Exam One
1/269
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
270 Terms
At the down of man science began through human observations. What are human observations?
How we use animals and plants to improve our daily lives.
What is the relationship between science and society?
Science influences societal development by providing knowledge that drives innovation, informs policy, and enhances quality of life. While society tells scientists what they can and can not observe.
Where is it believed that human civilization began?
In the middle east.
What was the first form of science utilizewd by humans?
The domestication of the world around them.
What was likely the first animal domesticated and why?
The gazelle was because the hid could be used for clothes, the meat for food and the bones for tools.
What was perhaps the most important domesticated animal for human civilization?
The dog, as it provided companionship, assistance in hunting, and protection.
What was another name for the middle east?
Mesopotamia
What was the counterpart to gazelles in the region of the world known as eurasia?
Reindeer
What was more important to the survival of humans the domestication of plants or animals?
Plants, as they provided a stable food source and enabled the development of agriculture.
What rivers made up the fertile cresent?
The Nile, Tigris, and Euphrates Rivers
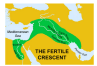
Where was the best soil for humans to plant crops located at in the fertile cresent?
The flood planes
What was the result of the domestication of plants for human civilization?
It led to stable food supplies, population growth, and the establishment of permanent settlements.
Spontaneous Generation was the first theory of heredity. What is spontaneous generation?
Living structures form without descent form similar organisms.
What are some notable examples of individuals who believed in spontaneous generation?
Aristotle, Shakespeare, Religions
What did Jean Babtist can Helmont do?
He conducted experiments that supported the theory of spontaneous generation, demonstrating that mice could arise from decaying materials compiling his finding into a book.
How did Louis Pasteur disprove spontaneous generation?
He conducted experiments using sterilized broth in a swan necked flask and demonstrated that microbial life arose from contamination, not spontaneously.
What does it mean for someone to be an ovist?
Someone who believes that all organisms develop from pre-existing cells or structures, specifically that embryos arise from eggs. This theory contrasts with the idea of spontaneous generation.
What does it mean for someone to be a spermist?
Someone who believes that all organisms develop from sperm or male gametes, asserting that embryos arise from the fusion of sperm and egg. This theory is in contrast to the ovist perspective.
Who hypothesized thetinkings of ovists?
William Harvey “On the Generation of Animals” - all animals come from eggsand proposed that eggs are the source of all animal life, supporting the ovist perspective.
What did Malebranche believe?
Believed in the theory of preformation, asserting that organisms develop from miniature versions of themselves already present in the sperm or egg.
Who was the first to view sperm?
Antoine van leeuwenhoiek
What did Nocolaas Hartsoeker do?
Produced the image of Homunculus, a tiny human form curled up inside of a sperm cell.
What was pangenesis?
The theory proposed by Charles Darwin that body cells and structures shed some small pieces of themselves which collected in the reproductive organs prior to fertilization.
What are Gemmules?
Hypothetical particles proposed by Charles Darwin in his pangenesis theory, believed to carry information from body cells to the reproductive organs for inheritance.
Why did Darwin not like his own hypothesis, pangenesis?
He was uncomfortable with pangenesis because it lacked empirical evidence and contradicted the blending inheritance model. He also felt it did not adequately explain how traits were passed from one generation to the next.
What idea did pangenesis follow that was developed by Lamarck?
The idea of inheritance of acquired characteristics, suggesting that traits developed during an organism's life could be passed to offspring. Also known as Larmarckism..
What are the two important Ideas of Lamarckism?
Organisms evolve through the inheritance of acquired traits.
Use and disuse of characteristics can lead to changes that are passed on to future generations.
Who and whaat experiment disproved the theory of Lamarckism>?
Disproven by the experiments of August Weismann, particularly his work with mice, which demonstrated that acquired characteristics are not inherited. Known as the rat Tail Mutilation Experiment.
The results are however slightly inconclusive because the rats wanted to keep their tail but were forced to loose it.
What is the theory of Epigenesis?
The theory that the embryo is not performed in the ovum or the sperm, but that it develops gradually by the successive formation of new parts from information passed down. (DNA)
In the modern view of epigenetics after eight weeks what can play a role in the determination if a genetic trait is turned on or off?
The environment and external factors.
By using the work of previous scientist like Charles Darwin, Gregor Mendel was able to develop his theory of heredity and the Laws of Inheritance creating Dominant and Recessive Genes. Was his work immediately accepted?
No, it faced skepticism and was not widely recognized until later, when three individuals (de Vreis, Correns and von Tshermak) replicated Mendel’s work that people accept Mendels theory of Inheritance.
What did Bateson and Punnett discover?
Genetic Linkage
What did Morgan Hunt do?
He discovered sex-linked inheritance patterns in fruit flies. With his Caltech Fly Lab
What did Wilhelm Johnson do in 1909
Termed the word “gene” as the raw material of heritability. Coining the term in direct contrast to the idea of the pangene.
What is Genetics?
A branch of biology dealing with heredity and the expression of inherited traits.
What is heredity?
The transmission of traits from one generation to the next.
Why is it important to learn about heritability?
Currently there are over 10,000 genetic disorders (Down’s, cystic Fibrosis, etc.). By Examining modes of inheritance even at the DNA level and Analyzing what might be passed to the next generation, we may be able to develop genetic testing and genetic therapies to combat disease.
What is expression?
Once you get genetic material, how do you convert that into a phenotypic characteristic.
Why do we study gene expression?
Differences in gene expression can correlate with drug response or disease risk.
i.e. changes at the DNA level of a coding protein can affect how the protein is produce or how it works.
Fill in the Statement:
Genes ar the instructor or ______ ________ for making _______.
recipe book; proteinsinstruction manual; proteins.
If we learn how the genes are inherited and identify the proteins involved what can we do?
Learn how they are made and learn how the work leading to improved medicines and treatments for any number of current and future diseases.
What is Life?
An organism that is complex with the ability to take energy from the environment and transform it for growth. In addition the organism tends to go towards an equilibrium with their environment and respond to stimuli. The most important characteristic though is the biological requirement for life.
What are the macromolecules of life?
The builiding blocks of cells and are found in all living organisms including carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. These found molecules are made of some combination of six atoms: carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, hydrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus.
What is the basic unit, atoms involved, and purpose of the macromolecule carbohydrates?
Basic Unit: Sugar
Atoms: C, H, & O
Purpose: to provide energy and support cellular structure
What is the basic unit, atoms involved, and purpose of the macromolecule lipids?
Basic Unit: Fatty acids
Atoms: C, H, & O
Purpose: to store energy and form cell membranes, provide cushioning for cells and prevent heat loss.
What is the basic unit, atoms involved, and purpose of the macromolecule nucleic acids?
Basic Unit: Nucleotides
Two Types: DNA & RNA
Atoms: C, H, O, N, & P
Purpose: directs and controls ALL activities of the cell
What is the basic unit, atoms involved, and purpose of the macromolecule proteins?
Basic Unit - Amino Acid
Atoms - C, H, O, N, & S
Purpose: to provide a vast array of functions in the cell including metabolism, transport, and stimulus response
If the atoms that make up lipids are carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; why do we think that phosphorus is also involved?
It is an addition to the base unit of a lipid creating a new structure.
i.e. Phospholipids
What type of bond creates the shape of proteins?
Disulfide bonds
Essential amino acids are those that the body can create itself. Of the 20 amino acids that we deal with, how many are essential?
Nine
When DNA was first identified it was known as nuclein. What is this?
Also known as chromatin which is a mixture of proteins and nucleic acids or DNA
What was the results of Frederick Griffiths experiment with pneumonia bacteria on mice?
The experiment demonstrated that non-virulent bacteria could be transformed into virulent forms when exposed to heat-killed virulent bacteria, indicating the presence of a "transforming principle".
Why did most scientist up until the 1940s believe that protein was the genetic material of the cell and not nucleic acids?
They believed proteins were more complex and varied than nucleic acids, leading to the assumption that they carried genetic information.
Describe the experiment to determine DNA as the hereditary material performed by Avery, Macleod, and McCarty.
Conducted experiments using enzymes to selectively destroy proteins, RNA, and DNA in heat-killed virulent bacteria. They found that only the destruction of DNA prevented the transformation of non-virulent bacteria into virulent forms, providing strong evidence that DNA is the hereditary material.
Even after Avery and colleagues completed their experiment to prove DNA was genetic material, the scientific community was not convinced. Hershey and Chase performed another experiment to prove Avery’s theory. Describe this experiment.
Hershey and Chase used bacteriophages labeled with radioactive isotopes to determine whether DNA (32P) or protein (35S) was injected into bacteria. They found that only the DNA entered the bacterial cells, confirming that DNA is the genetic material.
Since DNA is the material for heredity, that made DNA the most important macromolecule in Genetics. What happened as a result?
This led to a greater understanding of genetic inheritance, molecular biology, and the mechanisms of evolution, ultimately shaping modern genetics and biotechnology.
How does basic recombinant DNA technology work?
It revolves around DNA making Protein. For example if large scale synthesis of a protein is needed, scientist will inject the necessary DNA into bacteria like E. coli to produce the desired protein through the bacterial machinery, allowing for mass production and study of proteins.
How do scientist gain a specific section of a DNA strand?
By using restriction enzymes to cut DNA at specific sequences.
Why did we create DNA libraries?
To store and manage large collections of DNA fragments for research and analysis, facilitating the study of genes and their functions.
What are some examples of how we induce medicines and pharmaceuticals formation into a bacteria or microorganism to mass produce it?
Insulin, Human growth hormone, and Hepatitis B Vaccine.
What breakthrough technology allowed us to begin to detect diseases caused by genetic inheritance.
The development of genetic testing technologies, such as DNA sequencing and polymerase chain reaction (PCR),
How is genetics used in Agriculture?
Genetics is used in agriculture to improve crop yield, resistance to pests and diseases, and enhance nutritional value through techniques such as selective breeding and genetic modification.
What was the first discovery in the world f DNA by Phoebus Levene?
Differentiated between DNA and RNA with the difference in sugars, identified the three major components of a nucleotide (Phosphate, Sugar, Base) and came up with the tetranucleotide hypothesis
What is the tetranucleotide hypothesis?
Formation of a circle with four nucleotides with each nitrogenous base being represented, making the percentages of each nitrogenous base 25%
What is the first piece of the puzzle to DNA discovered?
The identification of nucleotides and their components by Phoebus Levene.
What is the second piece of the puzzle to DNA discovered?
The discover of Dna being the molecule of Heredity by the experiments by Frederick Griffith; Avery, Macleod &McCarty; Hershey, & Chase
What is X-Ray diffraction?
The measuring of angles of x-rays around an object.
What did william astbury discover using X-ray diffraction?
DNA has regular structure, that repeats every 2.7nm , and that DNA lays basically flat, stacked and at a regular interval of 0.34nm.
What was the 3rd piece of the puzzle of DNA discovered?
The positioning of the bases by William Astbury.
What was the 4th piece of the puzzle of DNA discovered?
Chargaff’s Rules that DNA has equal amounts of adenine and thymine, as well as guanine and cytosine. In addition to the rule that the composition of DNA varies from one species to another in the relative amounts of the pairs.
What began in 1952?
The race for the structure of DNA
Who and what was the first proposed model of DNA?
Linus Pauling proposed the triple helix structure of deoxyribonucleic acid that was based on his work with developing is the alpha helical structure of a protein
Who all was involved in teh race for hte DNA structure in 1952?
Maurice Wilkins, Raymond Gosling, Linus Pauling, Rosalind Franklin, James Watson, and Francis Crick
What was the fifth and sixth pieces of the puzzle of DNA discovered
The crystal structure of DNA and the overall helical shape by Wilkins and Gosling
How were the seventh and eighth pieces of the puzzle of DNA discovered?
Rosalind Franklin identified the X-ray diffraction images originally used were not wet or dry and that DNA was affected by water. Therefore the phosphates had to be on the outside.
Originally Gosling and Franklin focuses on the DNA-A dry sampple and determine the ninth puzzle piece which is?
The size of the repeating units determined that DNA was symmetrical.
What is the famous picture of DNA on a wet mount that showed the tenth piece of the puzzle, that per twist in DNA there are 10 base pairs?
Image B-51
What was the last thing figured out in the puzzle of DNA?
The base pairs linking together,.
How was the shape of the bases determined?
By Watson by realizing that eh shape of the bases was complementary, allowing them to pair specifically, in the same size if adenine was hydrogen bonded to thymine and guanine to cytosine.
Watson and Crick put it all together but …
the evidence came from many other scientists
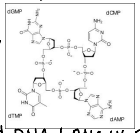
What is a nucleotide?
A nucleotide is the basic building block of DNA and RNA, consisting of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
What is a nucleoside?
A nucleoside is a molecule composed of a nitrogenous base linked to a sugar molecule, without a phosphate group, and is a component of nucleotides, and is involved ion the killing of pathogens and cancer cells as well.
What is a purine?
A two ringed heterocyclic nitrogenous base (9 atom ring structure)
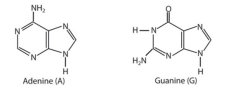
What are the Purine nitrogenous bases?
Adenine (A) and guanine (G)
What is a pyrimidine?
A single ringed nitrogenous base (6 atom ring structure)
What are the nitrogenous bases that make up the pyrimidines?
Thymine (T, only DNA), Cytosine (C), and Uracil (U, only RNA)
What is the difference between deoxyribose and ribose?
Deoxyribose is a five-carbon sugar found in DNA, lacking one oxygen atom at the 2’ carbon, compared to ribose, which is found in RNA that has the oxygen at the 2’ carbon.
Where does the phosphate attach to DNA?
The phosphate group attaches to the 5' carbon of the deoxyribose sugar in the DNA backbone.
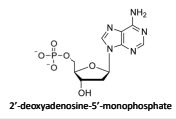
What is the bond between the nitrogenous base and the sugar in DNA at the 1’ carbon called?
N-glycosidic bond
What is a glycosidic bond?
A type of covalent bond that connects a carbohydrate (sugar) to another group, which can be another carbohydrate or a nitrogenous base in nucleic acids or any other molecule.
The nitrogenous base can be in two positions in DNA; anti or syn. What is the position of each?
The anti position is when the base is oriented away from the sugar, while the syn position has the base oriented towards the sugar.
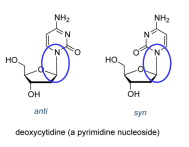
What configuration is favored by purines?
The anti configuration is favored by purines, allowing for optimal base pairing and stability in the DNA structure. The syn configuration is possible though and has a role in the formation of Z-DNA
Why does pyrimidines struggle to form the syn confirmation?
Pyrimidines struggle to form the syn conformation due to steric hindrance caused by their smaller structure, which makes it energetically unfavorable for the base to orient towards the sugar.
What bonds connect the phosphate to the carbon sugar at the 5’ carbon?
A phopsphodiester bond which is an ester bon between the oxygen of the phosphate and the sugar.
What do we look for to determine that the molecule is DNA?
We look for the presence of deoxyribose sugar, phosphate groups, and nitrogenous bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine) that form a double helix structure.
Two polynucleotide chains in an antiparallel structure of 5’ to 3’ and 3’ to 5’ make up DNA with phosphate molecules on the outside. What about the positions of the bases?
The nitrogenous bases are oriented inward, pairing specifically (adenine with thymine, cytosine with guanine) through hydrogen bonds, and are perpendicular to the sugar-phosphate backbone and helical axis. .
How many hydrogen bonds are between adenine and thymine?
Two hydrogen bonds connect the nucleotide
How many hydrogen bonds are between cytosine and guanine?
Three hydrogen bonds connect the nucleotide.
Is the bond between cytosine and guanine or adenine and thymine stronger?
The bond between cytosine and guanine is stronger due to the presence of three hydrogen bonds, compared to the two hydrogen bonds between adenine and thymine.
What does it mean for DNA to pseudosymmetrical?
Pseudosymmetrical in DNA refers to the structural similarity in the double helix, where the two strands are complementary and run in opposite directions, creating a balanced appearance. Which results in the helices formed having grooves with identical or different shapes and sizes, contributing to the functional diversity of the DNA molecule.