IB Bio HL C2 Quiz Review: Signalling and Muscles
1/88
Earn XP
Description and Tags
need to add c2.1.12, c2.1.13, c2.1.14 and 3.3.1-.9
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
What are two examples of chemical signaling?
Neurotransmitters and hormones
What are the 3 types of hormones?
amines, peptides/proteins, steroids
What are hormones?
Chemical signals secreted from endocrine glands that travel through the blood stream to receptors in cells
What are amine hormones?
Small molecules synthesized by modification of amino acids
What are 2 examples of amine hormones?
Melatonin and epinephrine
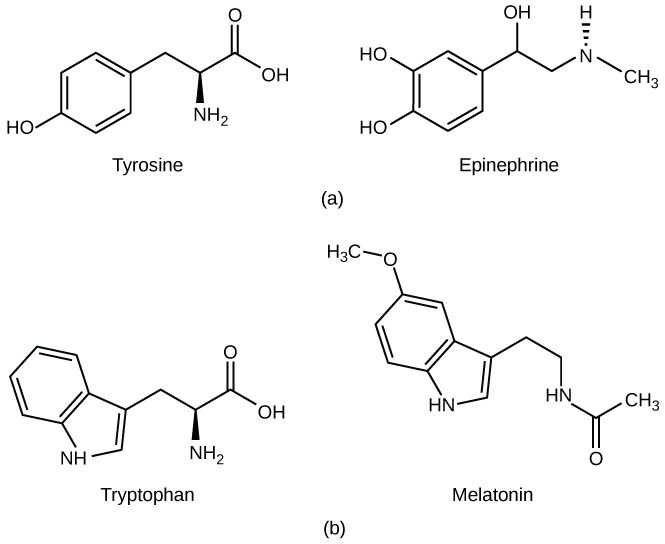
What is melatonin derived from?
Tryptophan
What is epinephrine derived from?
Tyrosine
What is the purpose of melatonin?
Secreted by the pineal gland to regulate the circadian rhythm
What is the purpose of epinephrine?
Secreted by the adrenal glands to activate flight vs fight response
Peptides and proteins are ________ and therefore can’t pass through hydrophobic center of plasma membranes of cells, so their receptors are found on the surface of target cells
water soluble
A ________ forms a peptide bond between amino acids
condensation reaction
Examples of peptides (short polypeptide chains)
antidiuretic hormone (water retention in kidneys), oxytocin (contractions), and gonadotropin-releasing hormone (puberty)
Examples of protein (larger polypeptide chains)
insulin (lowers blood glucose levels), glucagon (raises blood glucose levels)
Examples of glycoprotein (larger polypeptide chains)
FSH and LH (menstrual cycle and production of eggs and sperm)
What are steroid hormones?
Lipids derived from cholesterol
steroid hormones are ____ in water
insoluble
Examples of steroid hormones:
estrogen (ovaries- female sex characteristics/mesntrual cycle)
progesterone (ovaries/placenta- prepares for fertilized egg/pregnancy/milk secretion)
testosterone (testes- male sex characteristics)
What are neurotransmitters?
Chemicals that transmit signals across a synpase, ONLY HAVE LOCAL EFFECT
What are the types of neurotransmitters based on chemical structure?
amines
amino acids
peptides
esters
gasses
What are examples of neurotransmitters?
amino acids: glutamic acid, GABA
amines: dopamine, serotonin
peptides: endorphines
esters: acetylcholine
gases: nitric oxide, carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide
________ signaling involves the use of a chemical signal from a sending cell to a receiving cell that had the complementary receptor
Cell-to-cell
____ signaling involves diffusion between adjacent cells while _____ signaling involves molecules being transported all throughout the body
Local, distant
Ligand
chemical that binds to another specific molecule
Examples of signaling ligands:
Hormones, neurotransmitters, cytokines, calcium ions
Receptor
Protein in or on the target cell that sets off a response when the ligand binds to it
Transmembrane receptors (cell surface receptors) are
integral membrane proteins
Ex of transmembrane receptors (cell surface receptors):
ligand gated ion channels
g-protein coupled receptors
enzyme-linked hormone receptors
intracellular receptors are
found inside the cell
Ex of intracellular receptors
cytoplasmic and nuclear receptors for steroid hormones
Transmembrane receptors contain 3 parts:
Extracellular part that binds to signalling molecule
Hydrophobic amino acid part that interacts with the hydrophobic tails inside the membrane
Intracellular portion that’s composed of hydrophilic amino acids that interacts with the cytoplasm
Ion channel linked receptors (transmembrane), like the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor work by
Opening when the ligand binds, allowing ions to diffuse into the cell, changing the voltage across the plasma membrane
Epinephrine receptors are _____
G-protein linked receptors
G-protein linked receptors work by:
Using 7 membrane spanning regions to activate G-proteins in a cell
Enzyme linked receptors work by:
Activating a sequence of reactions in a cell when a ligand binds to it’s receptor site
Insulin receptors are an example of _________
Enzyme linked receptors
Intracellular receptors are
small signaling molecules that can cross the lipid bilayer
Intracellular receptors have _______ ______ _____ on their surface so they can remain dissolved in aqueous solutions
hydrophilic amino acids
The three steps of the chemical sign
Reception: cell detects a signal in environment
Transduction: change is activated
Response
Signalling molecules are called _____ __________
first messengers
first messengers are often
hormones or neurotransmitters that bind to specific receptors
Peptide hormones and neurotransmitters typically ______ molecules that must bind to transmembrane receptors
hydrophilic
Can steroid hormones pass through the phospholipid bilayer?
Yes
Steroid hormones are hydrophobic/hydrophilic?
hydrophobic
Transduction happens when the binding of the signaling molecule to the receptor induces:
a change in the shape of the receptor
Signalling cascade
series of metabolic reactions in which one reaction triggers the next
Second messengers
Small molecules in the cell that act as intracellular messengers in response to extracellular molecules
Examples of secondary messengers
cAMP, nitric oxide and Ca2+ ions
Signalling cascades are only necessary for _____ hydrophilic ligands
hydrophilic
2 types of channel gated proteins:
voltage gated channel
ligand gated channel
Gated channel proteins are selectively permeable meaning:
they can open or close in response to a signal
Voltage gated channels’ purposes:
muscle cell contraction and neuronal signaling
Ligand gated channels work by
Opening to allow positively charged ions to pass through ion channel when ligand has bound to the channel
Acetylcholine receptors work by:
accepting Ach that’s diffused across membrane from presynaptic neuron to bind to transmembrane acetylcholine receptor on the posynaptic cell
When Ach binds, the acetylcholine receptor (AchR) undergoes conformational change which:
open pore in protein allowing sodium ions to move through facilitated diffusion
The Na+ ions that move in after the AchR changes shape causes the postsynaptic cell to
depolarize, triggering action potential
All G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) consist of
single polypeptide folded in a globular shape embedded in plasma membrane
What does the extracellular loop of the GPCR do?
Forms binding site that signaling molecules attach to
What does the intracellular loop of the GPCR do?
Attach to G-protein complex which contains alpha, beta and gamma protein subunits
______ is bound to alpha subunit of the G-protein complex and the entire GPC is attached to a nearby GPCR
GDP (guanosine diphosphate)
GPCR activation occurs when
Ligand binds to GPCR, changing shape
Shape change causes GDP to detach from alpha subunit
GTP binds in its place
GTP binding causes GP subunits to separate
GTP-bound alpha subunit
GTP-bound beta-gamma subunit
Both remain anchored to plasma membrane but can diffuse to interact with other membrane proteins
Odor/taste molecules, pheromones, hormones (glucagon, epinephrine, gonadotropin-releasing hormone, oxytocin) and neurotransmitters (acetylcholine) are examples of _________
GPCRs
Epinephrine is an _____ hormone
amine
Adrenaline means
ad (at) + renal (kidney)
Epinephrine means
epi (above) + nephron (kidney)
Effects of epinephrine reaction:
Hydrolysis of glycogen by liver releasing glucose into bloodstream
Increase of ventilation rate
Dilation of bronchioles
Stimulation of skeletal muscle contraction
Triggers sweat
Increase of heart rate by firing of SA node of heart
Epinephrine is _____ and cannot pass through hydrophobic center of the membrane
hydrophilic
Epinephrine receptors are found on ______ of target cells
surface
Epinephrine binds to transmembrane receptors known as
adrenergic receptors
Epinephrine receptor activation occurs when:
Epinephrine binds to GPCR causing conformational change
Change causes GDP to detach from alpha subunit
GTP binds in its place
GTP binding causes GP subunits to separate into alpha and beta-gamma
Subunits diffuse laterally to interact w other membrane proteins
Epinephrine signal transduction occurs when activated alpha subunit of GP activates enzyme known as
adenylate cyclase
Epinephrine _____ adenylyl cyclase while melatonin ______ it.
activates, inhibits
Epinephrine signal transduction
Adenylyl cyclase is activated by alpha subunit
Activated adenylyl cyclase catalyzes the conversion of ATP to cyclic AMP
cAMP (modified adenine nucleotide) is composed of
single phosphate attached to two carbons of ribose sugar that’s linked to adenine
epinephrine response occurs when
cAMP (2ndary messenger) rapidly diffuses through cytoplasm
cAMP activates other molecules that propagates signal into physiological change
Insulin is a _____ hormone
protein
Insulin is made up of
non-conjugated protein (made of folded amino acid chains)
Insulin’s function:
causes cells to uptake glucose from the blood to be:
used in cellular respiration
converted to glycogen
Insulin stimulates
skeletal muscles
liver
adipose tissue
Is insulin hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
hydrophilic
What hormone binds to a Receptor Tyrosine Kinase?
Insulin
What is a kinase?
Enzyme that can transfer a phosphate group from ATP to another molecule (phosphorylation)
Insulin receptor activation occurs when
Insulin binds to the receptor
Binding causes receptors tails to connect
Tyrosine kinase in receptor tail phosphorylates tyrosines in the other tail
Insulin signal transduction occurs when
phosphorylated tyrosine kinase launches metabolic reactions within cell
Insulin response occurs when:
vesicles embedded with glucose-transport proteins move to plasma membrane
vesicles fuse w/ membrane and transport protein becomes part of plasma membrane
glucose transport then allows glucose into the cell through facilitated diffusion
Process of steroid hormone
Hormone diffuses through the cell membrane
Binds to the receptor in cytoplasm/nucleus, forming hormone-receptor complex
Hormone-receptor complex attaches to the DNA at a specific gene.
Hormone-receptor complex acts as a transcription factor, turning “on” the transcription of the DNA into mRNA
The mRNA is translated into a protein at the ribosome
The protein has an effect in the cell
How does testosterone cause a response in the cell?
Testosterone diffuses thru the cell membrane of a muscle cell
Testosterone binds to its receptor within the cytoplasm, forming a hormone-receptor complex
The hormone-receptor complex moves into the nucleus through a nuclear pore, where it acts as a transcription factor, attaches to the DNA at the gene that codes for a protein called the Serum Response Factor
Binding of the hormone-receptor complex to the DNA activates the transcription of the Serum Response Factor gene into mRNA
The mRNA is translated into a Serum Response Factor protein
The Serum Response Factor protein causes growth of the muscle cell
What are 3 examples of steroid hormones in humans?
Estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone
Where is estrogen secreted from?
ovaries