Lecture 10 - Social development Part 2
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Partner selection 2 ways
→ “Birds of a feather flock together” or “Opposites attract” ?
1. Similarity → Homogamy
2. Complementarity
What are Filter theories?
1. Similarities in physical appearance, race or ethnicity, education, socioeconomic status, religion → provides basis for dating
2. More disclose about themselves, look for similarity in values, attitudes, beliefs, and personality traits → if compatible: relationship may survive
• Influence of personality traits like emotional stability and agreeableness
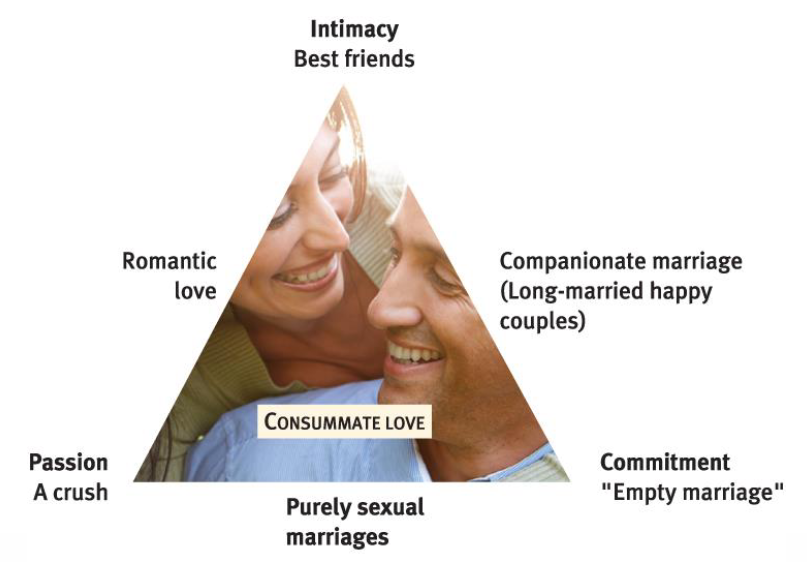
Sternbergs’s Triangular Theory of love
Three components of adult love relationships
1. Passion (sexual arousal)
2. Intimacy (feelings of closeness)
3. Commitment (marriage; exclusive, lifelong cohabiting relationships)
• Change across relationship:
passion → intimacy → commitment
➔ Keeping passion and intimacy takes work
Attachment styles in Adulthood
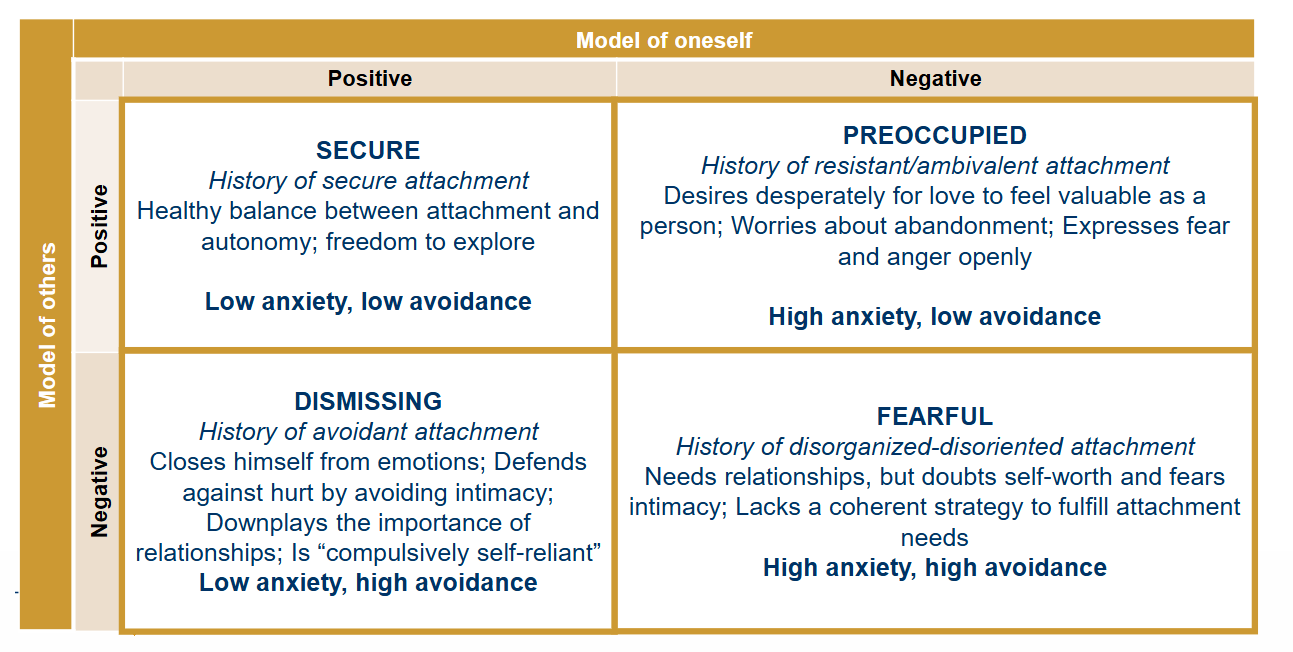
Secure attachment style
Positive model of self
Positive model of others
History of secure attachment
Healthy balance between attachment and autonomy;
Freedom to explore.
Low anxiety, low avoidance
Preoccupied Attachment style
Negative model of oneself
Positive model of others
History of resistant/ambivalent attachment.
Desires desperately for love to feel valuable as a person;
Worries about abandonment;
Expresses fear and anger openly.
High anxiety, low avoidance.
Dismissing Attachment style
Positive model of oneself
Negative model of others
History of avoidant attachment
Closes himself from emotions
Defends against hurt by avoiding intimacy
Downplays the importance of relationships
IS “compulsively self-reliant”
Low anxiety, high avoidance
Fearful Attachment style
Negative model of onself
Negative model of others
History of disorganized-disoriented attachment
Needs relationships, but doubts self-worth and fears intimacy
Lacks a coherent strategy to fulfill attachment needs
High anxiety, high avoidance
Challenges for new parents
▪ Alterations in hormones, neurobiology
▪ Physical health
▪ Self-concept, identity
▪ Perceived efficacy
▪ Emotional health
▪ Relationships
▪ Social networks
▪ Varying degrees of exhaustion, depression, anxiety, marital conflict,
emotional lability, social isolation, feelings of guilt
▪ Disconnect between media representation of parenthood and the reality
Which challenges are linked to parenting?
Relationship threats
• Less time for intimacy: Time is invested in children, household, work
• Division of labor: Women are forced into gender-typical roles, have to cut back career
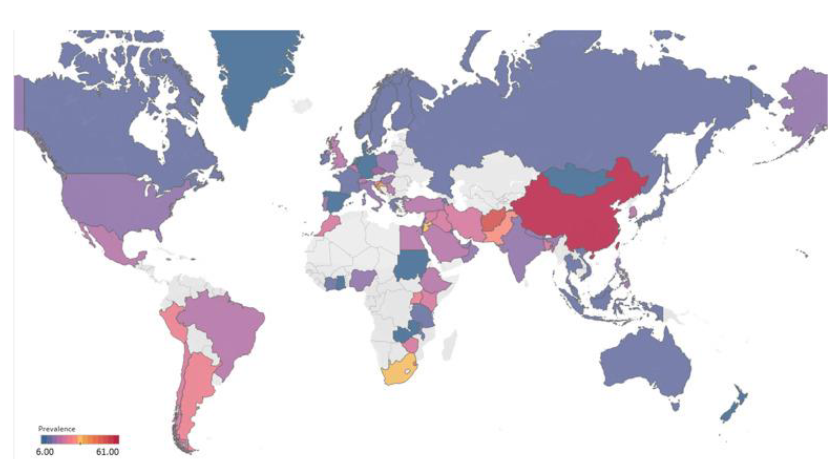
Mental health of new parents across the world
17% of new mothers develop postpartum depression
• Large global differences (6% in Denmark to 61% in Afghanistan)
What are some risk factors for developing postpartum depression?
Risk factors include:
• Education
• Income
• Stress (financial, life events)
• Complications at birth
• Social support/network
• Perinatal mental health
• Planned pregnancy
• Violence
Wang et al (2021)
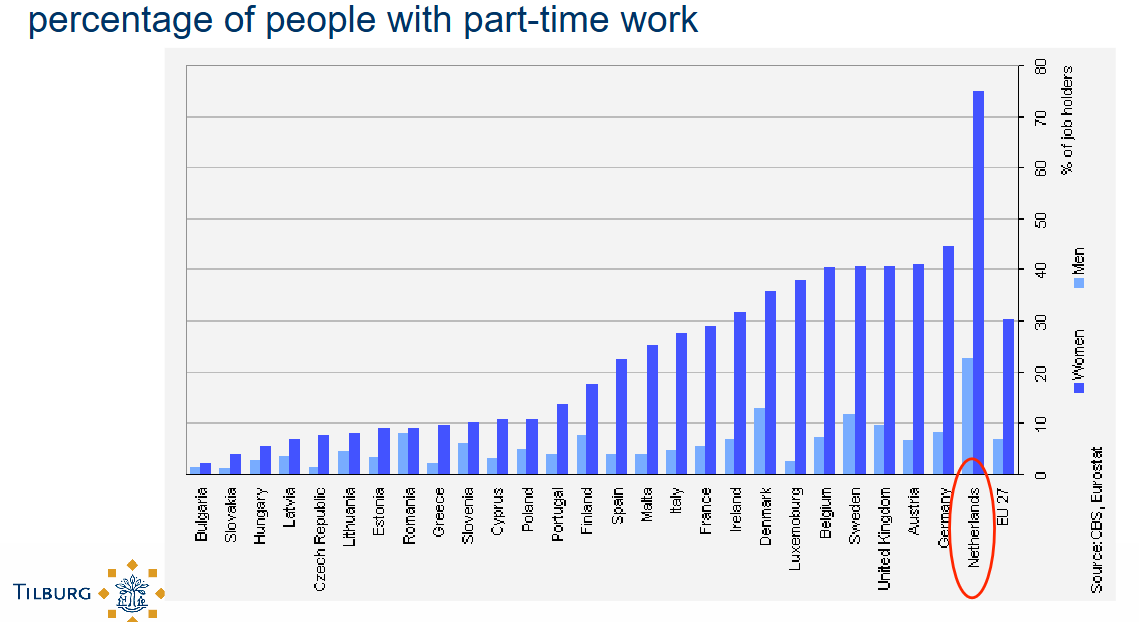
Divison of labor as new parents
Influence of attachment on romantic relationships
• Secure: positive emotions, longer relationships, can discuss problems well
• Dismissing: fear of intimacy, shut down, inhibit feelings
• Preoccupied: obsessive and jealous, emotional during conflicts
What influences internal working models?
Internal working models are shaped by early parent-child relationships, but influenced by the quality of later relationships (sensitive partners can make a difference!)
Does marriage make people happy?
Robust evidence: marriage status is linked to better health and subjective well-being
• Stronger effects for men than for women
• But: benefits of marriage apply to happy marriages
• Also: No differences in midlife happiness in married vs. long-term
cohabiting couples
➢ Research should go beyond
→ Marriage quality!
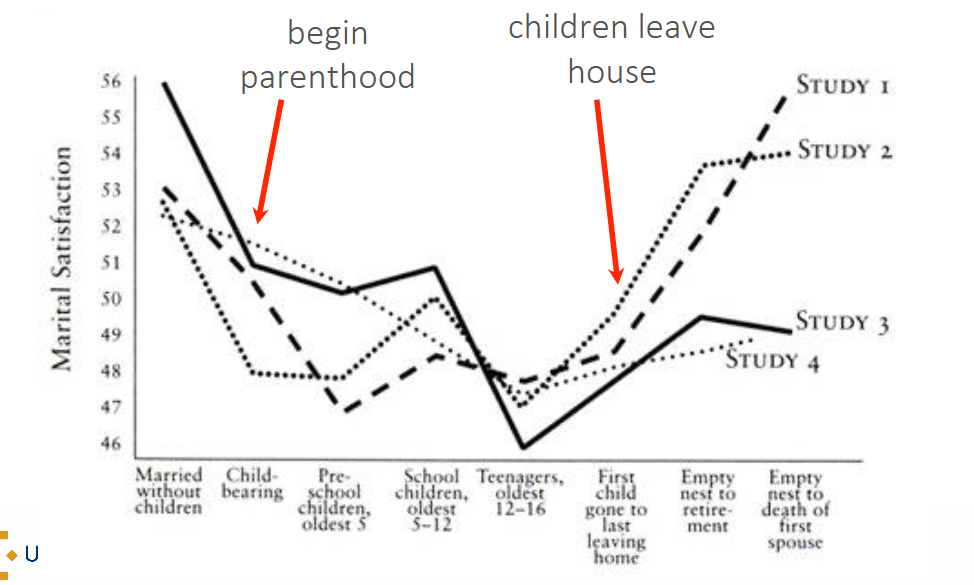
Main marital pathway
• Marriage begins with high expectations, after which disenchantment sets in
• Happiness is at its peak during honeymoon phase
• Satisfaction rapidly slopes downward, and then tends to decline more slowly or level out around year four
• Positive change occurs with empty nest
• Yet, most couples far more satisfied than dissatisfied with their marriage even after “honeymoon” phase → still happy but more realistic view
When is happiness at its peak during marriage?
During honeymoon phase
When does positive change occur in marriage?
Empty nest
When does marriage satisfaction decline?
Satisfaction rapidly slopes downward, and then tends to decline more slowly
or level out around year four
Marital satisfaction and family transitions
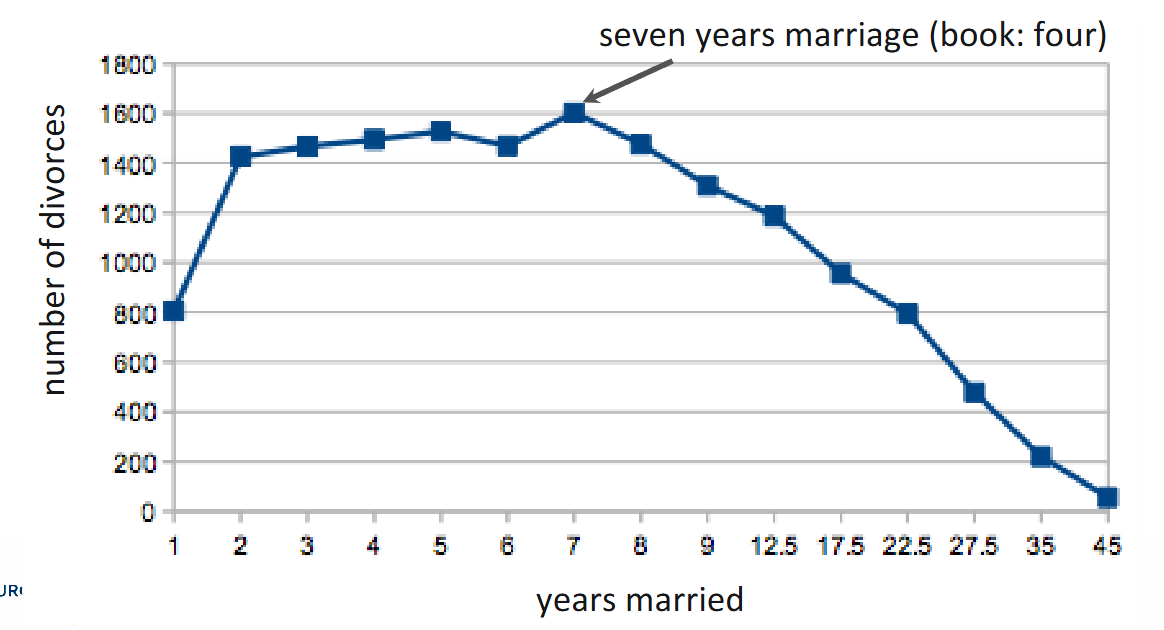
After how many years of marriage is divorce risk highest?
What are some consequences of Separation?
Separation can cause overload of changes: moving, housework burden, legal hassles, financial problems...
What are 2 positive and 2 negative changes following Divorce?
Positive changes
Production of emotional growth and feelings of self-sufficiency.
Relief for some who were unhappy.
Negative changes
Disengagement of one parent through lack of contact or not paying child support.
Challenges with discipline or lack of connection to stepchildren.
Research of Amato & Hohmann-Marriott (2007) on Calling it quits on marriage
• Divorce after bad marriage: Increase in happiness
• Divorce after good marriage: Decrease in happiness

Deinstitutionalization
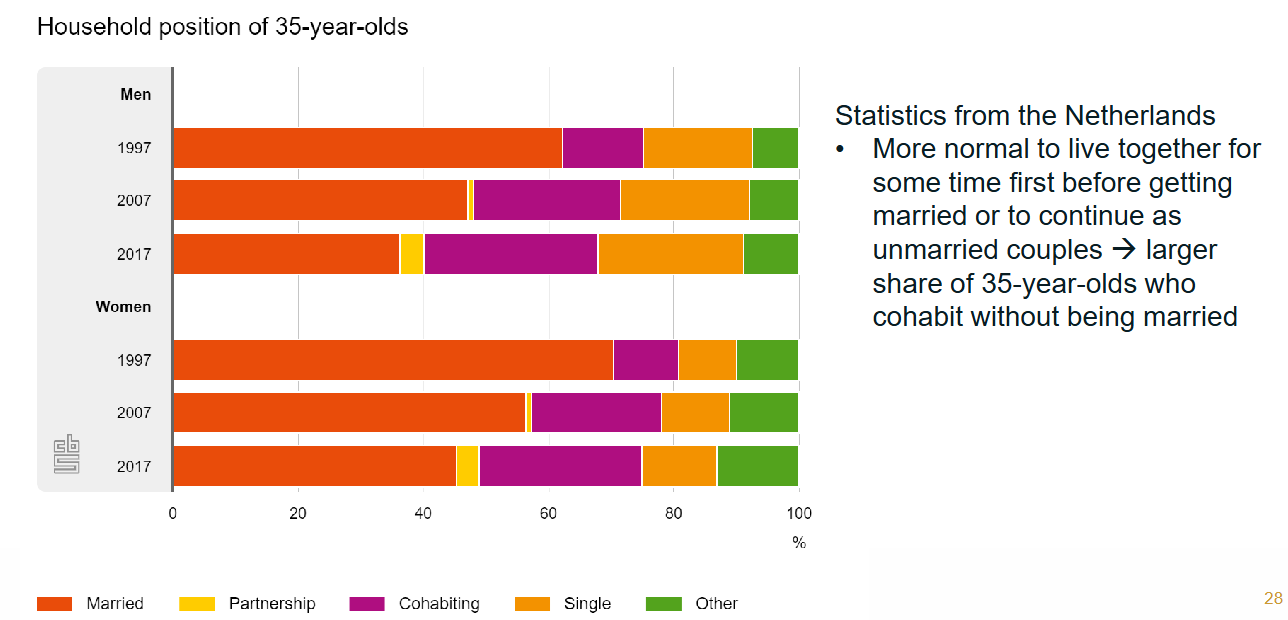
Decline in marriage and emergence of alternative family forms during last third of 20th century.
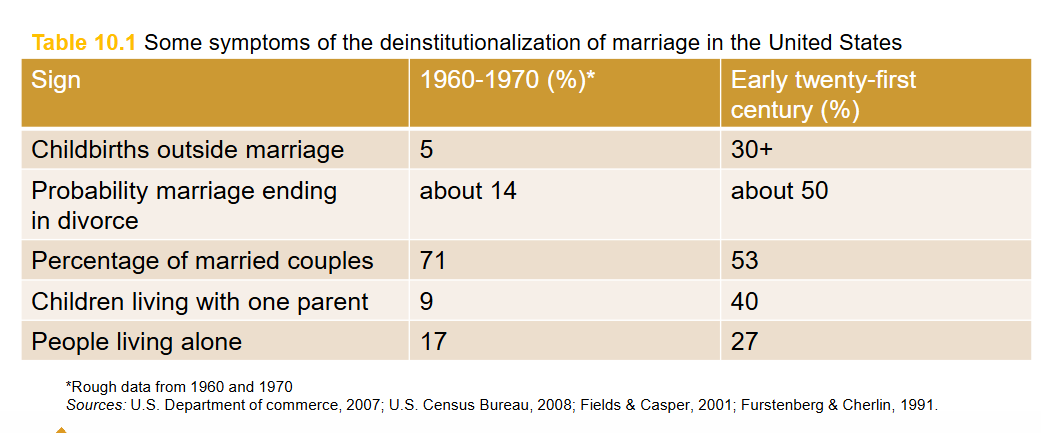
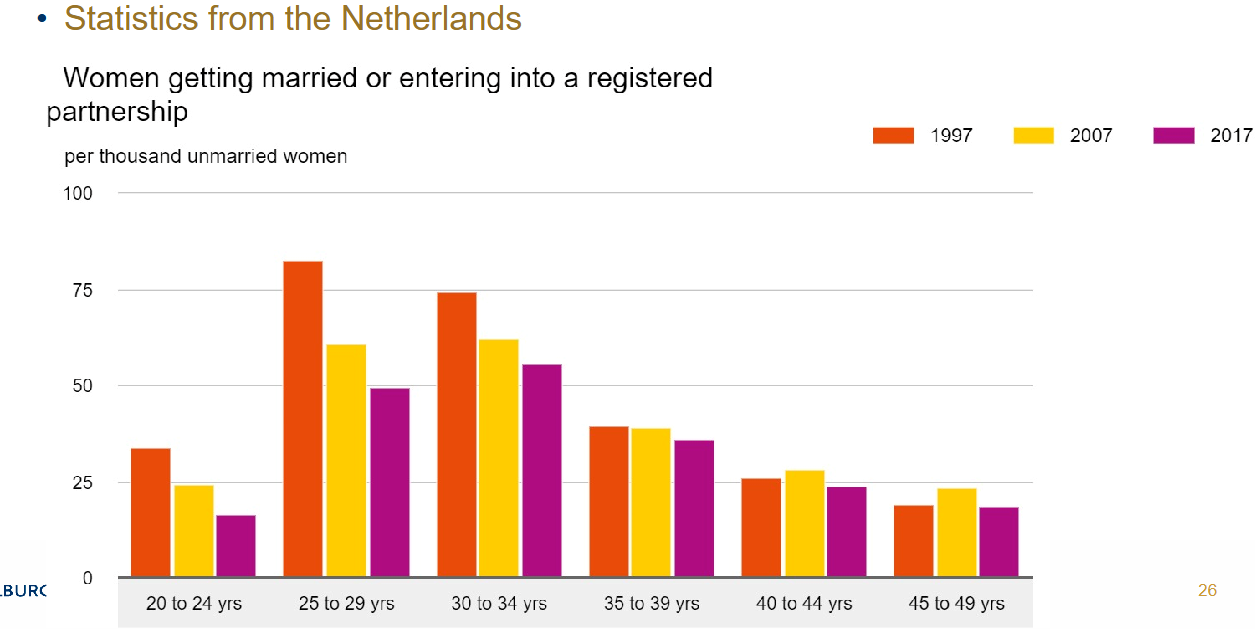
Amount of marriages declines
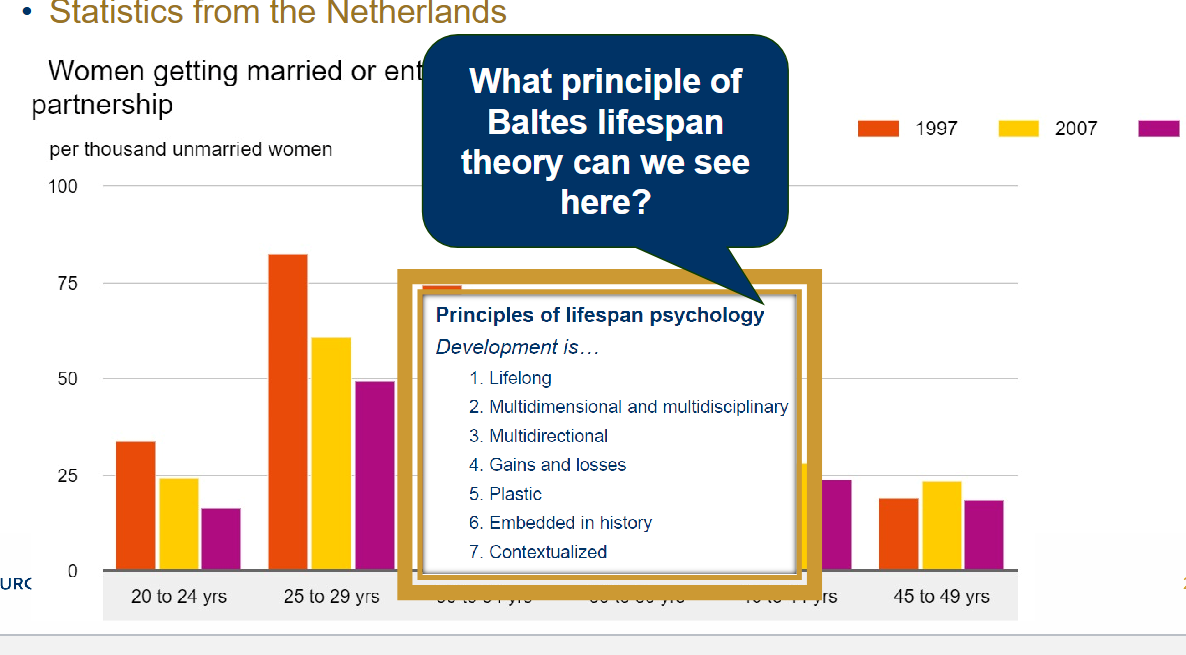
Historical embeddedness
As the changing norms around marriage and cohabitation reflect how development is influenced by historical and cultural contexts.
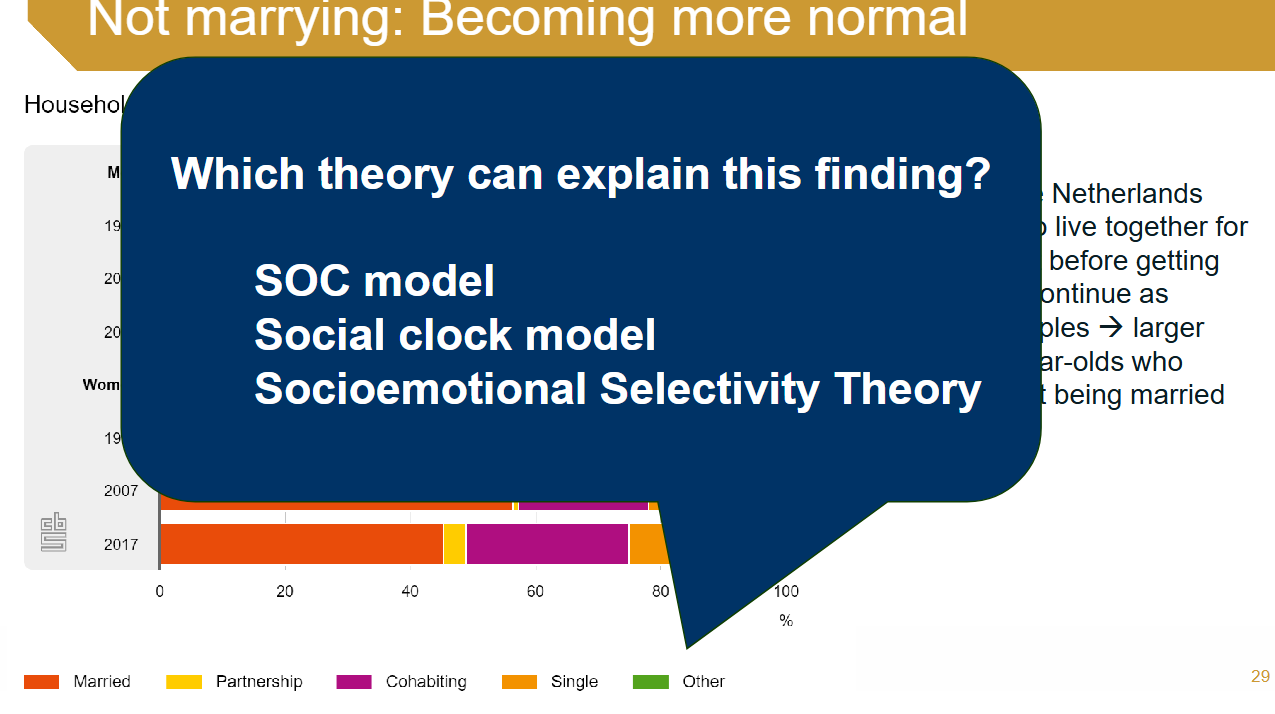
Social clock model
This model emphasizes societal expectations for the timing of life events, such as marriage or parenthood.
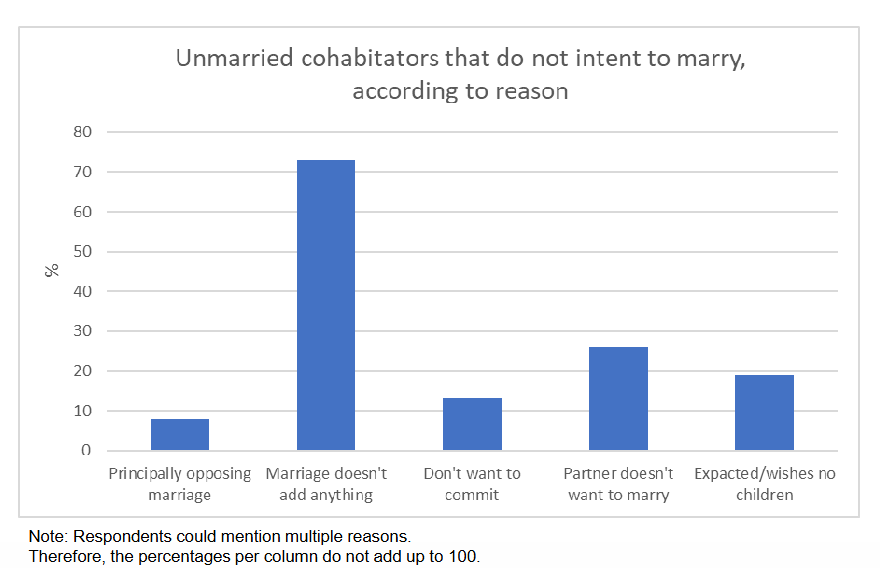
Unmarried cohabitors that do not intend to marry, according to reason
Diverse lifestyles — non-heterosexual marriage


The factor can be found in the Macrosystem, as it reflects societal changes, such as the legalization of same-sex marriage, which influence relationship satisfaction among non-heterosexual couples.