Phylogenetic Relationships
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Phylogenetic Trees
hypothesized evolutionary relations based on share derived traits (synapomorphies)
Derived trait
a new trait that evolved from an old trait
Phylogenetic trees give extinct groups
the same worth as living groups
How does phylogenetic trees should how groups are related?
splits in ancestral populations
True/False: Phylogenetic trees have an implied goal or hierarchy.
False
Can phylogenetic trees be biased and how?
yes, based on data included and how it is presented
Operational Taxonomic Units (OTUs)
species/groups on the tree
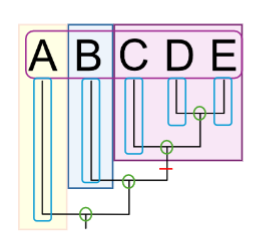
What are the Operational Taxonomic Units (OTUs) on this phylogenetic tree?
A, B, C, D, E (outlined in pink)
Nodes & Branches
show relationships
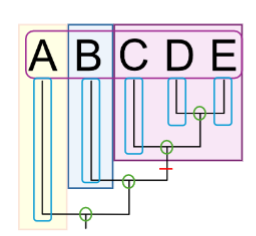
What are the nodes on this phylogenetic tree?
green circles
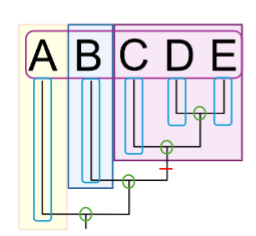
What are the branches on this phylogenetic tree?
outlined in blue
Terminal Branch
leads to Operational Taxonomic Units (OTU)
Internal Branch
lead to a node
Synapomorphy
a shared derived character; can be mapped into branches
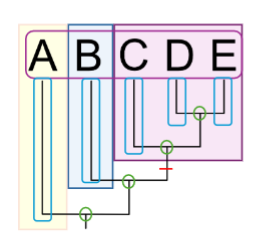
What is the synapomorphy on this phylogenetic tree?
red line
Monophyletic Group
a single common ancestor and all descendants
What is the monophyletic group on this phylogenetic tree?
shaded in purple
Sister Taxa
the next most closely related group to monophyletic group
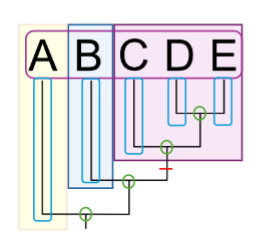
What is the sister taxa on this phylogenetic tree?
shaded in blue
Out Group
most distantly related of all groups
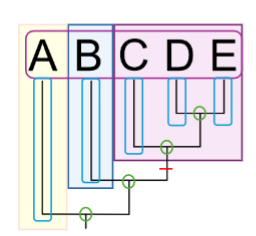
What is the out group on this phylogenetic tree?
shaded in yellow
What can be traits on a phylogenetic tree?
all of the above
Absence of a trait is not a
synapomorphy
Parsimony
the preferred explanation for patterns in the data is the simplest explanation