The characteristics of Plants 12.1
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
1
New cards
Equation for Photosynthesis
carbon dioxide+ water →(solar energy) glucose + oxygen
2
New cards
What are two ways that plants protect themselves from herbivores?
Many plants can produce toxic or bad tasting substance or they can produce a tough,hair or prickly outer layer to keep herbivores away.
3
New cards
How do plants use carbohydrates?
In plants carbohydrate produced by photosynthesis are well known for their essential role as vital sources of energy.
4
New cards
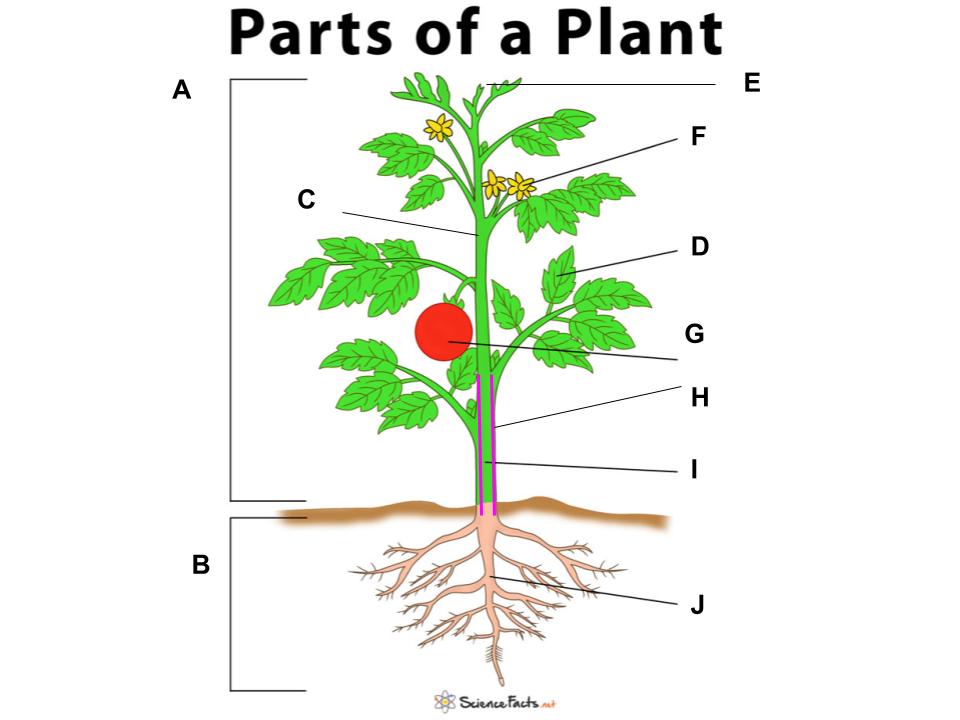
(a)root system (b) shoot system (c) dermal tissue (d) leaf: helps in photosynthesis (e) apical meristem: produces the root cap. (f)flower: helps in reproduction (g)fruit: protects the seed (h)vascular tissues: transports water, minerals, and sugars to different parts of the plant. (i)stem: helps support the plant. (j)root: absorbs water and minerals.
5
New cards
Dermal tissue
protects against injury, herbivores, diseases and water loss
6
New cards
ground tissues
stores carbohydrates and support and protects plant body
7
New cards
Where is the meristematic tissue located in a plant? Why do you think it’s located there
It can be found near the tips of roots and stems. The cells present in these tissues constantly divide to produce new cells. They are there to help make the plant grow. This leads to an increase in height and girth of plants.
8
New cards
What are three types of ground tissues in vascular plants? What role does each play to aid in plant survival?
__**parenchyma**__-thin celled walls living at maturity, They play a key role in photosynthesis and are also involved in the storage of water, nutrients, and food. Parenchyma tissue can also help with wound healing and regeneration.
__**collenchyma**__-thick cells wells, living at maturity, Collenchyma tissue can also help with the transport of water and nutrients.
__**sclerenchyma**__-cells with lignin in their cell walls, dead at maturity, They provide mechanical support to the plant and can also help with the transport of water and nutrients
__**collenchyma**__-thick cells wells, living at maturity, Collenchyma tissue can also help with the transport of water and nutrients.
__**sclerenchyma**__-cells with lignin in their cell walls, dead at maturity, They provide mechanical support to the plant and can also help with the transport of water and nutrients
9
New cards
True or false? Only gymnosperms and angiosperms have seeds and pollen
True
10
New cards
Why did scientists recently reclassify dicots into multiple groups?
Because recent DNA studies proved that placing all dicot species into one group does not reflect the evolutionary relationships among these species.
11
New cards
What is the major difference between seeds of monocot and seeds of the angiosperms.
Monocots have one cotyledon and endosperm whereas dicots have two cotyledons but no endosperm.
12
New cards
Plants are unique in part because they are immobile. What other aspects of plants makes them unique?
Each plants species has specific adaptation for a particular range of environmental conditions. For example most plants absorb nutrients from water in soil, pitcher plants obtain nutrients by digesting other organisms.
13
New cards
Why do plants need to exchange gases with the environment?
In order to carry out photosynthesis.
14
New cards
Which two tissues make up plant vascular tissues? What roles do these tissues play in the life of a plant?
Xylem and phloem. Xylem carries water and dissolved substances up from the roots. Phloem is a tissue that transports sugars and other dissolved substances throughout the plant and down to the roots.
15
New cards
Which type of plant tissues would you expect to be most commonly used as a food source. Why?
The phloem tissue would be used more commonly as a food source as it carries important sugars, organic compounds and minerals around a plant.
16
New cards
Which types of tissue play a protective role in the plant?
The epidermis is a single layer of cells that covers plants' leaves, flowers, roots and stems.
17
New cards
How might the fact that plants don’t move influence their ability to adapt to climate change and other environnemental tissues
Plants cannot move like animals, which means they have to deal with the environmental conditions they are in. This can make it difficult for them to adapt to changes in climate and other environmental stresses. However, plants have evolved different ways to deal with these challenges, such as tolerating extreme temperatures, drought, or salt in the soil. They can also change their growth and development in response to changes in their environment. Even though plants cannot move, they have the ability to adapt and survive in different environments.