By cells dividing
Which organelles are found in the animal cells?
Nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm, mitochondria, and ribosomes
What are the organelles in plant cells
Nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm, mitochondria, ribosomes, chloroplasts, vacuole, cell wall
What is the function of the cell membrane?
Controls what moves in and out of the cell
What is the function of the cytoplasm?
A liquid gel where many chemical reactions take place
What is the function of ribosomesV?
Its a structure where proteins are made
What is the function of chloroplasts?
Absorb light for photosynthesis
What is the function of the cell wall?
Supports the plant cell. Made of a chemical called cellulose which gives the cell strength
What is the function of the vacuole?
A bag of liquid in the plant cell. Important to keep cells rigid to give support. Contains cell sap
Which factors speed up the rate of diffusion?
Larger concentration gradient, high temperature, larger particles and larger surface area
Bigger concentration gradient = ___ rate of diffusion
Faster
How is a nerve cell adapted to its function?
Covered in fat to increase the speed of nerve impulses, branched to connect to other cells, very long to carry impulses a long way
Why is osmosis passive?
It requires no energy
What does partially-permeable membrane mean?
Selective - only lets certain particles past
What moves into plants roots?
Minerals, water and nutrients
How does water move into the root hair cell?
Osmosis
How do mineral ions move into the root hair cell?
Active transportation
What are examples of active transportation?
Glucose absorbed from the intestine into the blood, plants moving mineral ions for a healthy growth
What is the meristem?
The region at tips of roots and shoots where cell division happens
What are the 3 stages of the cell cycle?
Replication, mitosis, and division