31 - Heart rate. Stroke volume and cardiac output changes under different physiological conditions.
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
sections
what is heart rate
what is tachycardia and bradycardia
cause for increased heart rate
cause for decreased heart rate
stroke volume
preload
afterload
cardiac output
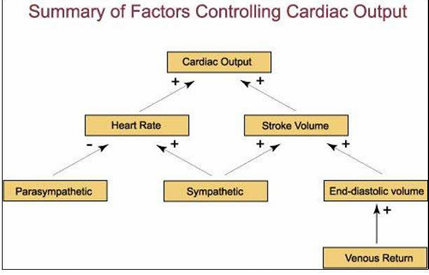
summary of factors controlling cardiac output
what is heart rate
Heart rate HR- the speed of the heart beat, measured by the number of contractions of the heart per minute, beats bpm
number of beats per minute (usually 60-90 bpm at rest)
heart rate is dependent on cardiovascular fitness and age. There are different things which can cause changes in HR.
what is tachycardia and bradycardia
Tachycardia- increased HR
Bradycardia- decrease HR.
cause for increased heart rate
High temperature
Sympathetic stimulation
By hormones, T3/T4, circulation of catecholamines
Increased Ca2+
cause for decreased heart rate
low temperature
Vagal stimulation
Parasympathetic stimualtion
Decreased catecholamines, thyroid hormones, Ca2+ , Na+
Increase K+
stroke volume
The total volume of blood pumped by the ventricles per beat during ventricular systole.
The blood is pumped out of the heart and to the rest of the body.
SV=EDV-ESV
EDV = end diastolic volume (140-70= 70 mL)
ESV= end systolic volume
The stroke volume for both ventricles, is usually 70 ml.
affected by preload and afterload
preload
the volume of venous blood flow into the heart accompanied by a corresponding change in the length of the myocardial fibres
Is the degree to which the ventricles are stretched, prior to contraction.
Preload of the ventricles increase when the heart rate decreases, this allows for the ventricles to fill up with blood.
…………………………………………………………………………………..
Preload is the amount of blood in the ventricles before they contract.
It increases when:
The atria contract more strongly, pushing more blood into the ventricles.
Venous pressure rises, sending more blood into the heart.
Preload decreases when:
Venous pressure drops.
Heart rate increases, giving less time for the ventricles to fill.
Valve problems (like mitral or tricuspid stenosis) block blood flow into the ventricles.
Atrial issues (like flutter or fibrillation) reduce how well the atria push blood into the ventricles.
afterload
is the level of resistance to the blood flow, which depends on the blood pressure in the aorta during a systole.
Afterload is dependent on the blood pressure of the aorta during systole.
An increase in afterload leads to a decrease in stroke volume. A decrease in afterload leads to an increase in stroke volume.
Afterload increases by aortic valve stenosis and ventricular dialation which leads to an increase in aortic pressure and systems resistance
cardiac output
Is the volume of blood pumped by a particular ventricle per unit time
It is the quantity of blood that flows through circulation
Cardiac output can be measured as : CO=HR X SV
summary of factors controlling cardiac output