Excitation Contraction Coupling and Force Regulation
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
what is skeletal muscle innervated by?
motoneurons of somatic nervous system
what is excitation-contraction coupling?
Process by which muscle AP causes rise of intracellular Ca2+ and actin-myosin interaction.
When muscle action potentials (excitation) triggers a contraction (force generation and or muscle shortening)
describe the structure of myofibrils
organised bundles of thick and thin filaments which generate contraction
why are Ca2+ needed in muscle contraction?
to allow interaction between actin and myosin
what do triads compose of?
a segment of T-tubule between 2 sacs of SR
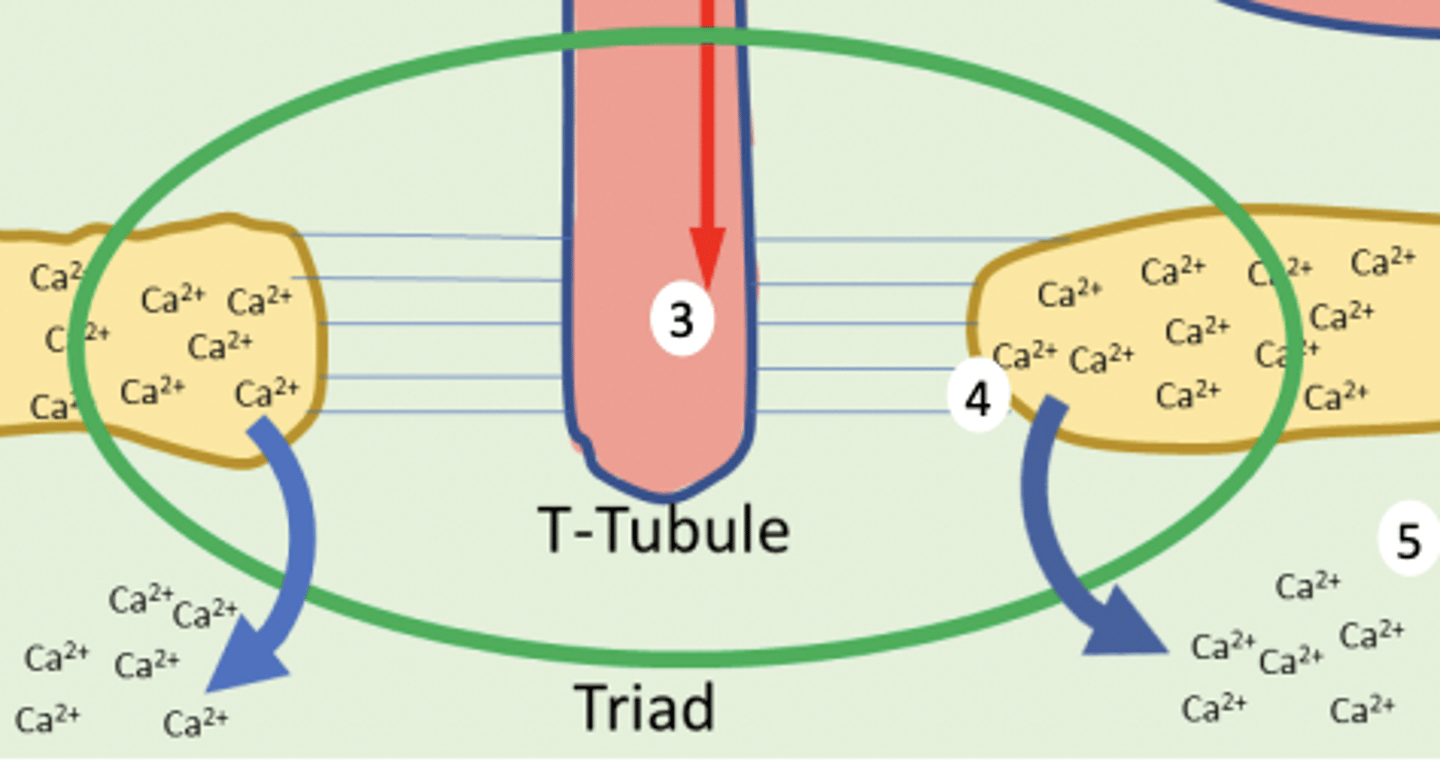
what is the role of triads?
Site of physical and functional contact between T-tubule and SR membranes
what is the sarcolemma?
muscle cell membrane
propagates the AP to end of muscle fibres
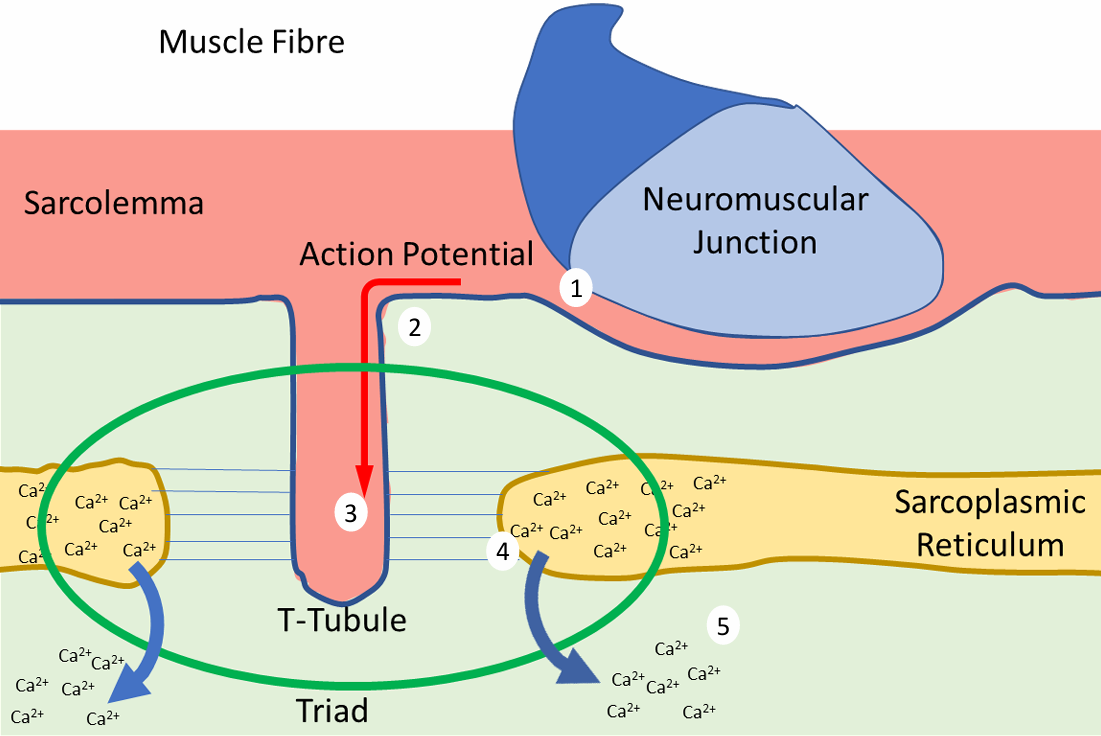
Excitation Contraction Coupling (Skeletal Muscle)
AP runs along sarcolemma from NMJ
AP travels into centre of muscle fibre down T-Tubule
AP reaches Triad where voltage gated sensors (T-Tubules) react with Ca2+ - release channels (SR)
Ca2+ release channels open
Ca2+ leaves SR down concentration gradient
Ca2+ binds to thin filament, cross bridge cycling can begin
Upon relaxation Ca2+ pumped back into SR
how does Ca2+ go from SR to thin filamment?
diffusion
what happens to Ca2+ upon relaxation?
pumped back into SR
DHP receptor changes shape in response to ....?
AP
what is DHP receptor?
a voltage sensor which changes shape in response to an AP, thereafter causing a change of shape in RyR (Ryanodine receptors)
what causes a change of shape in RyR?
physical contact between DHP and RyR molecules
what allows Ca2+ to exit SR and interact to myofilaments?
DHP receptor changes shape leads to RyR changing shape
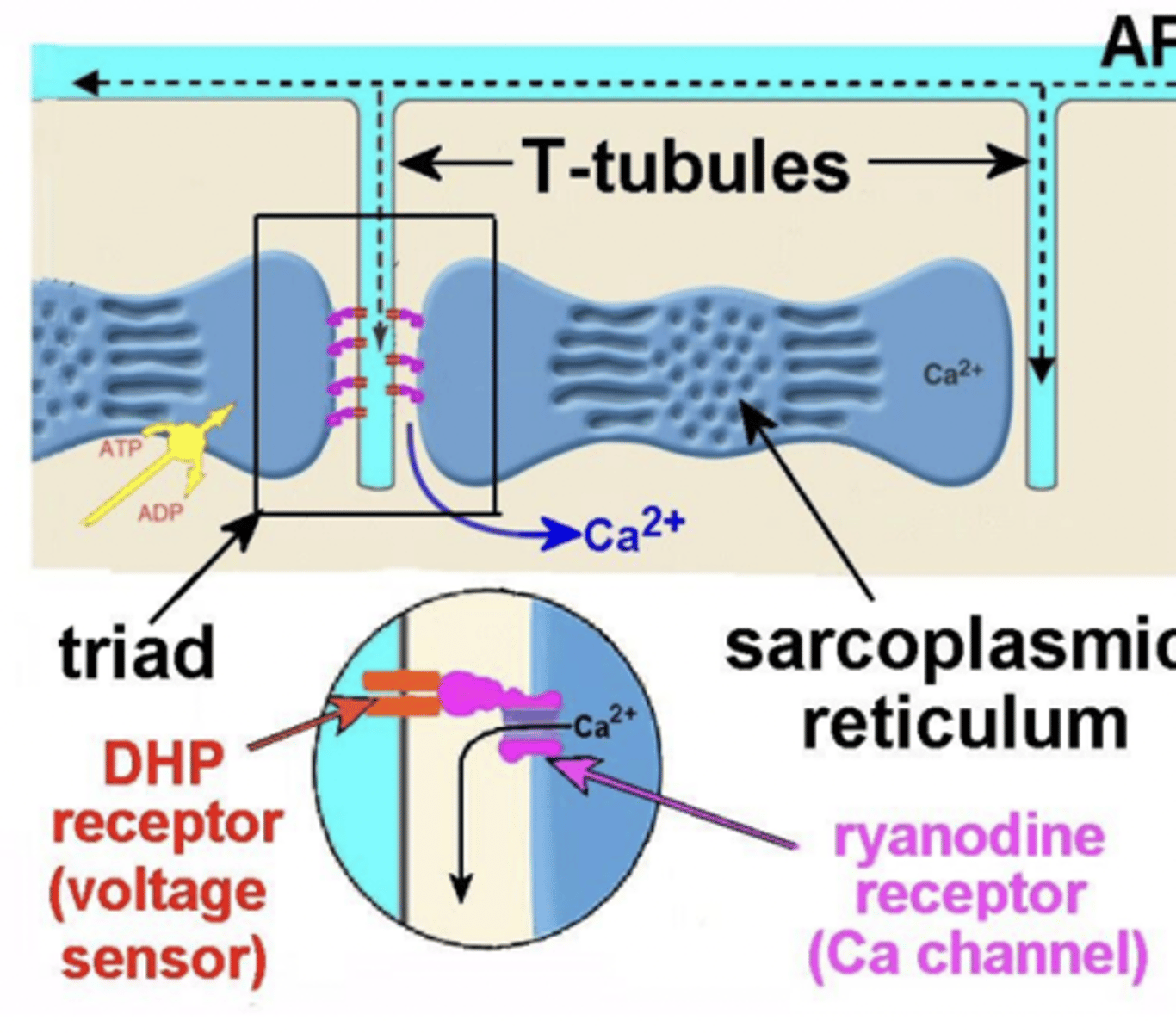
what is steric blocking?
mechanism is what enables Ca2+ to operate the on-off switch
what is the role of t-tubules in muscle contraction?
propagates APs deep into fibre
what are the 3 membrane systems?
sarcolemma, t-tubules, SR

what is a twitch?
a contraction that occurs in response to a single stimulus (AP)
what does the speed of a twitch depend on?
the type of fibre
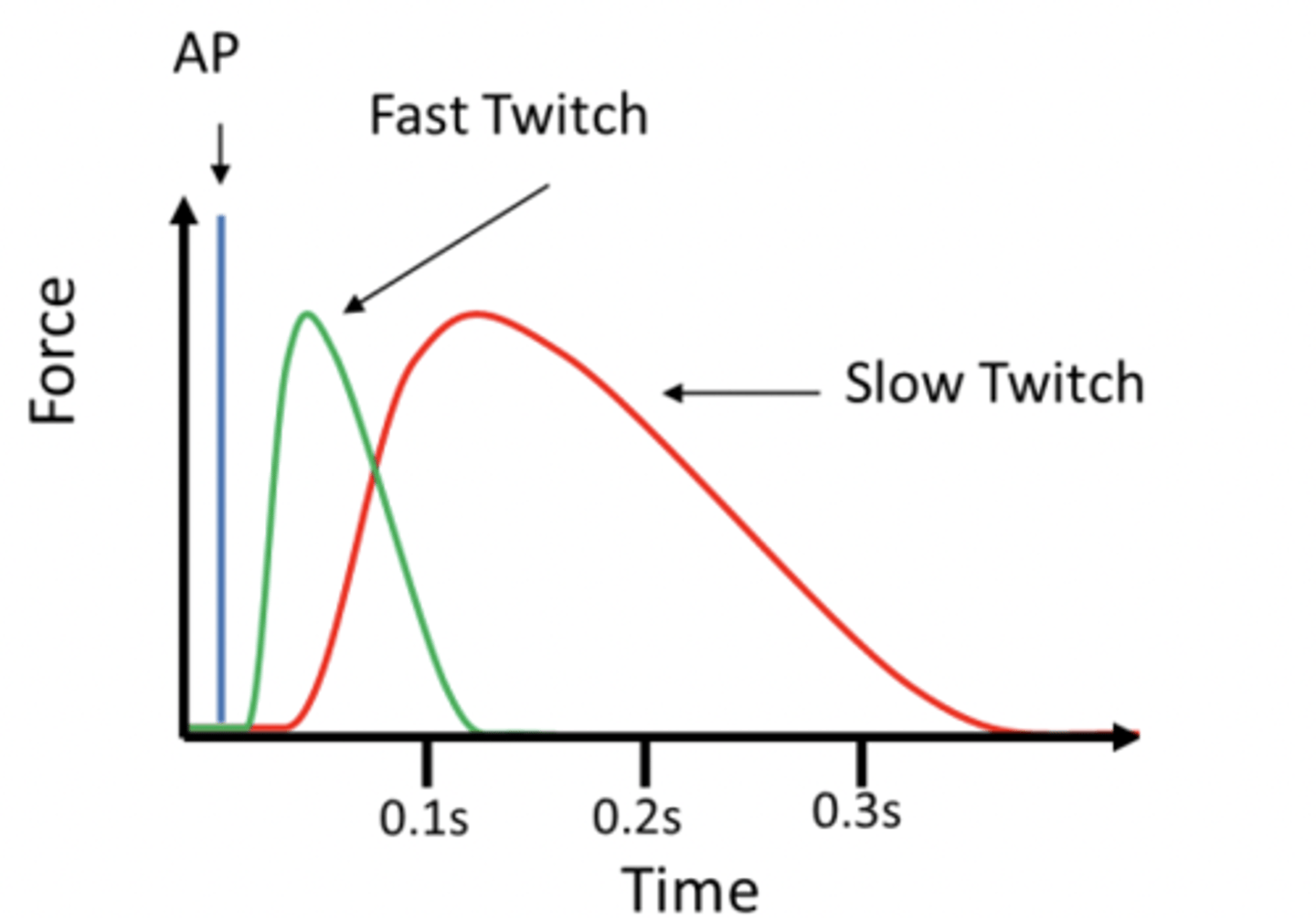
Why do fast fibres shorten quicker?
because their myosin has a faster ATPase and therefore they can form more cross bridges per second
what is the genetic cause of MH (Malignant hyperthermia/hyperpyrexia)
defective RyR or DHPR gene
what is the problem with having a defective RyR or DHPR gene?
excessive Ca release when patients are exposed to gases like halothane
what are effects of generaliased muscle contractions?
large rises of body temp
lactate release
acidosis
release of K from muscle raising blood potassium
slow (red) twitch fibres are what type?
I
fast (white) twitch fibres are what type?
II (a & x)
comment on the Fatigue Resistance of type 1 muscle fibres
high resistance
comment on the Fatigue Resistance of type 2 muscle fibres
moderate - low resistance
which type of twitch muscle holds a higher no of mitochondria?
type 1
which type of twitch muscle has a higher capillary density?
type 1
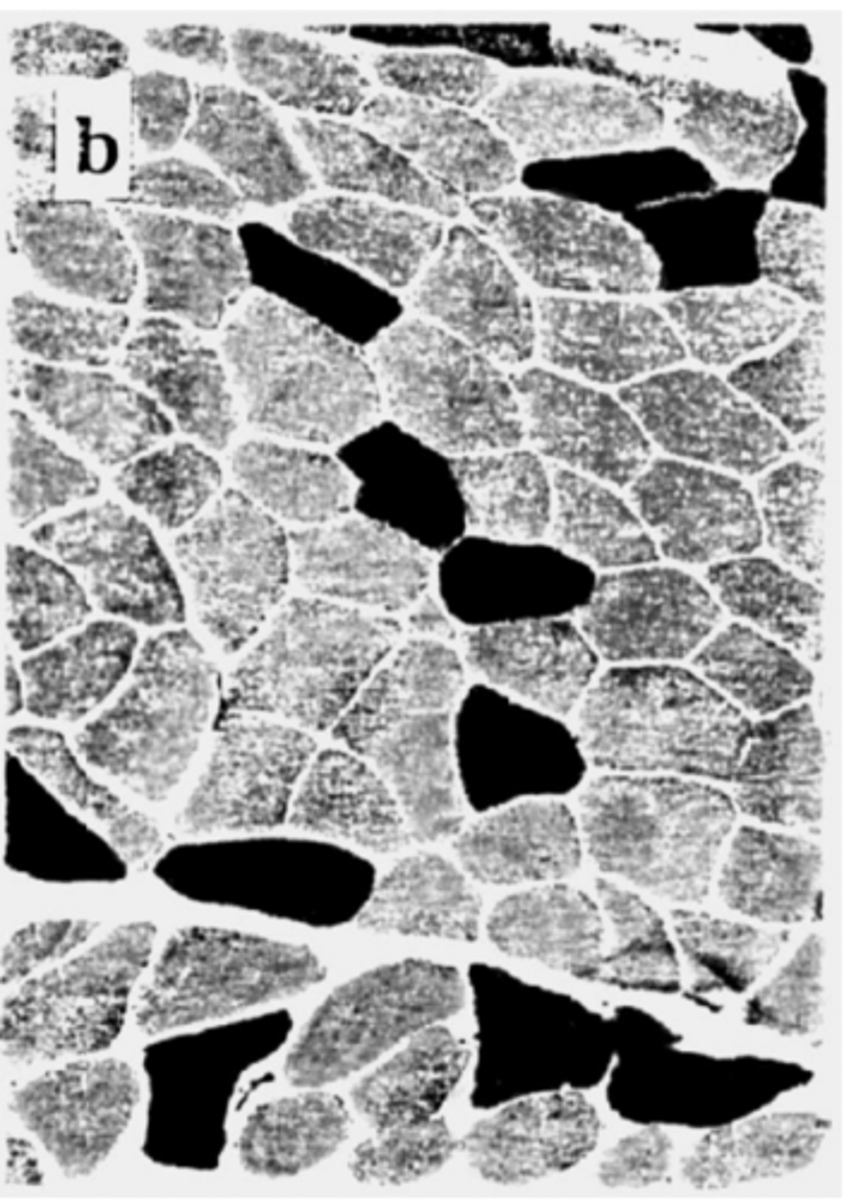
a high jumper would mainly have what type of fibre?
type 1 (fast/red)
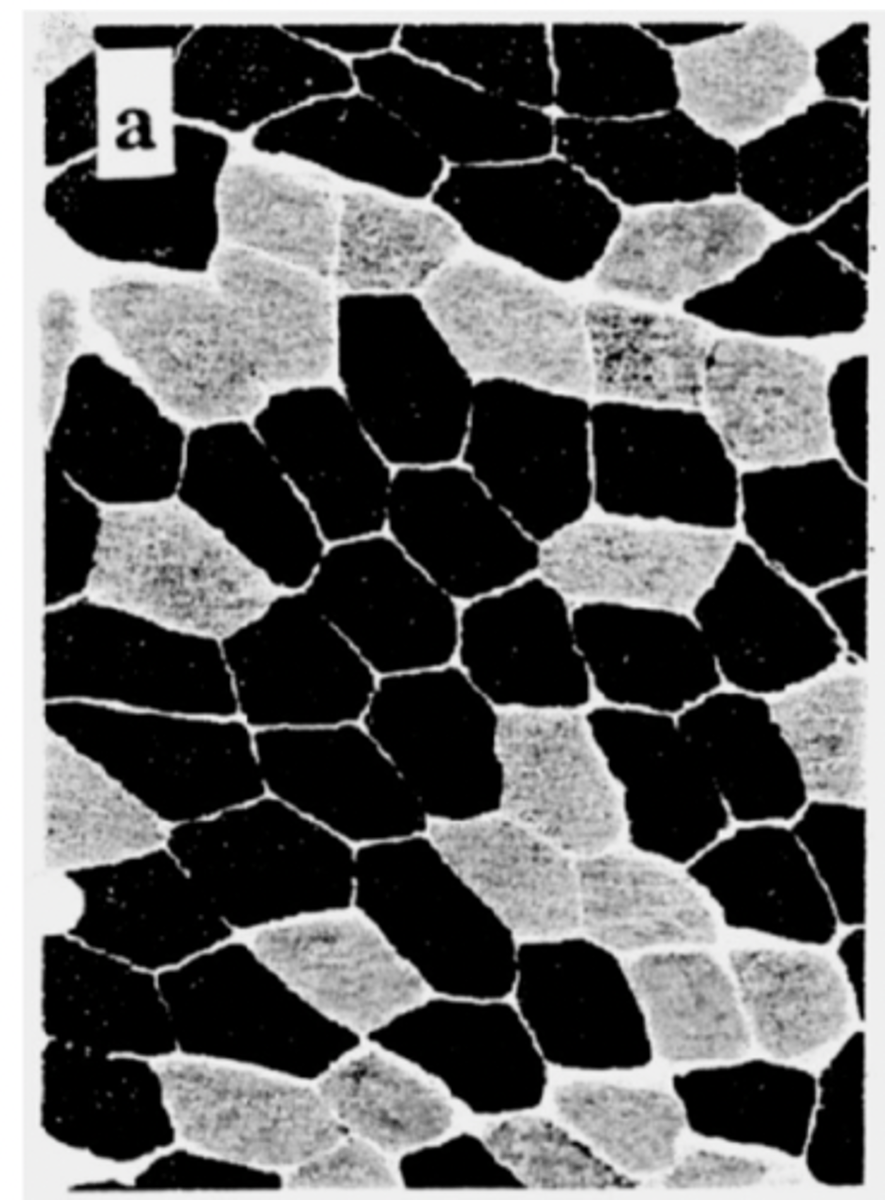
a marathon runner would mainly have what type of fibre?
type 2 (slow/white)
what is Tetanus?
The mechanical response (ACTION) to multiple stimuli/APT
when does summation occur in muscle contraction?
when twitches occur in quick succession and overlap
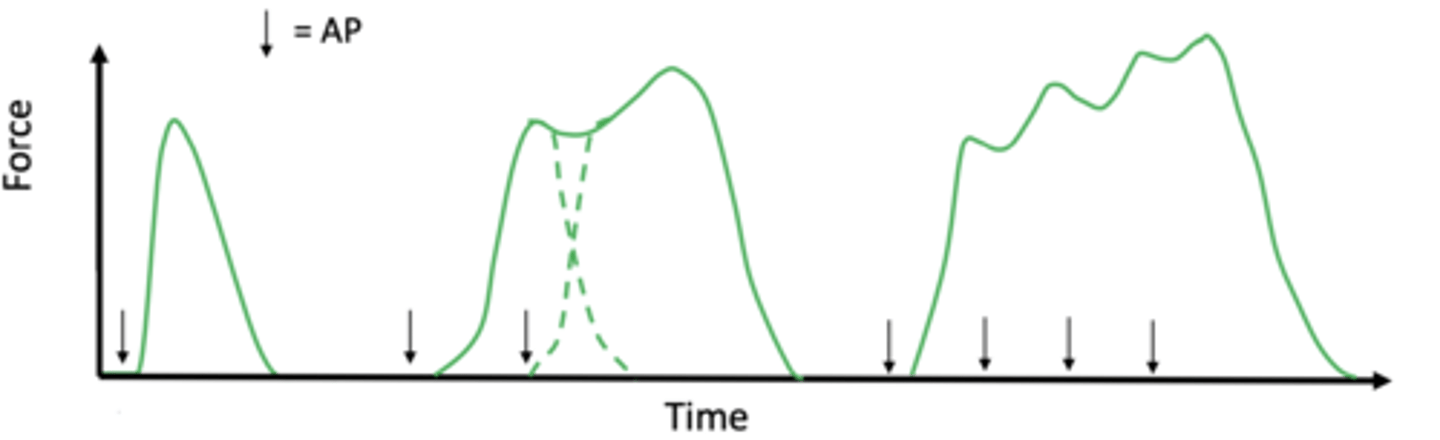
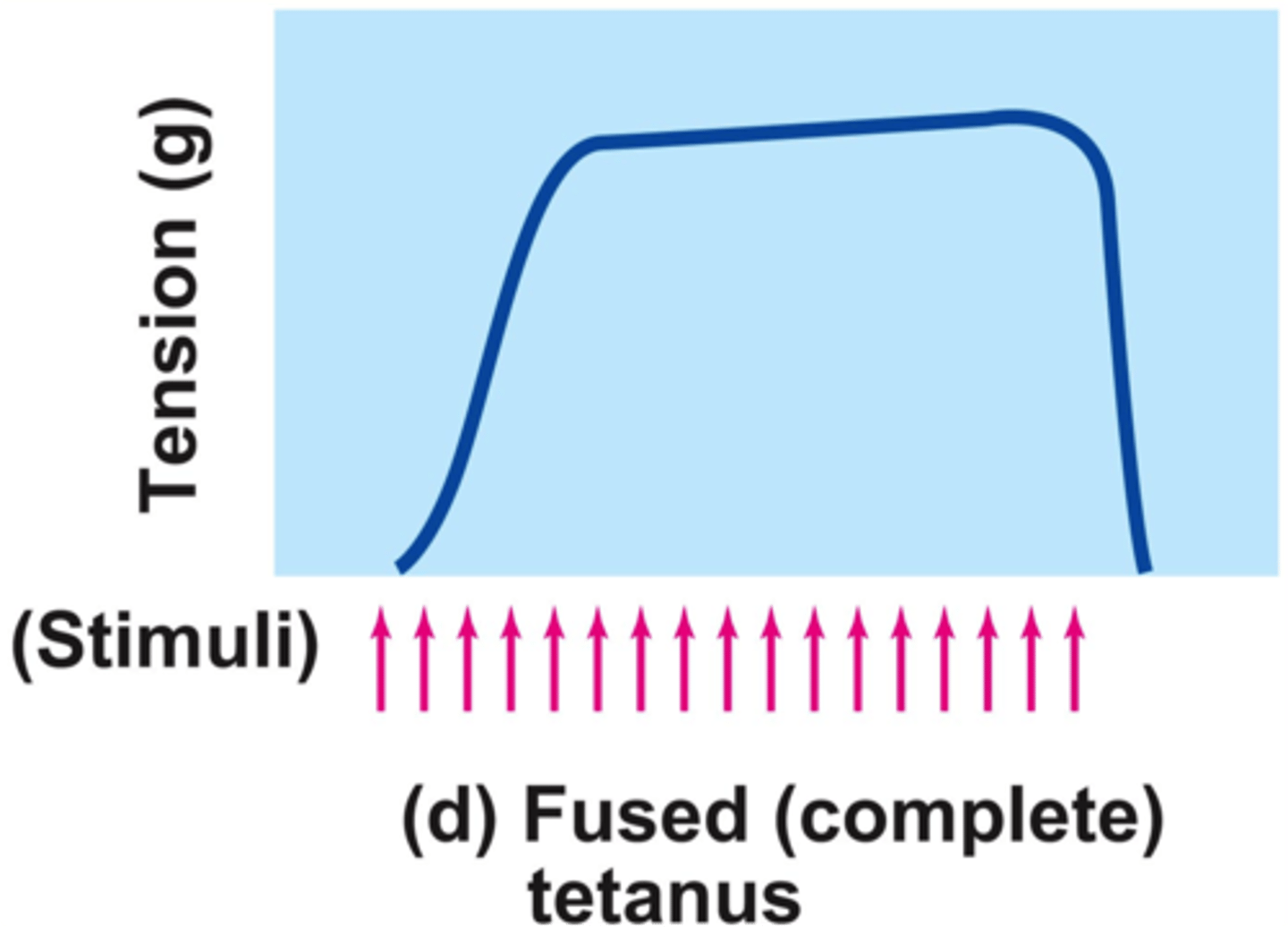
what is fused tetanus?
Rapid stimulation resulting in no muscle relaxation
how many times higher is the forced produced by fused tetanus compared to a twitch?
3-5x
what is rate recruitment?
method to regulate muscle force- the rate at which AP fires
more Ca2+ = ?
more contraction + more force
A single AP will cause a twitch contraction to last how long?
100- 300ms
what does a high frequency stimulation result in?
complete fusion of contractile response – a fused tetanus (Increased fire rate)
each single muscle fibre is innervated by ...?
1 motoneuron
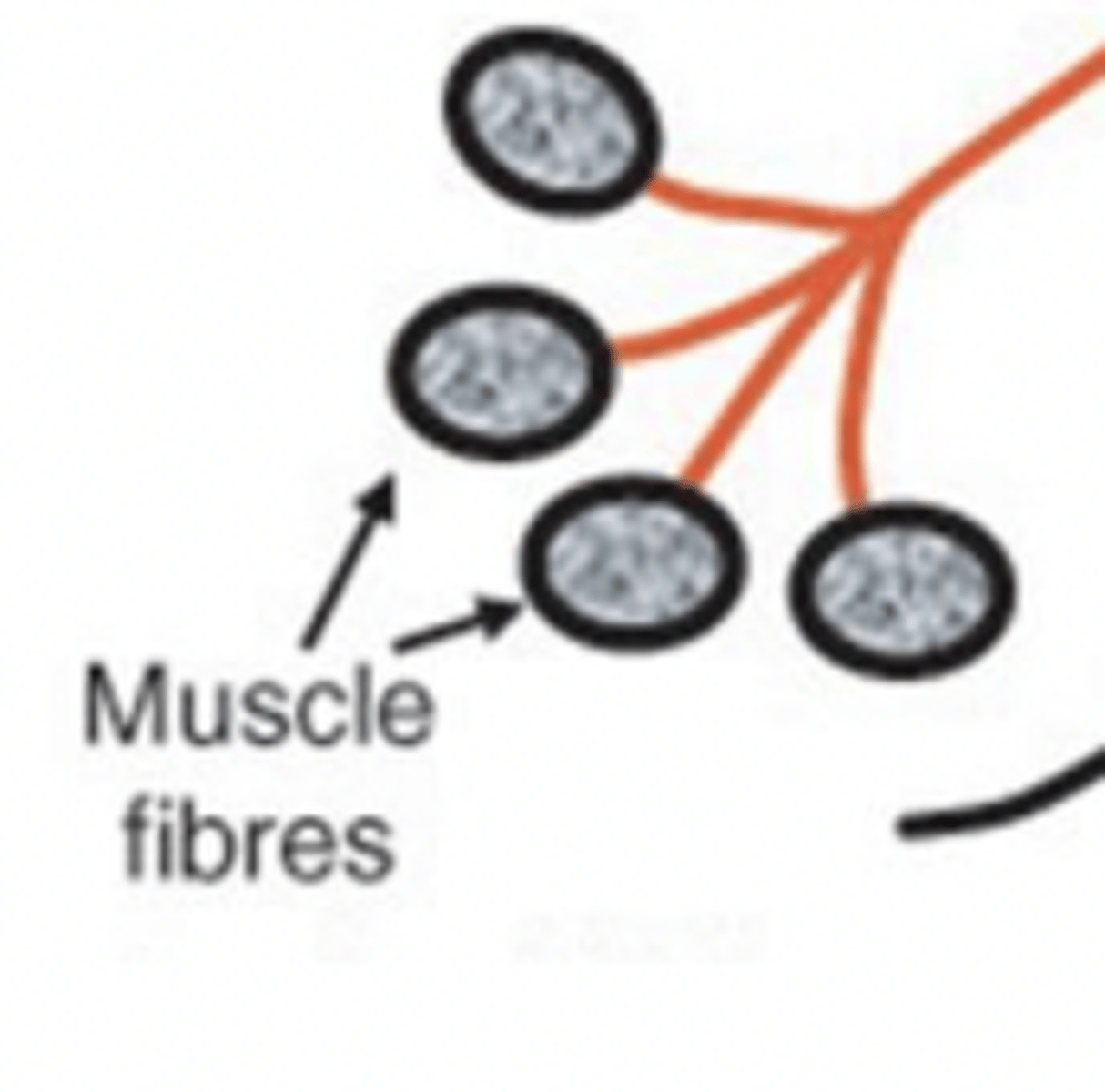
what is the MU?
motor unit
what does the motor unit consist of?
motoneuron, axon and all the muscle fibres it innervates
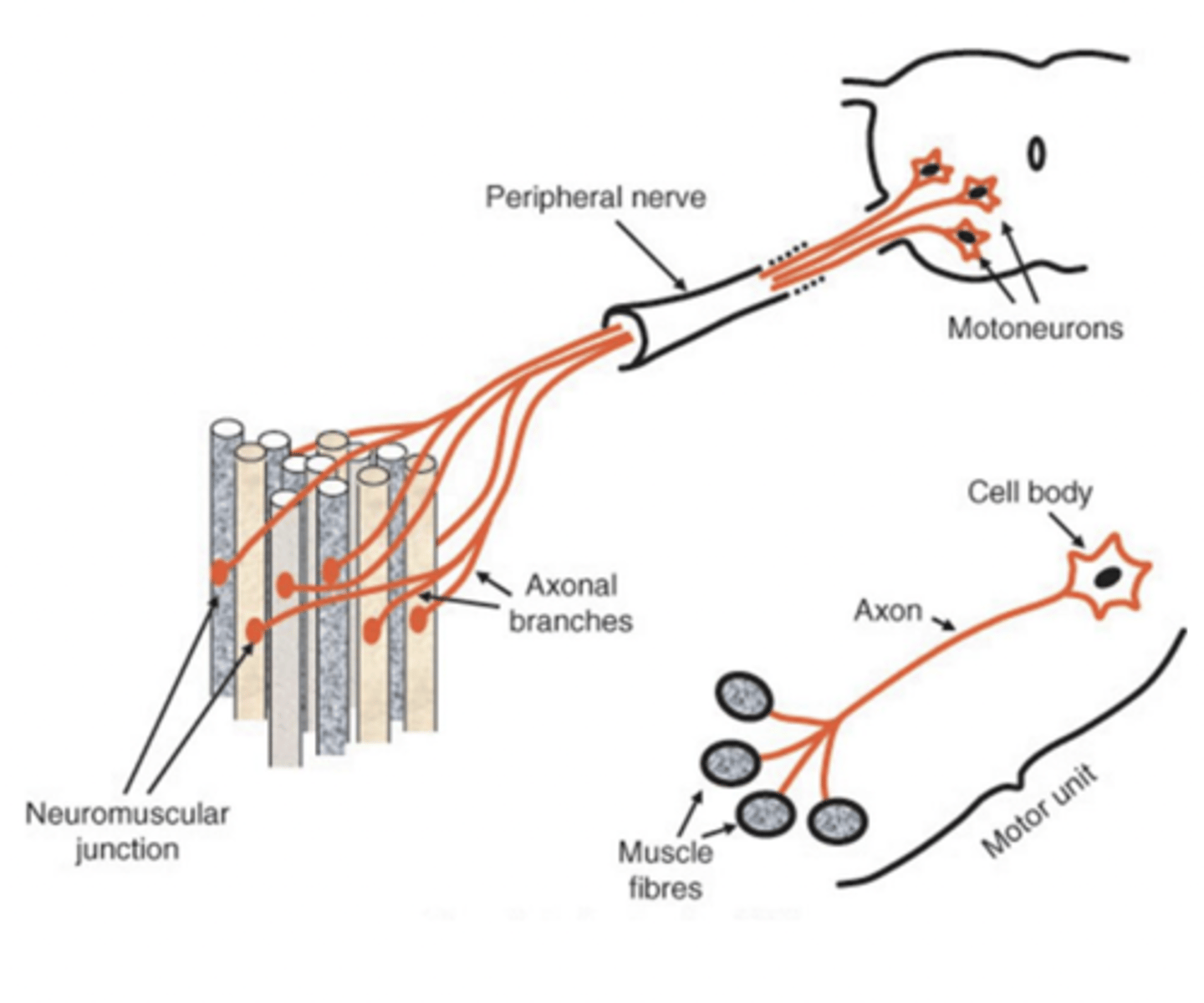
what 2 factors determine the size of a MU?
number of muscle fibres and their diameter
the force output of a muscle is _____ _____ to its fibre cross-sectional area
directly proportional (larger diameter=more force)
What is motor unit recruitment?
increasing the number of active motor units
what is muscle hypertrophy?
increase in muscle size

what MUs are recuited first?
smallest MUs e.g.
what type of twitch fibre is low force fatigue resistant?
slow twitch type 1, low force fatigue resistant fibres (slow twitch type I)
What are the 3 forms of Troponin?
TN-I ~ Troponin I (TN-I) is a protein that binds to the Actin
TN-C ~ Troponin C (TN-C) is a protein that binds calcium ions, which leads to a conformational change that allows muscle contraction
TN-T ~ Troponin T (TN-T) is a protein that binds to tropomyosin, anchoring the troponin complex to the thin filament in muscle fibers
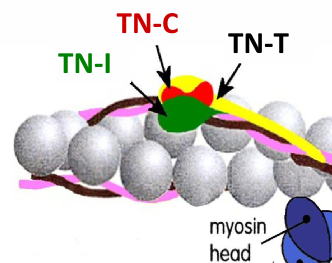
On-Off switch and Ca2+
Actin is surrounded by “regulatory” proteins
Ca2+ binds to troponin which causes a change in shape
Tropomyosin is moved out of the way and myosin binding site is revealed
Myosin binds to actin and molecules pull
“steric blocking” mechanism is what enables Ca2+ to operate the on-off switch
What is the difference between Fused and Unfused Tetanus?
Speed of summation!
Fused (25 stimuli per second)
Unfused Tetanus (10 stimuli per second)