Thermodynamics
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
defintions, calculations and tips
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Definition of Internal Energy
the sum of the random distribution of kinetic energies and potential energies
Definition of Latent Heat (2 marks)
the energy required to the change the state of 1 kg of a substance without a change in temperature
What’s the difference between 0 C and 0 K?
0 C= 273K
0 K= Absolute zero
Definition of Specific heat capacity (2
The energy required to increase the temperature of 1kg of substance by 1 kelvin without a change in state.
What is the unit for specific heat capacity?
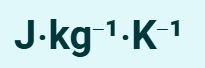
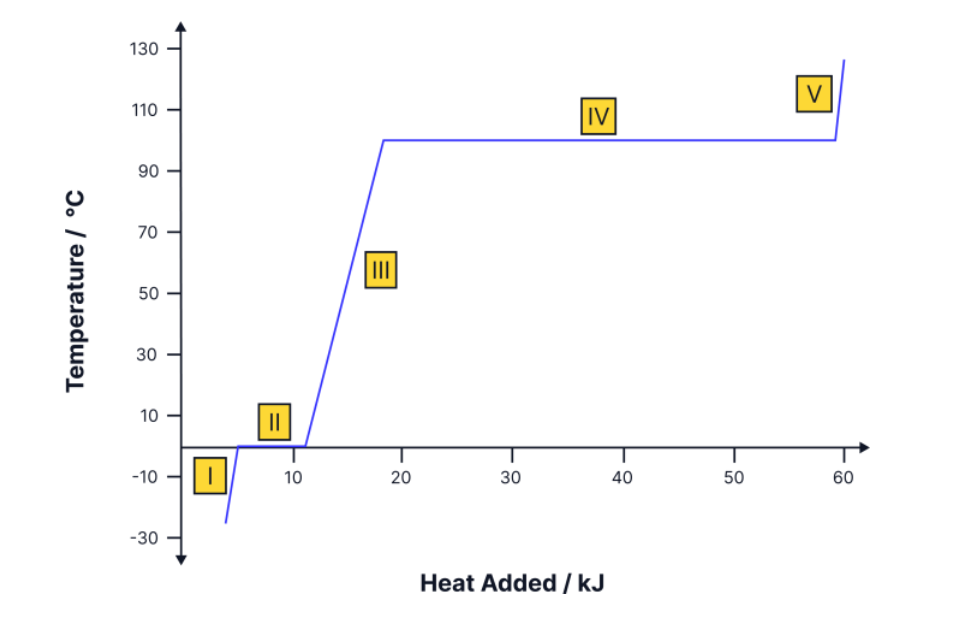
explain what is happening at points 1-5
1-Increase KE, because the Temp increases
2-change in state, bc no Temp change
increase in PE- solid to a liquid
3-Increase KE, because Temp increases
4-change in state, bc no Temp change
Increase in PE- liquid to a gas
5-Increase in KE, because the Temp increases
If something is heated at a constant rate what does that mean?
The power is always the same
What are the two equations to work out energy?
E=mcΔT
E=Pt
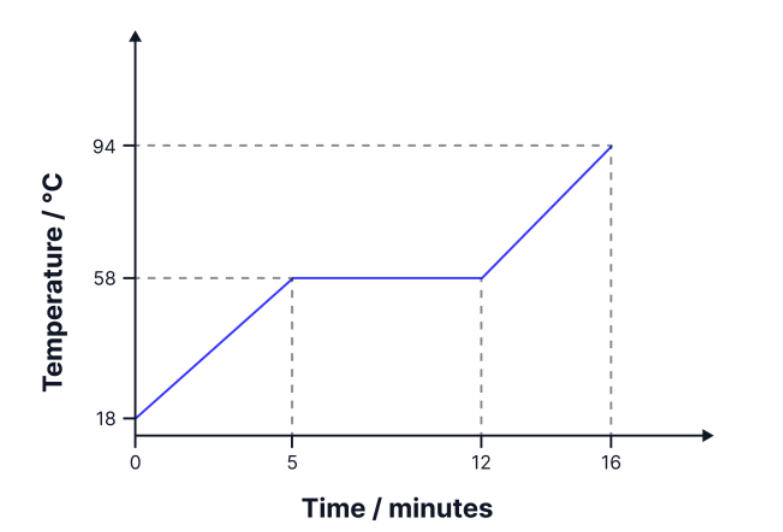
A solid mass of 1,500 g is heated at a constant rate, producing the graph opposite. The specific heat capacity of the solid is 1200 Jkg-1K-1 . 1. Calculate the specific latent heat of fusion of the material.
what about its specific heat capacity?
How long will a 2 kW kettle take to raise the temperature of 800 g of water from 20℃ to 100℃? The specific heat capacity of water is 4200 Jkg-1K-1 . In reality, will it take more or less time?
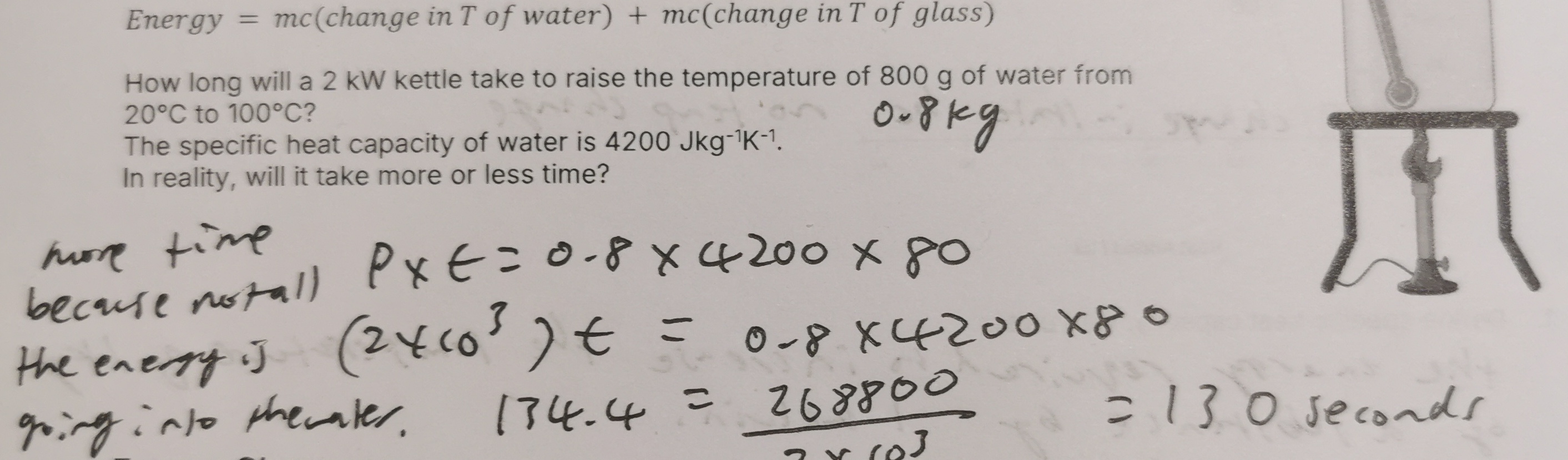
1.4 kg of water at 17°C cools to 0°C and then freezes to form ice, also at 0°C. Calculate the energy released. (4 marks) Specific heat capacity of water = 4,200 Jkg–1K–1 Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 3.4 × 105 Jkg–1
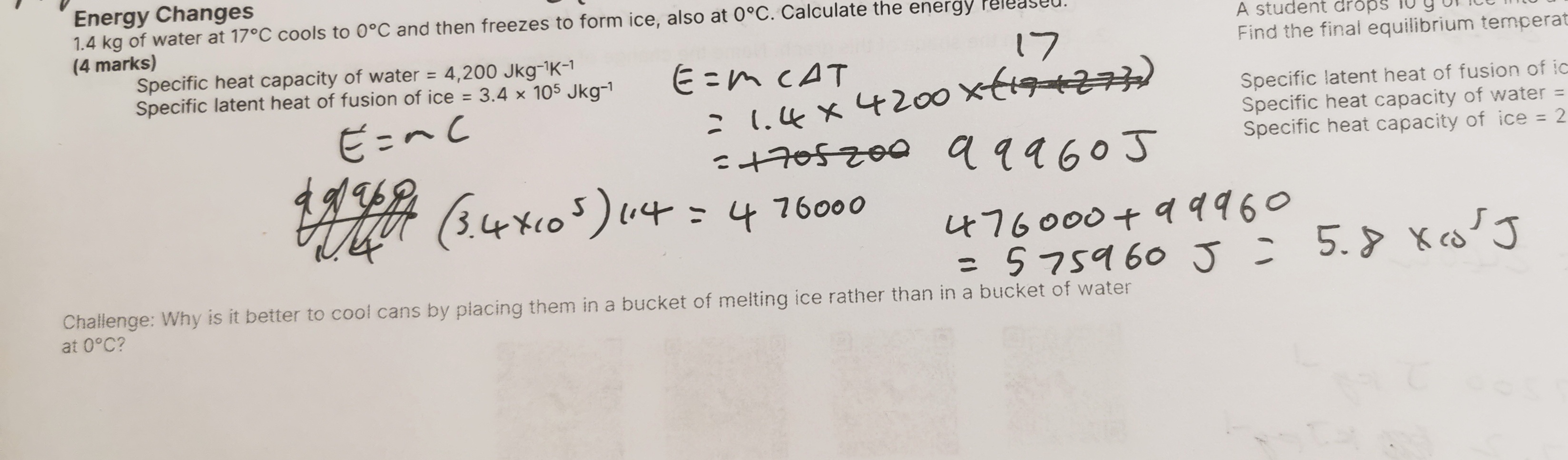
Why is it better to cool cans by placing them in a bucket of ice rather than in a bucket of water?
The ice will take in energy from the cans to change state into water, and then the water will take in energy. so more energy is absorbed from the cans, so there is a greater change in energy in the cans.
so Ice has a more cooling effect
Calculate the energy needed to melt 5.0 kg of ice at 0°C and heat the melted ice to 50°C. Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 3.36 × 105 Jkg–1 Specific heat capacity of water = 4,200 Jkg–1K–1
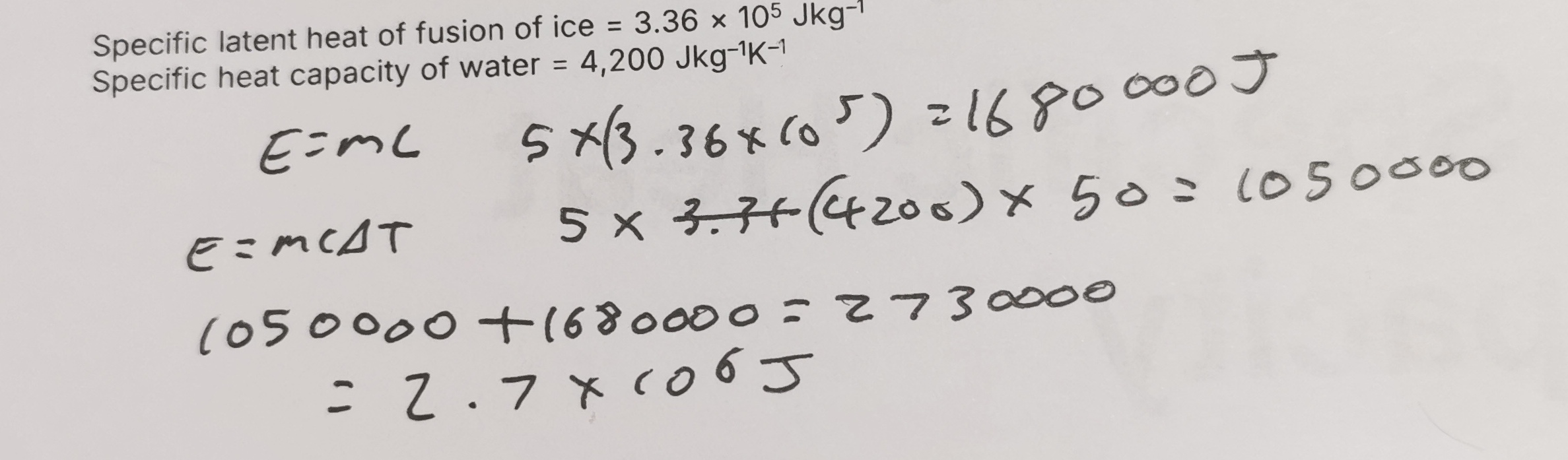
11 g of ice is dropped into a bucket with 0.7 kg of water at 25 degrees Celsius. The ice is initially at -5 degrees Celsius. Calculate the equilibrium temperature reached. 5. Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 3.36 × 10⁵ Jkg⁻¹ 6. Specific heat capacity of water = 4,200 Jkg⁻¹K⁻¹ 7. Specific heat capacity of ice = 2,100 Jkg⁻¹K⁻¹

Define Kinetic theory
The idea that the microscopic movement of particles will predict the macroscopic behaviour of a substance.
Define what absolute zero means
The theoretical temperature at which molecules will no longer move and KE is zero
Define what absolute temperature means
Any temperature scales that starts at absolute zero
Find the average speed/velocity of theis group of particles using the root mean squared calculation.
Particle 1= 500 ms
Particle 2=520 ms
Particle 3=505 ms
Particle 4=545 ms
Particle 5=501 ms
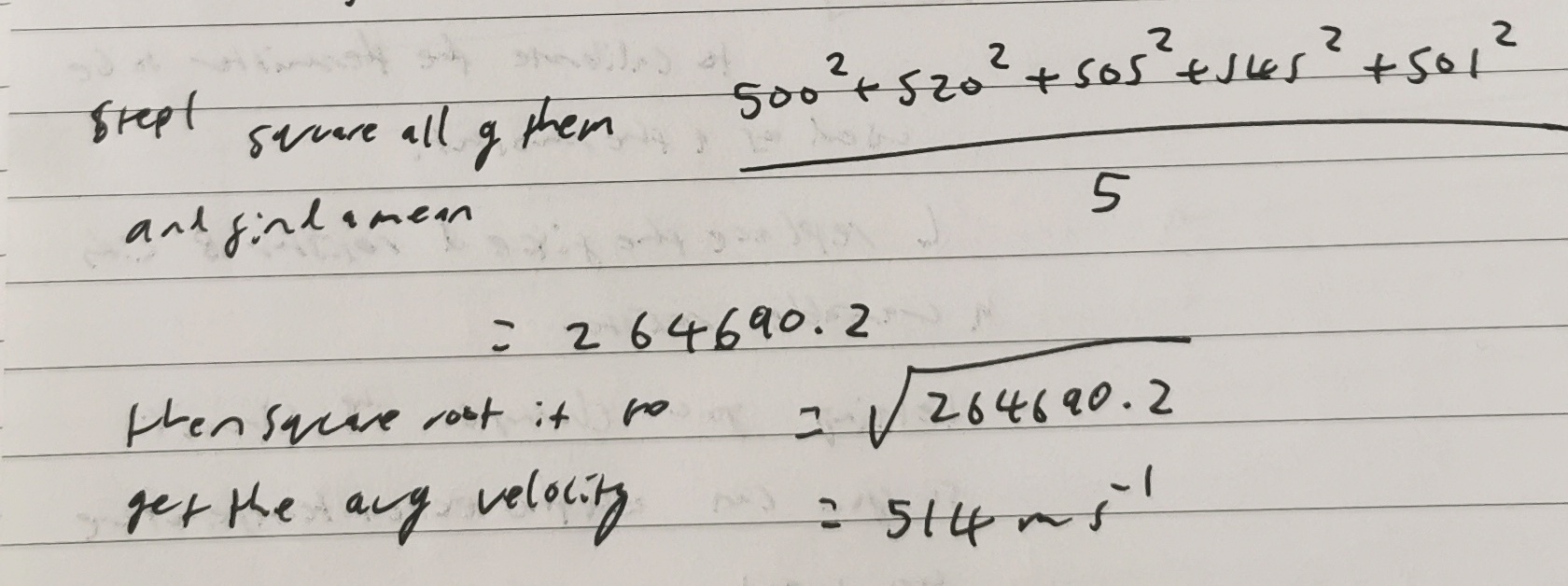
What is the value for the Boltzmann constant?
1.38×10^-23 JK^-1
What is the RMS speed of helium molecules in a child's balloon at 20 C? And it's atomic mass in 6.65×10^-27 kg?

What is the Maxwell Boltzmann distribution?
A mathematical function that describes the distribution of energies of particles at a given temperature
Define root mean-sqaured speed (rms)
The square root of arithmetic mean value of speed of a particle in an ideal gas.
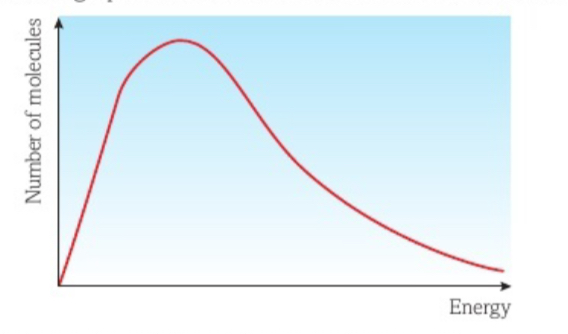
What would be represented by the area underneath the Maxwell Boltzmann curve?
The total sum of energies of all the particles
State 5 assumptions about the properties and behaviour of ideal gases.
All collisions between molecules are elastic
the time of collisions is negligible compared to the time between collisions.
the volume of molecules is negligible compared to the volume of gas.
particles exert forces on each other
the movement of particles is random
An ideal gas is stored in a cold room in a container. When moved to a warmer room the pressure of the gas increases. Explain in terms of the kinetic theory why this happens.
the average kinetic energy of particles increases
more frequent collisions
there is a greater change in momentum in collisions greater force per unit area.
A wire has Young’s modulus E. A second wire is made of the same material but with three times the length and half the diameter as the first wire. What is the Young’s modulus of the second wire?
A. 0.25E
B. E
C. 6E
D. 12E
B because young modulus stays the same
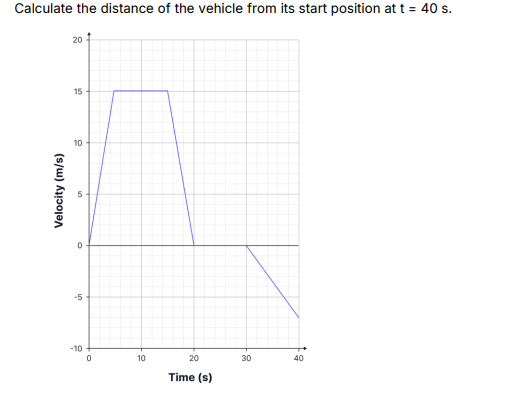
calculating the displacement not distance
190m
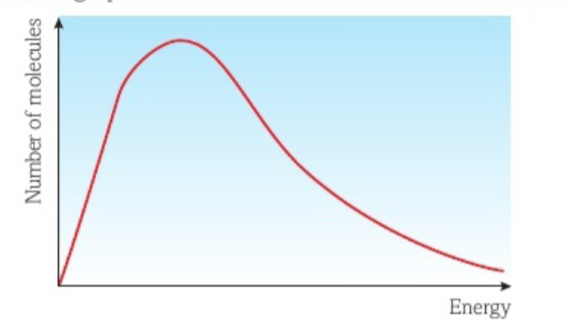
What are the 3 conditions of the Maxwell Boltzmann distribution?
There are no molecules with zero energy
Only a few molecules have high energy
There is no maximum value for energy a molecule can have
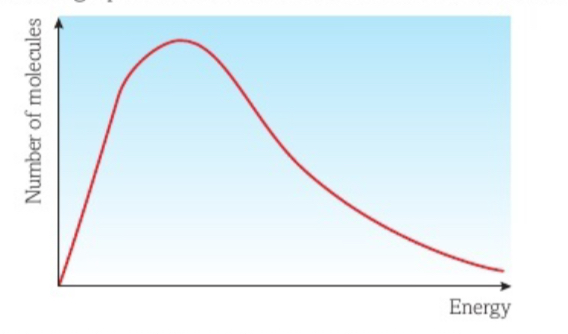
Explain what happens in the maxwell Boltzmann distribution graph as the temperature increases
Molecules will gain more Kinetic Energy
Therefore move at higher speeds
Therefore particles have more internal energy and the peak will move towards higher energies (right)
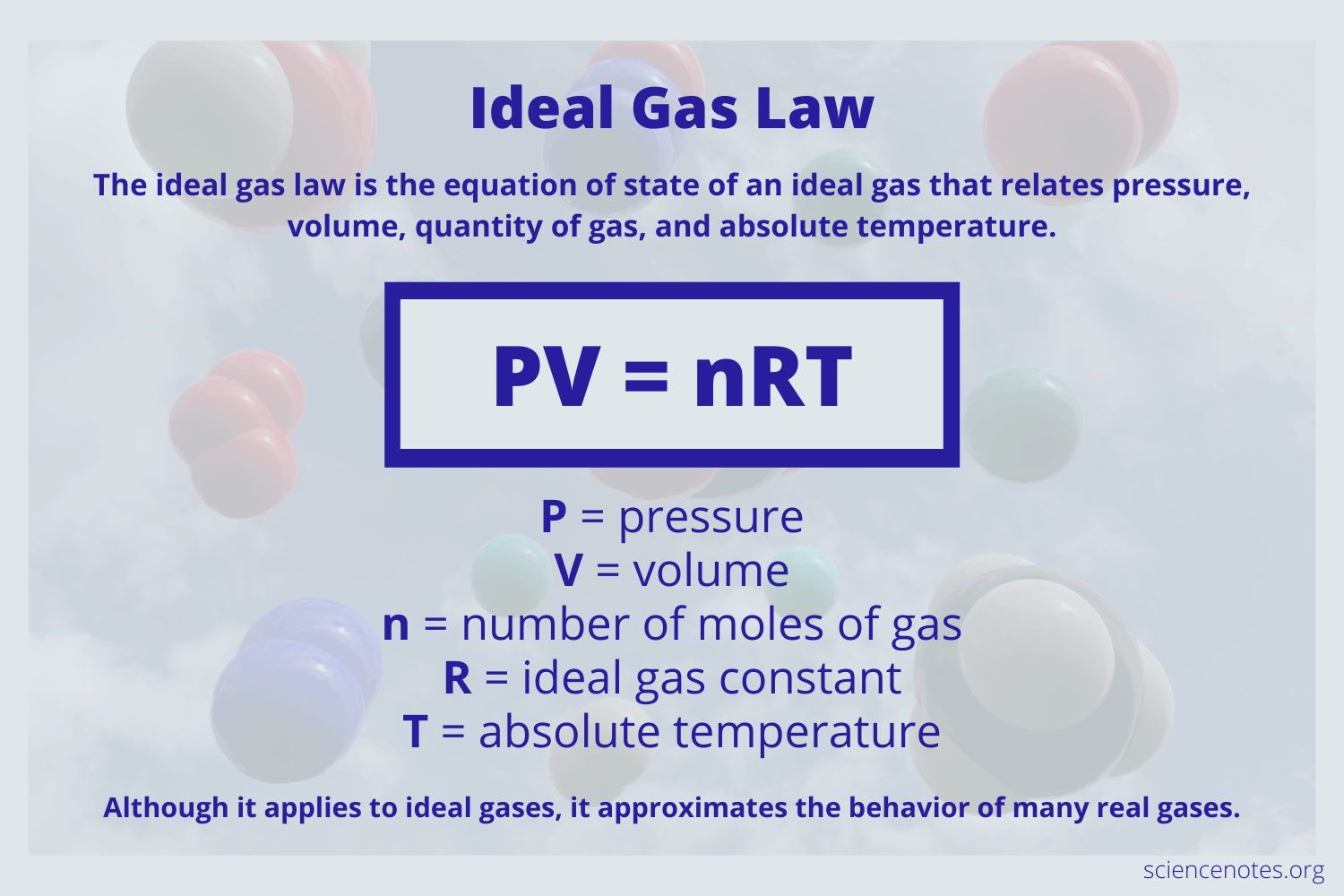
What is the ideal gas law? And what does each letter mean
State Charles law
For a constant mass of a gas at a constant pressure
The volume occupied by the gas is proportional to its absolute temperature.
V≈T
State Boyles law
For a constant mass of a glass at a constant pressure
The pressure exerted by the gas is inversely proportional to the volume it occupies.
P≈1/V
State the pressure law
For a constant mass of a gas at a constant volume
The pressure exerted by the gas is proportional to its absolute temperature.
P≈T
State the Gay Lussacs law
For a constant mass of a gas at a constant volume
The pressure exerted by the gas is proportional to its absolute temperature.
P≈T
What 3 factors is the temperature of an object is affected by?
Amount of heat energy transferred
The mass of the k jest
The specific heat capacity of the material
What 2 factors is the change of the state of substance is affected by?
The mass of the solid substance
The specific latent heat of fusion or vaporisation of the substance
Define root mean squared speed
Is the square root of the arithmetic mean value of the squared speeds of particles in an ideal gas
What is the first property of an ideal gas?
The molecules have negligible size
What is the second property of an ideal gas?
The molecules are identical
What is the third property of an ideal gas?
All collisions are perfectly elastic
And the time between collisions is significantly larger than the time of a collision
What is the fourth property of an ideal gas?
The molecules do not exert a force on each other
Except in collisions
What is the fifth property of an ideal gas?
There is a large number of molecules
For statistics to be applied
What is the sixth property of an ideal gas?
The motion of the molecules is random
What is the regular gas equation?
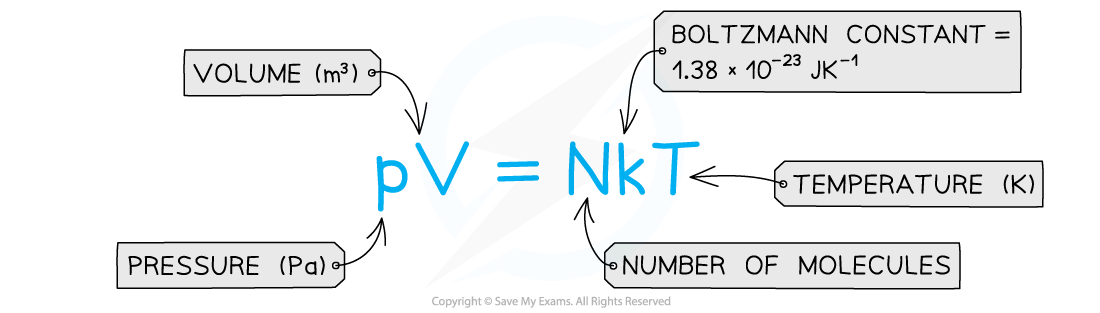
What is the equation for the root mean squared speed of an ideal gas?
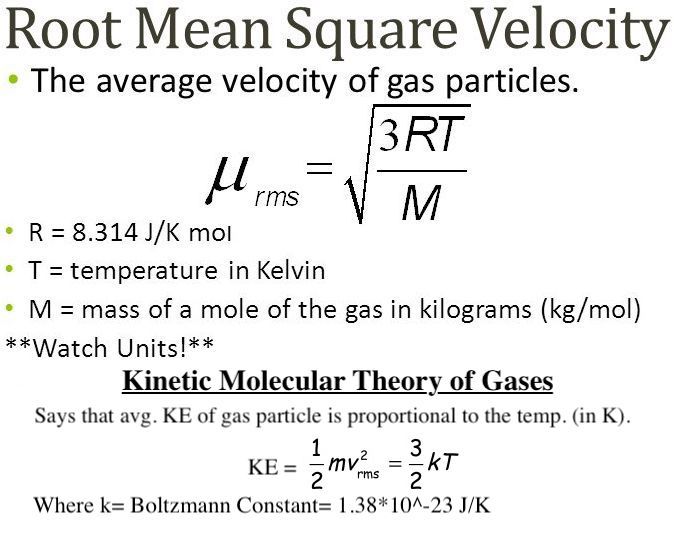
Mnemonics for the gas laws
Big Penguins are Over Vaping
Charles Vapes Too much
Gay Lussac’s Tiny Penguins