human resource management (unit 6)✅
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Employee engagement
When an employee is positively present during the performance of work by willingly contributing intellectual effort, experiencing positive emotions and meaningful connections to others
Motivation
Describes the factors that arouse, maintain and channel behaviour towards a goal
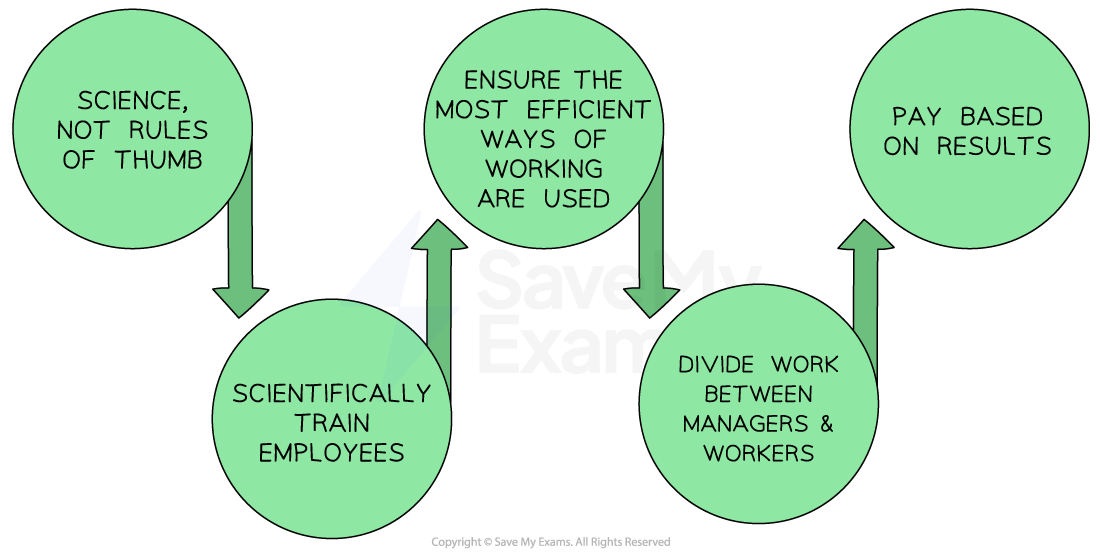
Frederick Taylor on motivation
Saw it as the consequence of external factors. Employees should be closely supervised and paid piece-rate. Employees could be motivated by monetary rewards for achieving precise goals
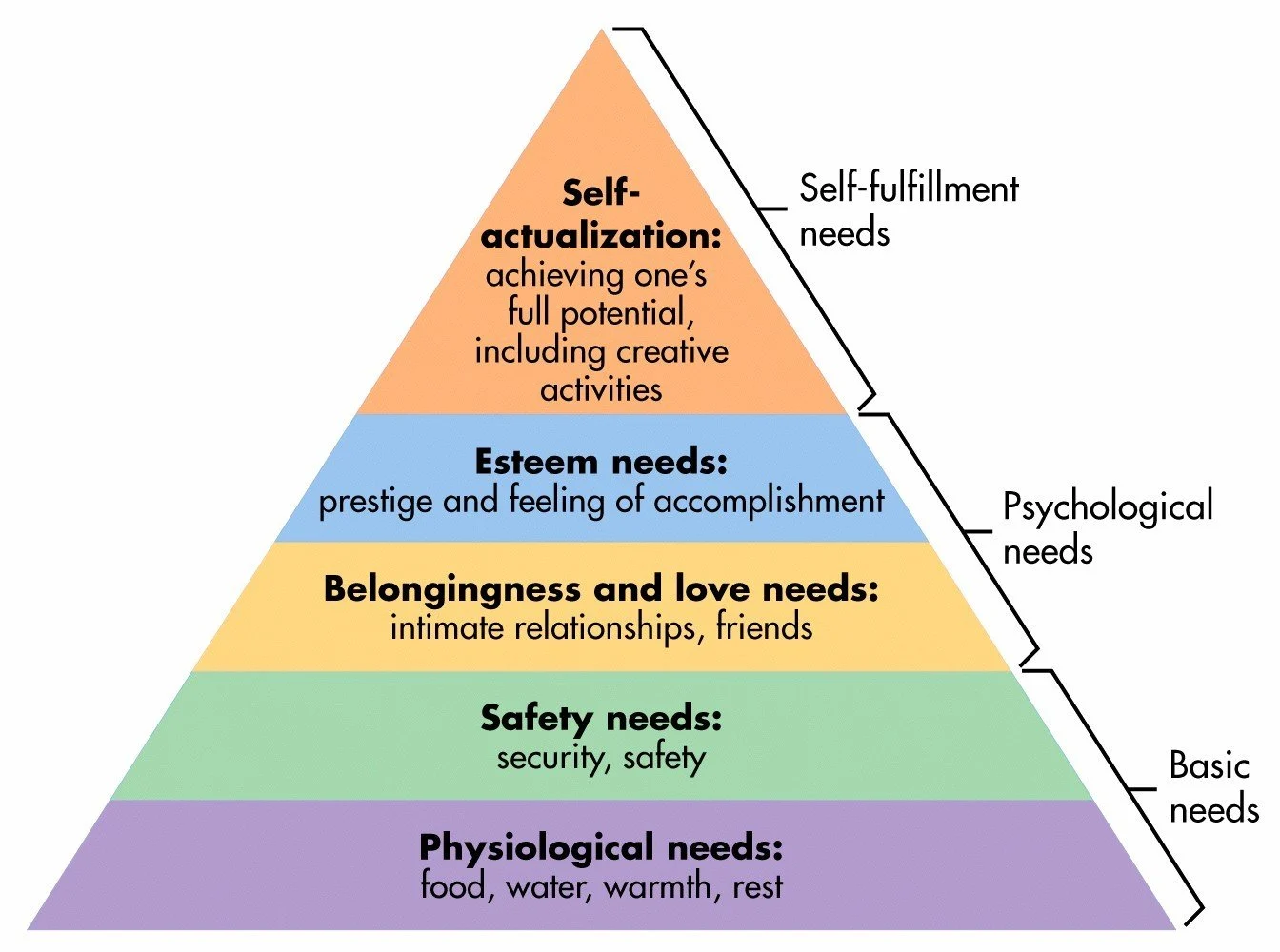
Abraham Maslow on motivation
Considered the needs of employees that must be met to motivate them. He identified 5 categories which he put in a hierarchy and once employees reached one level in this hierarchy they could be motivated by being given the opportunity to meet needs in the next level
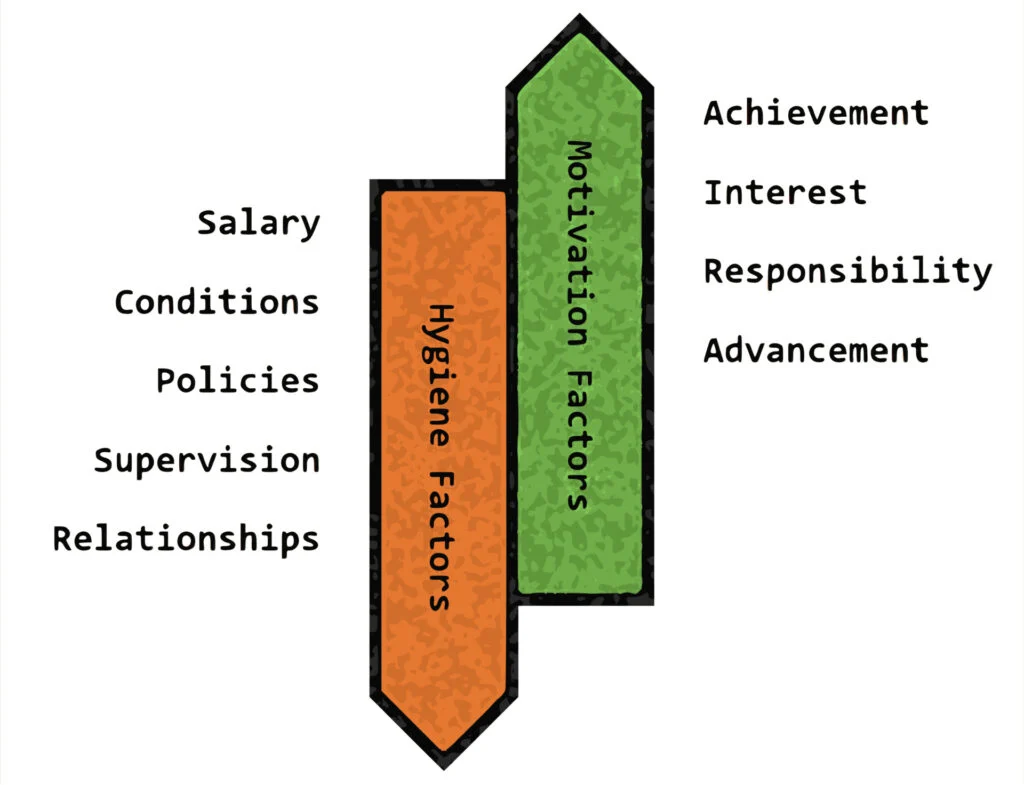
Frederick Herzberg on motivation
Split the factors which influence motivation into 2 categories. Hygiene factors such as pay, do not positively motivate but they have the potential to demotivate. In contrast motivators such as recognition for achievement can positively motivate employees
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
Taylorism
Herzberg’s two factor theory
Financial methods of motivation
Piece rate
Commission
Performance related pay
Salary schemes
Non-financial methods of motivating employees
Empowerment
Teamwork
Job rotation
Flexible working
Job enrichment
Benefits of motivated and engaged employees
Low levels of absenteeism
Low levels of labour turnover
Good relations
High labour productivity
Influences on the choice of methods of motivation
Costs involved
Attitude of the management team
Training
Skill level of workforce
Effectiveness of communciation
Importance of publics perception of the business
Employee representations
Trade unions
Work councils
Communicating effectively with employees
Appreciating the nature of effective communciation
Using the appropriate style of management
Adapting the organisational structure to encourage effective communication
Arbitration
A procedure for the settling of a dispute, under which the parties agree to be bound by the decision of a third party
Industrial dispute
Disagreement between an employer and its employees, usually represented by a trade union, over some aspect of the terms or conditions of employment
Conciliation
Method of resolving individual or collective disputes in which a neutral third party encourages the continuation of negotiations
Managing employer-employee relations can…
Be divided into 2 sections:
Avoiding industrial disputes
Resolving industrial disputes
Human Resources (HR)
A function responsible for the use of labour within the organisation
HR objectives
Labour productivity
Number and location of the business’s workforce
Employee engagement and involvement
Training
Talent development
Diversity
Alignment of values
Hard HR approach
Treating employees as a resource to be used optimally, employees are another resource to be deployed as efficiently as possible in pursuit of strategic targets
Soft HR approach
Based on the notion that employees are the most valuable asset a business has and they should be developed to maximise their value to the organisation
Labour productivity
Total output per time period ÷ Number of employees at work
Unit labour costs
Total labour costs ÷ Number of units produced
Labour turnover
(Number of staff leaving during year ÷ Average number of staff) x 100
Labour retention
(Number of employees employed for 1 year or more ÷ Average number of staff) x 100
HR plan
Assesses the current and future capacity of a business’s workforce and sets out actions necessary to meet the business’s future human resource needs
4 models of organisational structures
Functional
Product based
Matrix
Regional
Job design
Process of grouping together or dividing up tasks and responsibilities to create complete jobs
Job enrichment
Occurs when employees jobs are redesigned to provide them with more challenging and complex tasks
Organisational design
A process to ensure that the organisation is appropriately designed to deliver organisation objectives in the short and long term
Key factors in organisational design
Levels of hierarchy
Span of control
Delegation
Authority
Centralisation and decentralisation
Elements of the HR flow
HR planning
Recruitment and selection
Training
Dismissal and redundancy
Redeployment