HUMANBIOLOGY_MODULEONETWO
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
149 Terms
energy
the ability to do work.
order of life’s organizational hierarchy
AMOCTO
The first law of thermodynamics
how energy can be converted between different forms. Cannot be created or destroyed.
metabolism
the biochemical reactions of a cell.
metabolism: catabolic
breaking something down to release energy
metabolism: anabolic
building something up and require energy
chemical reactions: endergonic reactions
require energy, products contain more energy than reactants, building complex molecules from simpler ones.
chemical reactions: exergonic reactions
release energy, products contain less energy than reactants, breaking complex molecules into simpler ones.
atp (adenosine triphosphate)
a molecule whose high-energy phosphate bonds power many biological processes.
enzyme
an organic molecule that catalyzes a chemical reaction without being consumed.
activation energy
energy required for a chemical reaction to begin.
negative feedback
regulatory mechanism in which a change in a condition triggers action that reverses the change.
passive transport
movement of a solute across a membrane without the direct expenditure of energy.
diffusion
the passive movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
active transport
movement of a substance across a membrane against its concentration gradient, using a carrier protein and energy from ATP.
active transport: movement
move from an area of low concentration to high concentration
concentration gradient
difference in solute concentrations between two adjacent regions
endocytosis
form of transport in which a membrane engulfs substances to bring them into a cell.
endocytosis: pinocytosis
small particles
endocytosis: phagocytosis
large particles
receptor-mediated endocytosis
a specialized form of pinocytosis that uses a receptor protein to recognize compatible molecules and take them into the cell.
Cell
The smallest unit of life that can function independently.
Organism
A single living individual; organisms consist of one or more cells.
Atom
A particle of matter; composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Molecule
Two or more atoms joined by chemical bonds.
Organelles
A membrane-bounded structure with a specific function inside a cell.
Tissue
Group of cells that interact and provide a specific function; multicellular life only.
Organ
Two or more tissues that interact and function as an integrated unit; multicellular life only.
Organ System
Two or more physically or functionally linked organs; multicellular life only.
Population
A group of the same species of organism living in the same place and time.
Community
All populations that occupy the same region.
Ecosystem
The living and nonliving components of an area.
Biosphere
Part of Earth where life can exist.
Multicellular
Having or consisting of many cells.
Unicellular
Consisting of a single cell.
Primary Producer
Species forming the base of a food web by extracting energy and nutrients from nonliving sources; an autotroph; plants, microbes, and some bacteria.
Consumers
Organisms that eat other organisms; heterotrophs; living or dead.
Decomposers
Organisms that consume wastes and dead organic matter, returning inorganic nutrients to the ecosystem.
Homeostasis
A state of internal constancy in the presence of changing external conditions.
Asexual Reproduction
Offspring arise from only one parent.
Sexual Reproduction
The combination of genetic material from two individuals to create a third individual.
Evolution
Genetic change over time in a population.
Adaptation
Inherited trait that permits an organism to survive and reproduce.
Taxonomy
The science of describing, naming, and classifying organisms.
Scientific Method
A systematic approach to understanding the natural world based on evidence and testable hypotheses.
Hypothesis
A testable, tentative explanation based on prior knowledge.
Prediction
Anticipated outcome of the test of a hypothesis.
Observations and Questions
Initial observations and questions that lead to hypotheses and predictions.
Experimental Design
A careful plan to test a hypothesis.
Variable
Any changeable element in an experiment.
Independent variable
What is manipulated; a factor that is hypothesized to influence a dependent variable.
Dependent variable
What is measured; the response that may be under the influence of an independent variable.
Standardized variable
Held constant for all subjects.
Control
Untreated group used for comparison.
Placebo
Inert substance sometimes administered to a control group.
Sample size
Number of subjects in each treatment and control group.
Statistically significant
Unlikely to be attributed to chance; the probability that results arose purely by chance is low.
Theory
Well-supported scientific explanation.
Fact
A repeatable observation that everyone can agree on; a collection of facts by itself does not explain anything.
Technology
The practical application of scientific knowledge.
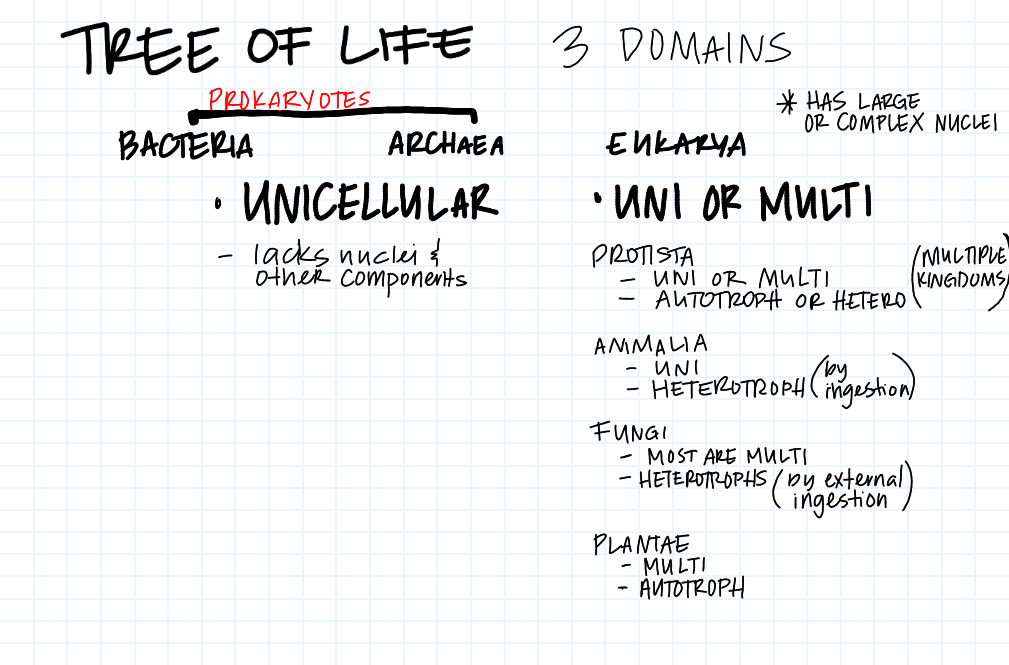
Tree of Life
Image
How many domains does the Tree of Life have?
Three domains: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya.
What are Bacteria and Archaea under?
The two prokaryotic domains of life
True or False: Bacteria and Archaea are unicellular.
True
What domains lacks nuclei and other components?
Bacteria and Archaea
What are the four major kingdoms within the domain Eukarya?
Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia.
Protista
A diverse group of eukaryotic organisms, mostly unicellular, that do not fit into the other eukaryotic kingdoms.
Fungi
Eukaryotic organisms, including yeasts, molds, and mushrooms, characterized by their absorption of nutrients from their environment.
Plantae
The kingdom comprising multicellular organisms that produce their own food through photosynthesis, such as plants.
Animalia
The kingdom comprising multicellular, heterotrophic organisms that typically ingest their food, such as animals.
The scientific method
The process of science, though it varies depending on the situation, generally adheres to an organized sequence of steps.
Scientific Method Steps
Hypothesis 2. Experiment 3. Analysis 4. Conclusion and Reporting
Pillbugs (Rollie Poly)
omnivores, the feed on decaying matter.
How do pillbugs detect food? (smell, taste, touch, sight, sound)
smell
Pillbug: Positive Response?
movement toward a stimulus
Pillbug: Negative Response?
movement away from it
Pillbug: Defense (neither + or -)?
rolling up
choice chamber
two circular chambers with a channel in between. the first chamber has a control substance and the second chamber has a test substance.
substance that takes up space and is made of atoms
matter
a pure substance consisting of atoms containing a characteristic number of protons
element
a particle of matter; composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons
atom
a particle in an atom’s nucleus carrying a positive charge
proton
a particle in an atom’s nucleus that is electrically neutral
neutron
central part of an atom
nucleus (atom)
a negatively charged particle that makes up part of an atom
electron
the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus
mass number
any of the forms of an element, each having a different number of neutrons in the nucleus
isotope
two or more atoms joined by chemical bonds
molecule
volume of space where a particular electron is likely to be
orbital
attraction between oppositely charged ions
ionic bond
type of chemical bond in which two atoms share electrons
covalent bond
weak chemical bond between opposite partial charges on two molecules or within one large molecule
hydrogen bond
the attraction of water molecules to one another
cohesion
a chemical in which other substances dissolve, forming a solution
solvent
a chemical that dissolves in a solvent, forming a solution
solute
a mixture of a solute dissolved in a solvent
solution
interaction in which bonds break and new bonds form
chemical reaction
neither acidic nor basic
neutral (solution)
the result of a chemical reaction
product
compound containing both carbon and hydrogen
organic molecule