Neurophysiology Lecture 5
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The vertebral column and spinal cord
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Bony Formula for Vertebral Column in Canines
Cervical: 7
Thoracic: 13
Lumbar: 7
Sacral: 3
Coccygeal: ~20
More thoracic, lumbar, sacral in larger animals
Coccygeal very species/breed dependent
Between which vertebral segments are intervertebral discs NOT found? (3 areas along spine)
1) Sacral - fused
2) Coccygeal - fused
2) Between skull and C2
Skull and C1, and between C1 and C2 - no IVDs
Atlas and axis form a joint together
What is the purpose of intervertebral discs?
Shock absorbers
Viscous, fibrous ring on outside AKA annulus fibrosis
Points of flexion/extension which allow spine to move without compromising the cord
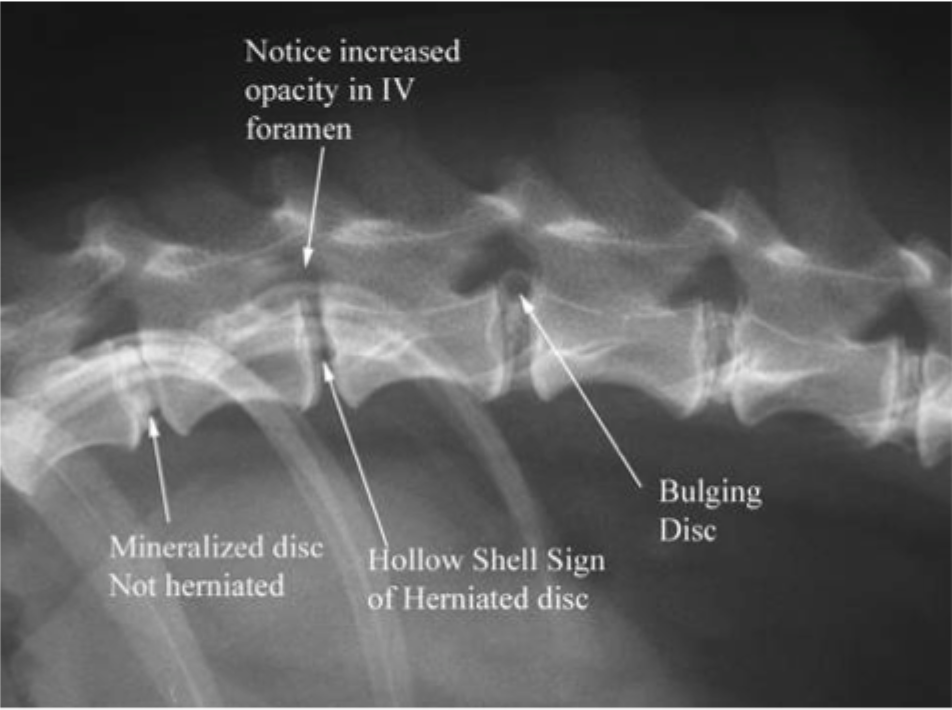
Name the condition: a prolapse of intervertebral discs with subsequent neurological signs
IVDD
Intervertebral disc disease
Annulus fibrosis ruptures
disc gets pushed into the spinal cord (neurologic symptoms)
What is the tissue that surrounds the spinal cord called?
the Meninges
Name the 3 layers of the meninges
1) Pia mater
Closest to spinal cord
2) Arachnoid mater
Middle, very thin
3) Dura mater
Outside, very thick
Name the three spaces between the meninges
1) Subarachnoid space
Between Pia mater and Arachnoid mater
Filled with CSF
2) Subdural space
Between Dura mater and Arachnoid mater
Filled with serous fluid
3) Epidural space
External to the Dura mater
Anesthetics injected here
Name the regions of the spinal cord
Cervical
Thoracic
Lumbar
Sacral
Caudal
Do the spinal cord segments line up with the vertebral column segments?
i.e. the nerve for T3 leaves the T3 segment of the vertebral column
Yes,
EXCEPT for an extra cervical segment
The exit for the first 7 vertebrae happen in front of the vertebrae it is named for
Nerve and spinal root for C1 exit in front of C1
At C7, the spinal root exits in front of C7 and then a root also exits from behind it, which is called C8
From there on out they exit from behind the vertebrae they are named for
Vertebral column
C7
Spinal cord
C8
Term meaning:
The area of skin innervated by the sensory fibers from an individual spinal nerve/spinal segment
Dermatome
Term meaning:
The muscles innervated by the motor fibers from an individual spinal nerve/segment
Myotome
The spinal cord terminates shorter than the vertebral column.
In which region (with correlating numbers) does the spinal cord terminate?
Lumbar; L4 - L6 (vertebrae)
What is the distal lumbar region called where the spinal cord is absent but vertebral column still continues?
Cauda equina
How many enlargements are there along the spinal cord?
Name them
2
Cervical (cervicothoracic) enlargement
Lumbosacral enlargement
Why are the cervicothoracic and lumbosacral sections of the SC enlarged?
These are specific places where the nerves that innervate the fore and hind limbs come off of
What are the segments of the SC that encompass the forelimb nerve innervation (cervicothoracic)?
C6, C7, C8, T1, (T2)
What are the segments of the SC that encompass the hindlimb nerve innervation (lumbosacral)?
L4, L5, L6, L7, S1 (S2)
List the FOUR zones of spinal cord relevance when localizing a lesion
1) Above cervical enlargement
C1 - C5
2) Within cervicothoracic enlargement
C6 - (T2)
3) Between upper and lower enlargements
T3 - L3
4) In lumbosacral enlargement
L4 - S4
Never localize past lumbosacral enlargement
What are the two gross physical divisions within the spinal cord?
Gray matter and white matter
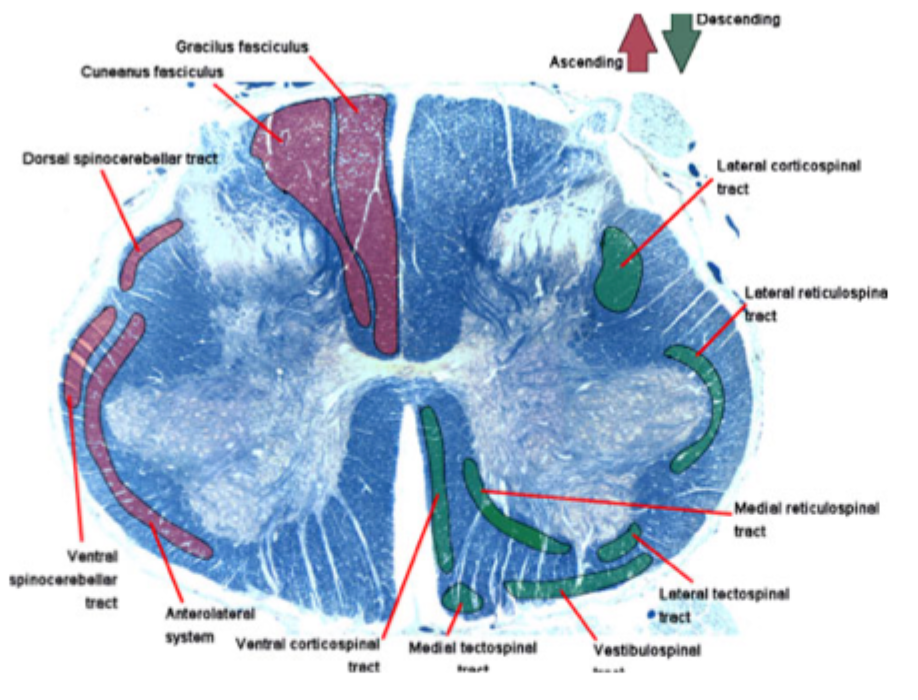
What is the white matter of the spinal cord made up of?
What pathways does it it contain?
Made up of axons
makes it white due to myelin which doesn’t stain well
Composed of funiculi/columns which have tracts that carry sensory or motor information
Dorsal column - sensory tracts
Lateral column - sensory and motor
Ventral column - sensory and motor
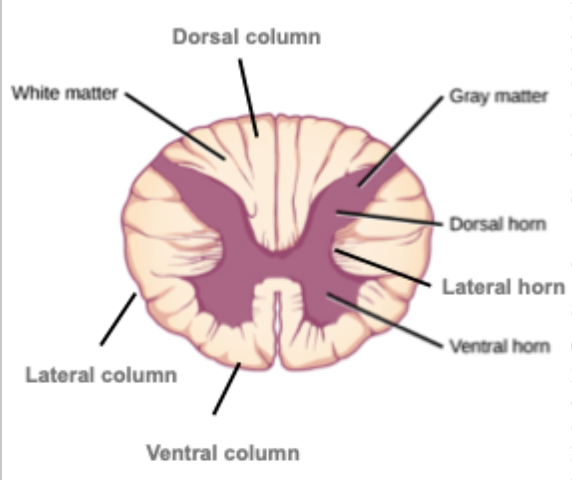
What is the gray matter of the spinal cord made up of?
What pathways does it it contain?
Made up of neuron cell bodies
Composed of gray matter horns
Dorsal horn - sensory neurons (2°)
Ventral horn - motor neurons (1°)
All lower motor neurons
Contract or relax somewhere on the outside
Lateral horn - autonomic neurons
Only in thoracic and first few lumbar/sacral segments
Interneurons found here, involved in relay pathways
In the gray matter, what is the difference between the neurons found in the dorsal root and ventral root specifically?
1) Dorsal root - 2° neurons
Axons from the sensory neuron enter the SC here
The first neurons that they usually synapse on (2°) are the first neurons encountered
Synapse ALWAYS enters through dorsal horn - sensory
Spinal nerve always in ganglion
2) Ventral root
Axons of motor neuron exit the spinal cord here
Nerve cell bodies where these axons originate are physically close to this root
Synapse ALWAYS leaves through ventral root - motor
LMNs in central gray matter horn
In regard to white matter tracts and gray matter in general, what does it mean if they are organized somatotopically?
There is a strict relationship between where the tract/neuron is and the kind of information it conducts/mediates
With SC injuries, specific signs can be explained by the damage to specific neuron types
Tracts relay ONE type of information
How are white matter tracts typically named?
According to where they originate and terminate
Ex: spinothalamic
Contains axons that relay APs from SC to thalamus
How many neurons are in a tract?
Do they always ascend and descend from the spinal cord on the same side?
A tract is a chain of two or three neurons
sensory comes in through DR, synapses in GM and then axon leaves and ascends through brain
No! Some tracts stay on the same side, but most cross over at some point in the pathway
All pathways are paired too; one tract on left and right sides of SC
What are the two primary arteries that supply the spinal cord with blood?
1) The ventral spinal artery
Follows ventral surface of cord
2) Paired dorsolateral spinal arteries
Along base of dorsal roots of spinal nerves
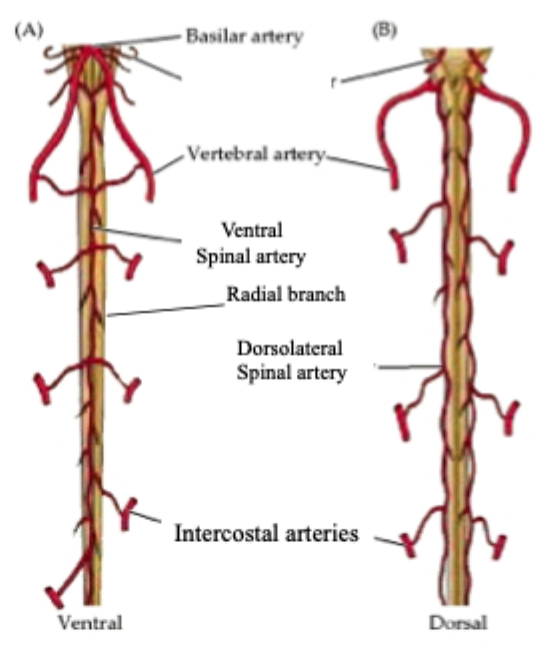
Depending on the region, what are the three arteries that feed into the ventral spinal artery and the dorsolateral spinal arteries?
1) Vertebral artery
Cervical/anterior thoracic
2) Intercostal artery
Thoracic
3) Aorta
Lumbar
What supplies the core of the spinal cord?
Radial branches splitting off of these arteries
What is the term for when fibrocartilage from an IVD gets in the vascular supply, causing a myocardial infarction?
Fibrocartilagenous embolic myelopathy (FCEM)