HHP: Chapter 12 Structure of Heart
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Components of Cardiovascular System
Blood
Heart
Blood Vessels
Blood
Medium to carry substances through the body
Heart
Mechanical pump that moves blood via bulk flow
Blood Vessels
Structures carrying blood throughout body
Transportation in different organisms
Single Celled: Diffusion
Multi-Cellular: Bulk Flow
Transportation of Nutrients
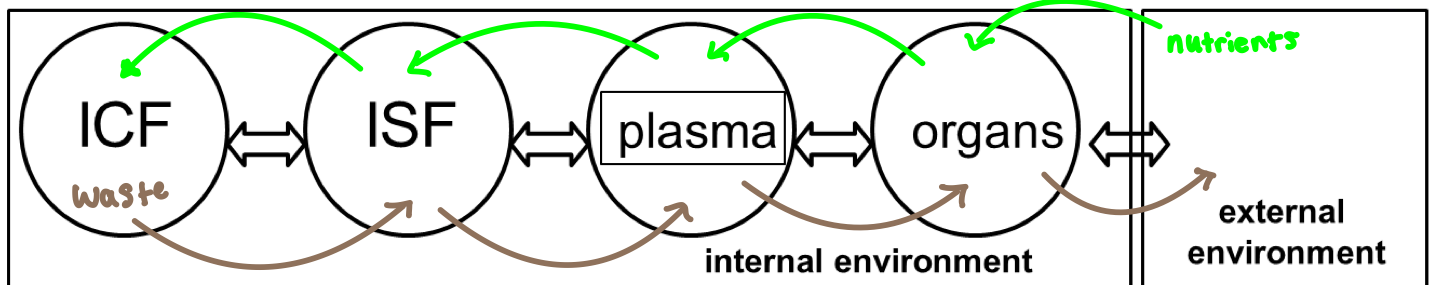
Diffusion occurs over four different compartments
4 Different compartments involved in diffusion
Intracellular Fluid
Interstitial Fluid
Plasma
Organs
Where do all blood cells descend from
Multipotent Hematopoietic Stem Cells
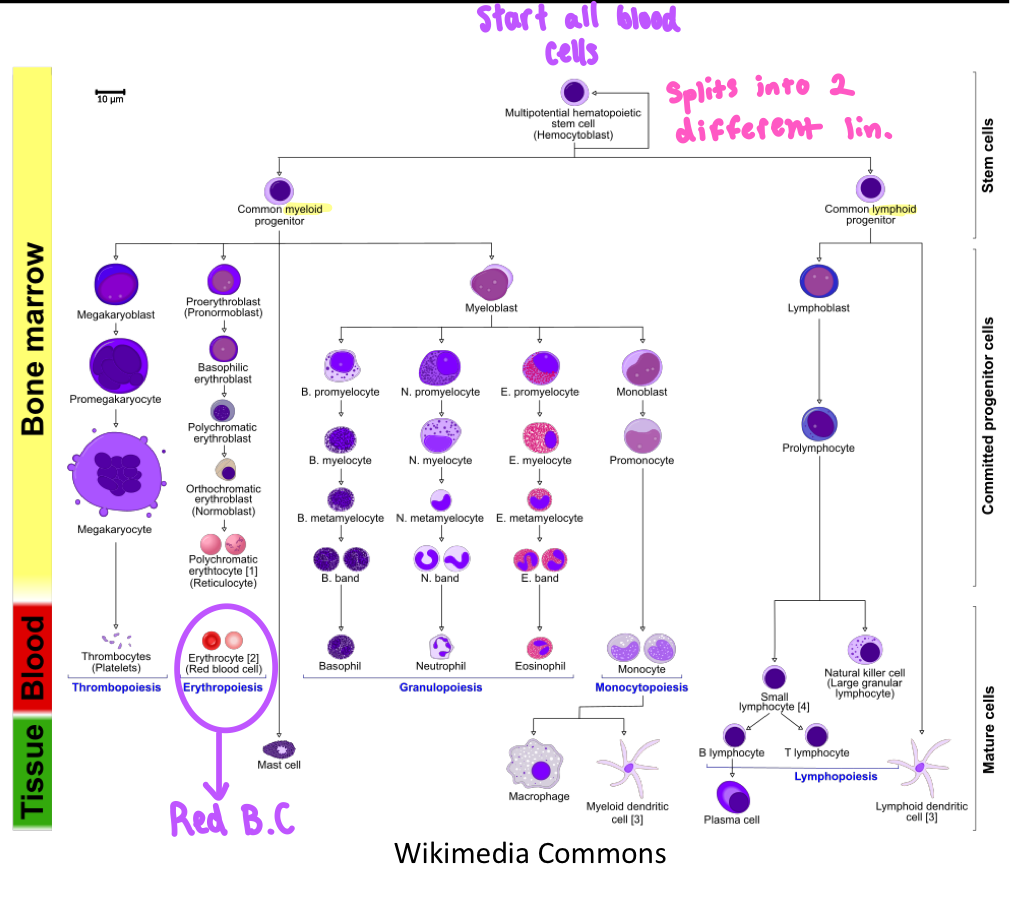
Where does cell differentiation occur?
Bone Marrow
2 types of cell differentiaton
Myeloid Cells
Lymphocyte Cells
Formed elements of blood
Erythrocytes (Red BC)
Leukocytes (White BC)
Platelets (Cell Fragments)
Erythrocytes
Red Blood Cells
Transport O2
99% of Cells
Leukocytes
White Blood Cells
Immune FunctionP
Platelets
Cell Fragments
Blood Clotting
2 things blood is composed of
Formed elements and plasma
Plasma
90% water
Plasma Proteins move water through compartments based on non penetrating proteins
Hormones
Mineral Electrocytes
Gases: O2 and CO2
Metabolic Wastes
Male and Female Blood Amount
M: 5.5 L
F: 4.5 L
Hematocrit
Shows percentage of how much of blood is composed of RBCs
Splits plasma, leukocytes/platelets, and Erythrocytes
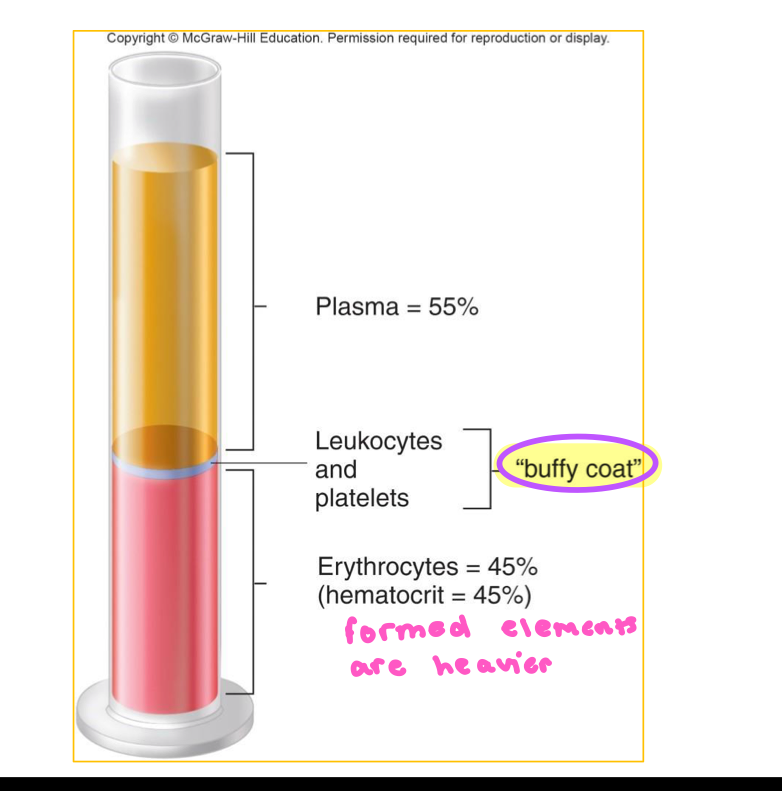
Male and Female % of RBCs
Males: 45%
Females: 42%
Plasma: 55%
Right and Left Atria
Receiving chambers for blood returning to heart
Superior
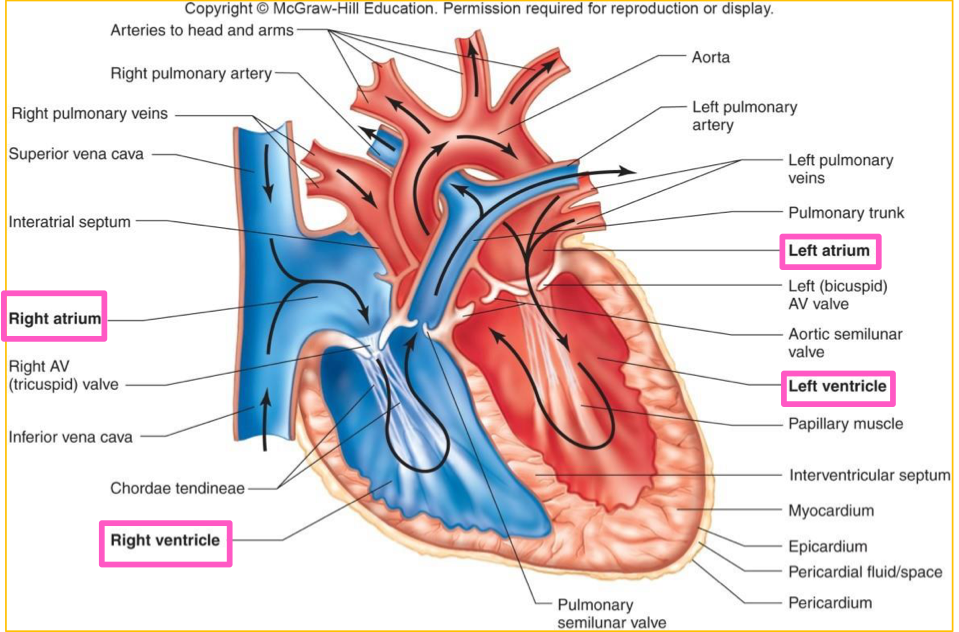
Right and Left Ventricle
Pumping Chambers
Create force for blood flow
Inferior and larger
Right Heart
Pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs
Left Heart
Pumps oxygenated blood throughout rest of body
Pericardium
Fibrous sac enclosing heart
Myocardium
Walls of Heart that encircles heart
Endothelium
Lines chambers and vessels
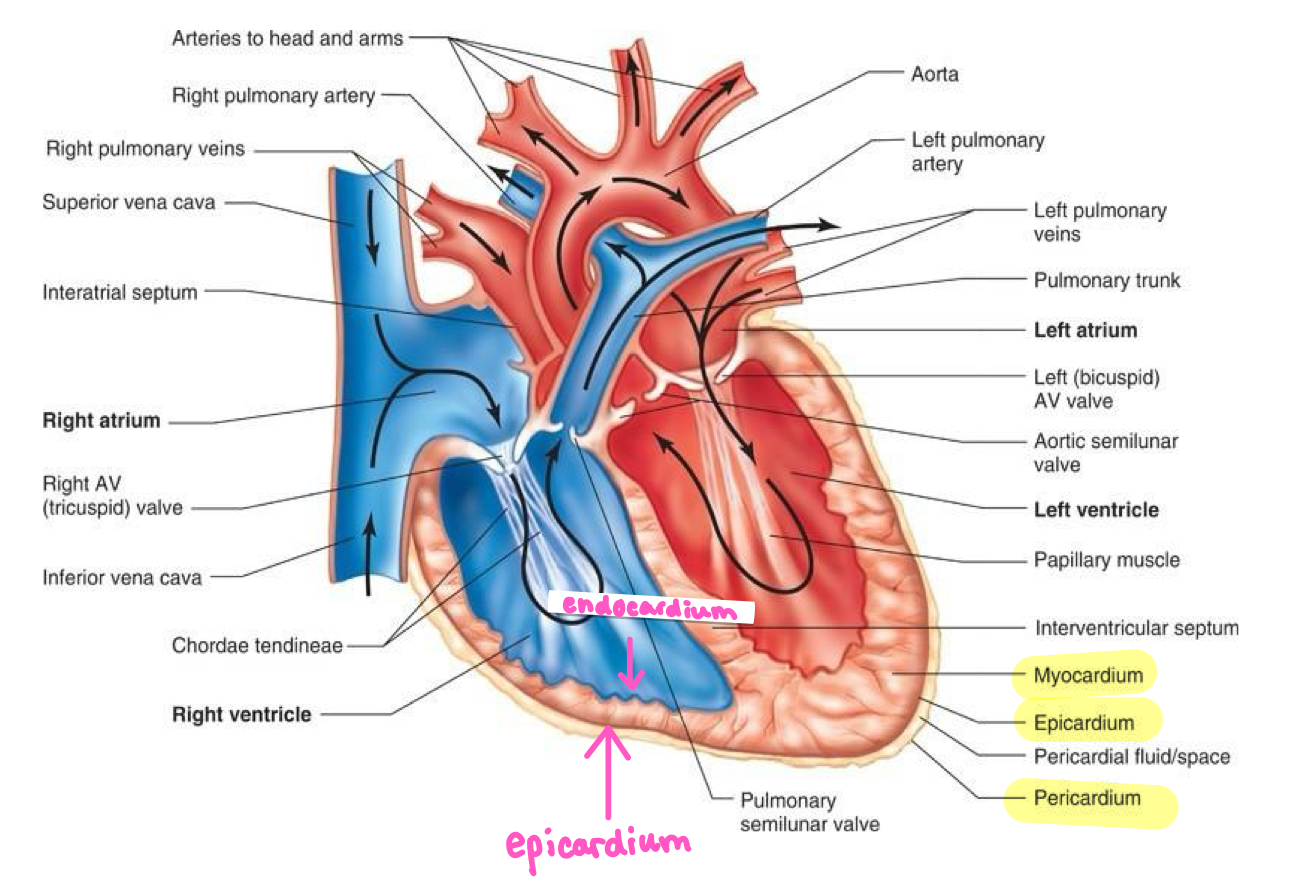
Atria and Ventricle Myocardium
Thinner and Atria
Thicker in Ventricles because stronger pumping
Thicker on left side due to pumping to entire body
Interventricular Septa
Separates right and left hearts
AV Valves
Valve that separates atria and ventricle
Right AV Valve
Tricuspid valve
Left AV Valve
Bicuspid valve / mitral valve
Semilunar Vavles
Prevent back flow from main arteries
Two Semilunar valves
Aortic and Pulmonar semilunar valves
Right Heart blood flow
Deoxygenated blood from tissues —> Vena Cava —> right atrium —> right ventricle —> tricuspid valve —> pulmonary blood vessels —> lungs
Left Heart Blood Flow
Oxygenated blood from pulmonary veins —> left atrium —> left ventricle —> aortic semilunar valve —> aorta —> blood vessels to rest of body
Circulation of Blood
Aorta —> Arteries —> Arterioles —> Capillaries —> Venules —> veins
Microcirculation
Arterioles —> capillaries —> venules
Capillaries
Where most nutrient transport occurs
Systemic Circulation
Circulation throughout body and not lungs
Systemic Circulation Path
Aorta —> Arterioles and capillaries in regional vascular beds —> Organ blood flow —> Venules, veins and vena cava
Pulmonary Circulation
Lungs
Pulmonary Circulation
Aorta —> Deoxygenated Pulmonary Arteries —> Arterioles —> Capillaries —> Venules —> Oxygenated Pulmonary Veins
Coronary Circulation
Pathway of how we get nutrients to the heart
Clots in this cause heart attacks