Meiosis & the Cell Cycle
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Independent Assortment
(during m1)
ensures genetic diversity between gametes produced by meiosis
crossing over
(during p1)
ensures every sperm and egg produced by meiosis is genetically unique
tetrad
2 replicated chromosomes joined, during crossover
gametes
formed from meiosis
multipotent
most specialized stem cells
totipotent
capable of developing into any cell type
not determined for any type of specilization
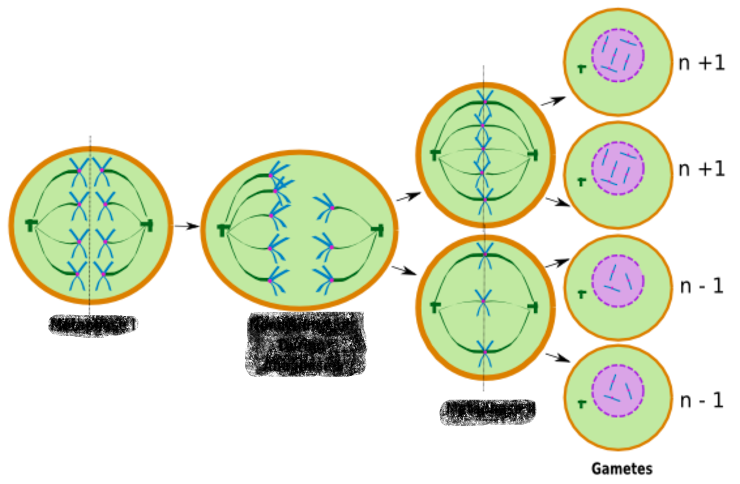
nondisjunction
The failure of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate properly during cell division, leading to an abnormal distribution of chromosomes in the daughter cells.
can occur in anaphase I or II
differentiation
gives each cell type a specific function
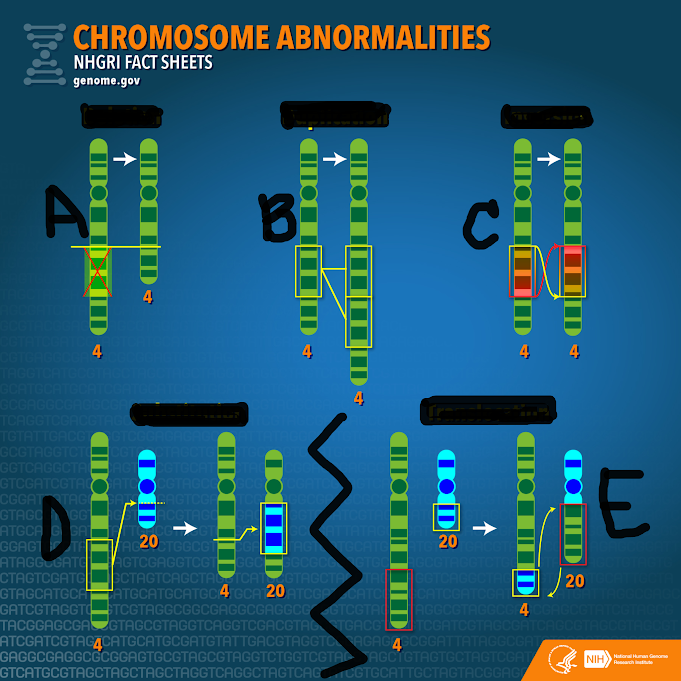
A, B, C
Which letter(s) is showing a mutation affecting only one homologous pair?
random fertilization, crossing over, chromosome assortment during metaphase
three processes lead to variation among offspring that have the same two parents
muscle, heart muscle, brain, nerves, spinal cord
Stem cell research would be most beneficial to replace which type of cells if they became damaged?
in meiosis, the number of chromosomes is halved and genetic variation is introduced, but not in mitosis
main difference between mitosis and meiosis
4 haploid gametes
result of meiosis
they are responsible for fertilization
why do gametes have to be haploid
fertilization
2 haploids join, creating a diploid zygote
random mating, crossing over, independent assortment of chromosomes
what ensures that every offspring produced by a couple is genetically unique