exam 2 study guide
1/162
Earn XP
Description and Tags
good luck vro
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
163 Terms
what is the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands?
endocrine secretes in, exocrine secretes out
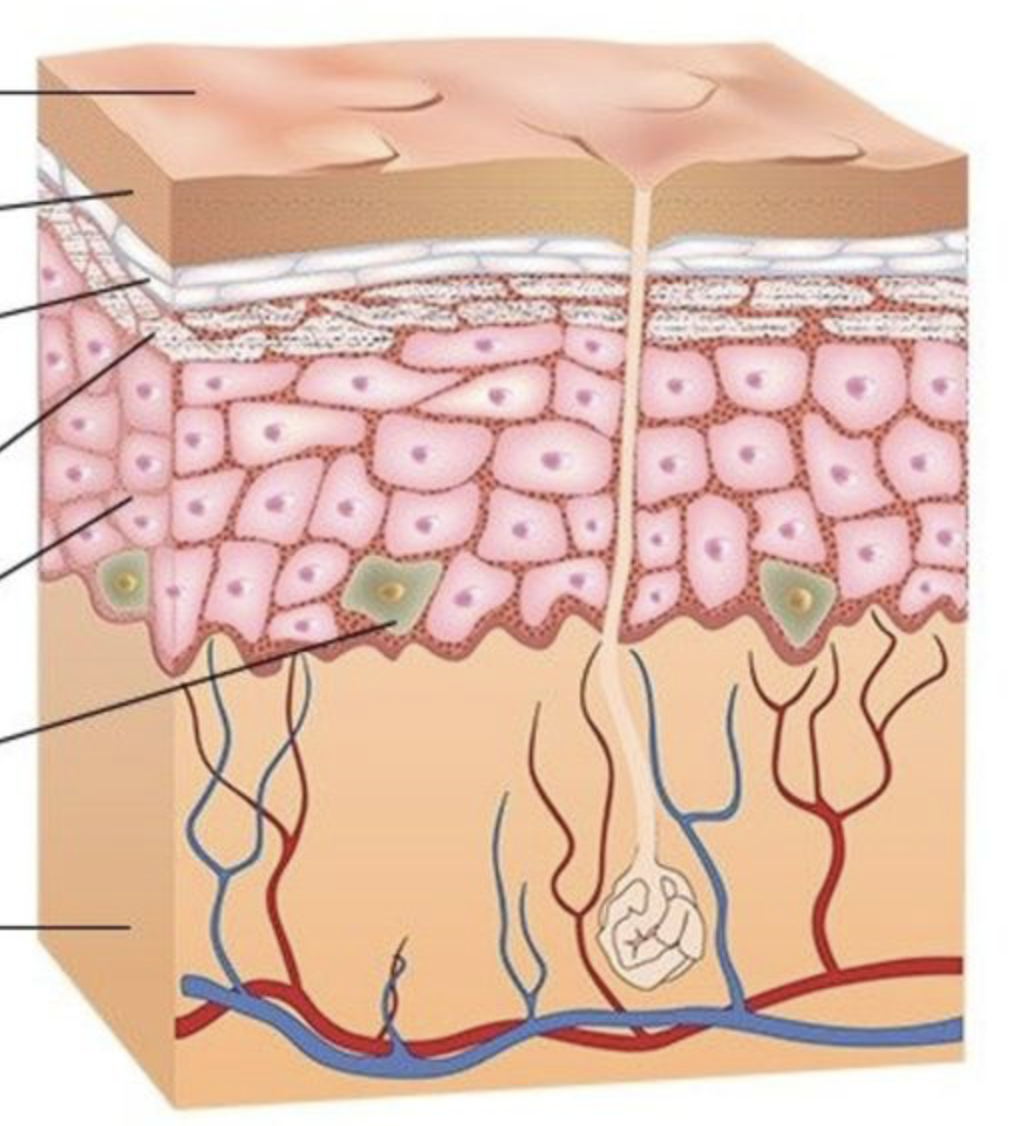
what are the different layers of the epidermis (in order)?
stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, stratum corneum
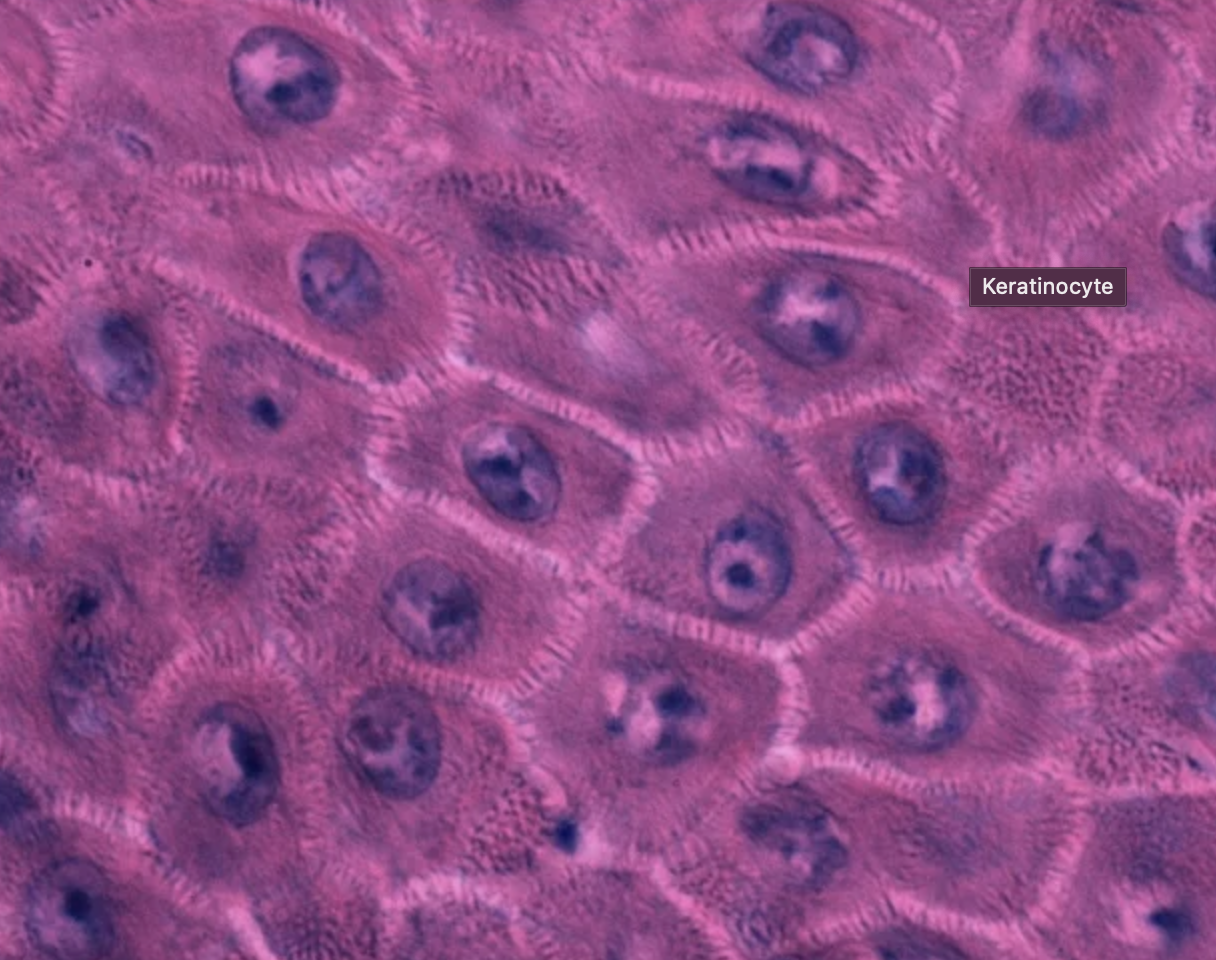
main function of keratinocytes
produces keratin, forms strong barrier of the skin
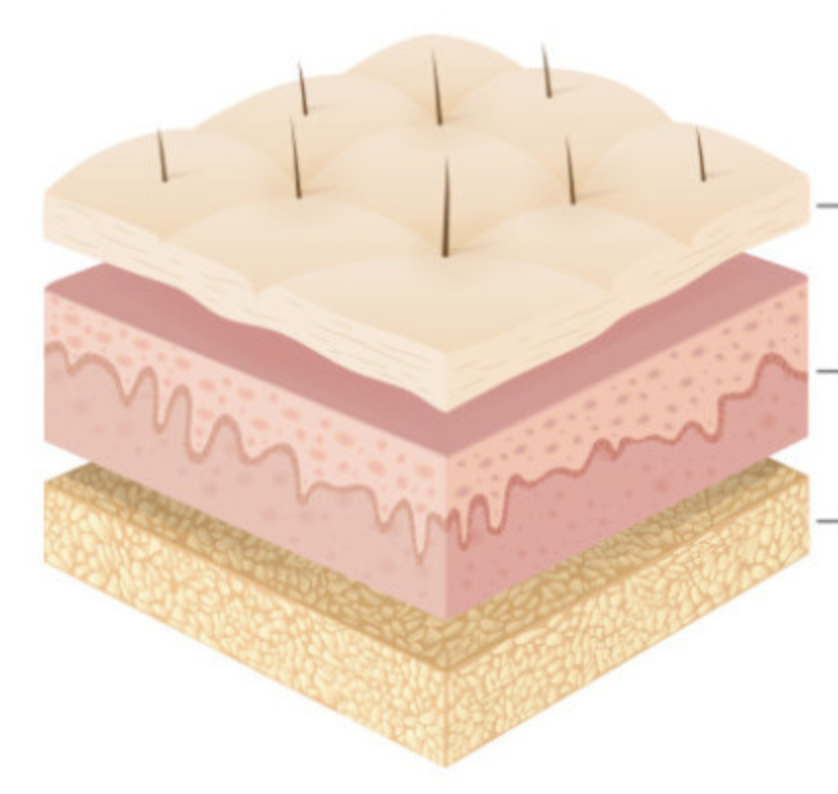
what are the 2 layers of the skin? what layer is associated with the skin? (name 3 layers of the skin
epidermis, dermis, hypodermis
how do you distinguish the 3 different types of burns?
by depth
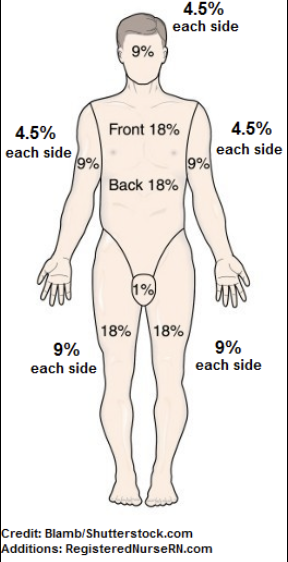
what is the “rule of nines”?
assess extent of burn injury
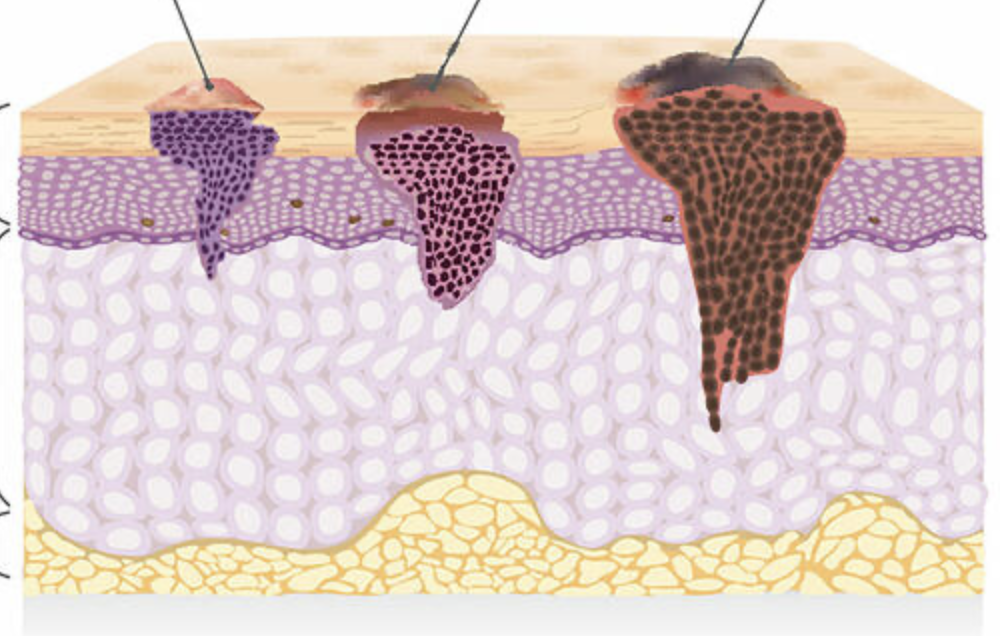
what are the 3 different types of skin cancer?
basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, melanoma
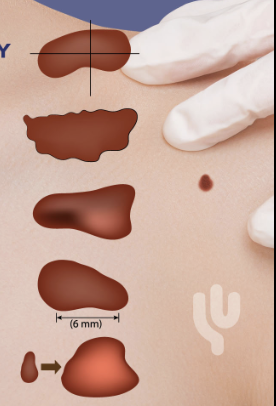
What is the ABCD rule?
analyzes skin lesions for potential melanoma
what do the letters stand for in the ABCD rule?
A: asymmetry, B: borders, C: colors, D: 6mm or larger
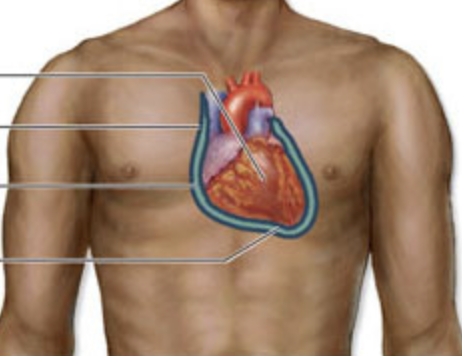
which serous membranes are found in the thoracic cavity
pleura (lungs), pericardium (heart)
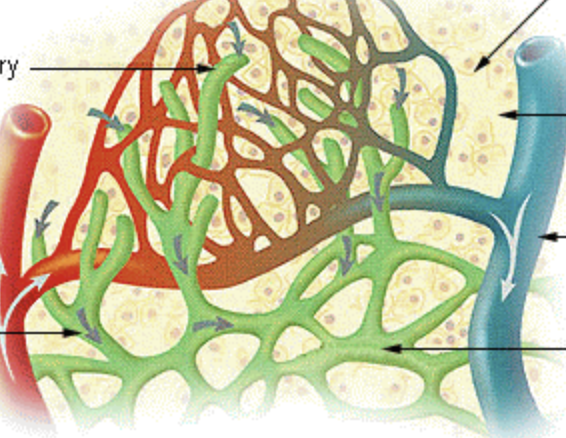
how is lymph returned to the circulatory system?
one way flow in lymphatic vessels (subclavian veins)
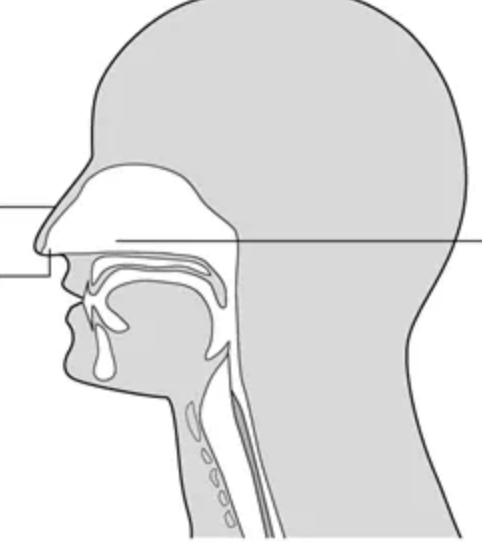
what are the nasal cavity structures
nasal septum, nasal conchas
main function of the nasal cavity structures?
conditions inhaled air and filters it
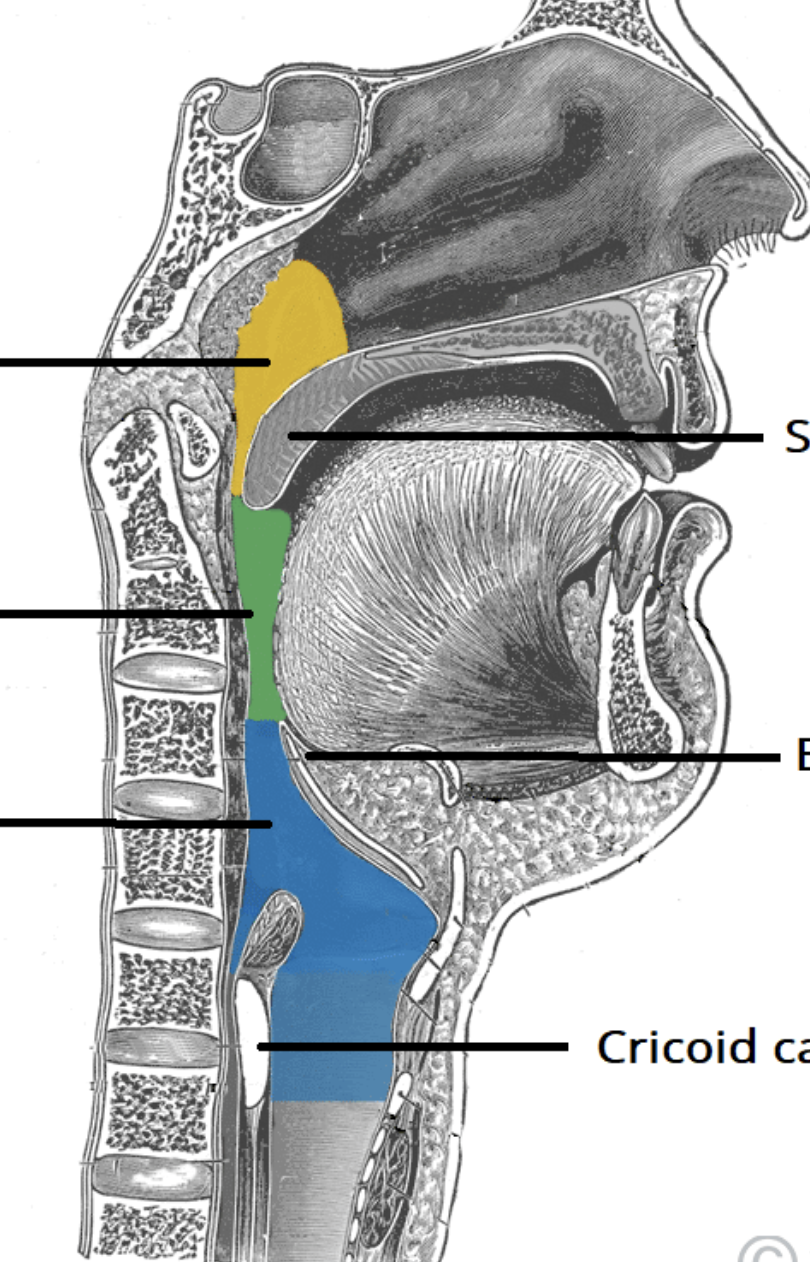
what are the regions of the pharynx
nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx
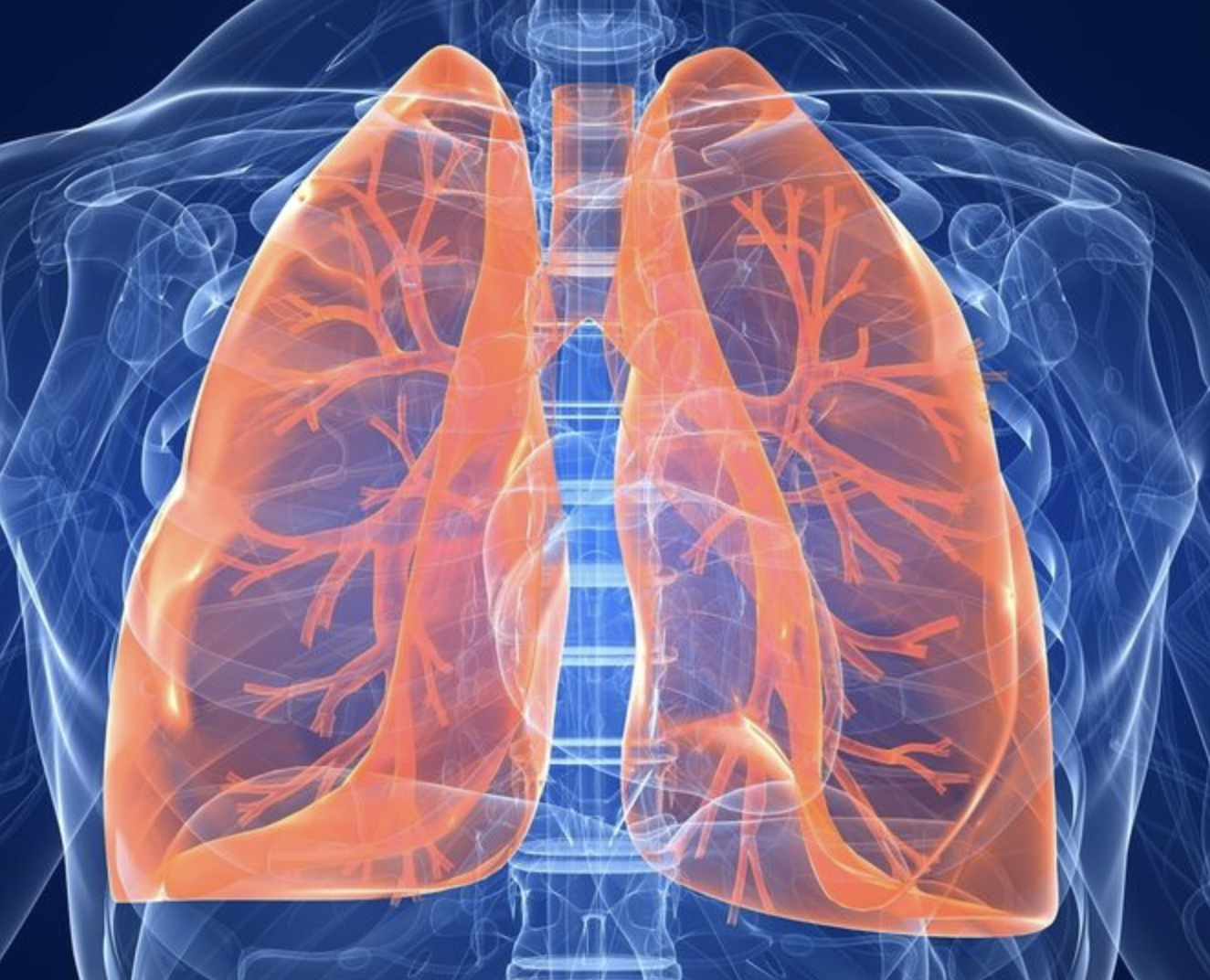
what are the structures of the lungs?
lobes, bronchial tree, alveoli
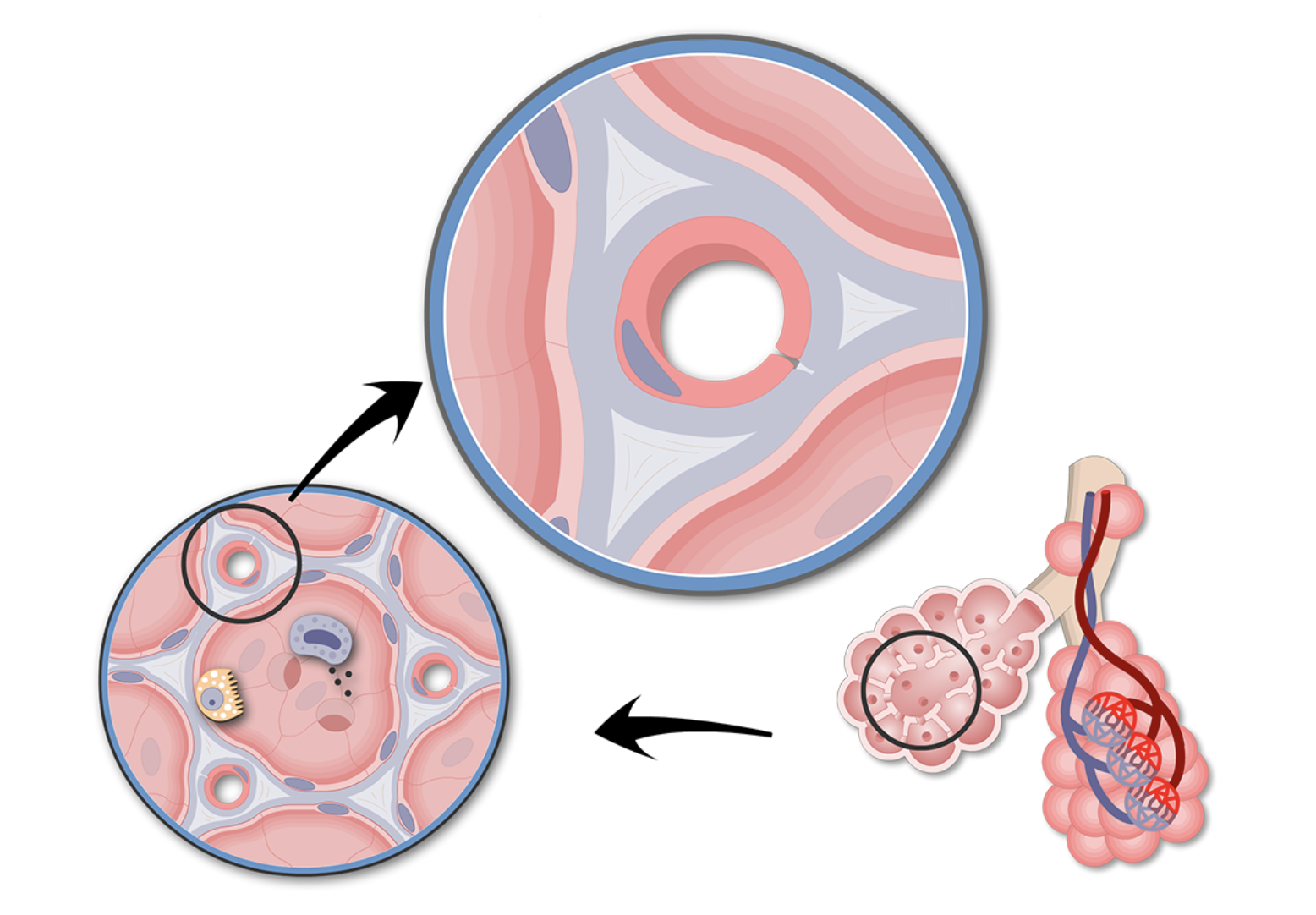
what kind of cells make up the respiratory membrane?
type 1 and 2 pneumocytes, endothelium cells
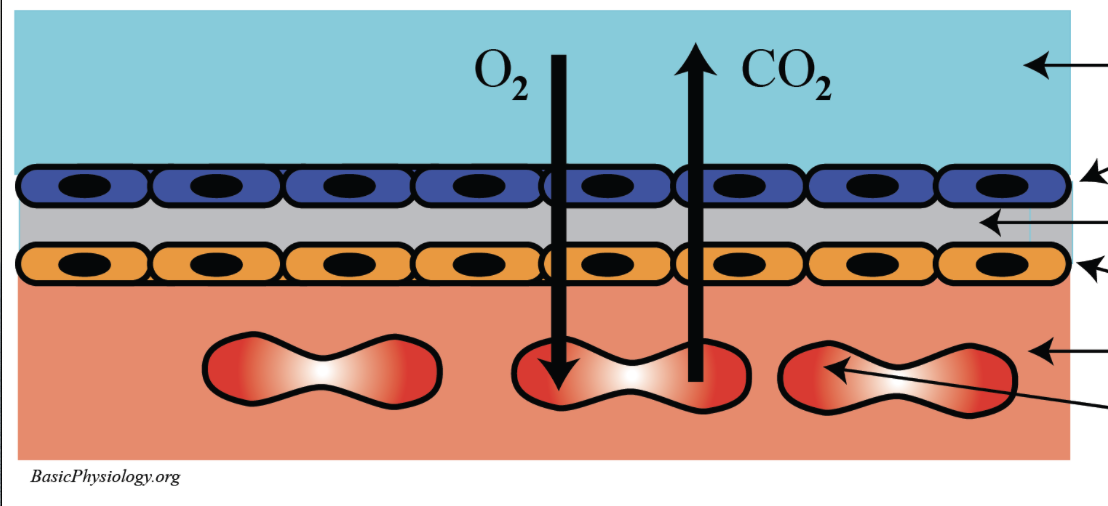
what is the function of the cells of the respiratory membrane?
facilitating diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide
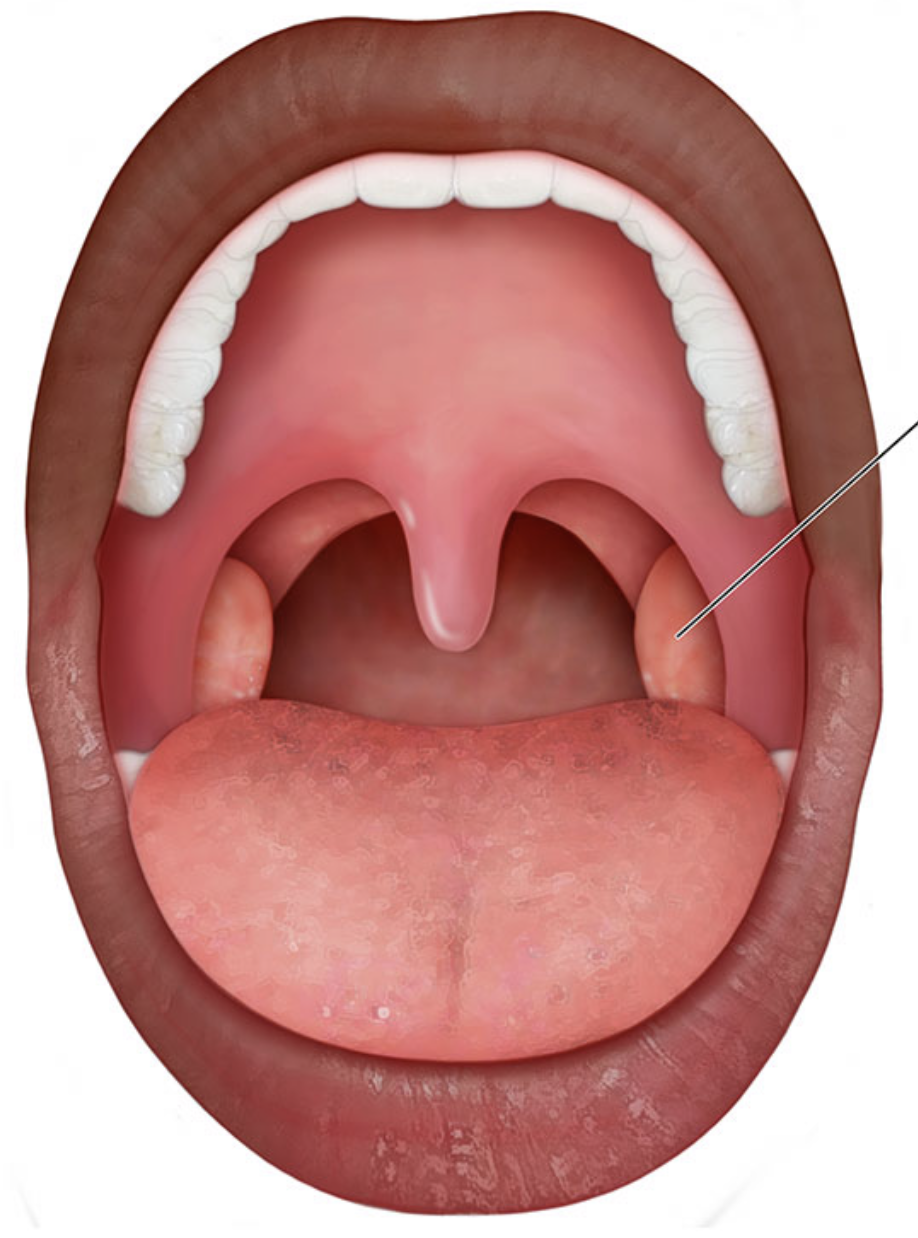
where are the palatine tonsils located
back of oropharynx (lateral walls)
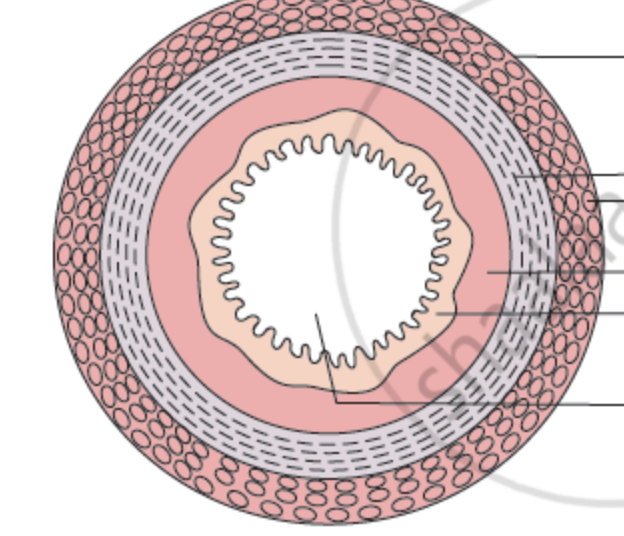
what are the 4 layers of the alimentary canal?
mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, serosa
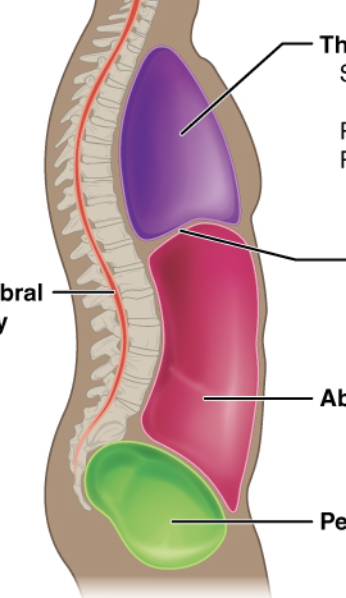
which serous membranes are found in the abdominal cavity?
peritoneum (parietal and visceral)
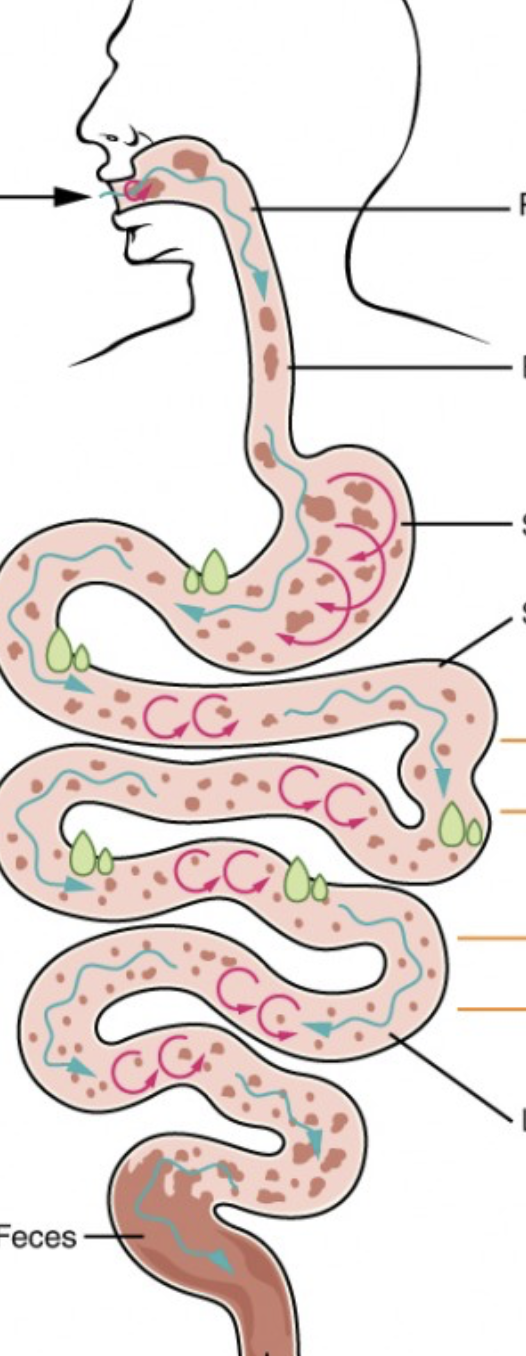
what are the different digestive processes that occur throughout the alimentary canal?
ingestion, propulsion, mechanical breakdown, digestion, absorption, defecation
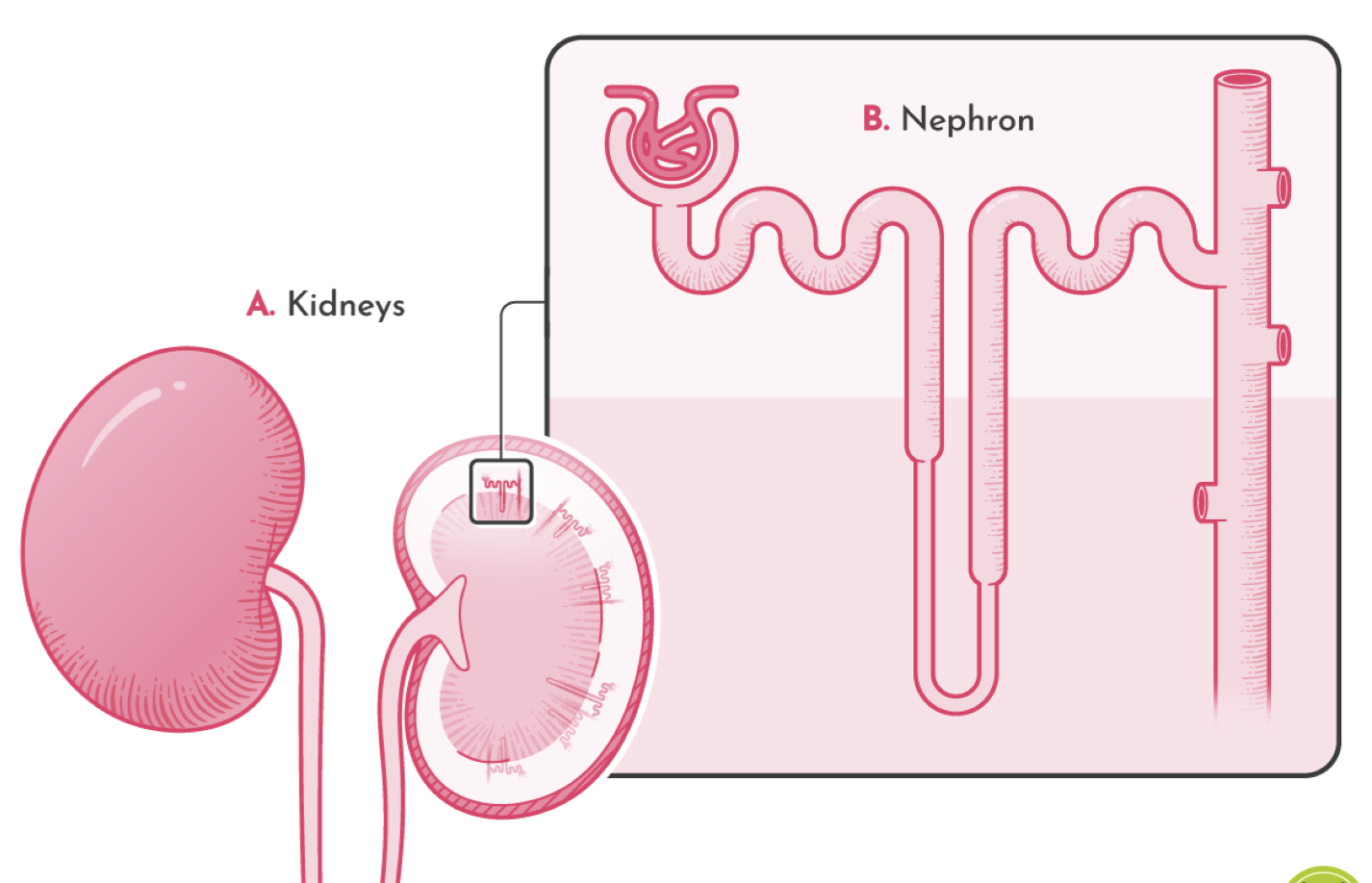
what are the parts of the nephron?
renal corpuscle, renal tubule, collecting duct
how is urine excreted?
kidneys, down to the bladder, out of the body
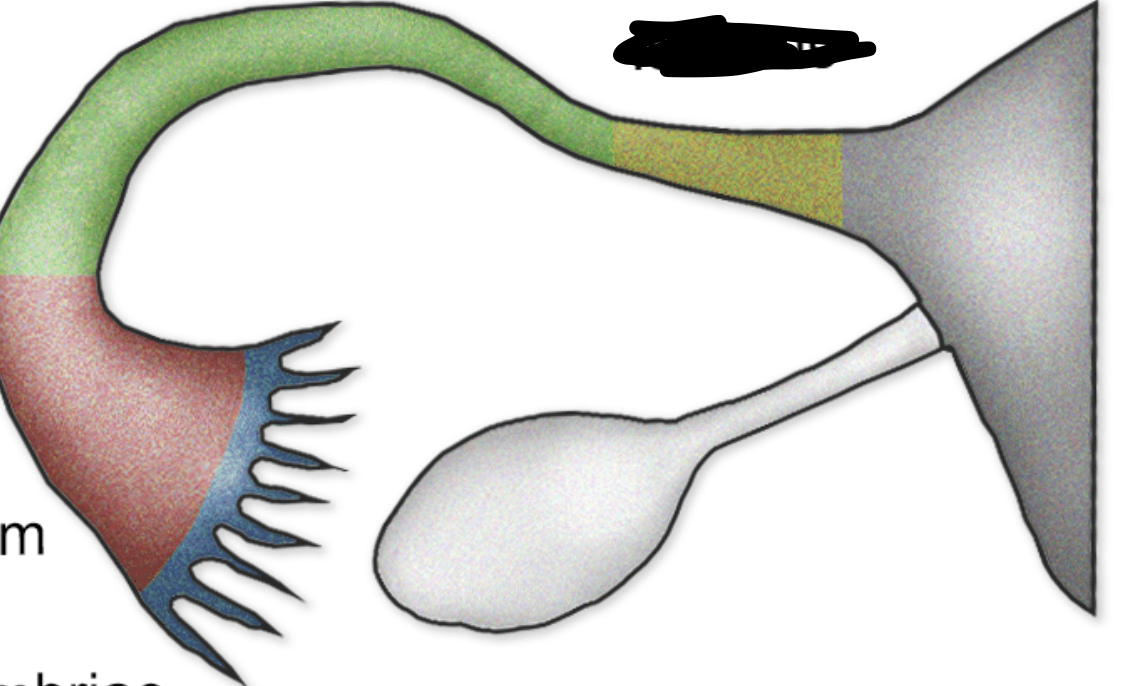
what are the regions of the uterine tubes?
fimbrae, infundibulum, ampulla, isthmus
what are the ducts of the male reproductive system?
epididymis, vas deferens, ejaculatory ducts, urethra
functions of the male accessory organs?
transports sperm and secretes protective fluids
functions of the uterus?
support pregnancy and expel baby via powerful contractions
how do leukocytes differ in appearance?
structure of nucleus, abundance/color of granules within cytoplasm
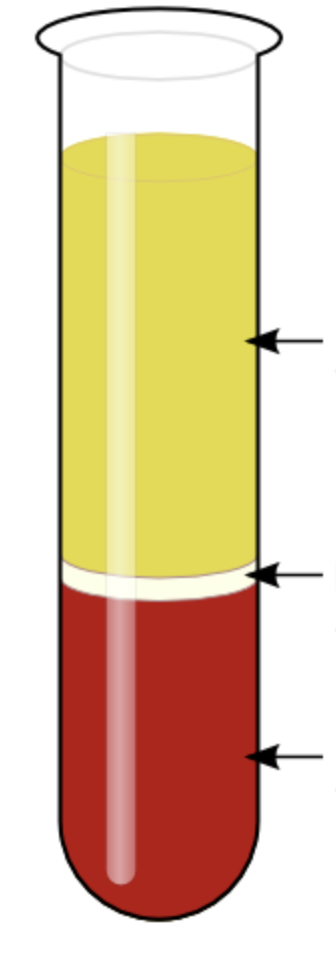
components of centrifuged blood?
plasma, Buffy coat (leukocytes and platelets), erythrocytes
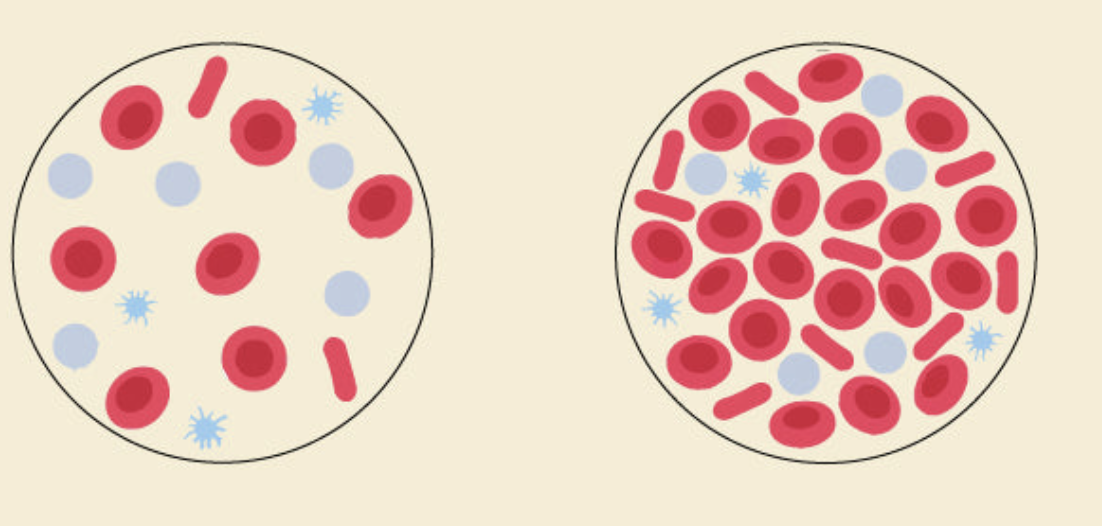
what are the erythrocyte disorders of blood?
anemias and polycythemias
what are the functions of the blood?
transport, protection, regulation
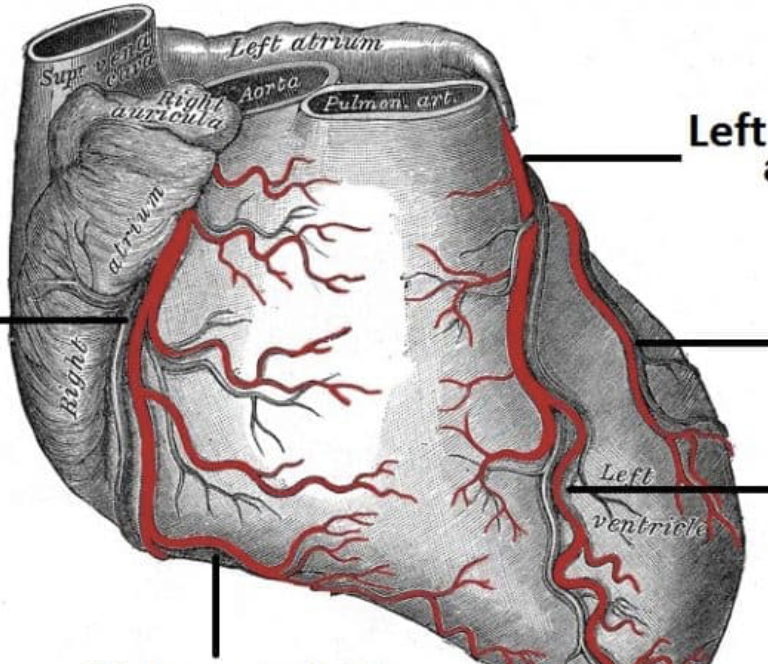
what are the branches of the heart blood vessels?
RCA and LCA
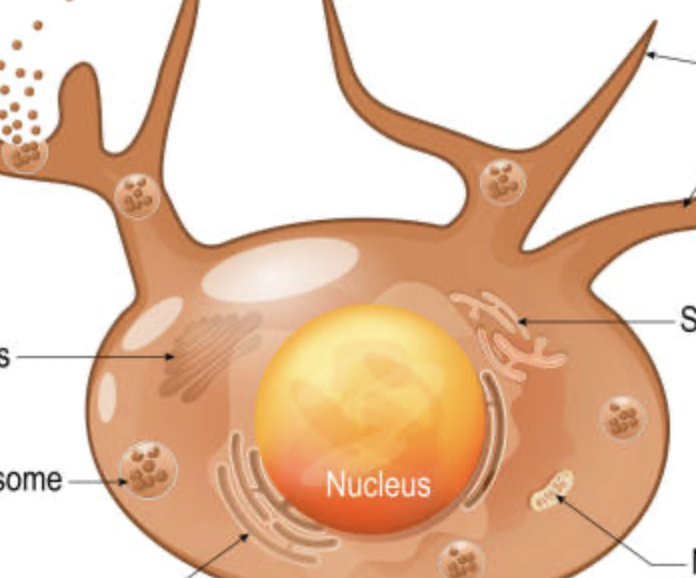
main function for the melanocytes
creates melanin for UV protection
main function of the langerhans cells
immune cells that defend against pathogens
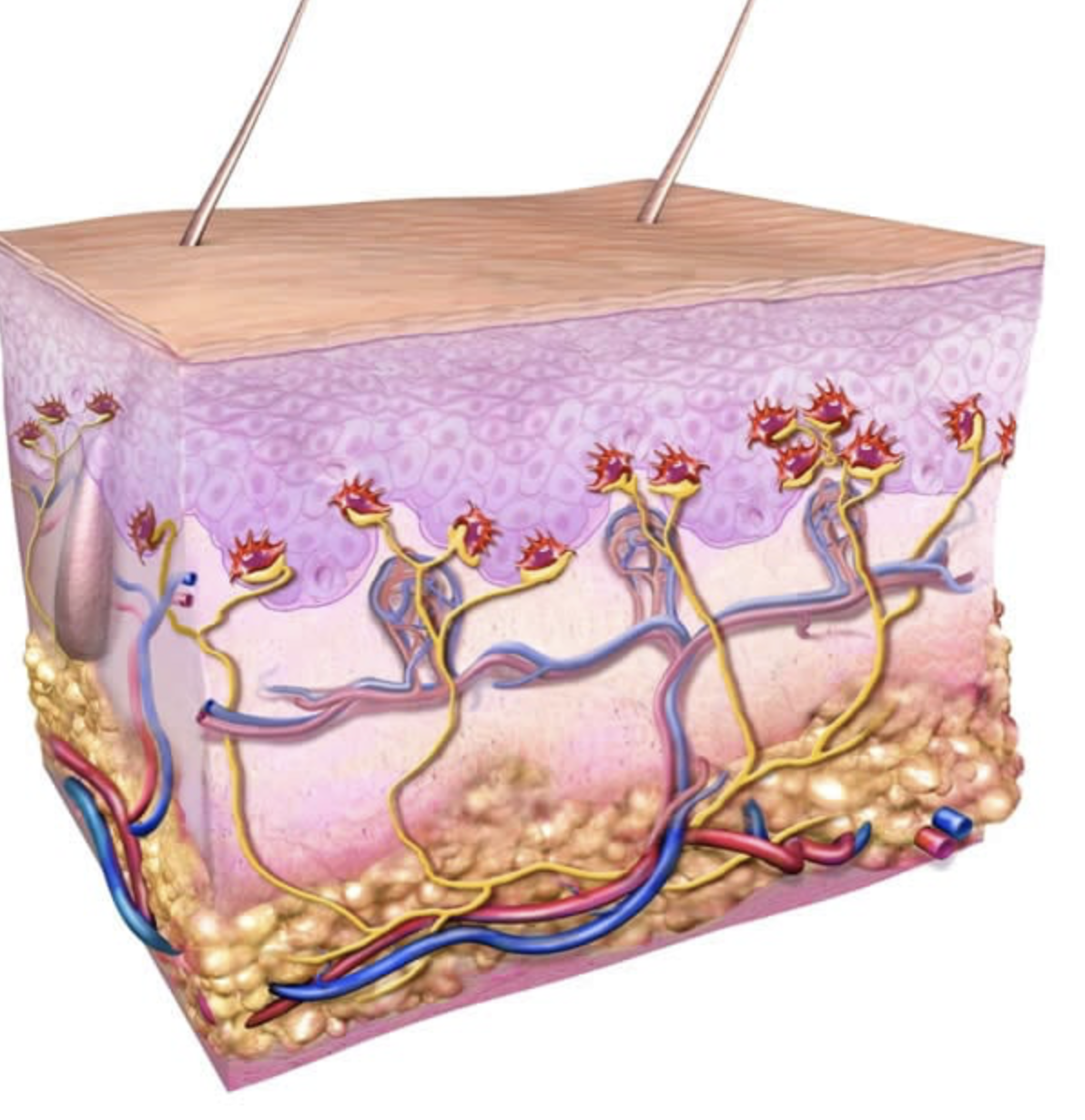
what is the function of the Merkel cells?
touch receptors
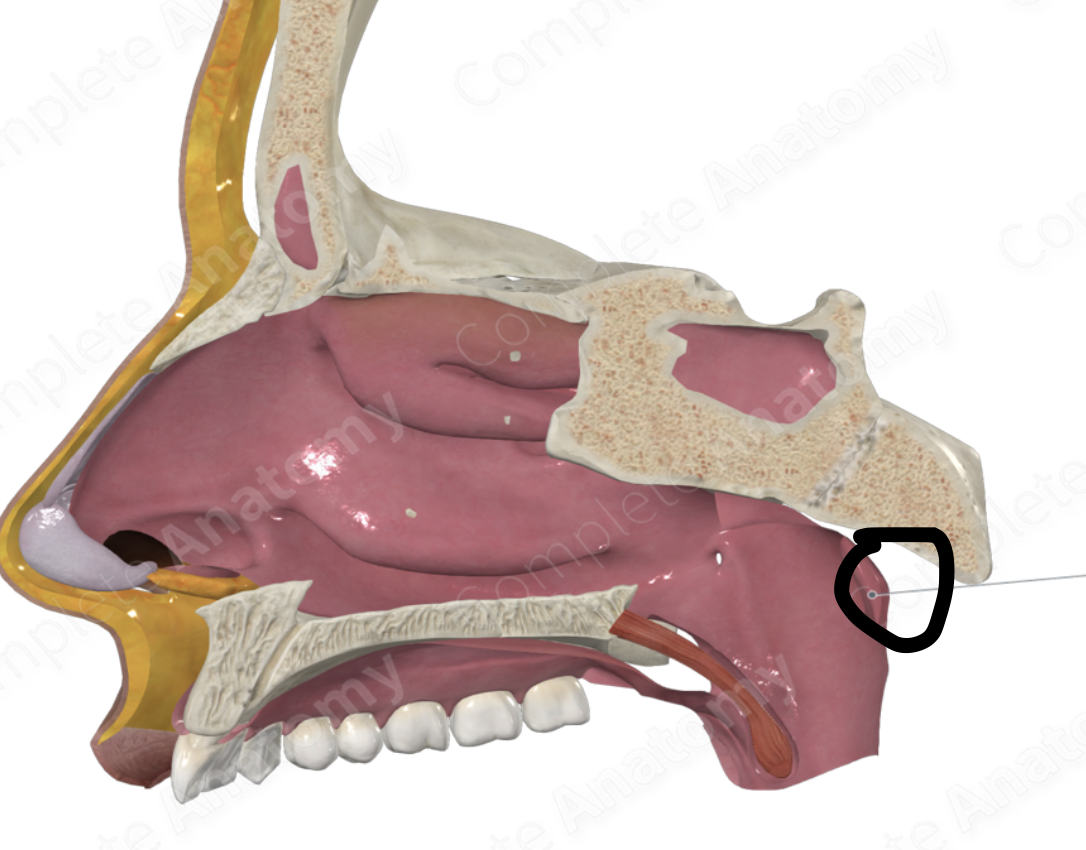
where are the pharyngeal tonsils located?
back wall of nasopharynx
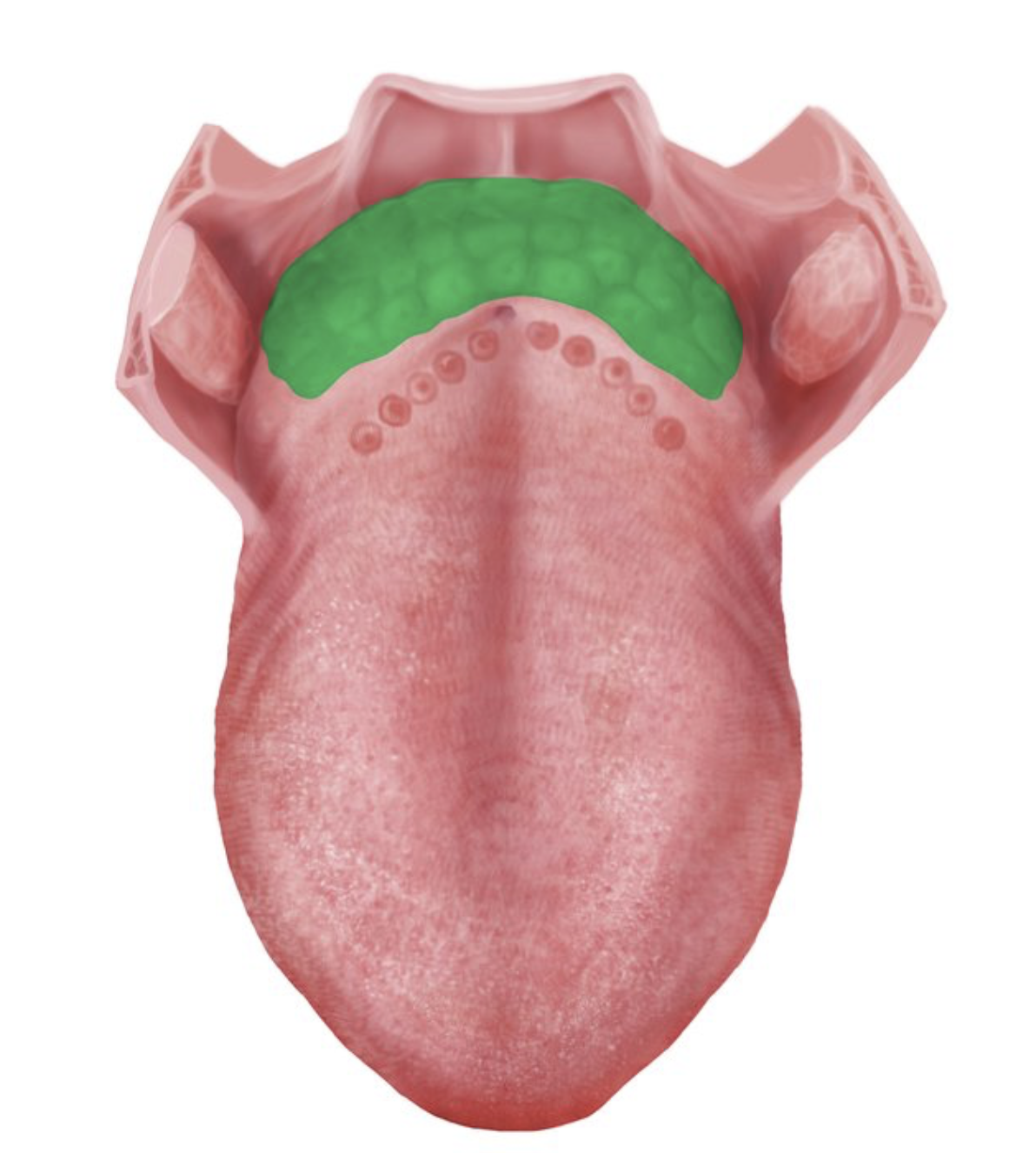
where are the lingual tonsils located?
base of tongue (posterior)
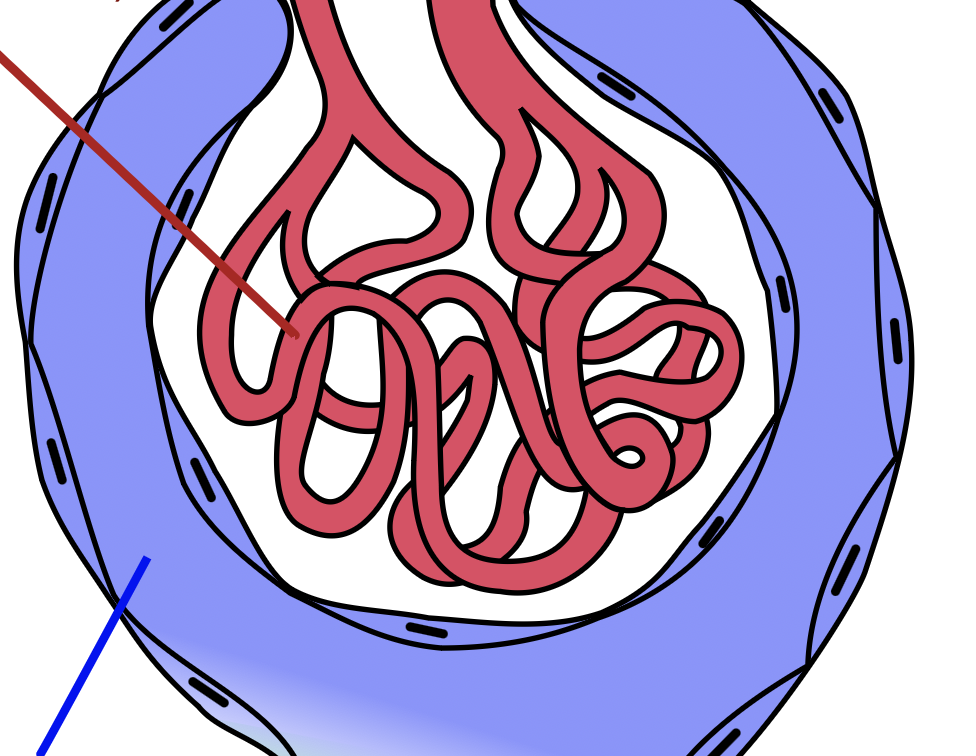
what are the parts of the renal corpuscle?
glomerulus, bowman’s capsule
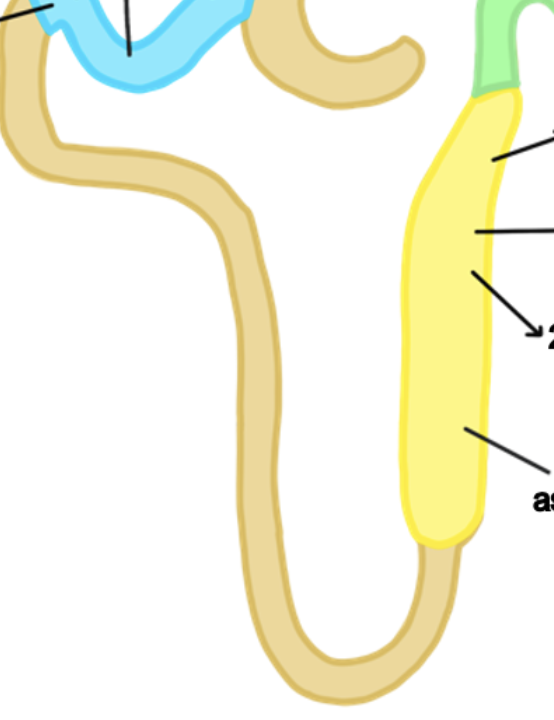
what are the parts of the renal tubule?
proximal convoluted tubule, distal convoluted tubule, loop of henle
what does the afferent arteriole do?
brings blood to glomerulus
what does the efferent arteriole do?
carries blood away from glomerulus
the peritubuluar capillaries and vasa recta surrounds what?
renal tubules
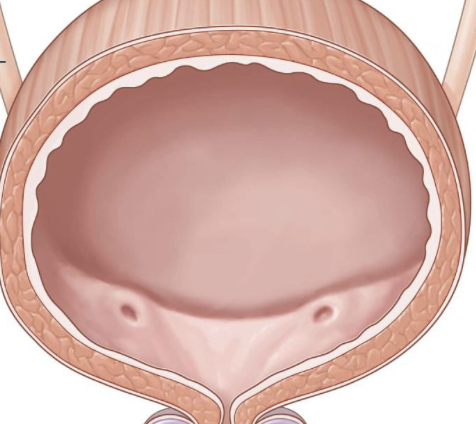
what are the internal features of the bladder?
trigone, ureteric orifices, internal urethral orifice, rugae
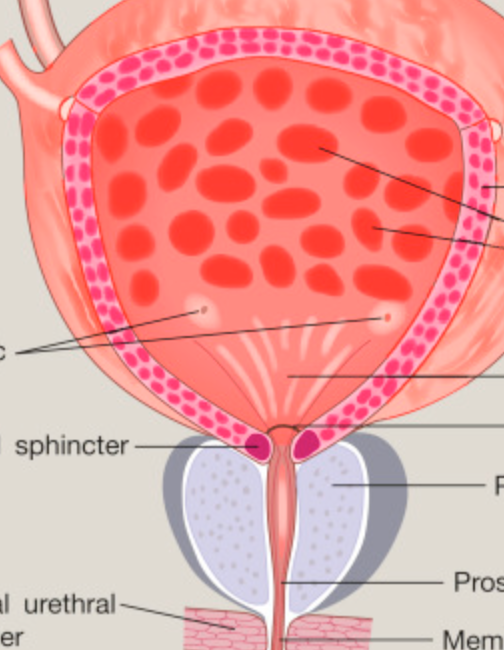
what are the muscles and sphincters of the bladder?
detrusor muscle, internal and external urethral sphincters
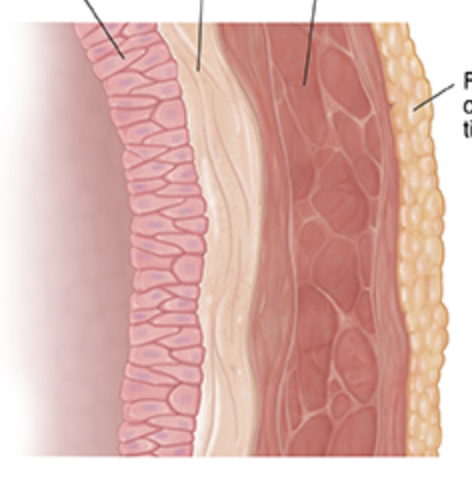
what are the layers of the bladder wall?
mucosa, muscularis propria, adventitia

what are the 4 chambers of the heart
right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, left ventricle
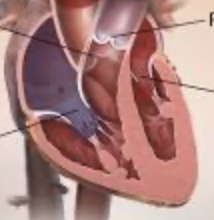
what are the 4 valves of the heart?
tricuspid, pulmonary, mitral, aortic
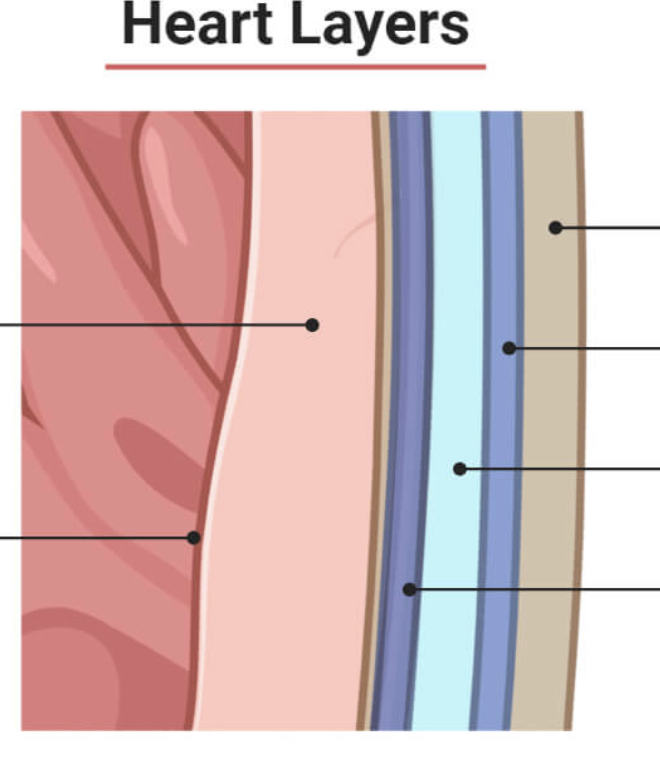
what are the layers of the heart?
endocardium, myocardium, pericardium
what is the function of the right atrium of the heart?
receives deoxygenated blood from the body
describe the pericardium
double layered sac that surrounds/protects the heart
mostly fibrous connective tissue, is vascular
connective tissue

melaoncytes produce pigment _____ granules that are packaged into melanosomes, (spider shaped cells located in deepest epidermis)
melanin
one layer of the epidermis that consists of single row stem cells that produce two daughter cells each time (deepest layer)
stratum basale
appear spikey and is several cell layers thick, (above the basale)
stratum spinosum
four to six cells thick, cells above this layer die, keratinatzion begins within this layer (hint: granola bar)
stratum granulosum
this layer is found only in thick skin, lies superficial to the stratum granulosum
stratum lucidum
this layer of the epidermis protects deeper cells from the environment and also prevents water loss, also known as horny layer (pause?!)
stratum corneum
controlled cell death is known as what?
apoptosis
superficial region of dermis that sends fingerlike projections up into epidermis
papillary layer
consists of coarse, dense fibrous connective tissue, provides strength and resiliency, lies deep to the papillary layer
reticular layer
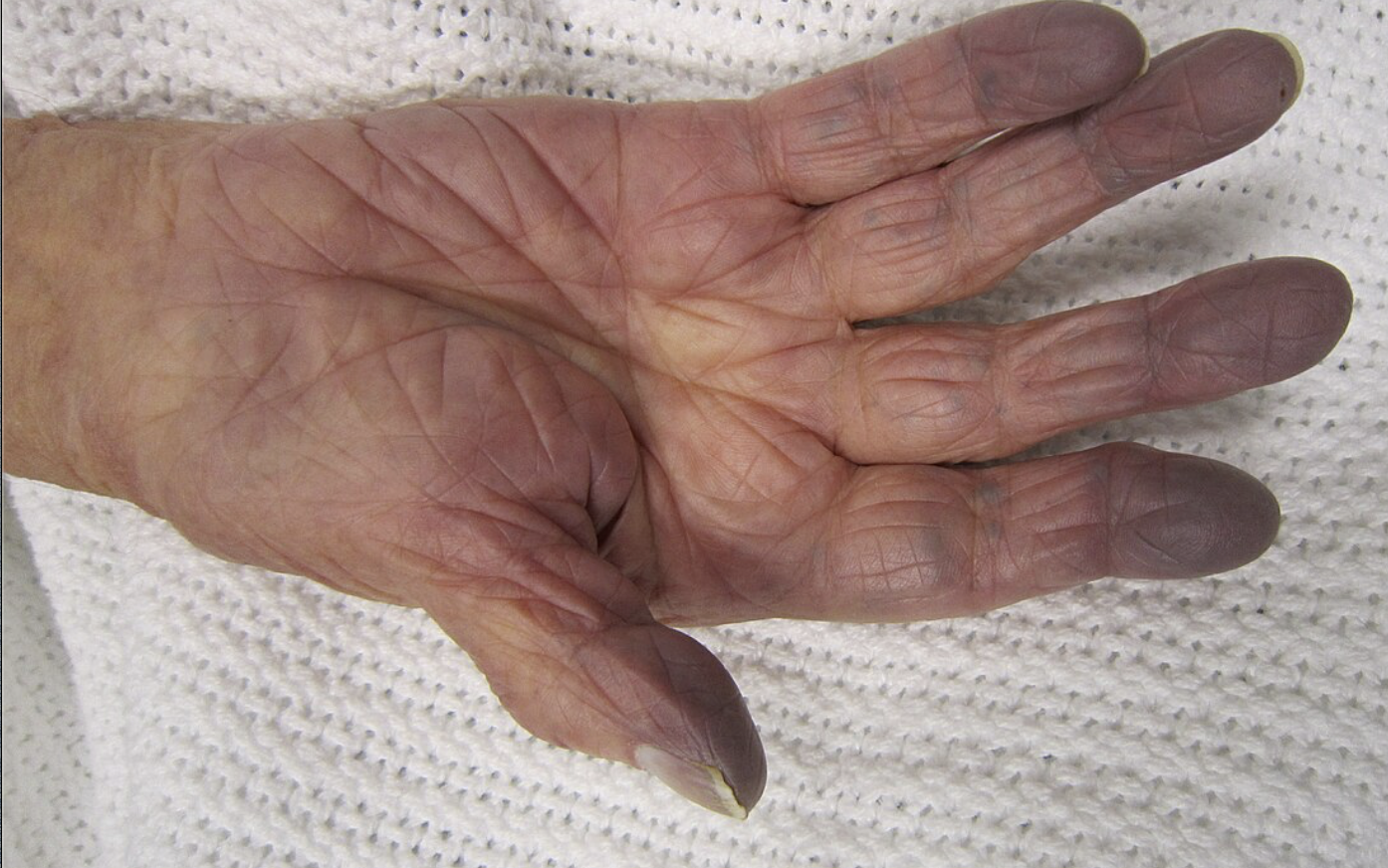
low oxygenation of hemoglobin
cyanosis
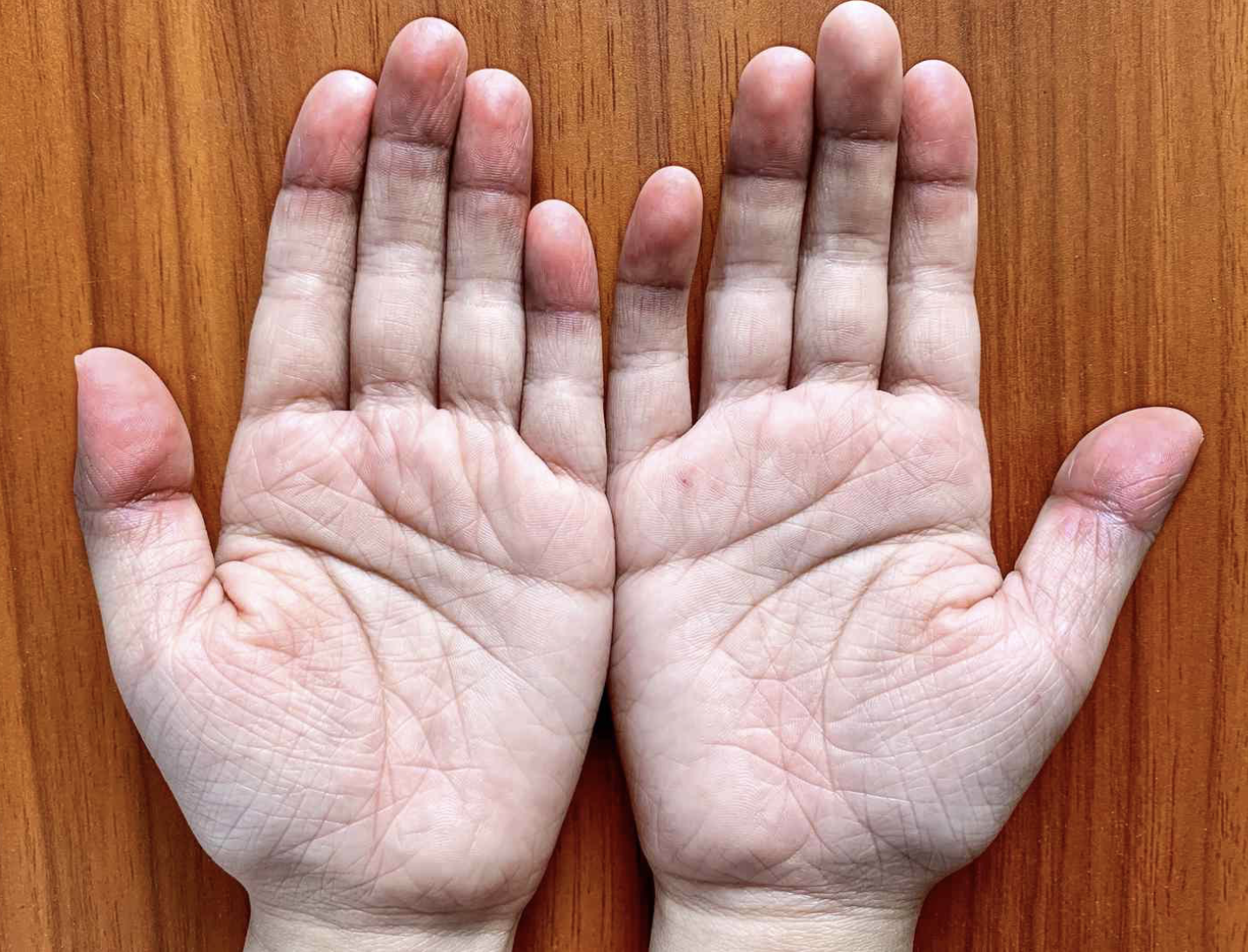
anemia, low blood pressure, fear, and anger are the symptoms associated with this skin disease
pallor
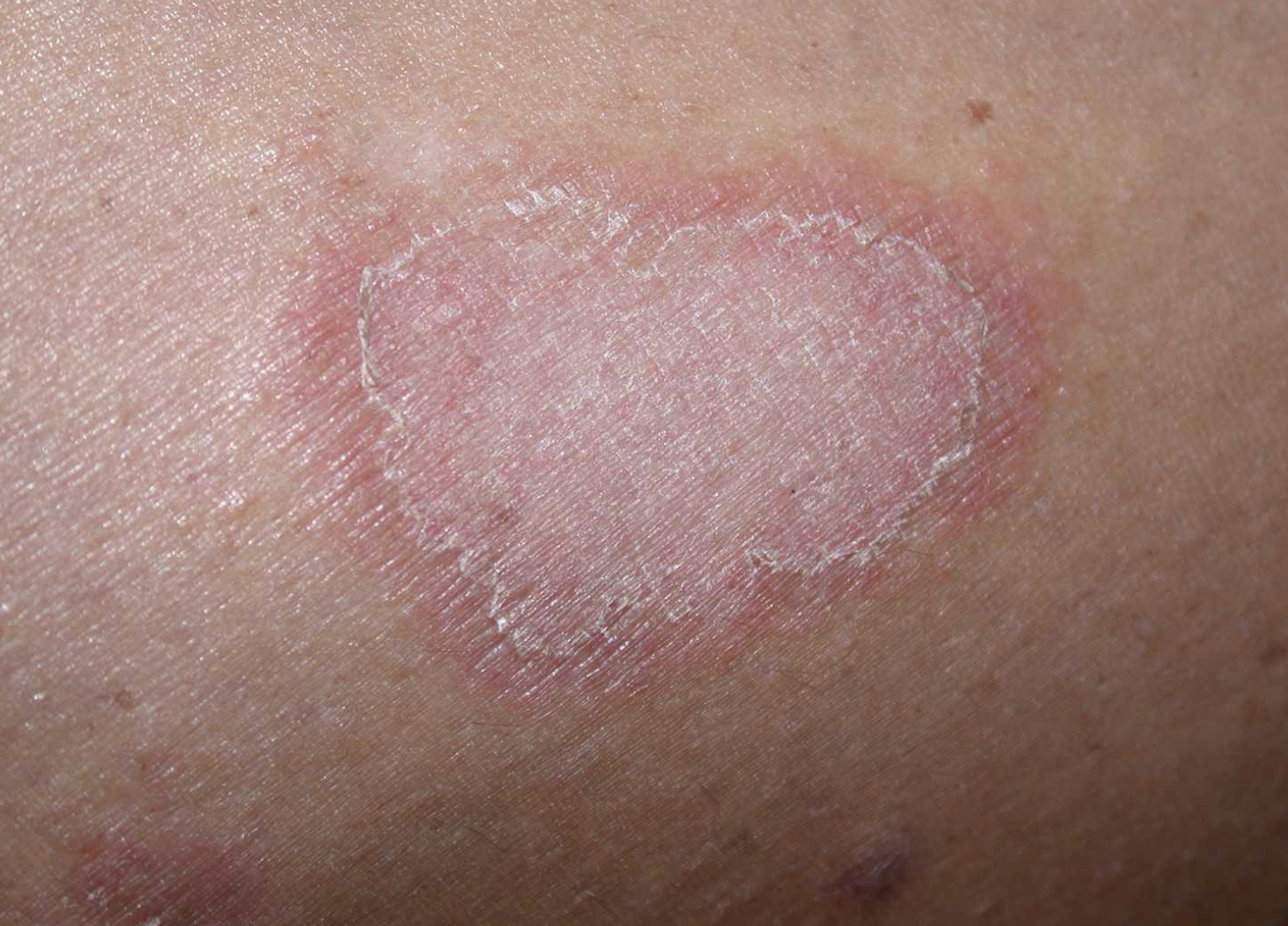
fever, hypertension, inflammation, allergy are the symptoms associated with this particular skin disease
erythema
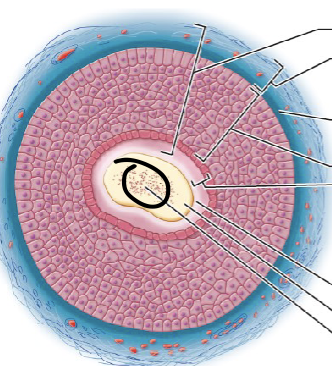
one aspect of the hair shaft; central core of large cells and air spaces
medulla
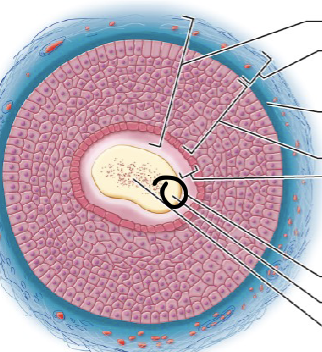
one aspect of the hair shaft; several layers of flattened cells surrounding medulla
cortex
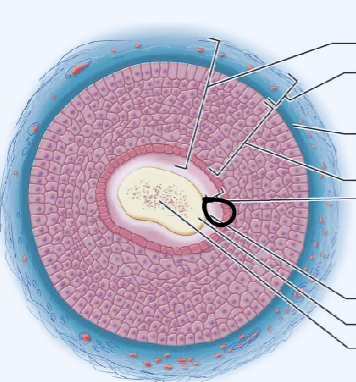
outer layer consisting of overlapping layers of single cells; one part of the hair shaft
cuticle
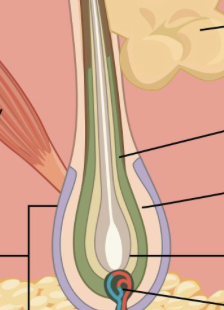
expanded, deep end of hair follicle is known as what?
hair bulb
sensory nerve endings that wrap around the hair bulb are known as what?
hair follicle receptors
actively dividing area of bulb that produces hair cells
hair matrix
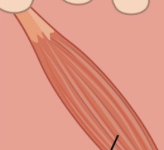
small band of smooth muscle attached to the follicle
arrector pili
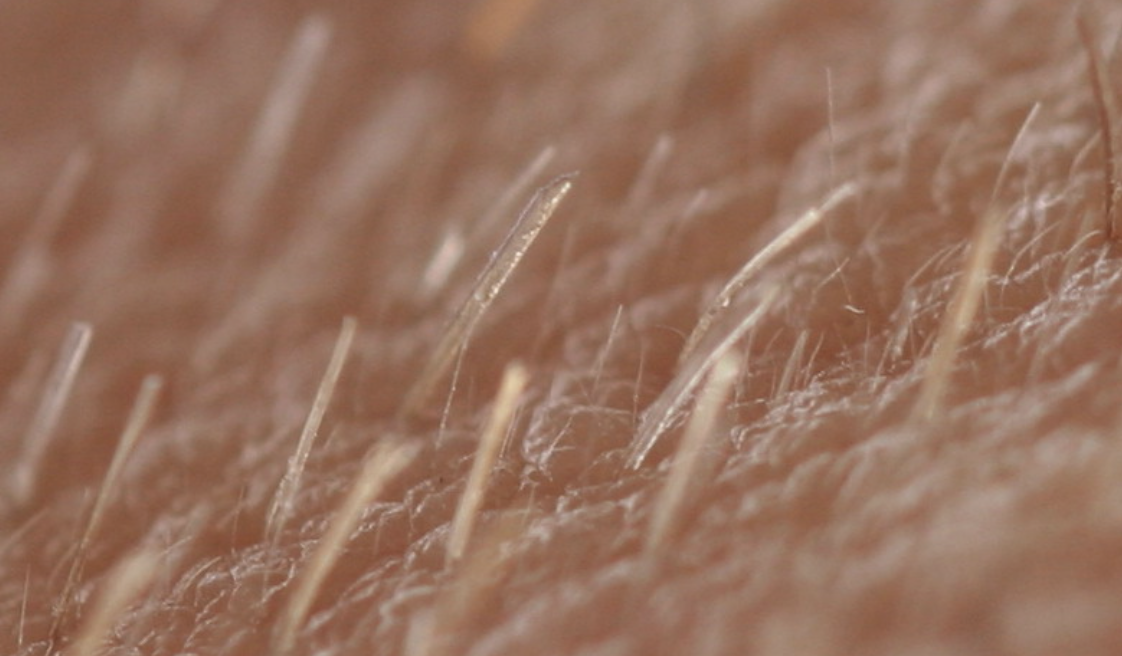

known as the peach fuzz; hair that covers the majority of the body
vellus hair
thick coarse pigmented hair found on parts of the body such as the scalp, eyebrows, and the eyelashes
terminal hair
nail fold that projects onto surface of nail body
eponychium
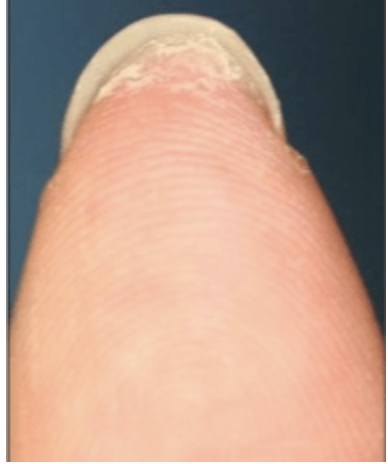
area free under free eye of plate that accumlates the dirt (part of the nail)
hyponychium
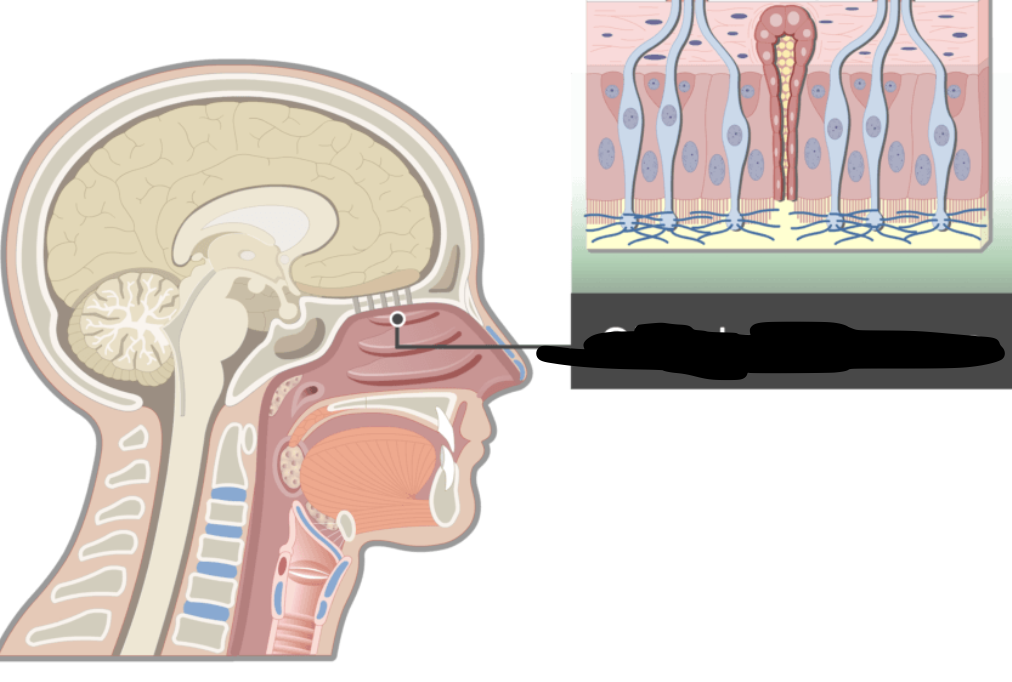
lines superior region of the nasal cavity and contains ______ epithelium
olfactory mucosa
lines nasal cavity and contains pseudo stratified ciliated columnar epithelium that contains goblet cells (part of respiration process)
respiratory mucosa
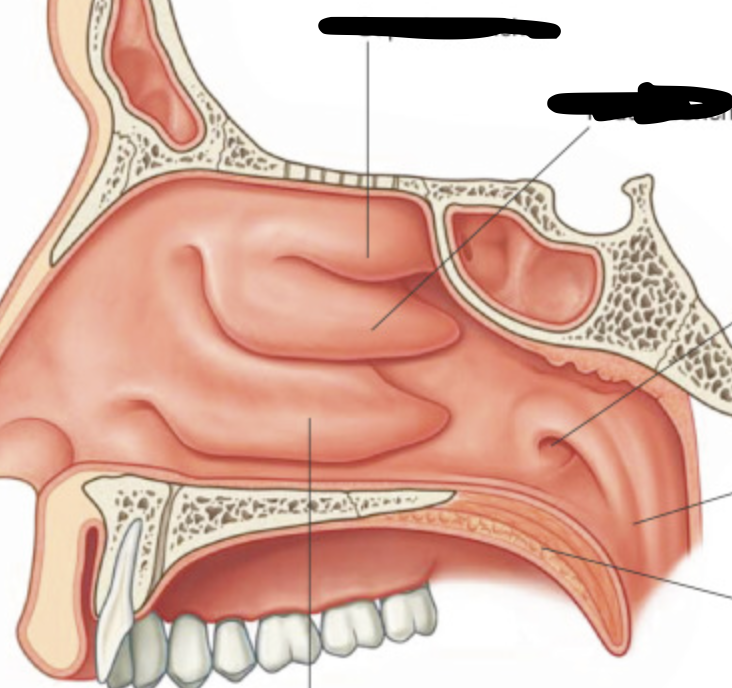
groove inferior to each nasal concha (superior middle and inferior concha)
nasal meatus
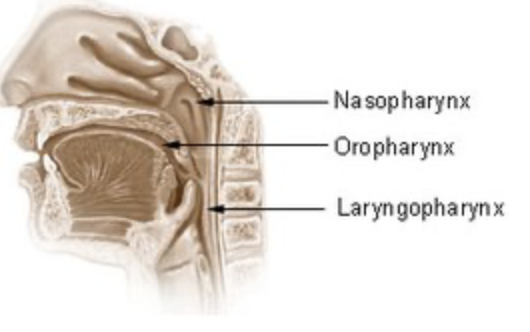
connects nasal cavity and mouth to larynx and esophagus, constructed by skeletal muscle, funnel shaped muscular tube
pharynx
isthmus of fauces
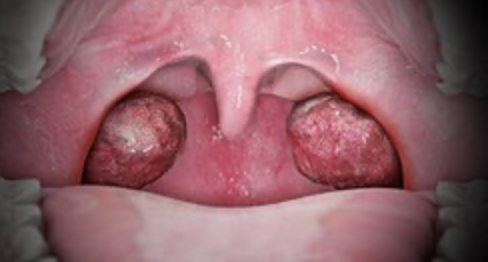
hint: this country is in war with Israel
palatine tonsils
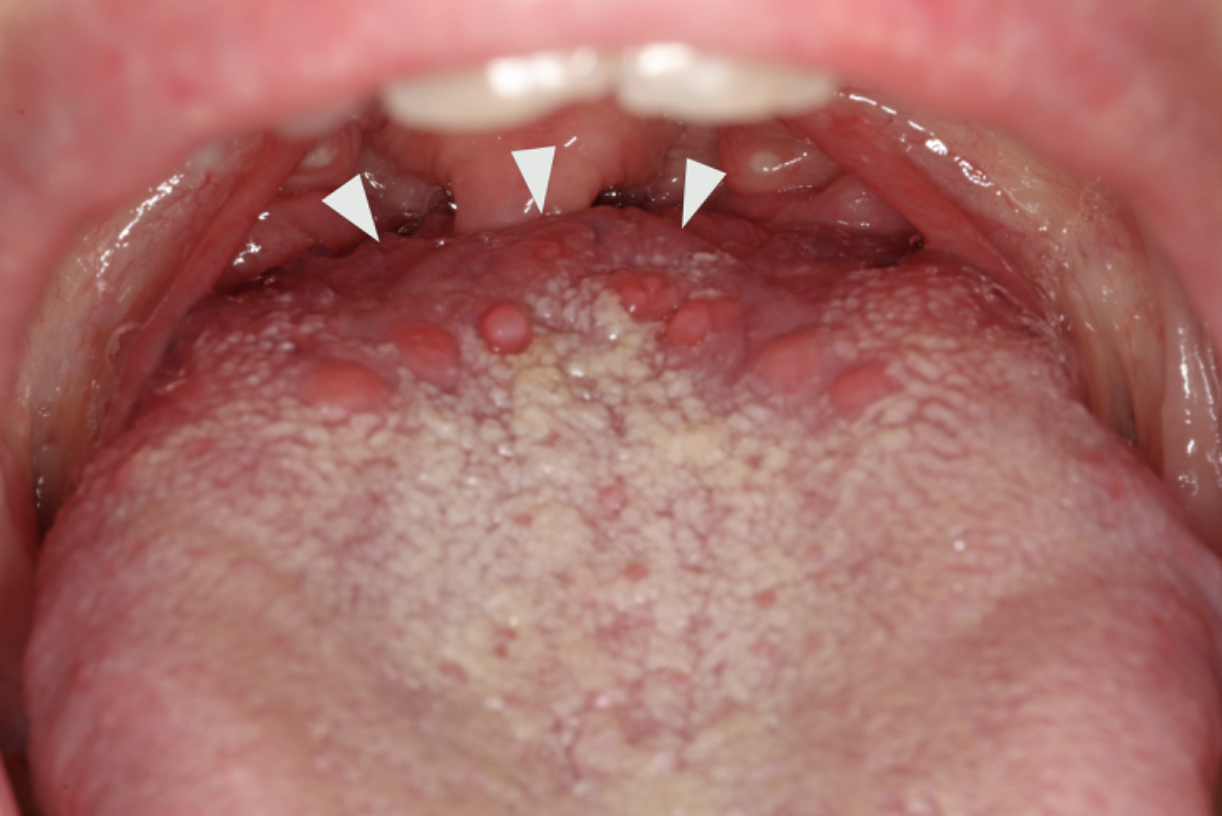
lingual tonsils
consists of elastic cartilage, covers laryngeal inlet during swallowing, covered in tase bud containing mucosa
epiglottis
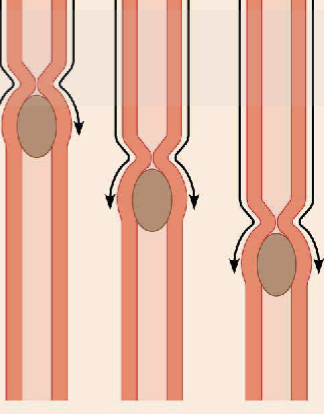
major means of propulsion of food that involves alternating waves of contraction and relaxation
peristalsis
includes chewing, mixing food with saliva, churning food in stomach, and segmentation
mechanical breakdown
series of catabolic steps, involves enzymes that break down complex food molecules into chemical building blocks
digestion
passage of digested fragments from lumen of go tract into blood or lymph
absorption
elimination of indigestible substances via anus in form of feces (takin a shit)
defecation
double layer of peritoneum layers fused back to back, provides routes for blood vessels lymphatics, and nerves
mesentery
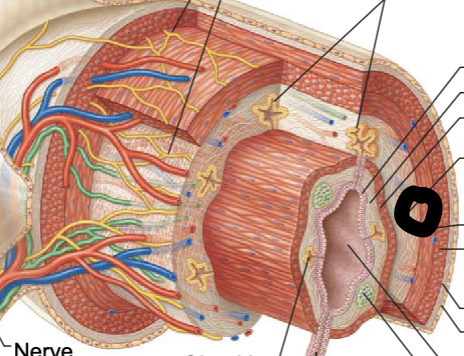
contains blood and lymphatic vessels, lymphoid follicles, and submucosal nerve plexus that supply surrounding GI tract issues
submucosa
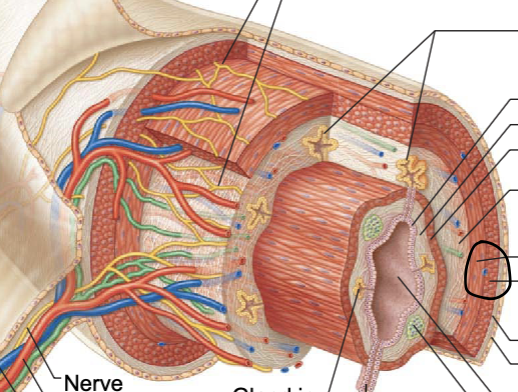
contains inner circular muscle layer and outer longitudinal layers
muscularis externa
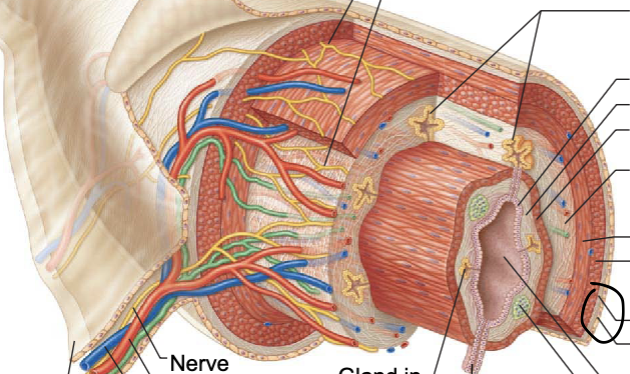
outermost layer which is made up of the visceral peritoneum
serosa
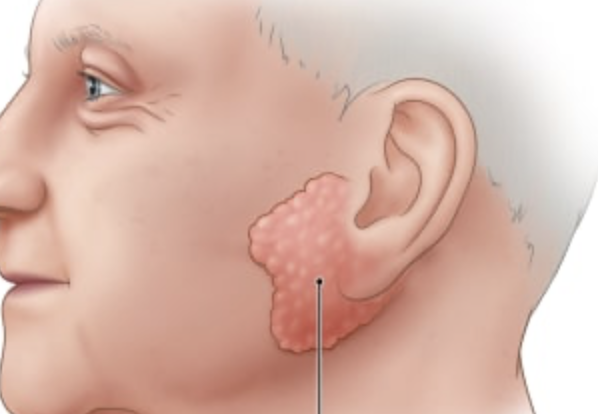
anterior to ear and external to masseter muscle; opens into oral vestibule and next to second upper molar
parotid gland
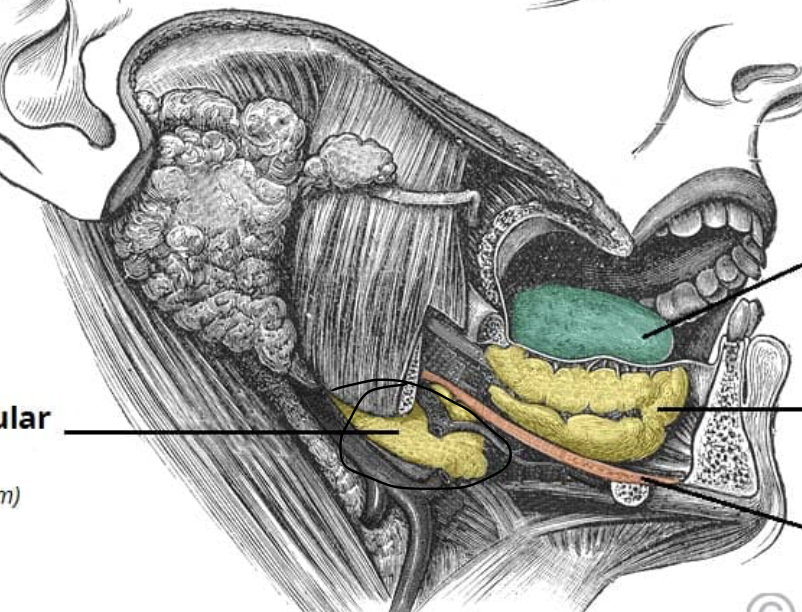
medial to body of mandible; duct opens at base of lingual frenulum
submandibular gland
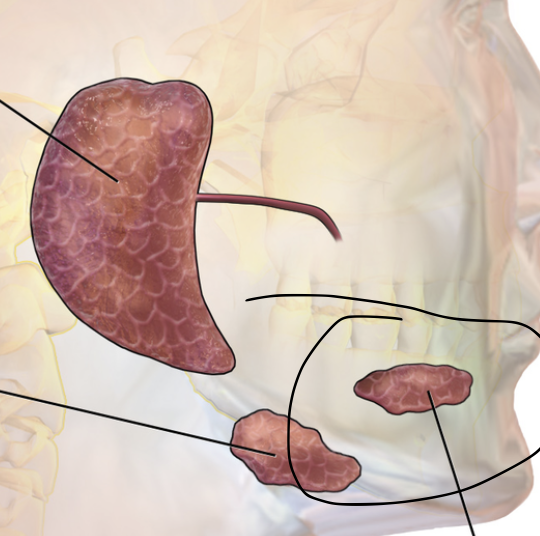
anterior to submandibular gland under tongue; opens visa 10-12 ducts into floor of mouth
sublingual gland
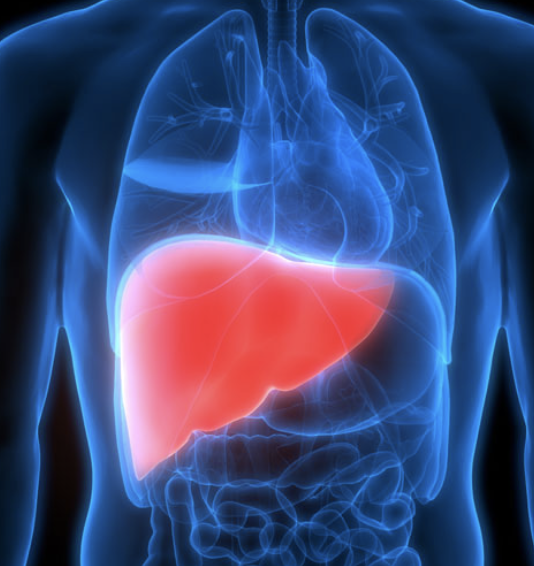
digestive function is production of bile
liver
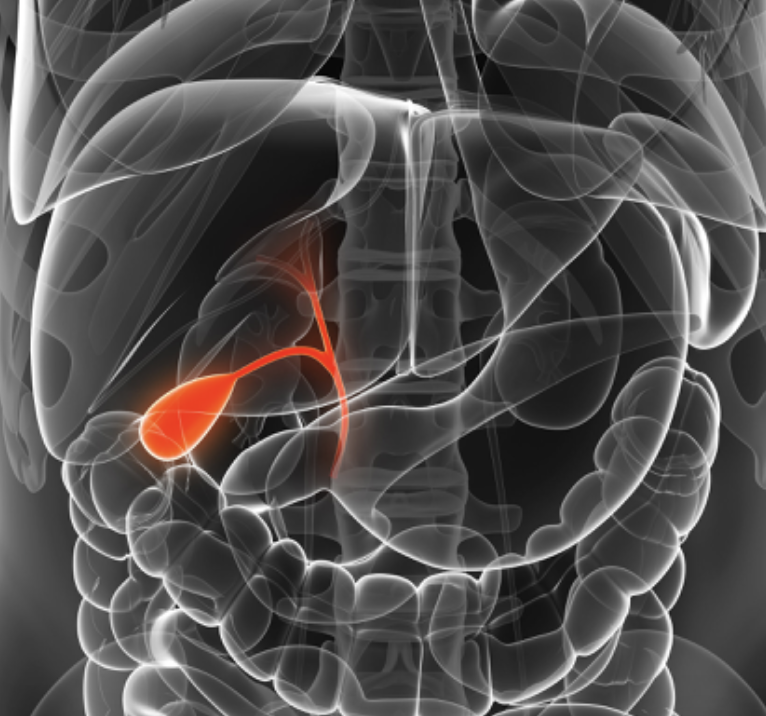
chief function is the storage of bile
galbladder
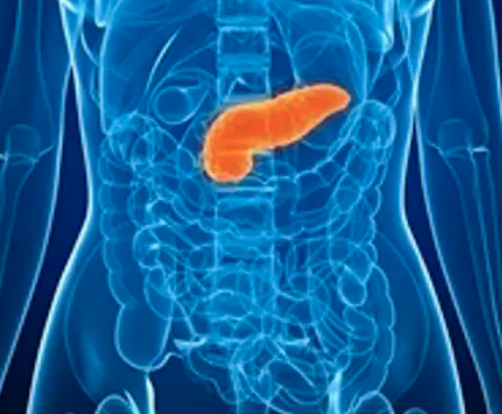
supplies most of enzymes needed to digest chyme, as well as bicarbonate to neutralize stomach acid
pancreas
clusters of secretory cells that produce pancreatic proenzymes
acini
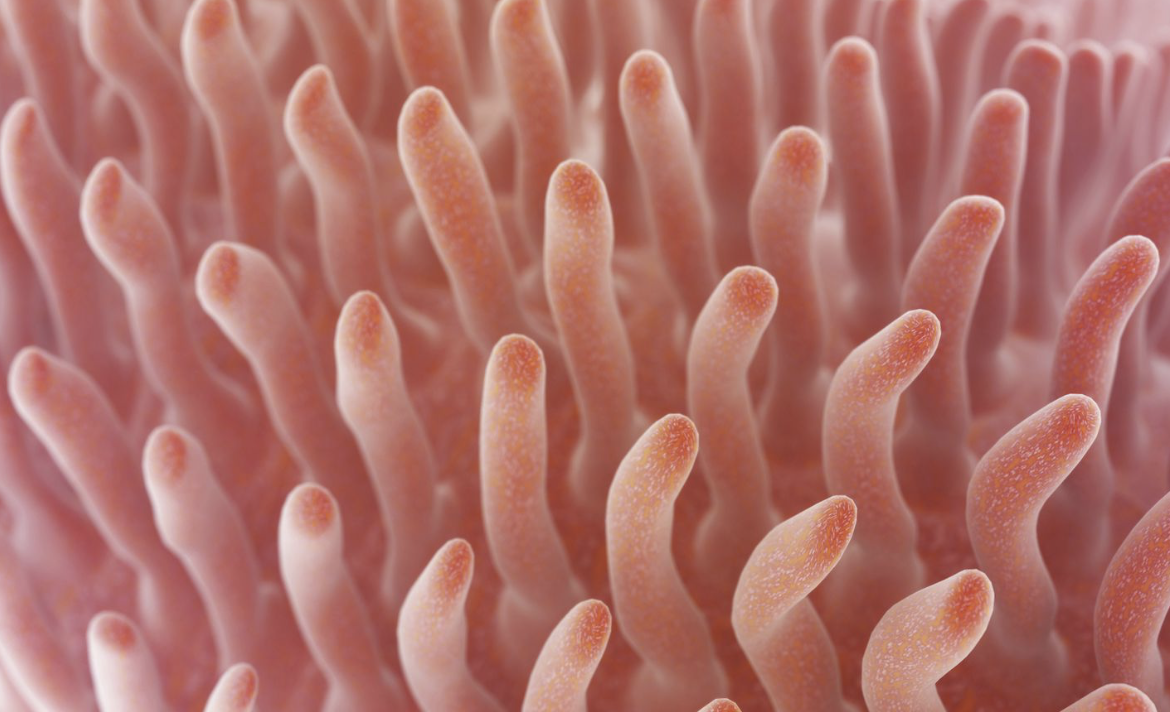
fingerlike projections of mucosa with core that contains dense capillary bed and lymphatic capillary called a lacteal for absorption
villi
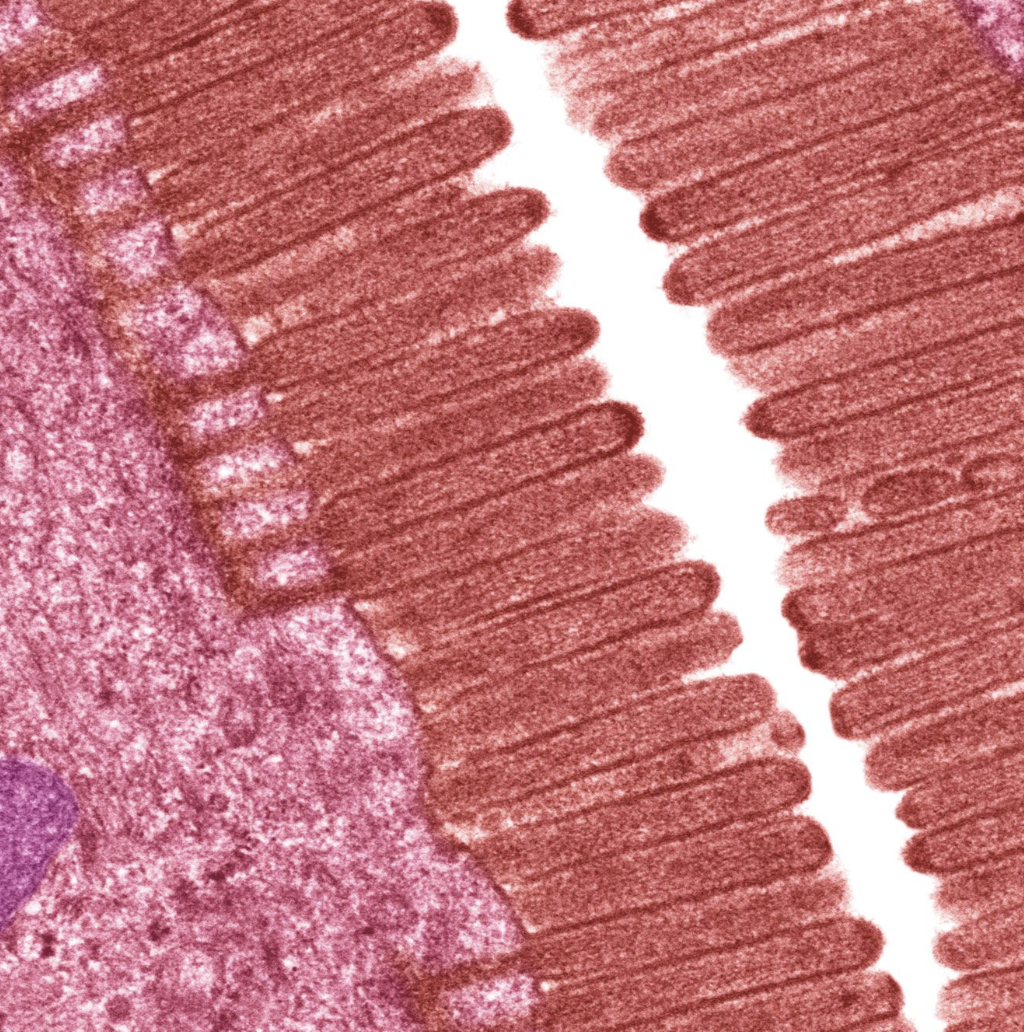
cytoplasmic extensions of mucosal cell that increases surface areatan
microvilli