Chem 241: Sensors
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Do sensors always involve measuring the concentration of the analyte directly?
No- many sensors involve measuring color change, fluorescence, change in conductivity, change in mass, or a shift in electrochemical potential
biosensor
uses biological components (enzymes, antigens, or enzyme receptors) for a highly selective response to one analyte
Point-of-Care Devices
a medical device used to obtain diagnostic results at or near the "point of care," main goal is to be fast and accurate, a point of care may be at a hospital, dr's office, EMT work, or home, example is blood glucose testing, testing for infectious diseases, etc
ASSURED criteria
criteria for a POC device:
affordable, sensitive, specific, user-friendly, rapid, robust, equipment free, deliverable
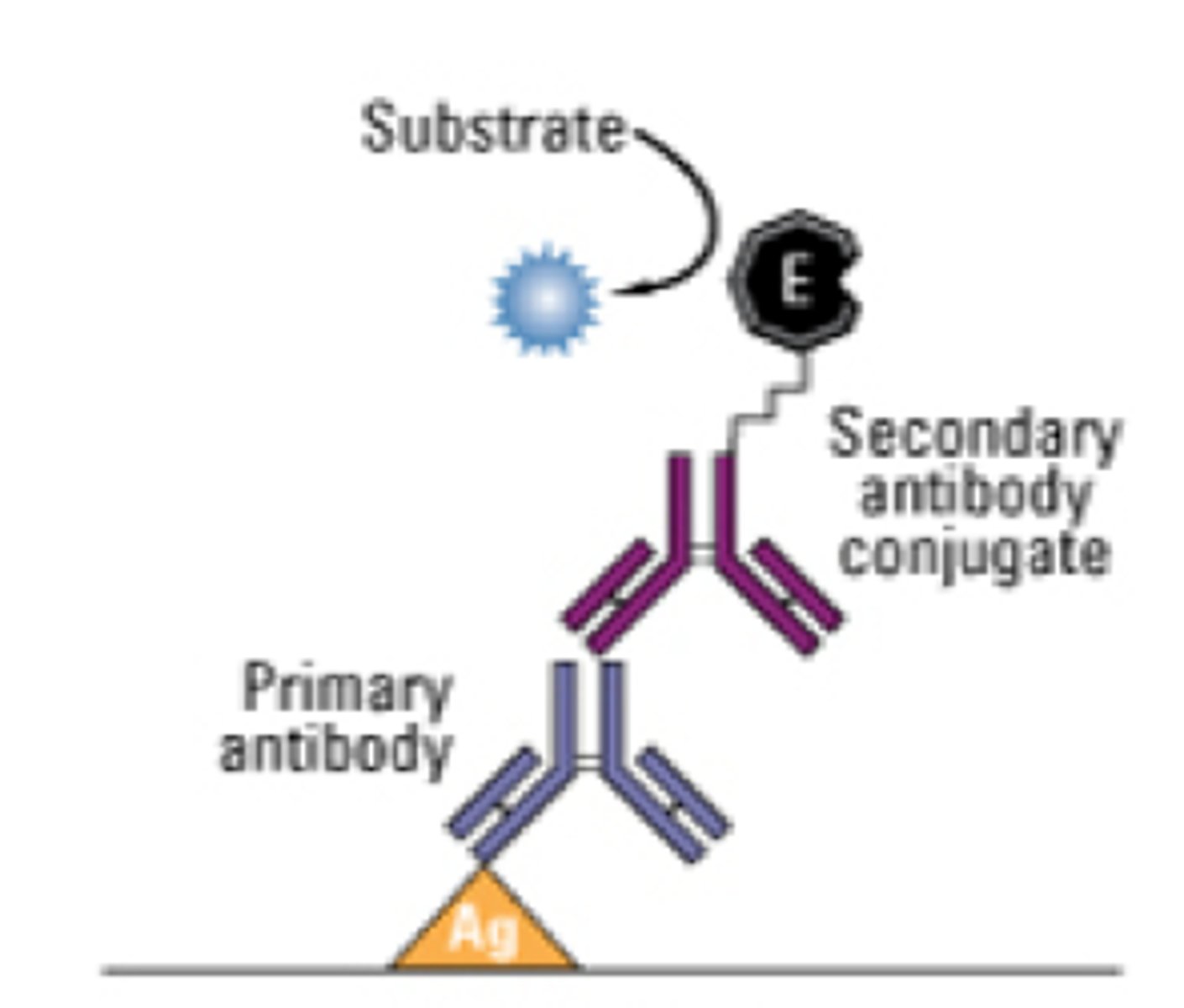
ELISA
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, sensitivity is due to the enzyme in which 1 molecule catalyzes the same reaction multiple times, producing many molecules of the colored/fluorescent product that can be detected visually/spectroscopically
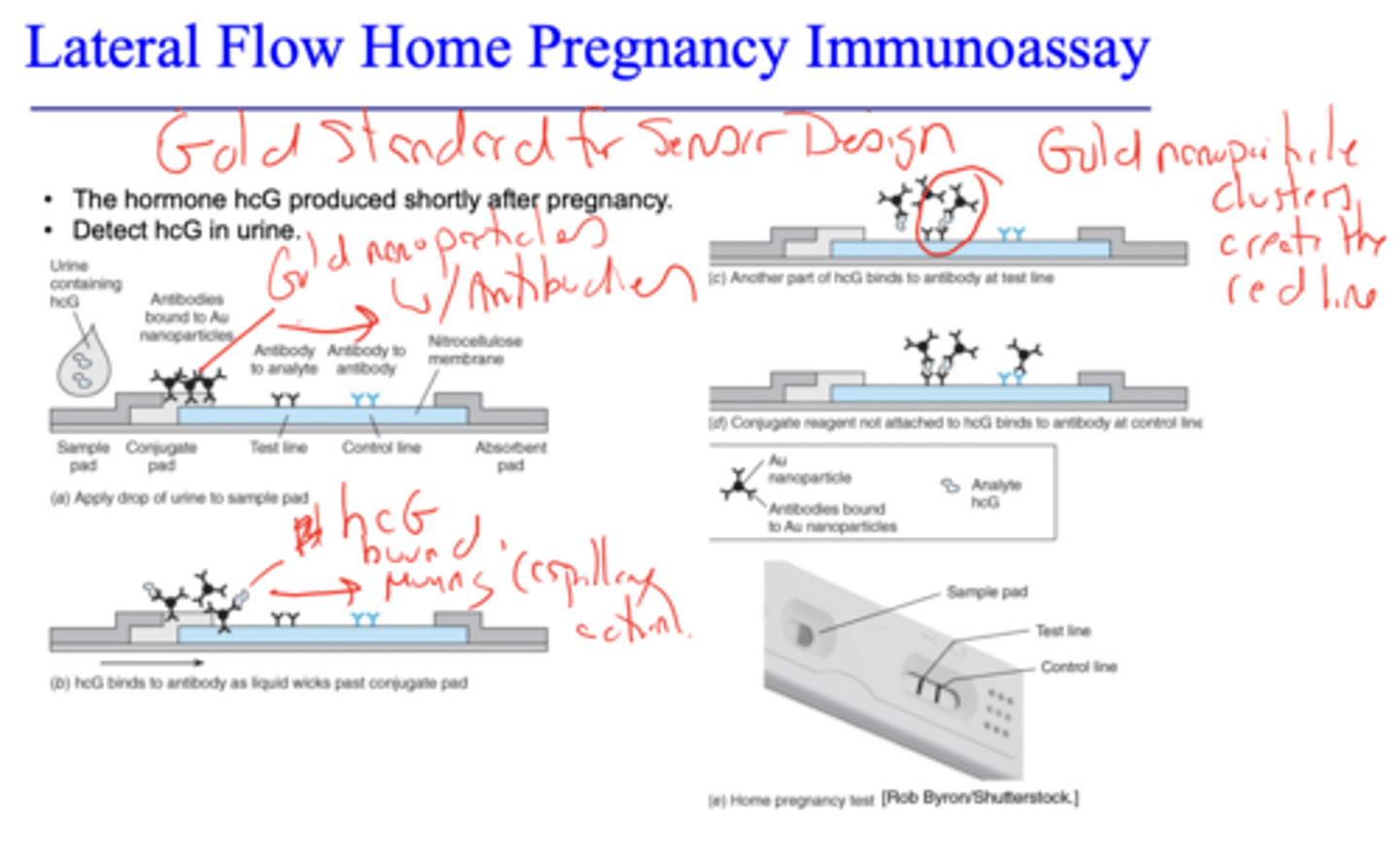
Lateral Flow Home Pregnancy Immunoassay
detects hormone hcG that is produced shortly after pregnancy in urine
gold standard for designing sensors (POC that meets ASSURED criteria)
False positives occur from cross-reactivity between molecules similar in shape to the antigen and the immobilized antibodies
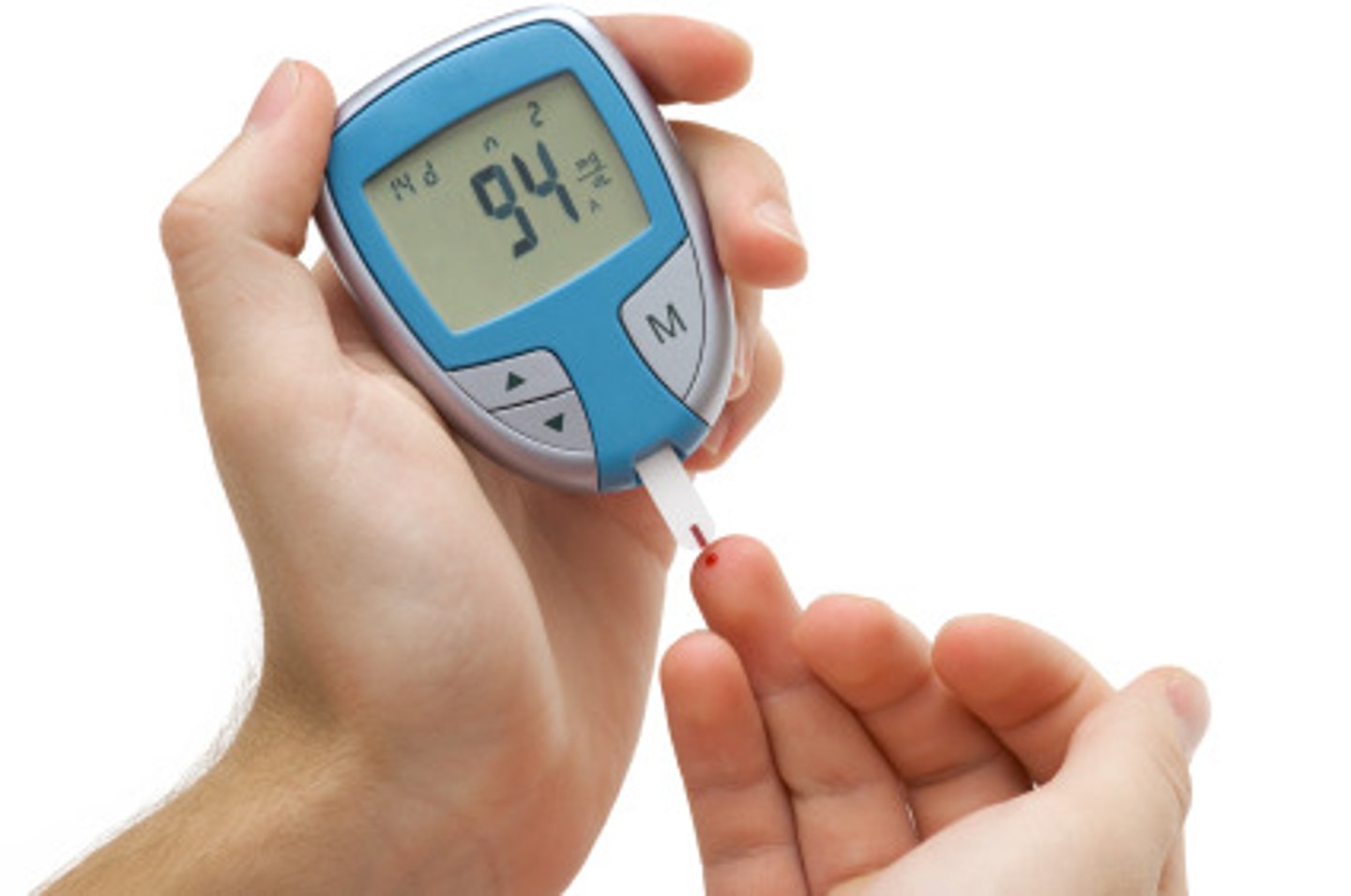
blood glucose monitor
amperometric, relates the current (I) to the concentration of glucose indirectly; has working and reference electrode, reference electrode is to provide a constant potential; all reagents on a test strip
interferences: ascorbic acid, acetaminophen
amperometric measurement
measures current and relates to concentration at a constant potential
generations of blood glucose monitors
1st gen) hydrogen peroxide product of the reaction diffuses to the transducer and causes the electrical response, O2 is mediator that transports the electrons between the working electrode and glucose molecule (I = [H2O2] = [Glucose)
2nd gen) involves specific mediator to generate improved response, glucose oxidase as a redox mediator
3rd gen) reaction itself causes response using organic conducting materials based on charge-transfer complexes, superior selectivity
potentiometric measurements
measure cell potential (E in mV) or potential across an ion-selective electrode membrane with little to no current flow, ISEs fall into this category
use Nernst equation to relate cell potential to concentration
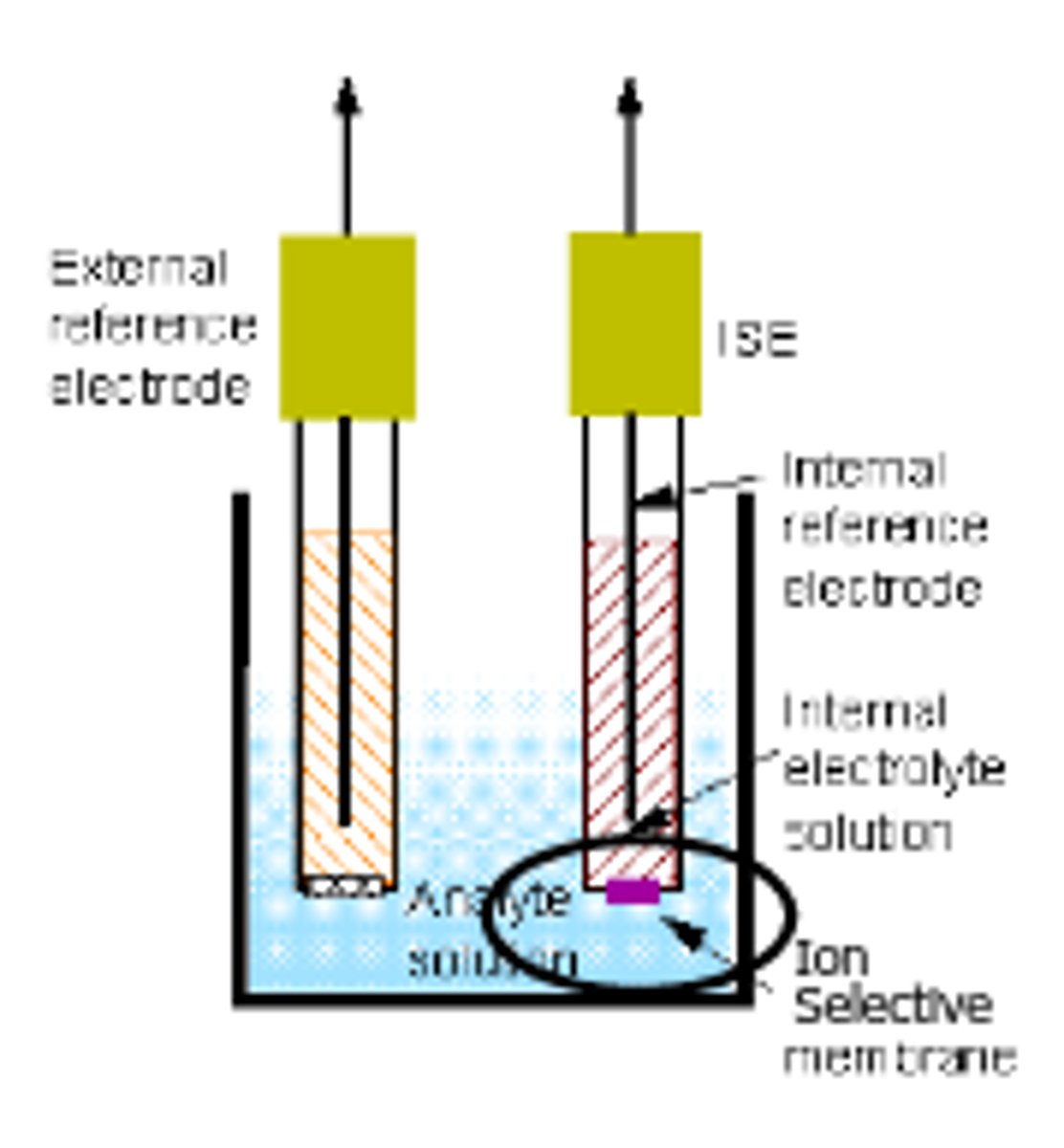
Ion Selective Electrodes (ISE)
not based on a REDOX reaction (no electron transfer), based on a potential difference across a membrane;
all ISEs have a permselective membrane, an inner and outer reference electrode, and a fixed concentration of the ion inside the electrode
the concentration of the analyte ion in the outer solution changes, causing the membrane potential to change
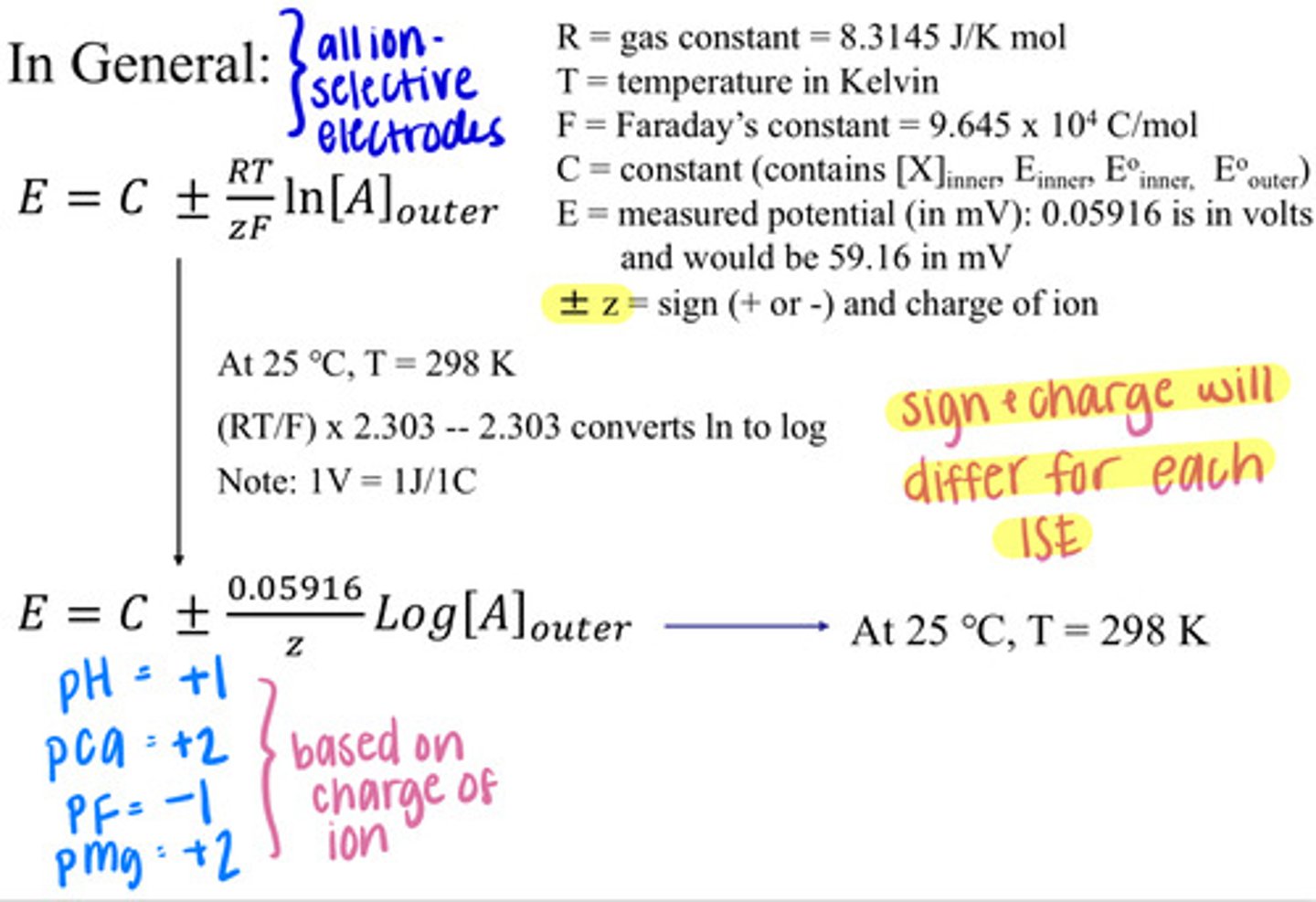
Nernst Equation for ISEs
*Alter the sign and charge for the equation based on the charge of the ion used
junction potentials
smaller junction potentials give a greater mobility, this is why Cl- and K+ are commonly used in ISEs
if the mobility of the ion is greater, it has the greater potential to attract the opposite charge. For example, if K+ > Na+, this means that K+ will have a more negative side of the liquid junction because it can attract more negative ions
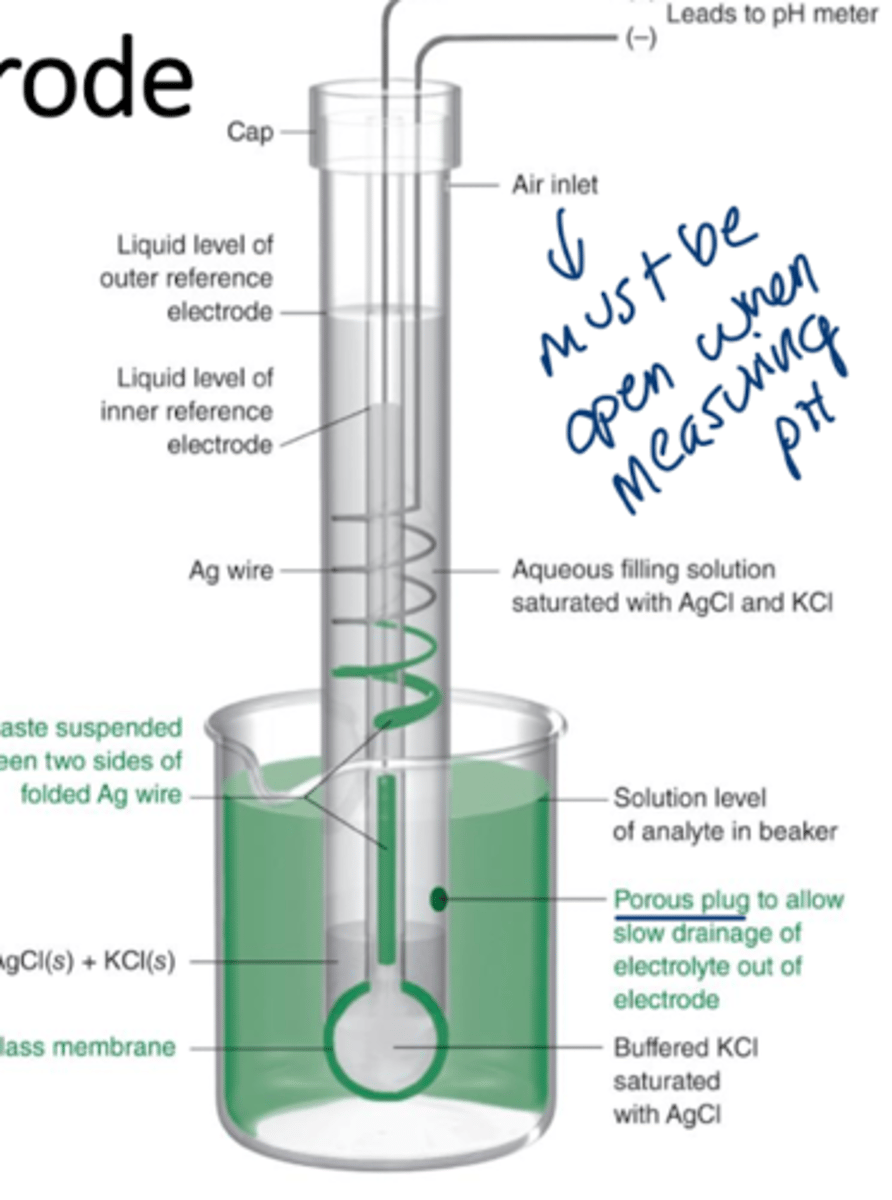
combination electrode
consists of a glass electrode with a concentric reference electrode built on the same body, pH electrodes are an example
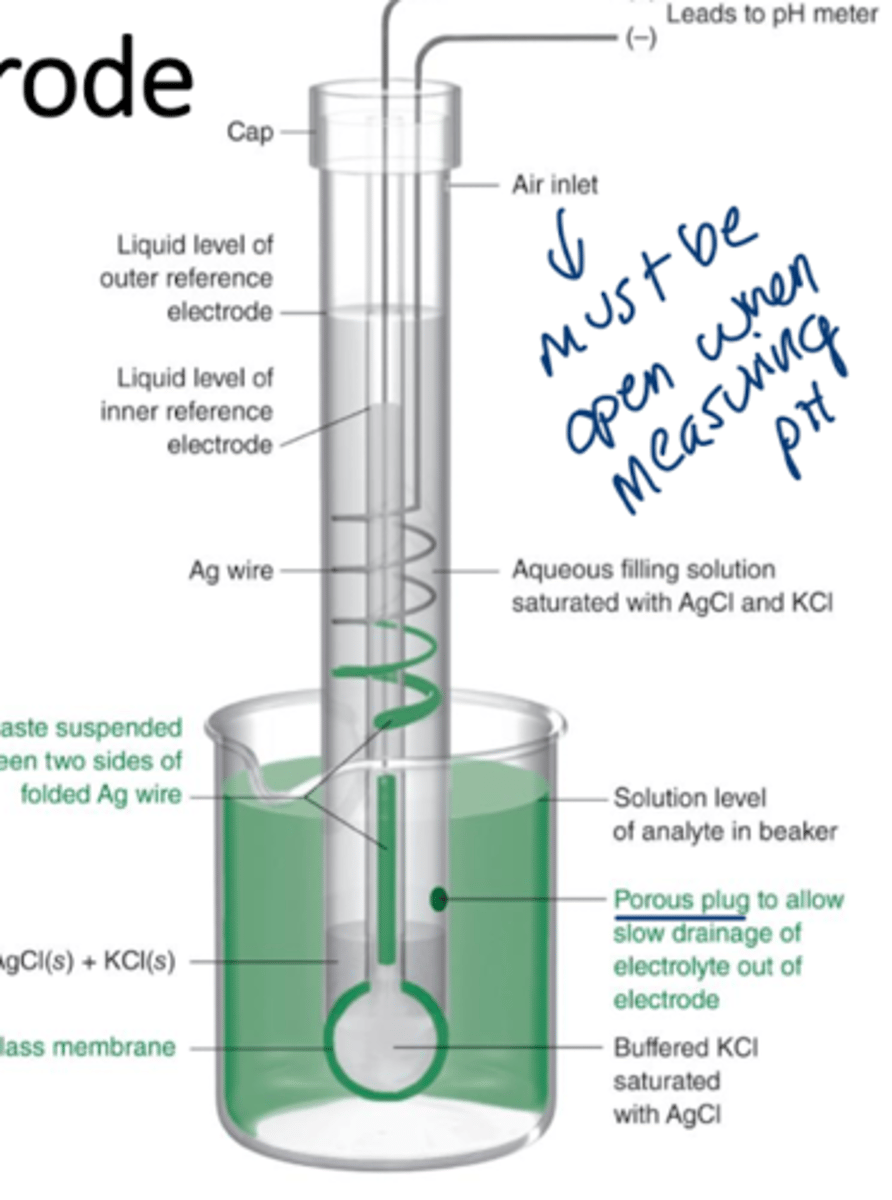
pH electrode
inner solution has a fixed concentration of H+ but the analyte (outside) solution varies in H+ concentration, the binding to silica glass sites (Si-OH) determines the difference in potential, which is read as the pH.
more H+ binding = lower pH
for every factor of 10 change in H+ at 25 C, a difference of 59.16 mV is observed
interfering species in ISEs
adds extra term in Nernst equation, and example is alkaline/sodium error
Spectral: overlap of analyte signal
Choose another wavelength for analysis, ICP, Monochromator
steps for using an ISE
1. the electrolyte is placed into an aqueous solution
2. analyte ions in the exchange sample solution equilibrate with ion-exchange sites in the membrane
3. Analyte ions diffuse out of the membrane
4. A charge imbalance, also called a potential difference, develops across the interface
5. the potential difference is measured using the internal and external reference electrodes
6. the concentration of the analyte ion in the external solution is determined from the potential difference
sodium error
in an alkaline solution with an increased concentration of Na+, the glass electrode indicates a pH that is lower than the actual pH
this is because Na+ binds to the same exchange sites as H+, and the electrodes respond to Na+ as if H+ was present
usually for pH of 11 or greater
potential errors when using a pH electrode
the glass mmb is not hydrated properly, not enough equilibration time, calibrated at a different temperature than the solution, acid error, sodium error
remember that no electrode is 100% selective for one ion
acid error
acidic conditions, glass is saturated with H+ and cannot be protonated, giving a more basic pH than the solution truly has
steps for using a pH electrode
1. electrode placed in aqueous solution
2. the surface of the thin glass membrane swells as it absorbs water
3. metal ions in the hydrated gel region diffuse out of the glass into solution
4. H+ diffuses into the glass in place of the metal ions
5. The potential difference is measured across the membrane by two reference electrodes
6. The potential difference is converted to a pH value
ion-exchange equilibrium
established at the glass membrane when in contact with a definite H+ concentration
Solid State Electrodes (the F- ISE)
Doping membrane crystals with EuF2 (Eu2+) creates anion vacancies and increases conduction; used to create a potential difference against a solid-state membrane
ionophores
aka ligand, organic ion-exchange agent that increase the permeability of membranes to ions, provides selectivity for the analyte ion, utilized by Ca2+ and K+ in liquid membrane electrodes
characteristics of the organic polymer mmb in an liquid membrane electrode
hydrophobic, filled with a viscous organic solution containing an ion exchanger, sometimes a ligand specific for the analyte ion
Ammonia ISE
1. use a gas-permeable membrane
2. increase the pH of the external solution to convert NH4+ > NH3
3. NH3 can pass across the gas permeable membrane
4. NH4+ to NH3 ratio is changed and the pH is increased
Spectral Interference
Overlap of analyte signal with signals due to other elements
Solution: choose another wavelength for analysis
ICP, Monochromator
Physical Interference
Matrix related issues affecting droplet size or transport, fix by matching matrix in standards and samples
Chemical Interference
Formation of stable compounds that will not atomize
Fix: use releasing (competes with interfering species for analyte, freeing analyte into the atomization zone, or protective agents (form volatile or soluble complexes with the analyte itself)
Ionization Interference
Loss of neutral atoms due to high temp ionization
Na ionizing in flame, add ionization suppressors which will decrease the extent of ionization in an analyte
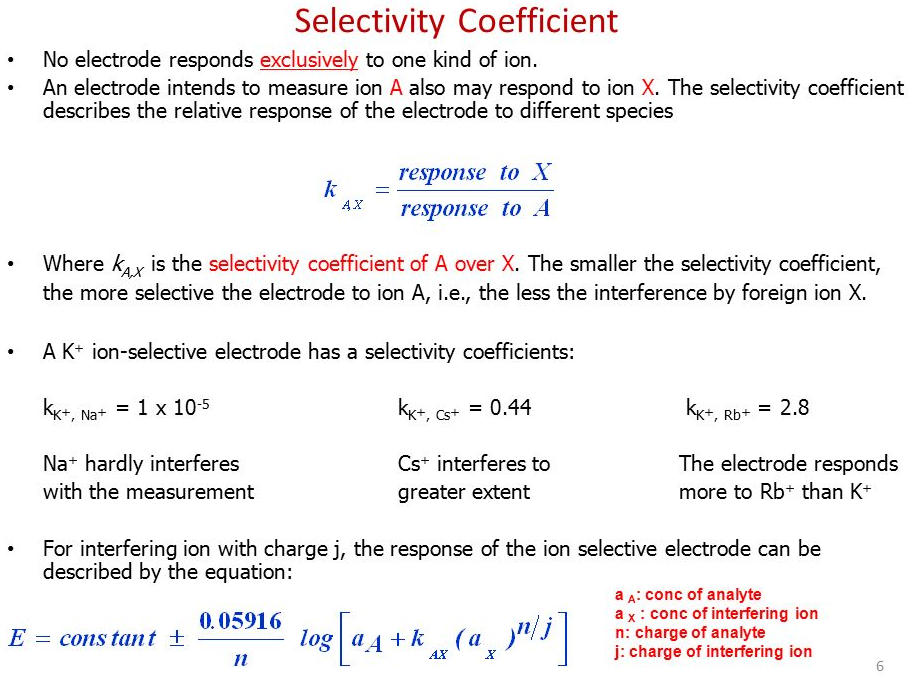
Selectivity Coefficient
Relative Response to different species of the same charge, plug into Nerst Equation to Correct
k Pot A,X = reponse to X (interferring)/ Reponse to A (ion you want to see a response to).
You want K to be small