Viruses, Bacterias etc - Unit 4 Biology
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Bio 11- Ms. Charlton
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
description of test
40 marks
18 questions
ALL WRITTEN
topics
1) virus structure what they are made from
2) tell her abt virus and draw it label
3) how they replicate and make copies (2 cycles down
lytic and lysogenic
(given diagram,label,or questioning regarding the cycle parts
4) prions (1 question:what they are (mis folded protein, vampire example,how they replicate,bumping into normal proteins)
(no need memorize types virus or diseases)
5) immunity: what body have to fight off pathogens - passive/ active immunity
6)how vaccines work (ques)
7)lines of defense AND (1st skin,2nd
SPECIFIC (T/BCELLS) VS NONSPECFIIC
8) BACTERIA: structure (Projaryotes) unique features
know bacteria,peptidoglycan
9) how do bacteria get neutriends the type, auto,decomposes,hetero umm
metabolism^
10)Falcultatigr anaerobes, obligated anaerobes
11) reproduction,why dangerous in us?
12) roles in ecosystem, nutrient cycling,N2 fixation
13) gram stating, different colours bc of different material of cell wall
14) Endotoxin/exotoxin
There are 3 main types of virus
what does ti mean?
animals
plants
bacteriophage
it means each type of virus is specific and will attack certain type of cell
virus are non () and made of ()
cellular . genetic material (dna/rna) and protein (codes)
virus survive by () that why they are called parasites
invading other living cells (host) and reproducing through them
Different between VIRUS and cells (living)
VIRUS: (non living)
CONTAIN GENETIC MATERIAL SMALL AMT.
NON cellular
Do not grow
do not respire
do not respond to stimuli (host by chance→no choose)
no movement]
need host to reproduce and survive
no metabolism (use of energy)
Living-like characteristics
:
genetic material (rna/dna)
evolve
reproduce
mutate
proteins
VIRUS come in all size and shape
can have tail, rod shape, cube,heliale
20-400 Nanometre
VIRUS BASIC STRUCTURES (MUST HAVES)*
CORE: dna/rna AKA NUCLEIC ACID →Genetic code for making new virus
Capside(coat): made of protein surrounds core
SOME ALSO HAVE
envelope: layer of stolen cell membrane around coat/capsid
tail
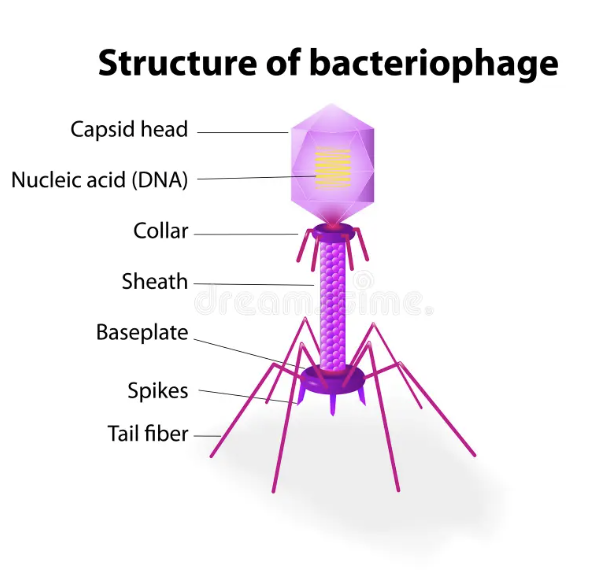
BACTERIOPHAGE (bacteria virus) made of ..
DRAW AND LABEL
core, capside, tail
TAIL: consist of 3 parts
1 . Collar: holds capsid to tail
2. base plate: holds to tail to the fibers
3. tail fibre: catch and attach phage (virus) to bacterial cell wall
tobacco mosaic virus (rna) is the first
virus to be isolated by humans damages crop
one virus cant attack both plant and animals cell bc
use the _and _ to think of cells and virus
virus only built to attack 1 type of cell
lock (cell) and key virus. only the right key can open the right lock
proteins of virus can only recognize and attach to their specialized
many variants of influenza bc it…
mutates ex. corona virus is a strain of influeza
HOW DOES retrovirus differ from other viruses? give example
retrovirus (ex. HIV human immuno-defficiency virus that ONLY kills WBC) can recerse transcribe rna into DNA.
Virus only get around from cell to cell by
WIND, WATER,FOOD , BODY FLUID contact.
therefore technically not moving
Virus reproduce through host cell by
using its cellular machinary (ENZYMES +RIBOSOMES) to create vral dna and rpoteins
viruses undergo 2 types of life cycles
lytic
lysogenic
BOTH LYTIC/LYSOGENIC begins when
when virus recognizes receptor sites on cell membrane and attaches (lock and key)
and has infected the cell through the 2 ways
cell infected by virus through either 1. or 2 . method
trickery (animal cells)
it makes cells think the virus is a part of them
Injection (plant/bacteria cells)
only dna/rna of virus injected into cell
lysogenic cycle ( dorment) enters lytic cycle bc of (4 reasons)
stress (emotional) ex. chickenpox→shingles
temp. change (physical)
Starvation
radiation
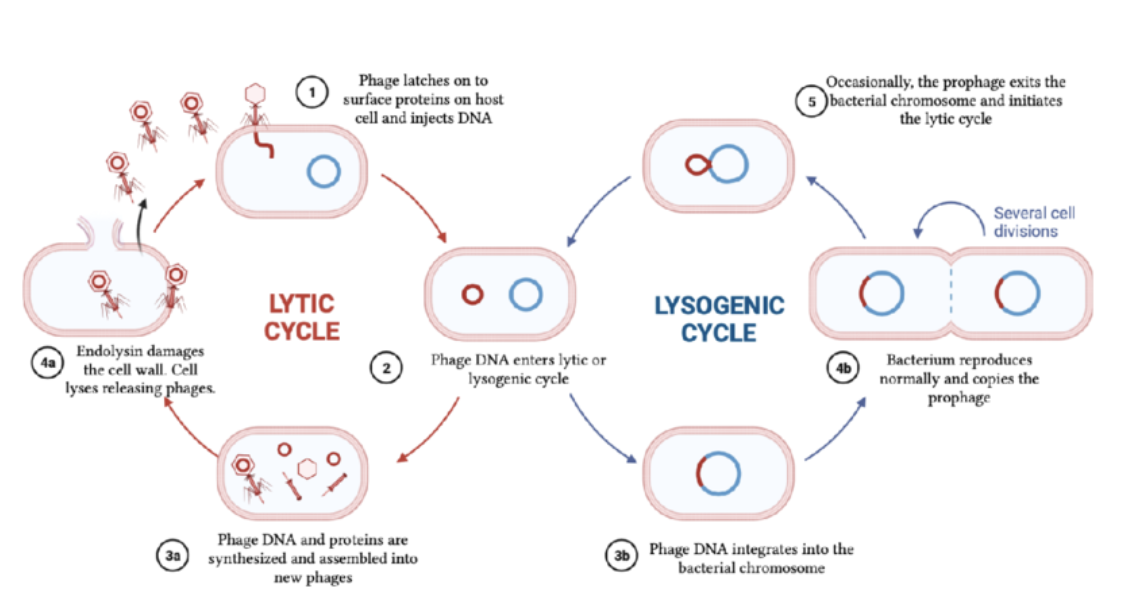
prophage define.
is prophage harmful?
viral dna is inserted into hoste’s genome. they cut the host’s dna and glue their own into a part of it.
harmful when it is active, →shifts to lytic cycle
when prophage active, the viral nucleic acid removes itself from host dna and directs synthesis of new virus infecition.
not harmful when dormant, bc all its doing is its viral nucleic acid is multiplyng as cell do
lysogenic panel by panel of BACTERIOPHAGE
virus finds host by chance and attach to cell
label: bacteriophage, host cell, host dna
Viral nucleuic acid inserted into host cell’s dna (rna or dna)
label: viral nucleic acid (dna/rna)
label: prophage- remainpart of host’s dna until environment triggers it to enter lytic phase.
inbetween:mitosis
viral rna multiplies as host cell multiplies THROUGH MITOSIS. the daughter cells now all have the viral dna from og cell
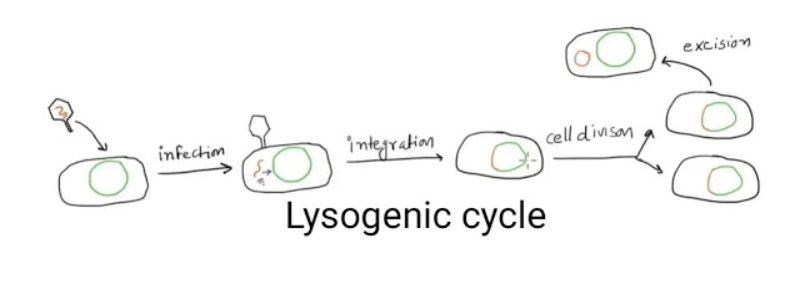
Lytic cycle
finds host by chance. attach itself to cell
injects viral dna into cell
viral dna uses ribosomes +enzymes (cellular machinary) to make thousand copies of parts of viruses
bew viruses assembled , reproduces until
cell lysis (cell bursts) virus released into environment and cell dies as membrane broken
Immunity - Pathogens
an organisms that causes diseases
virus
bacteria
fungi
protist
how are pathogens transmitted
air, food, water,insects, physical/sexual contact
Immune system is our —against—
defense mechanism
disease causign microoganisms
we can be immune 2 ways
active immunity
passive immunity
Active immunity
immunity from body produce antibodies after an invasion of pathogen
memory cells help remember the pathogen and the antibody for it
perminant
Passive immunity
Aqquired immunity from receiving antibodies from elsewhere
natural ex. mom through milk or artificial injection
temporary
vaccination how does it work?
immunisation through deliberate exposure to pathogen for your body to produce memory cells that make antibodies.
due to this→future encounter, body willl respond much faster and effectibely
to prevent illness from vaccine→ pathogen is killed/weakened (inactive) or a similar safe variant is used in vaccine
Lines of defenses
barriers (non specific)
WBC -all phagocytes (non specific)
lymphocytes identifies.. (specfic response)
1st line of defense (non spec and guards against all)
skin,nose,mouth.
skin:barrier
nose: cilia/mucus sweep out pathogens
mouth:ingested into stomache with digestic enzymes and acid kills
alsoo! sweat/saliva/tears /mucus all have enzymes to break down bacterial cell wall
2nd line of defense (non specific)
WBC are first immune system responders
phagocytes (wbc that kill and engulf)
macrophages/neutrophils
if unsucessful. other wbc initiate fever and innflamtion.
increase production of wbc and slows/stops bacterial reproduction
bc theyre heat sensitive!!
3rd line of defense (specific response to identified pathogens)
involves Lymphocytes (b,killer t cells ←wbc)
- they coordinate specific response to diff pathogens
INCLUDING ANTIBODY PRODUCTIONSS
phagocytes vs lymphocytes
phagocytes
most common
eat and kill anypathogens
nonspecific +2nd line defense
always working
Lymphocytes
B CELLS
become memory cells
remember virus encountered before
make antibodies
T cell (killer T cells)
kill infected cells
activate b cells
Prion diseases. theyre spread usually from
proteins capable of replication and cause infections. spread ususally from eating contaminated meat.
prions are produced by
mutations in gene coding in normal cell protein PrP
proteins depend on their shape. different mutations cause diff diseases of prions
Prions infect through
bumping into a healthy protein, binding to it bc of their irregular shape ad convert the regular to irregular shape.
ex. VAMPIRES
prions are special/different than other diseases bc
they only are protein, no genetic material
what are 3 medical procedures that spread prion disease
organ transplant, growth hormon injections,sugury (surgical instruments)
Bacteria INGDOM
(kingdom monera*→ EUBACTERIA + ARCHAEABACTERIA KINGDOM)
they are separated into separate kingdom bc of their differences in cell wall structure and biochemistry
BACTERIA characteristics
ALL PROKARYOTES ARE BACTERIA AND ALL BACTERIA ARE PROKARYOTES
no membrane bound organelles
no golgi, er, mitchondria,
UNICELLULAR
hetero/autotrophs
asexual repro. (limited sexual reproduction)
covered with PEPTIDOGLYCAN (CELL WALL MATERIAL)
general prokaryote structure
bacteria way smaller than eukaryotic cells bc not many organelles.
have many shapes
(bacillus) rod, coccus (circle) curved (spirillum)
interior structure of bacteria/prokaryotes
peptido glycan (cell wall)
capsule
CHROMOSOMES DNA (free floating)
flagellum for movement (not all have)
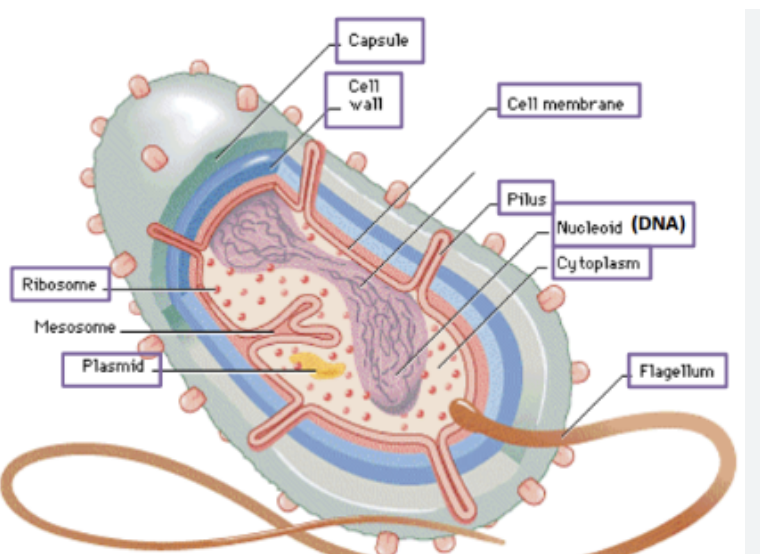
**3 differences between prokayotes and eukaryotes
Prokaryotes
Free floating Dna
Cell wall:peptidoglycan
Nomembrane bound organelles
Eukaryotes
Dna in nucleus
Cell wall plants: Celllulose- Fungi:Chitin
Membrane bound organelles
golgi, er, mitochondria
what did biologists use to distinguish 2 kingdom of bacteria?
their environments.
Eubacteria kingdom- everywhere
Archaeabacteria
only found in extreme habitats
their dna sequence closer to eukaryotes than bacteria
What characteristics of prokayrotes allow them to adapt to so many diff types of environemnts.
reproduce quickly
results: many generations in 30 min
therefore: mutates more
Evolutionarily old
more time to adapt
Ability to change. methods of energy capture or release
Bacteria (mainly kingdom archaea) undeergo cellular respiration/fermentation
distinguish between 1) obligate aerobes 2) obligate anaerobes 3) facultative anaerobes whicha re their METABOLISM
require oxygen
require no oxygen
survive underboth environment
oblogate aerobes (metabolism)
release/capture energy through cellular respiration live in oxygenrich environment
02 is more efficient in producing energy
obligate anaerobes(metabolism)
use fermentation method of release/capture energy
live in oxygen lackin environments
Facultative anaerobes(metabolism)
use cellular respiration or fermentation
oxygen rich or non environment
roles of bacterias in ecosystems
nitrogen fixer
Convert N2 in atmosphere to useful forms for organisms into in froms ofsoil
no3 and nh4
decomposers (nutrient flow)
break down and recycle dead’s matter back into ecosystem
return nutrients back into soil and help plants grow in better condition
producers
through photosynthesis, make chemical energy and , they are food source for many
Nutritional strategies of bacterias: autotrophs
autotrophs: make their own food 2 types
photoautotrophs use photosynthesis to creat energy molecules in form of sugar
Chemoautotrophs BACTERIA
use chemical energy to make glucose
*in equation: produce methane adter the glucose forming process
Nutritional strategies of bacterias: Heterotrophs
obtain nutrients from other organism
saprotrophic (dead eaters)
decomposers that use enzymes to break down matter
Parasitic (relies on host to break down food into simple usable molecules
growth and reproduction 3 ways of bacteria
binary fission
produces identical cells
Conjugation
limited sexual reproductionw here protein conects cellls together and bacteria exchance small set of genetic info, changing dna and creating new organism
Spore formation
when condition gets hardh, abcteria create endospore within tissues
endospore formation: make internal wall around dna w cutosplasm
***BACTERIA can also changed by transformation and transduction
transformation w dna fragments
shocks cell to take in dna and intergrate it or fails to intrgrate it(breaks down dna) and it fails
Transduction
process by which a virus transfers genetic material from one bacterium to another
horizontal gene transfer
humans are vertical gene transfers
Eubacteria hae 2 diff types of cell wall there for BIOLOGIStS USE _ to tell them apart
gram test
gram positive →purple blue
thick layer of petidoglycan that absorbs the colour on top of the cell memrbane
gram negative→ harder to treat→ pink
thin layer of peptidoglycan and has EXTRA outside layer of lipids/fat (header for peptido to absorb colour)
- overall thicker cell wall
BACTERIA IN OUR BODIES
common bacteria e.coli in humans are helpfl
we provide them nutrients and transportation
they provide digestion support, food, vistamin k
bacterias ingut make enzyme to digest callulose
pathology and pathogens
study of pathogens and organisms that produce disease in humans
2 types of bacteria toxins
endotoxins
exotoxins
exotoxins
toxins secreted by bacteria
HIGHLY TOXIC →neurotoxins
tetnus
endotoxins
toxins on inside of bacteria
released when cell lysis
weak toxic→diarrhea vomitting
*in cell wall of gram neg bacteria
Antibiotics defn
chemicals that kill/reduce growth of bateria
types of antibiotics
penicillin/amoxicillin
kills bacteria by slowing the production of cell wall
Tetracycline
Slows down protein syntheiss
Slfa drugs
Slows down bacteria cell metabolism
**preventing bacterial infection is easier than treating infection. to control bacterial growrth there are 4 ways
physical removal
soap +water
Heat steriliztion
bacterias are heat sensitive
Food processing
cooking
Disinfectants
alcohol wipes
superbugs- antibiotic resistant bacterias. why gets worse
overuse of antibiotics creates a seelctive pressure for bacterias to evolve
u also shouldnt overtake bc antiobiotics also affect your good bacterias ex. gut
gram negative are more resistant to antibiotics because of…
their extra lipid layer
overall thicker cell wall
when docters swab ur throat … if it is a
virus- they send u home
if bacteria→ they find the right antibiotics based on tpes of bacteria
4 things to. prevent bacterial infection daily by
washing hands
cooking food
disinfecting objects
refrigerate food to reduce bacterial growth
what do u expec to find in your vacinne?
you find killed/weekended bacteria