ANHB3323 (4) - Nucleus
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What happens inside the Nucleus (4 things)
1. transcription (DNA to mRNA)
2. processing/export of mRNA
3. DNA replication
4. DNA integrity/repair
Birth of Daughter Nuclei
Each cell division:
nuclear envelope breaks down and is reformed
Nuclear factors have to be re-imported via nuclear pores
Nuclear organisation has to be re-created
Each cell is established by the formation of a new nucleus
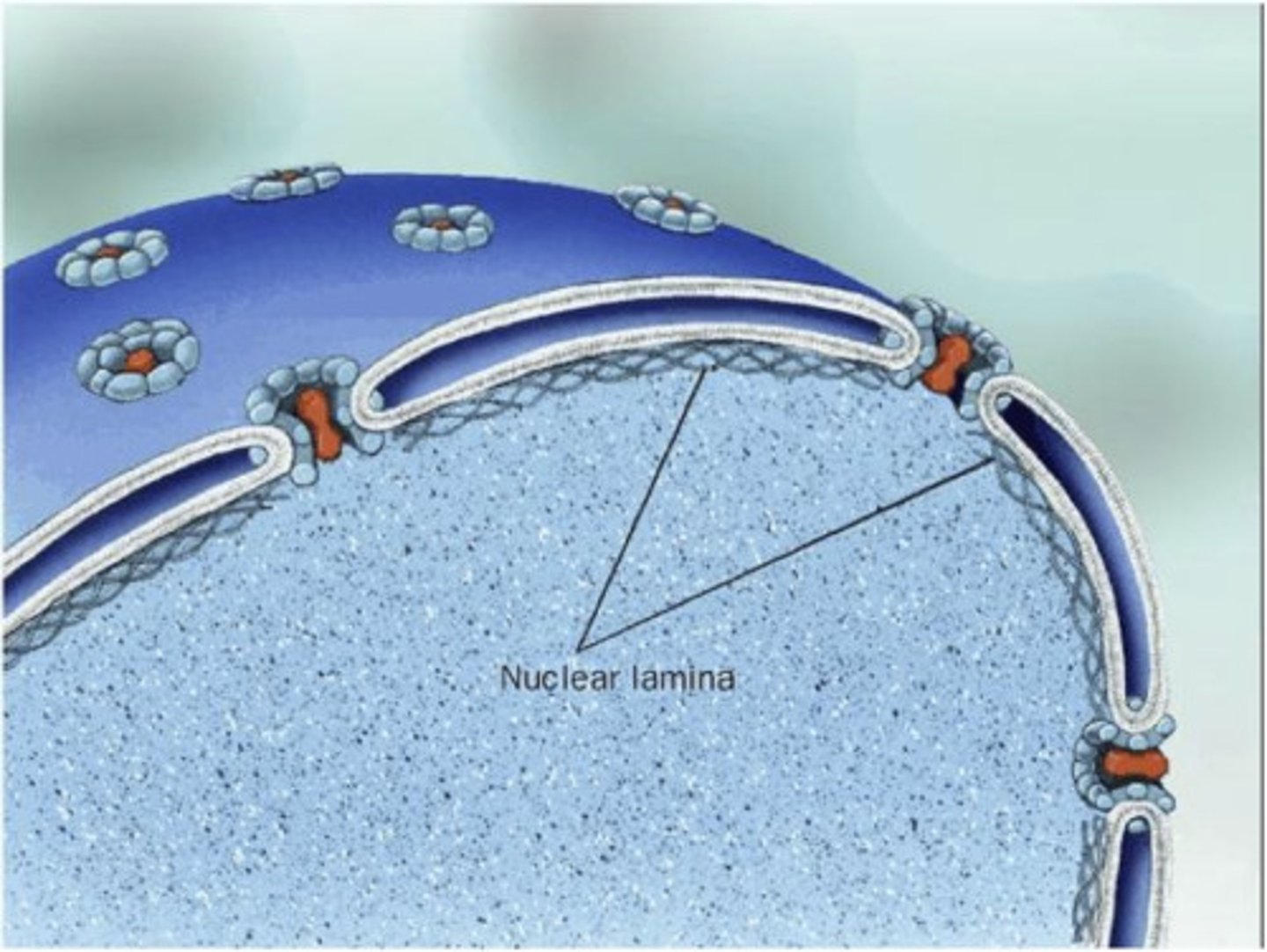
Nuclear envelope
Double Membrane:
1. Outer = continuous with Rough ER
2. Inner = associates with nuclear lamina
has pores for import/export, molecules sit in the space between the two sheets of membrane
Nuclear import/export
All molecules pass through nuclear pores
Passive diffusion:
- for molecules under 20-30kDa
Large proteins:
- have export/import signals
- need cargo molecules which act as carriers
Nuclear lamina
Composed of lamina proteins:
gives structural stability to nucleus
Mutations in Lamin Genes
Cause/lead to:
progeria (premature ageing)
other muscle diseases
Lamin Mutations
1. Nucleus cannot withstand mechanical stress
2. Alters nuclear organisation = gene expression changes
What is found inside the Nucleus?
Chromatin = DNA + packaging proteins
What is Chromatin connected to?
the Nuclear Lamina
Chromosome Territories
defined location of each chromosome:
- some at the periphery
- some in the centre
What influences Chromosome Territories?
Cell type + shape
Size of chromosome (larger chromosome are usually at the periphery)
Fluorescent in Situ Hybridisation (FISH)
Used to localise DNA sequences
How:
short fragments ('probe') of DNA complement sequence of interest
probe is labelled with fluorescent dye
target DNA is deanatured, allowing probe to anneal
It is possible to FISH on multiple chromosomes are the same time
Nucleolus (general info)
Forms around ribosomal DNA repeat
Densest part of cell
Nucleolus function
Site of:
ribosome production
subnuclear sequestration of regulatory molecules
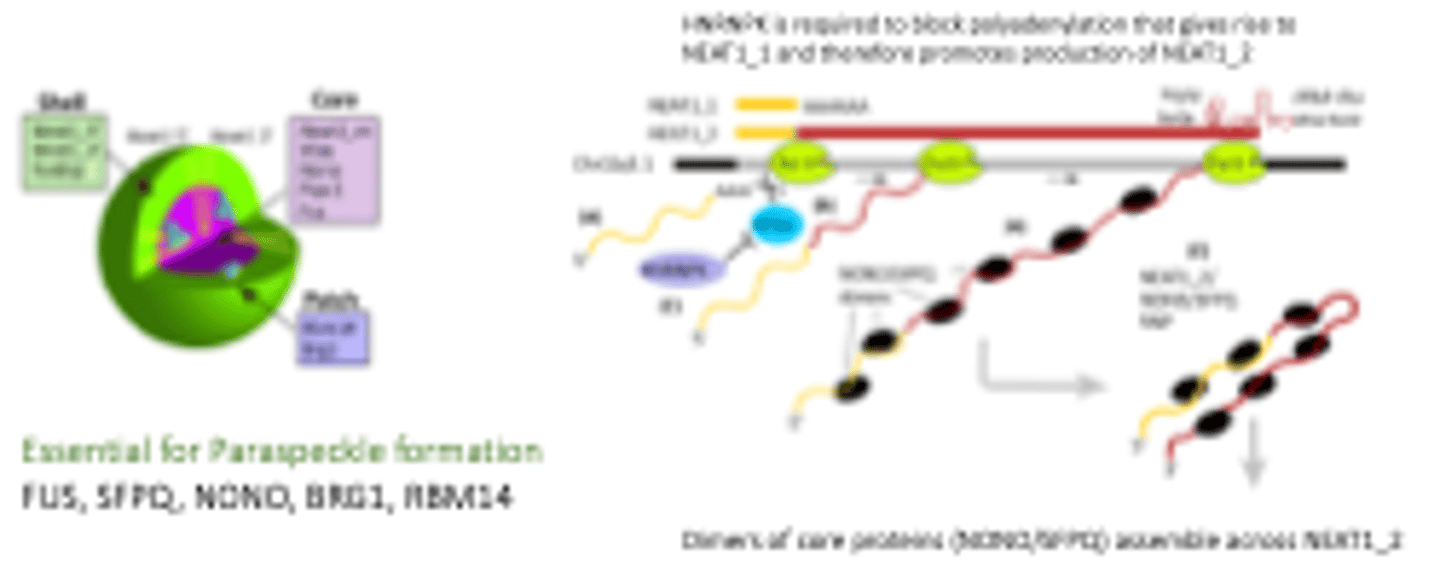
Paraspeckles (general info)
Stress-induced subnuclear bodies
Built around long noncoding RNA (NEAT1)
Paraspeckles function
Regulate gene expression by:
- Sequestration of paraspeckle proteins
Paraspeckle substructure
Has distinct zones:
- Core
- Shell
- Patch
Molecular movement
Despite crowding, molecules move rapidly throughout the nucleus
inactive genes in the middle
Actively transcribed genes are found at the edges or outside the territory
genes cluster together to be transcribed
How to determine how fast molecules move in living cells
Photodynamics, via fluorescent protein fusion:
- bleach protein
- image recovery of fluorescence (how long it takes to recover)