CMS II Final: Geriatrics
1/218
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
219 Terms
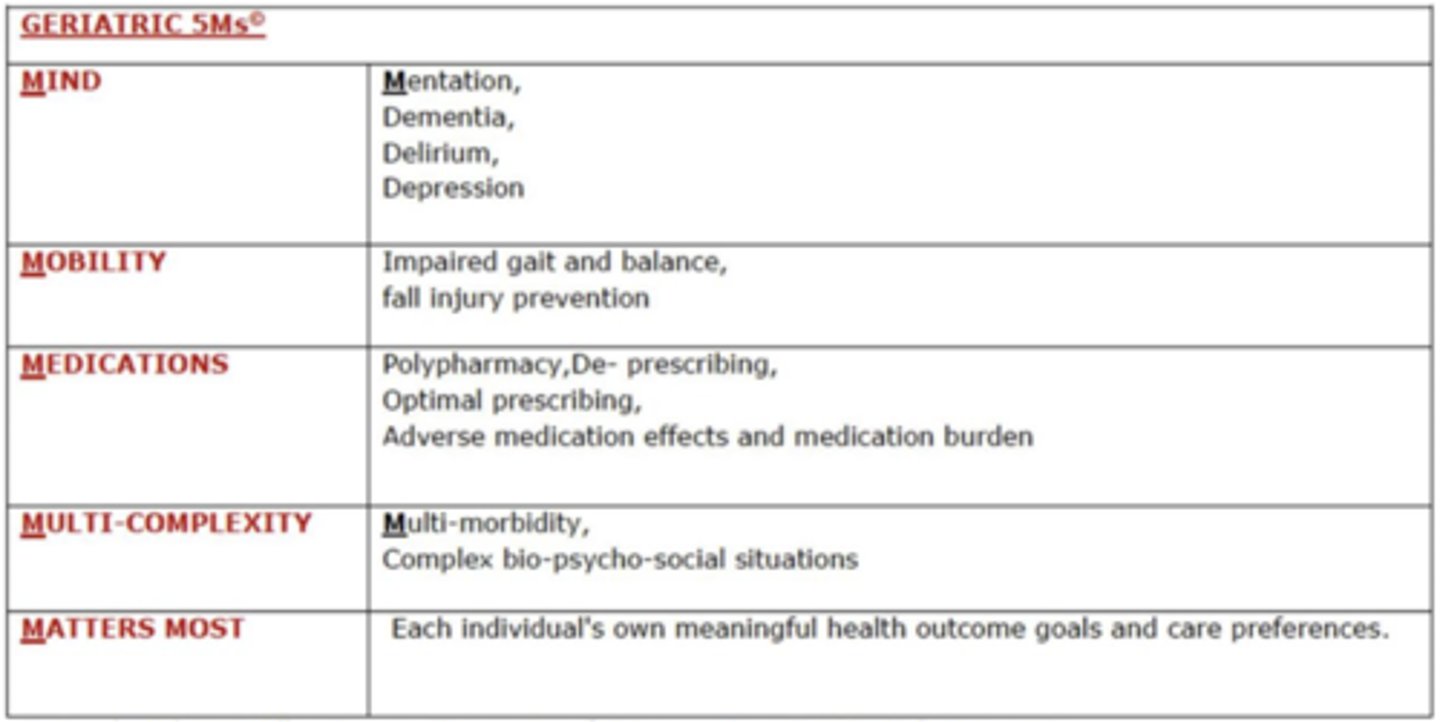
What are the 5 M's of in the framework of friendly care?
Mobility
Medication
Matters
Mentation
Multi-complexity
which lobes of the brain have the most prominent loss in aging?
frontal and temporal
which sections of the brain have the greatest neuronal loss due to aging?
cerebellum and cerebral cortex
how much does the blood flow to the brain decrease due to aging?
5-20%
which cognitive and behavioral changes are the most affected by aging?
- episodic and working memory
- executive function
which 2 primary CV disease increase with age?
HTN and CAD
what are the cardiovascular structural changes assoc. with aging?
- RA, LA volume increase
- LVH
- decreased SVC/IVC flow, myocytes
- aortic valve and mitral annulus thicken and calcify
- loss of stretch d/t hypertrophy
how is CO affected by aging?
does NOT change at rest
max CO and aerobic capacity are reduced
which heart sound is a normal finding for age >75 if in NSR?
S4 atrial gallop → secondary to rigid ventricle
how does HR change with aging?
resting HR unchanged
max HR decreased (220-age)
what causes increased CCB sensitivies in the elderly?
SA node function declines and leads to arrhythmias and increased CCB sensitivities
chest wall compliance, resp muscle strength and FEV all _____________ due to aging
decrease
how is cough power altered due to aging?
diminished d/t decreased muscle strength and increased closing capacity
how is mucociliary clearance changed due to aging?
slow and less efficient; delayed recovery after infection →increased tendency for infection
how is air/gas exchange changed due to aging?
lung tissue loses elasticity bc muscles aren't as strong/coordinated
how is the chest wall affected by aging?
- increased stiffness
- compliance decreases by 1/3 from age 30-75
- abd muscles play greater role than intercostals in chest expansion→ less effective supine and sitting, full expansion when standing
how is the diaphragm affected by aging?
- flattens and less efficient
- contributes to increased work of breathing during exercise
- increased breathing effort → difficulty weaning from ventilator
why is the elderly population at increased risk for aspiration?
- oropharynx thins → dec salivary production
- impaired strength/tongue coordination
- dec. mastication/gag reflex
- impaired food tolerance
why can reflux esophagitis become so severe in the elderly?
decreased sensation →severe reflux esophagitis despite minimal sx
(kinda like peripheral neuropathy in diabetics preventing sensation of ulcers)
what are the esophageal changes seen in the elderly?
- skeletal muscle of upper third hypertrophies
- muscle lose compliance and increases resistance to food passage
- decreased LES tone and strength of contractions →inc gastric acid exposure
- decreased sensation
what are the changes seen in the large intestine d/t aging?
- mucosal atrophy
- cellular and structural mucosal gland abnormalities
- colonic motility reduced
what conditions are increased in the elderly due to changes seen in the large intestine?
- chronic constipation
- risk of colon CA
- diverticula
- predisposition to fecal incontinence d/t dec in anal sphincter tone and thinning of the external sphincter
What happens to the renal mass, functional glomeruli, renal plasma blood flow and creatinine clearance in the aging population?
- renal mass dec by 30%
- glomeruli dec by 50%
- renal BF dec by 40%
- crcl decreases
what changes are seen in the bladder d/t aging?
- Dec. detrusor muscle contractility
- Dec. maximum bladder capacity
- Dec. maximum flow rate
- Dec. ability to withhold voiding
- Inc. in postvoid residual (retaining)
how does urinary incontinence affect the aging population?
11-34% of men
17-55% of women
what is sarcopenia?
loss of muscle mass, strength and performance
what is the normal rate of decline of mass of aging bones?
0.5% per year starting at 40
what is the normal change of aging bones?
trabecular # decreases, distance between trabeculae increases, osteoblasts DECREASE in # and activity progressively decreases.
osteoclasts are unchanged
what factors contribute to osteoporosis?
menopause
Vit D def
weight bearing activity reduced
what causes increased skin fragility seen in the elderly?
epidermis thins and dermoepidermal junction flattens → plays a role in wounds from shear stress and bleeding between dermis/epidermis occurs more often
what leads to delayed wound healing in the elderly?
thinning dermis and decreased vascularity →delayed wound healing
what are the ocular changes seen in the elderly?
- periorbital tissue atrophies, eyelids relax → ectropion/entropion
- conjunctiva atrophies and yellows
- cornea sensitivity declines by 50%
- arcus senilis from cholesterol/fat
- rigid iris →slow pupillary response
- presbyopia
- slower adaptation to low light, more sensitive to glare
what is the primary cause of conductive hearing loss? how do you eval?
cerumen impaction → whisper test evaluation
what instrument can be used to asses for hearing loss in the office?
audioscope →most accurate
what are the 5 MC chronic conditions in ppl >75?
hearing loss
cataracts
arthritis
HTN
Heart dz
what are the 10 topics used on the Barthel self-care index to assess functional independence?***
feeding
moving
personal toilet use
transfers (on/off toilet)
bathing self
walking
mobility ease
stairs
dressing
continence
what screening tools are used to assess delirium?
confusion assessment method (CAM) and 4 AT rapid clinical test
what screening tool is used for attention?
digital span memory test → quick assessment for attention
what is delirium defined as?
acute disturbance in attention, awareness, and baseline cognition that is not better explained by an underlying neurocog disorder
what are the 4 features assoc. with the CAM?
1. acute onset and fluctuating course
2. inattention
3. disorganized thinking
4. altered LOC
what are the hyperactive sx of delirium?
- restless
- agitated
- refusing care
- emotional lability
- can be mistaken for psychosis or mania
what are the mixed sx of delirium?
can be normal or fluctuating activity
what are the hypoactive sx of delirium?
- sluggish, lethargic
- can be mistaken for depression
MC and poor prognosis!
what is the strongest RF for development of delirium?
dementia
what is the primary neurotransmitter of the RAS system? how is this affected in the elderly?
Ach = responsible for regulating alertness and attention→ elderly pts are hypocholinergic → disruption of RAS leads to deficiencies in all domains of cognition
what are the predisposing factors of delirium?
- cognitive impairment/dementia
- prior episode
- medical comorbidities
- functionally dependent
- sensory impairment
- malnutrition/dehydration
- advanced age
- male sex
what are the precipitating factors of delirium?
- acute cardiac or pulm events
- bed rest
- drug withdrawal
- fecal impaction
- fluid/electrolyte disturbances
- infections
- meds
- restrains
- severe anemia
- uncontrolled pain
- urinary retention
what meds are precipitating factors for delirium?
sedatives
opiates
H2 blockers
anticholinergics
polypharmacy
what is the MCC of REVERSIBLE delirium?
drugs → benzos, opioids
what are the causes of reversible delirium?
D- Drugs
E - Electrolytes
L - Lack of drugs/water/food
I - Infection
R - Reduced sensory input
I - Intracranial causes
U - Urinary infection/fecal impaction
M - myocardial →MI, CHF, arrhythmia
what is the peak post op timeframe an individual can develops delirium?
2-7 days post up
peak inflam mediators on day 2
how do you manage a pt with delirium?
- management →tx underlying cause, give antipsychotics
- environment →lighting, orientation, sensory deprivation
- address behavioral issues
- anticipate and prevent complications
- restore function
what are the high risk drug categories assoc with delirium?
Benzodiazepines
Opioid analgesics
Nonbenzodiazepine sedative hypnotics
Antihistamines (esp first gen)
Alcohol
Anticholinergics
Anticonvulsants
TCAs
H2 blockers
Antiparkinsonian agents
Antipsychotics
Barbiturates
which 2 antipsychotics are appropriate and commonly used to tx delirium?
haldol and seroquel → avoid in old pts w/ parkinsonism (+ alcohol use for seroquel)
how is dementia defined?
decline in intellectual functioning significant enough to affect daily life and independence
what are the 6 cognitive domains of dementia?
1. learning and memory
2. language
3. executive function
4. complex attention/concentration
5. perceptual motor/visuospatial
6. social cognition/emotion
what is the MC form of dementia?
alzheimer's
what is the DSM-5 criteria for major neurocognitive disorders?
- evidence of significant cognitive decline from a previous level of performance in 1+ category
- cognitive defects interfere with independence in everyday activities
- cognitive deficits do not occur exclusively in the context of a delirium
- cognitive deficits are not better explained by another mental disorder
what is vascular dementia?
dementia caused by CV dz or impaired cerebral blood flow; progression is typically sudden or stepwise
what is the DSM-5 criteria for vacular dementia?
- criteria met for major/mild neurocog disorders
- clinical features consistent with vascular etio →onset related to CV event, evidence for decline in complex attention
- evidence of CV disease
- sx not explained by another dz
what is mixed dementia?
dementia that is secondary to coexistence of more than 1 dementia- producing condition → alzheimer's, vasc. dementia, alcohol-related dementia, normal pressure hydrocephalus, chronic subdural hematoma, HIV
what is cognitive impairment without an overall decline in function?
mild cognitive impairment (MCI) → precursor to dementia or secondary to reversible condition
what is dementia that onsets alongside or within 12 months of motor sx?
dementia w lewy bodies
what is dementia that is onset >12 months AFTER appearance of motor sx?
parkinson's disease dementia →motor sx first!!
who does Pick's disease (frontotemporal dementia) typically present in?
<60
gradual but faster onset than alzheimers
what are the s/sx of Pick's disease?
cognitive = executive → disinhibition, apathy, behavior changes
motor = none
which dx shows atrophy in frontal and temporal lobes on imaging?
pick's disease
what is the triad of sx seen in normal pressure hydrocephalus?
progressive dementia
urinary incontinence
gait instability
which genetic disorder has a strong correlation with an early onset of Alzheimer's?
down syndrome, trisomy 21
what dx should be on your differential assoc with dementia?
- normal cognition
- mild cognitive impairment
- major depressive disorder
- delirium
- specific learning disability
- normal pressure hydrocephalus
- b12 deficiency
- hypothyroidism
- parkinson's
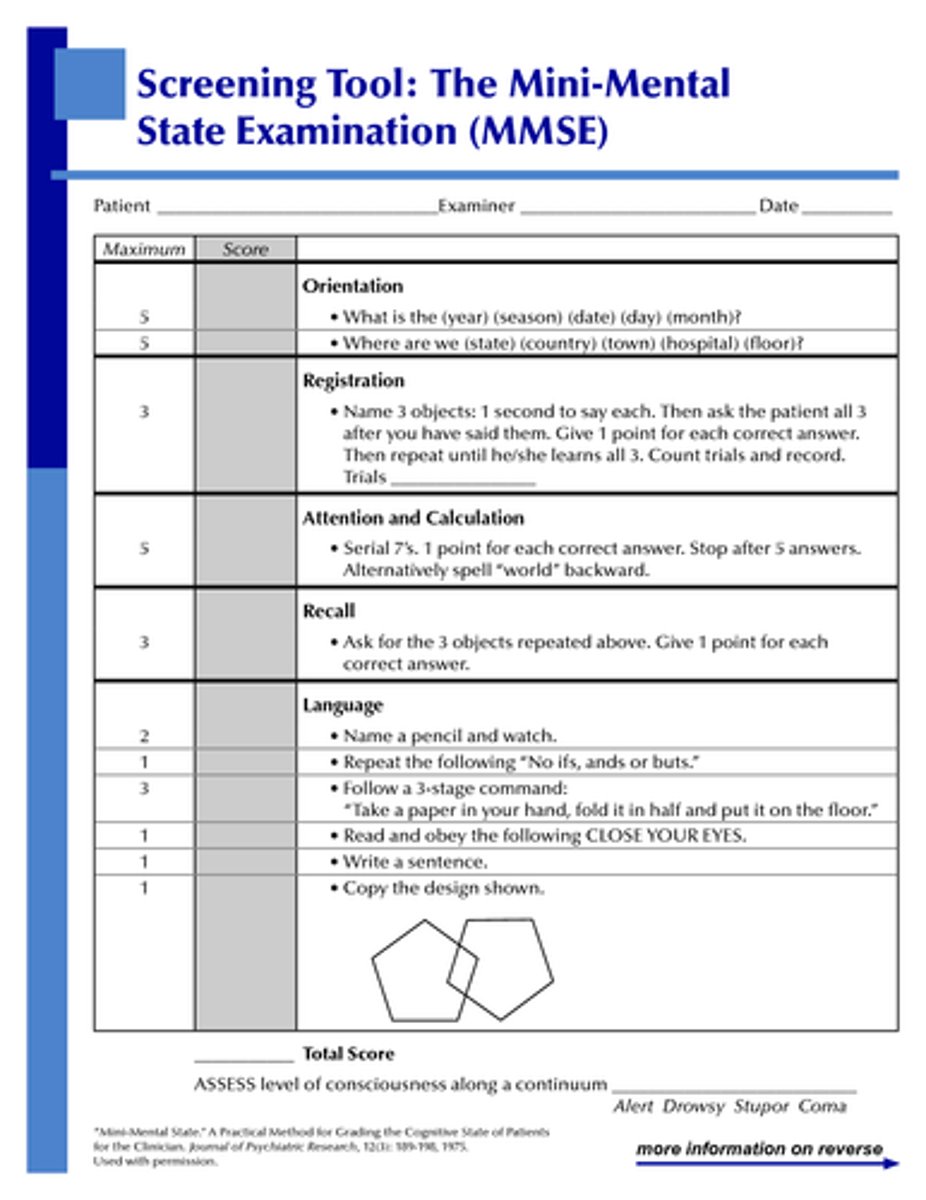
what MMSE score warrants further testing?
<24
which drugs are acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and have been shown to provide some benefit for mild/moderate dementia?
donepezil
rivastigmine
galantamine
what are the MC side effects of anticholinesterase inhibitors?
GI
which drug is an NMDA inhibitor approved for moderate/severe dementia?
Memantine (Namenda) → indicated for more advanced dz
reduces glutamate-mediated excitotoxicity
what are the common side effects of Namenda?
constipation
dizziness
HA
what are the 4 types of incontinence?
1. urge → leak when you gotta go
2. stress →laughing/coughing/sneezing
3. overflow →continuous leakage bc not emptying bladder
4. mixed →stress and urge
what are the 4 main drug classes assoc. with elderly hospitalization d/t adverse effects?
warfarin
insulin
oral antiplatelet (ASA)
hypoglycemic drugs
what are the RF of osteoporosis?
- asian/caucasian
- increasing age
- small body size
- family hx
- post menopause/hypogonadism
- smoking
- excess alcohol consumption
- low physical activity
- glucocorticoid use >3 months
what may you see on PE in a pt with osteoporosis?
- low body weight; BMI <19
- loss of height
- localized vertebral pain
- kyphosis
what is the recommended dose of calcium and vitamin D for osteoporosis?
1000-1500 calcium daily
400-800 IU Vit D daily
what is the first line tx for osteoporosis?
Bisphosphonates
what is the MCC of elder abuse?
self neglect
what are teh 3 MC osteoporotic fracture sites?
wrist
hip
vertebrae
what is failure to thrive? what are the MC indicators?
FTT = weight loss >5%, decreased appetite, poor nutrition, inactivity, dwindling physical function, malnutrition, cognitive impairment
1. depression
2. cognitive impairment
3. malnutrition
4. functional impairment
what exams can check cognition?
mini-cog
clock drawing
MMSE
what exams can check affect?
depression screening
>5 = sus depression
> 10 = def depression
what exams can check mobility?
timed up and go (TUG) test→stand, walk, turn, sit
>12-14 = inc. risk of falling
>20 = warrants comprehensive eval
what are the 7 domains involved in a geriatric rapid assessment?
1. functional status
2. mobility
3. nutrition
4. vision
5. hearing
6. cognitive function
7. depression
how do you screen for functional status, mobility, and nutrition?
functional status = ansewr yes to needing help w ADLs
mobility = TUG test >12
nutrition = answers yes to "have you lost more than 10 lbs in 6 months without trying" or BMI <20
how do you screen for vision?
vision = unable to read newspaper headline and sentence w corrective lenses, use Snellen chart. unable to read greater than 20/40
how do you screen for hearing, cognitive function, and depression?
hearing = unable to hear 40 dB at 1000 or 2000 Hz in one or both ears
cognitive function = 3 item recall
depression = answers yes to " do you often feel depressed"
which gait: pain-induced limp with shortened phase of gait on painful side?
antalgic
which gait: outward swing of leg in semicircle from hip?
circumduction
which gait: excessive plantar flexion and inversion of ankle?
equinovarus
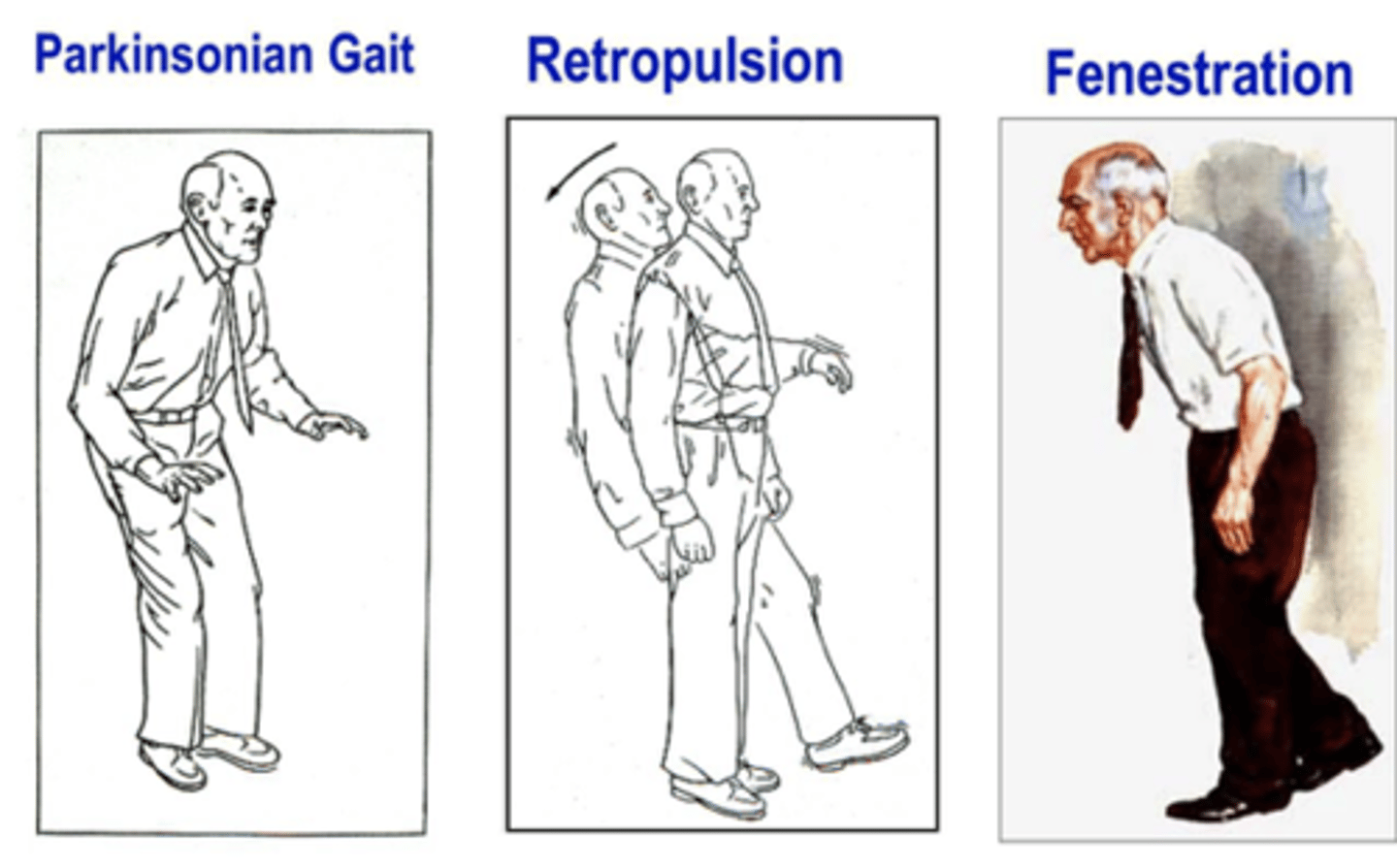
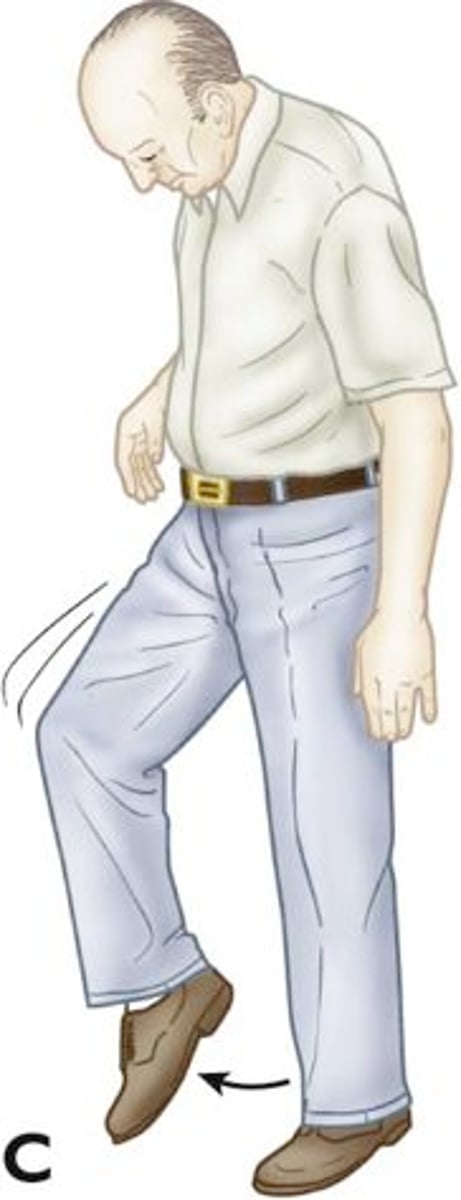
which gait: acceleration of gait?
festination
which gait: loss of ankle dorsiflexion secondary to weakness of ankle dorsiflexors?
foot drop

which gait: early, frequent audible foot-floor contact with steppage gait compensation?
foot slap
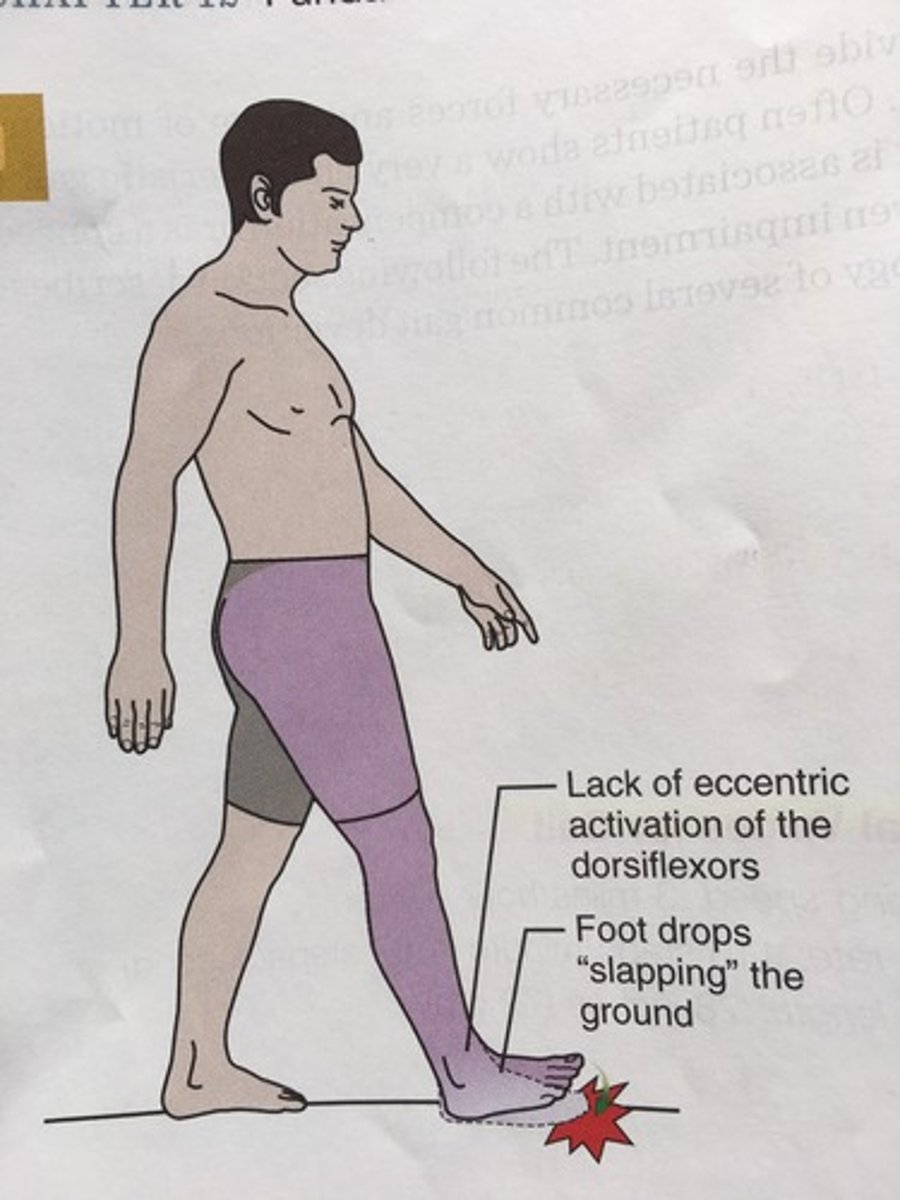
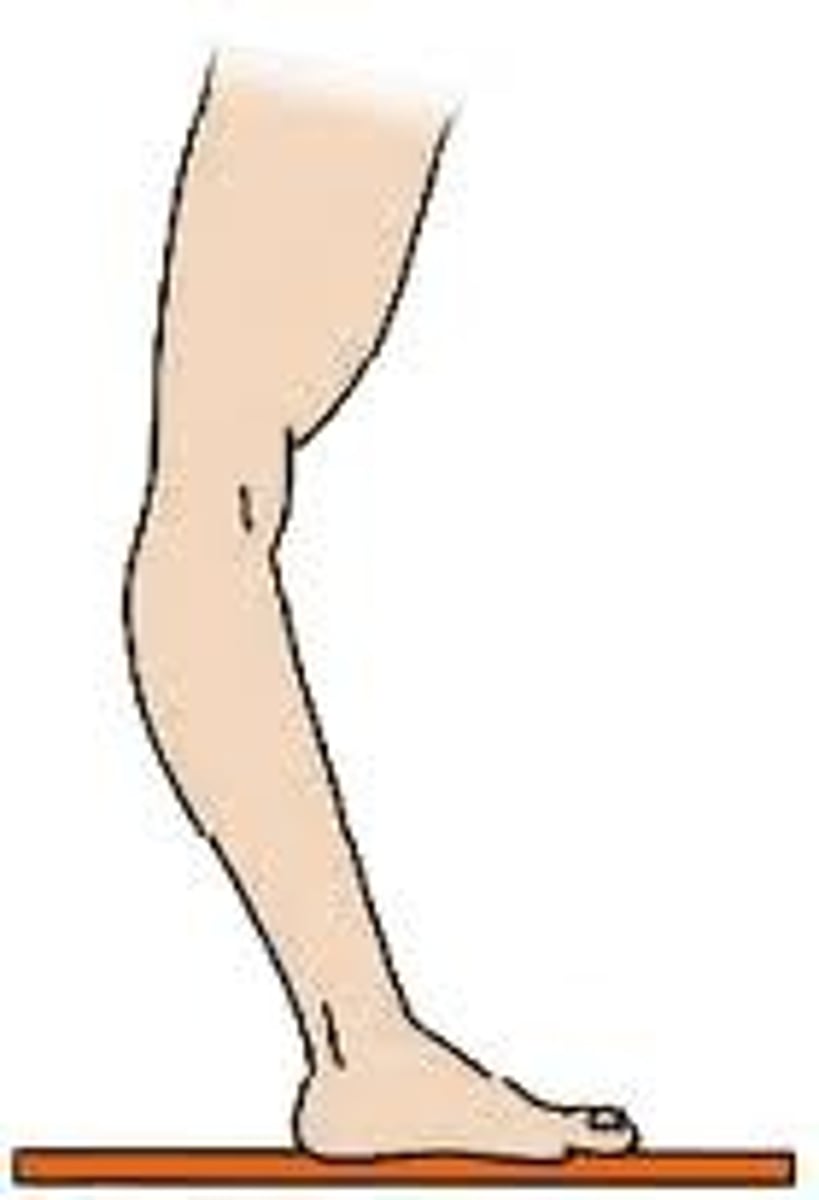
which gait: hyperextension of knee?
genu recurvatum
what is the tendency to fall foward?
propulsion
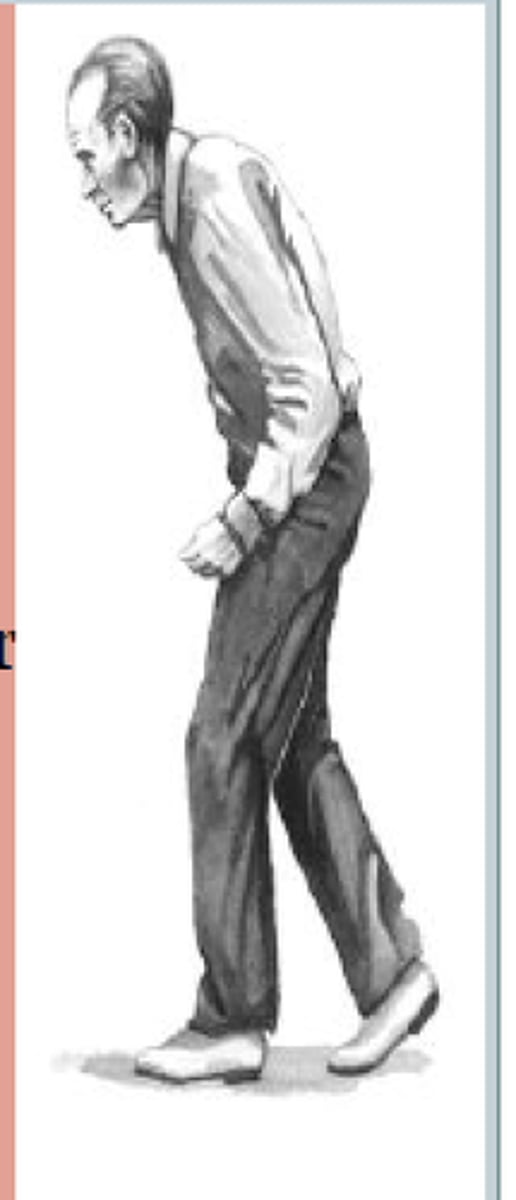

what is the tendency to fall backward?
retropulsion