Radiology- Bisecting Technique Chapter 20
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Bisecting technique
another method that can be used to expose periapical images, faster technique
Bisector
a ray that divides an angle into two congruent angles
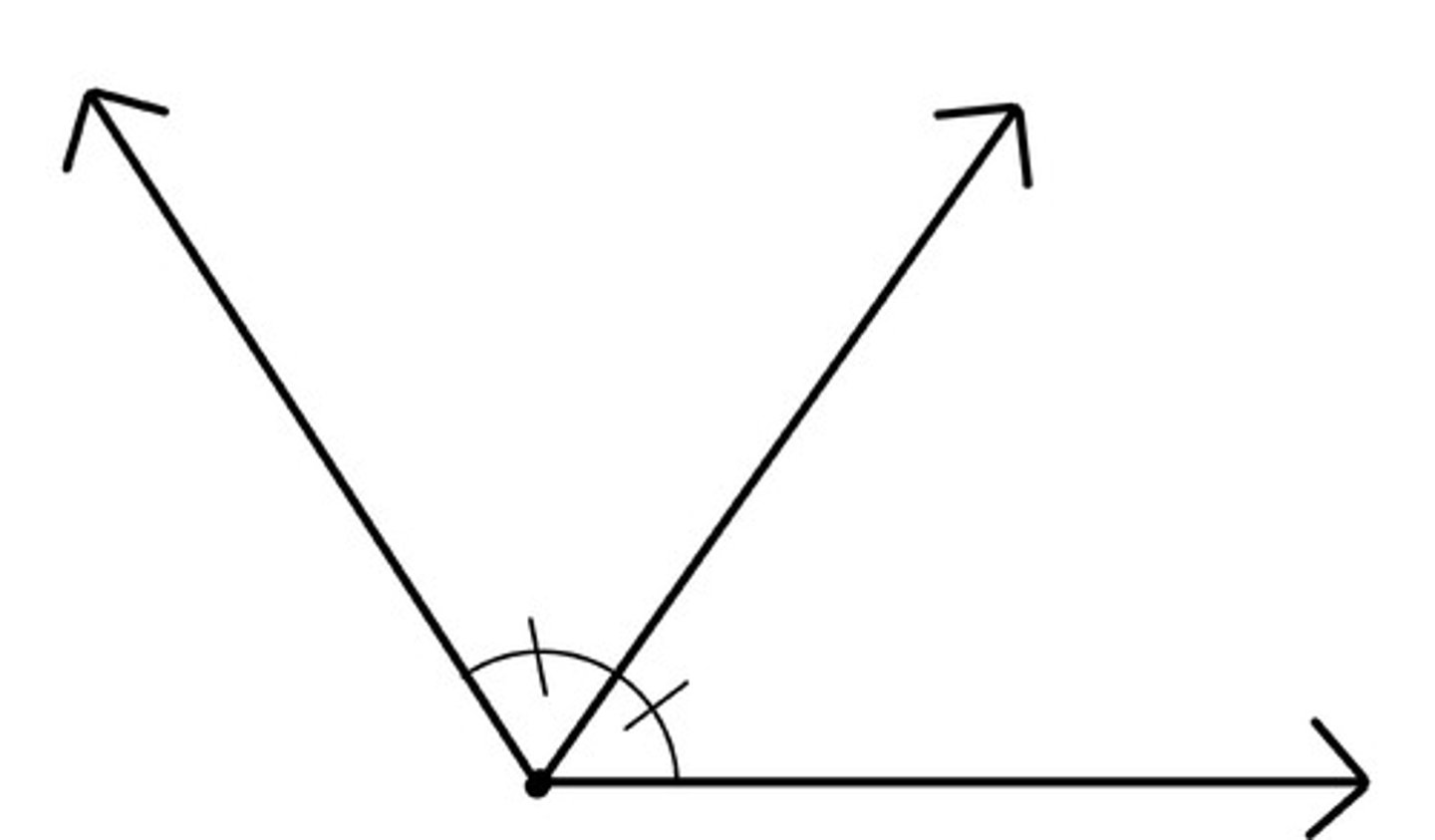
Angle
A figure formed by two rays with a common endpoint
Triangle
a three-sided polygon
equilateral triangle
3 congruent sides
right angle
an angle that measures 90 degrees
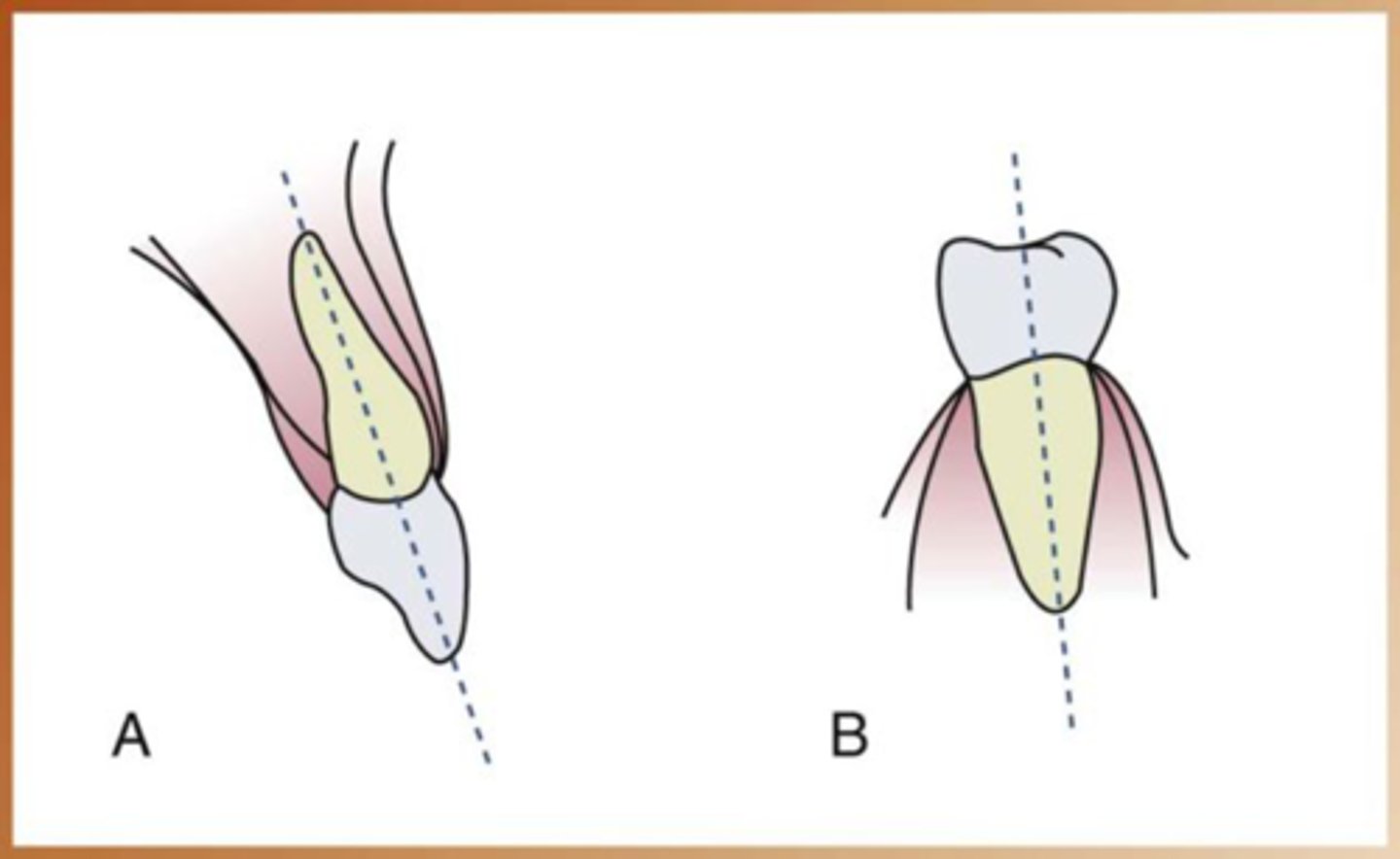
Long axis of the tooth
an imaginary line that divides the tooth longitudinally into two equal halves
Central Ray
The central portion of the primary beam of radiation.
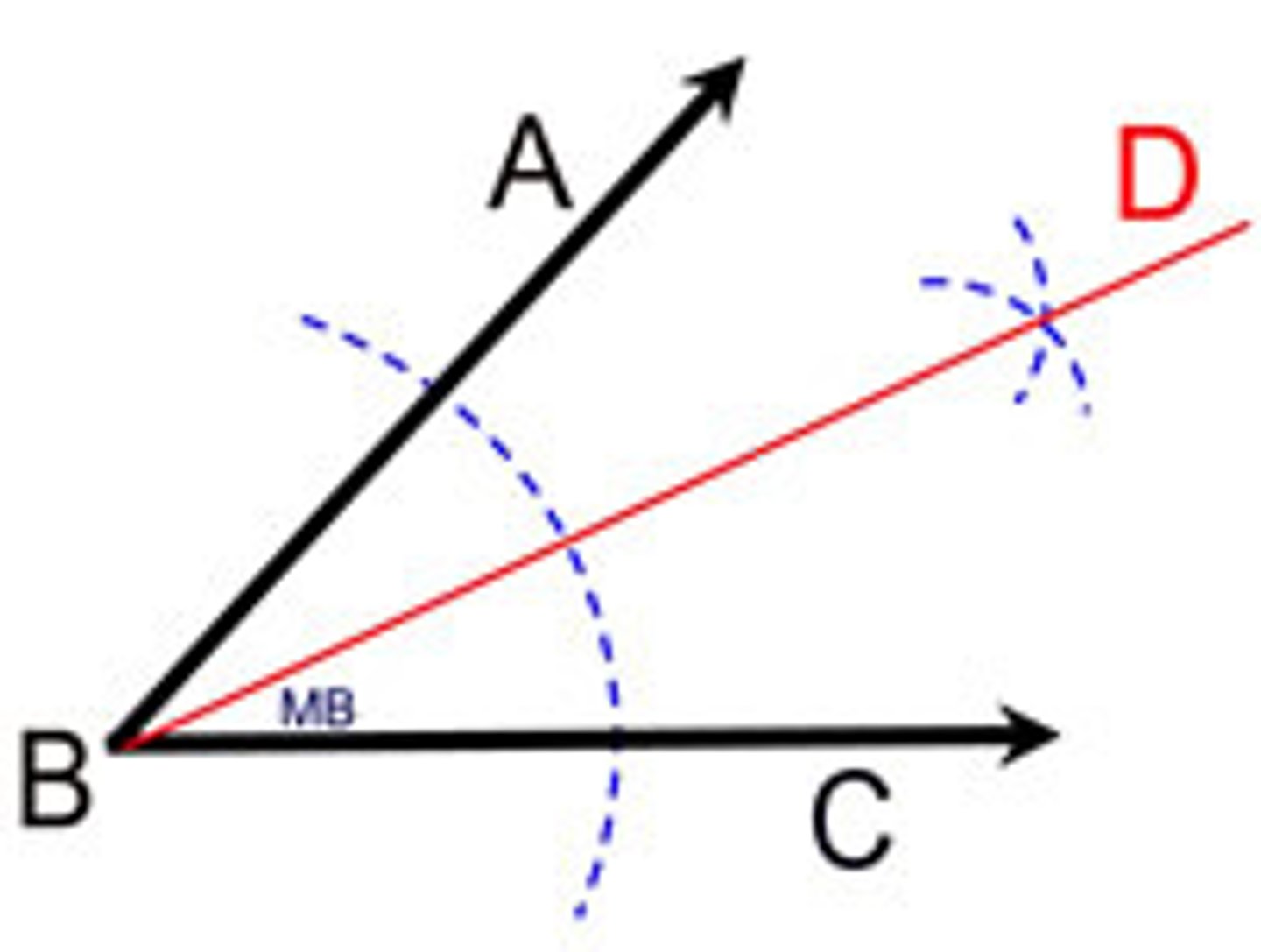
rule of isometry
two triangles are equal if they have two equal angles and share a common side
-in dental imaging this geometric principle is applied to bisecting material to form two imaginary equal triangles
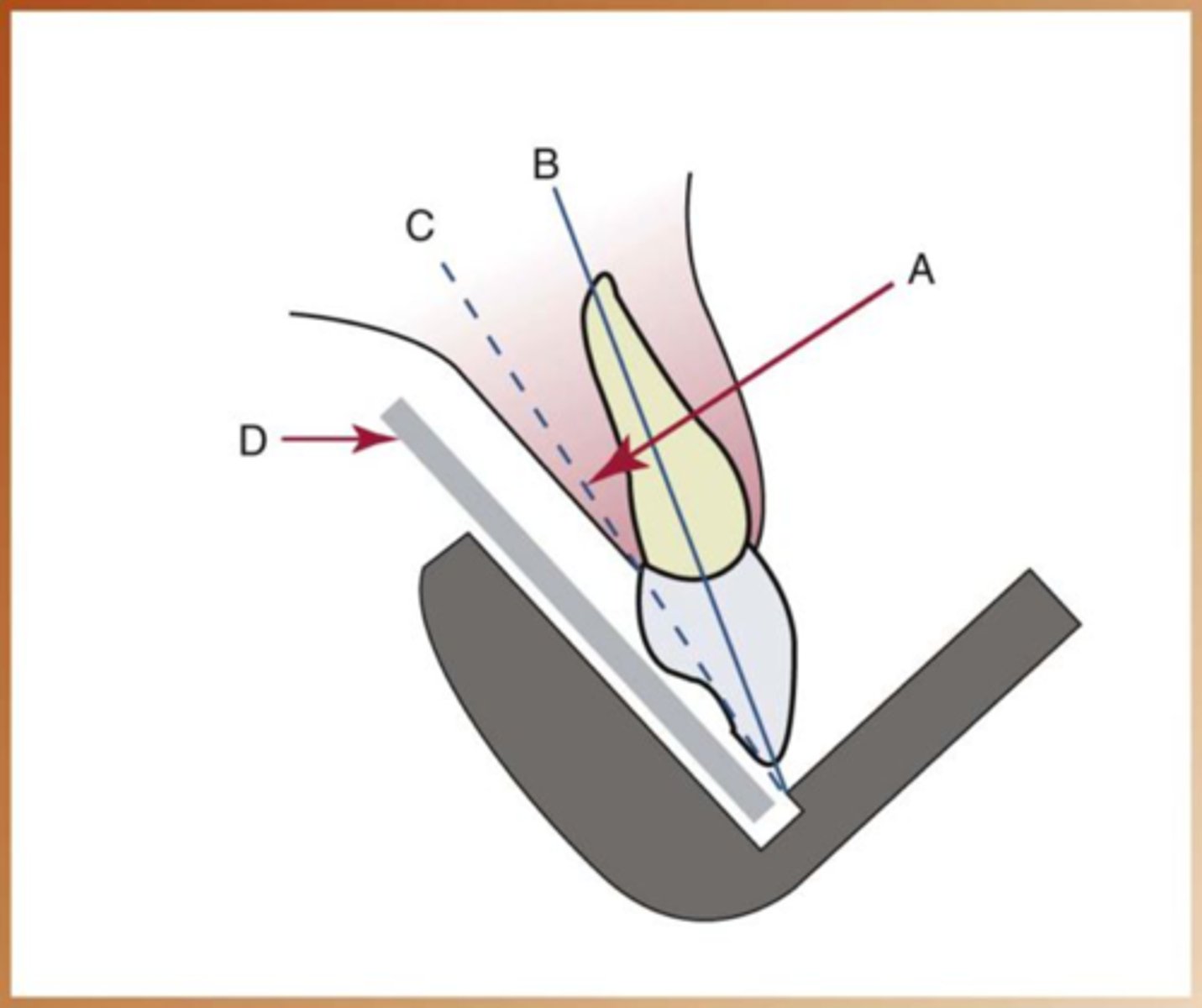
Bisecting technique steps
1. the receptor must be placed along the lingual surface of the tooth
2. the plane of the receptor and the long axis of tooth form an angle at point where the film contacts tooth
3. Imaginary bisector bisects the angle formed by the receptor and the long axis of tooth
4.the cental ray is directed perpendicular to the imaginary bisector
5. the two imaginary triangles that result are right triangles and congruent
Receptor holding device
used to position the receptor in the mouth and maintain it in position during exposure
-Stabe bite block
-Rinn Snap-A-Ray Holder
Receptors used for bisecting technique
Size 2 receptor used traditionally
-Anterior - long portion in a vertical direction
-Posterior - long portion is a horizontal direction
Horizontal angulation
the positioning of the tubehead and direction of the central ray in a horizontal or side-to-side plane
Correct horizontal angulation
The central ray is directed perpendicular to the curvature of the arch and through the contact areas of the teeth
Incorrect horizontal angulation
Overlapped contact areas
Vertical angulation
Refers to the positioning of the PID in a vertical, or up-and-down, plane
Correct vertical angulation
Results in a radiographic image that is the same length as the tooth
Incorrect vertical angulation
Results in a radiographic image that is not the same length as the tooth
Foreshortened image
results from excessive vertical angulation
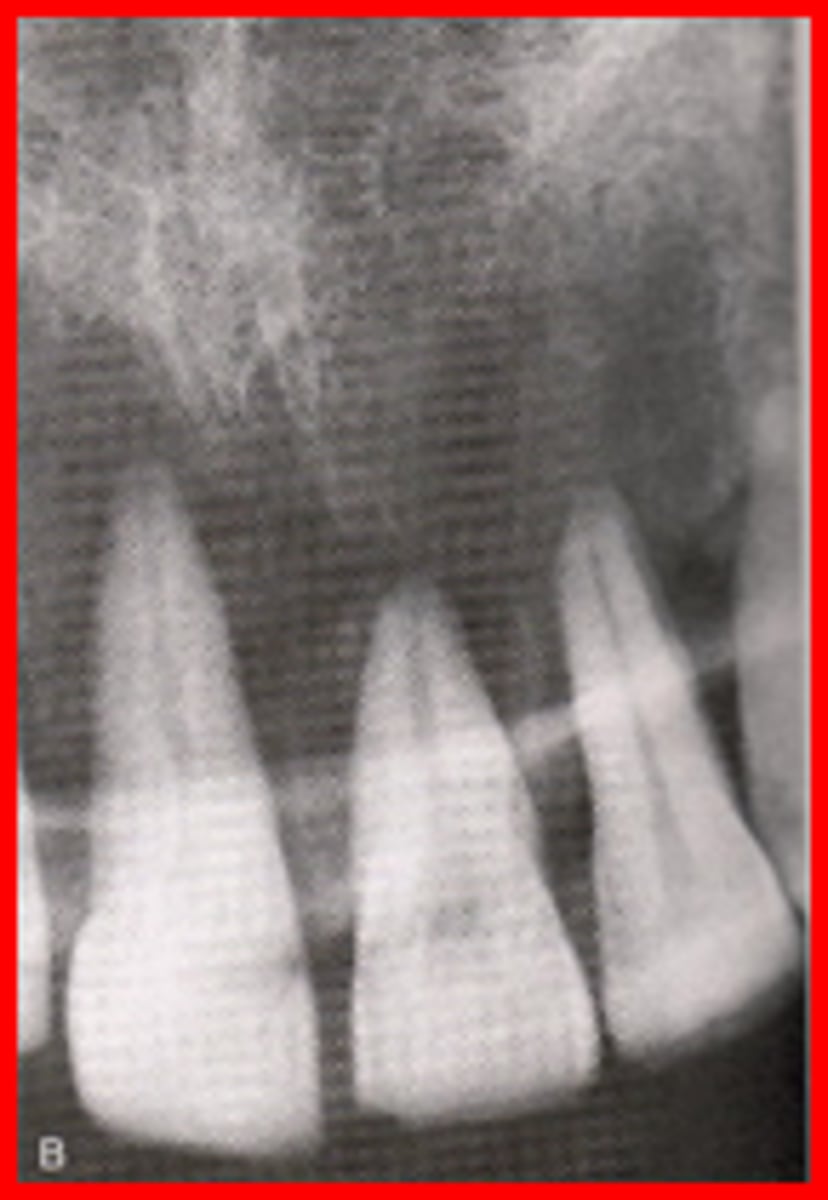
Elongated images
results from insufficient vertical angulation
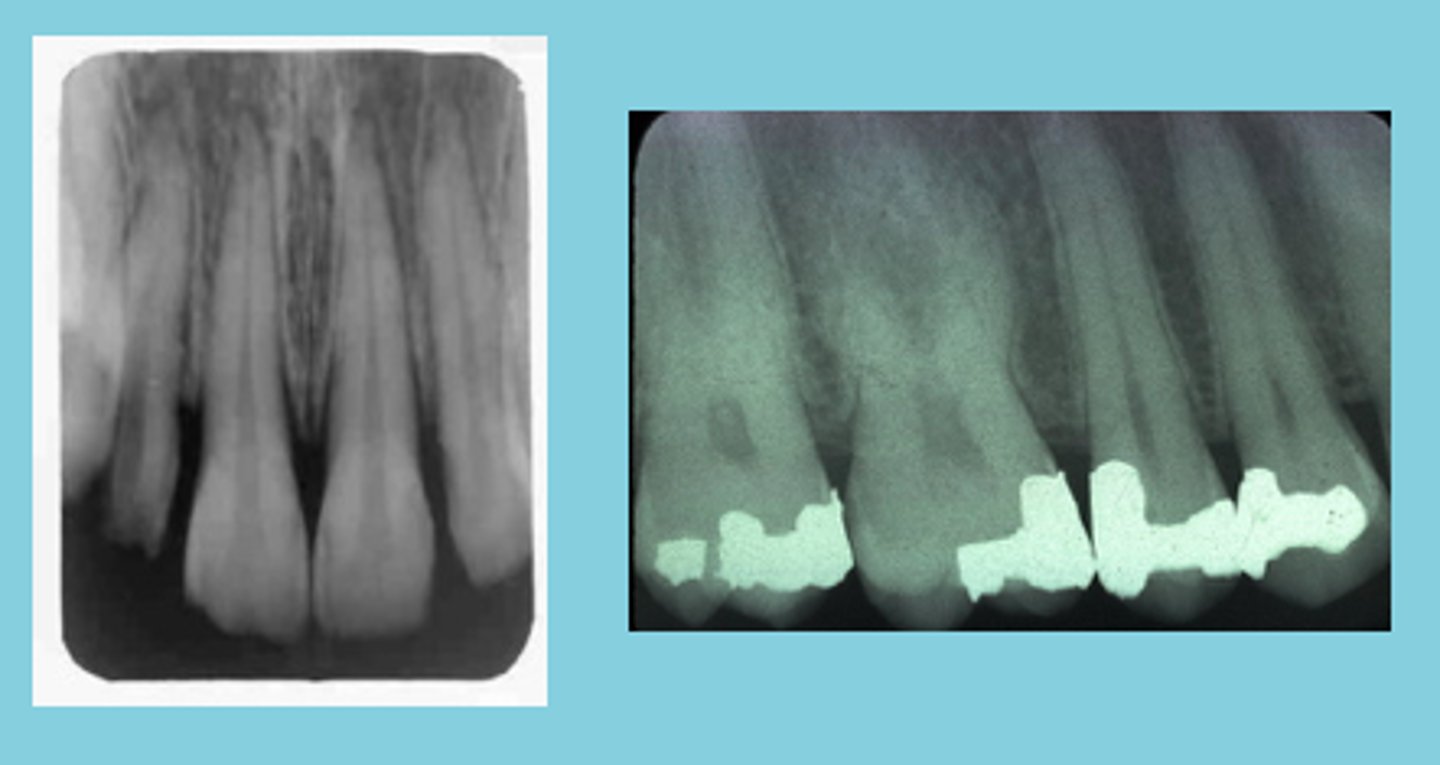
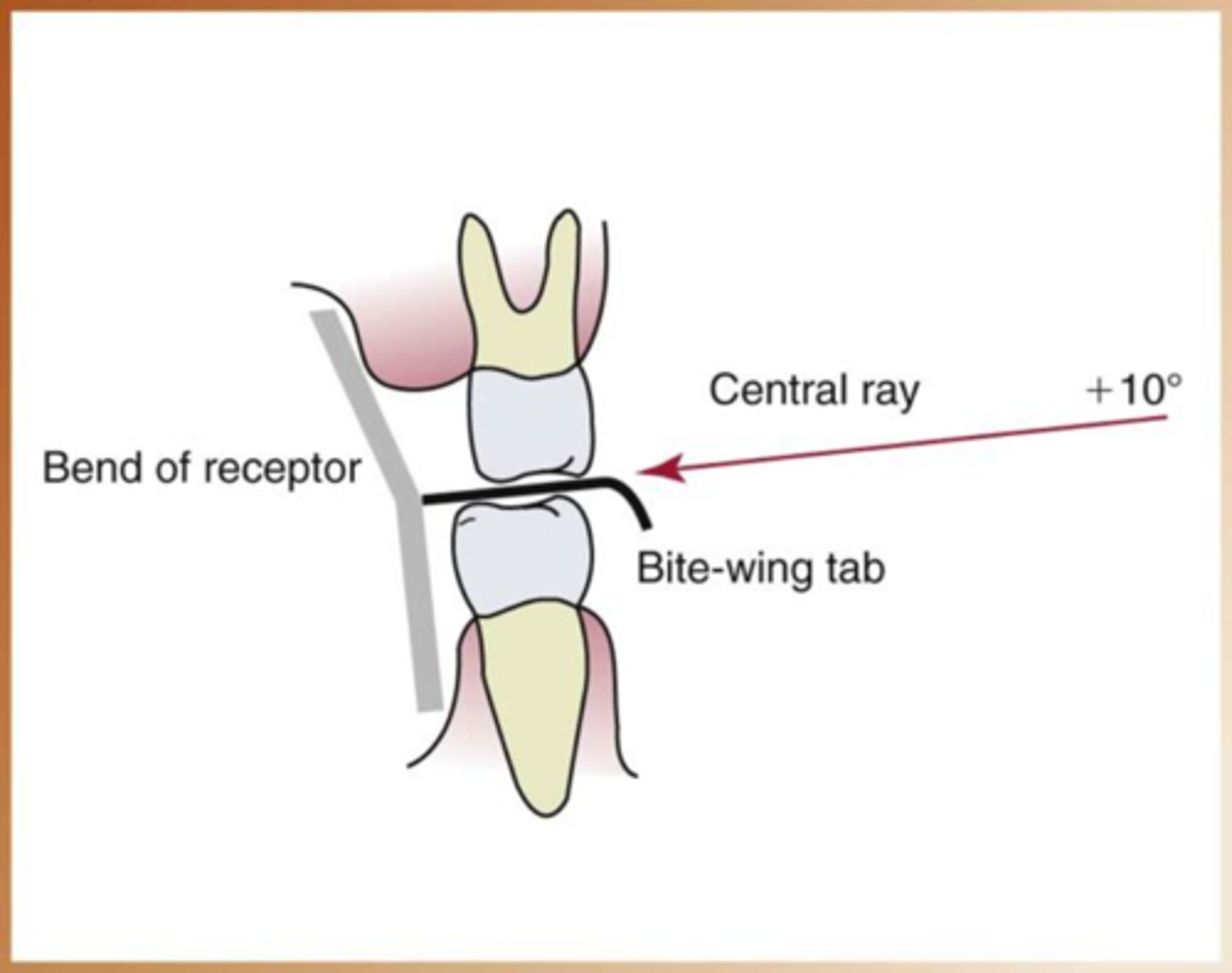
bitewings are supposed to be
10 degree angulation
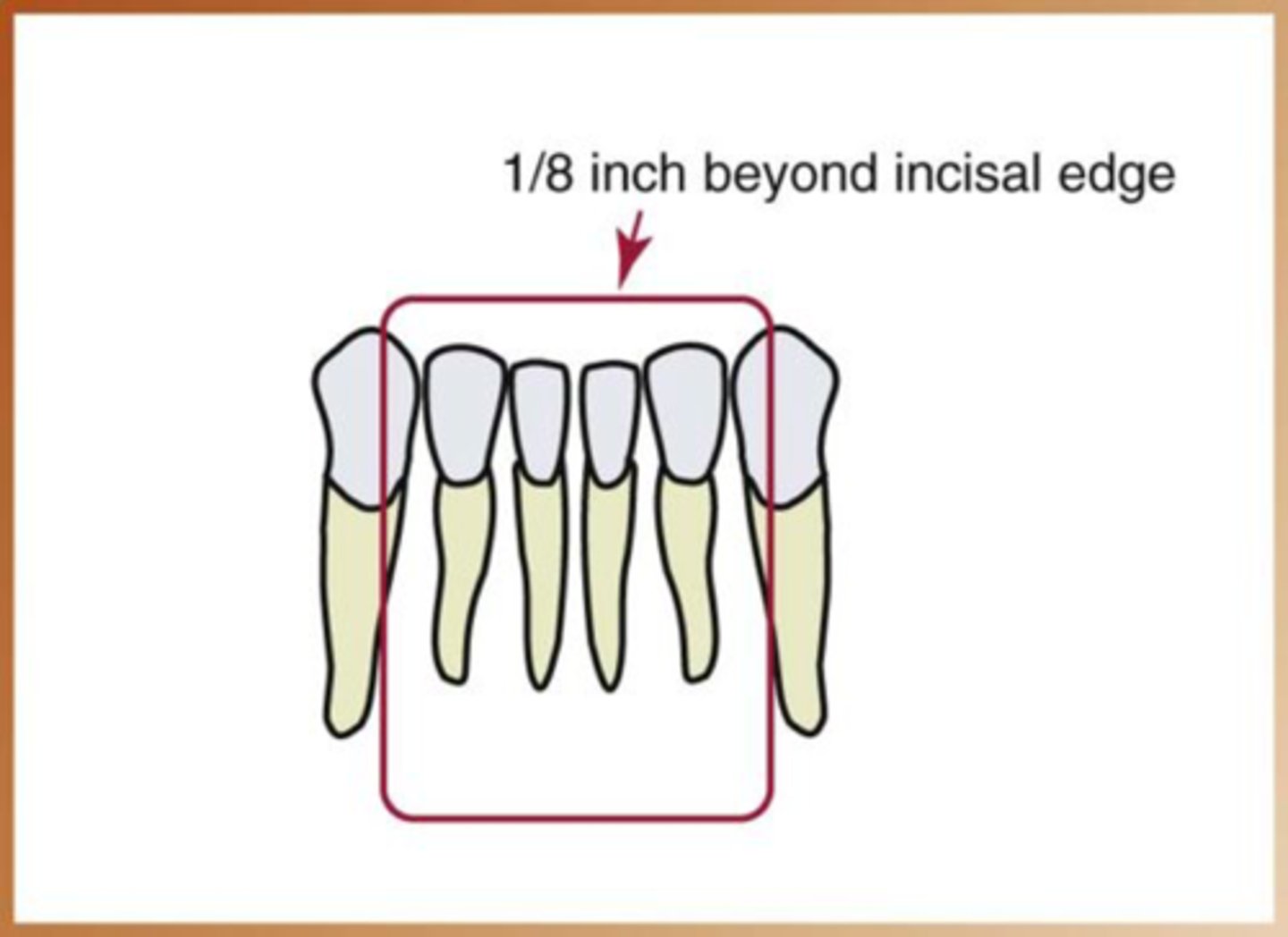
Steps of bisecting technique simplified
1. receptor placement
2. receptor position
3. vertical angulation
4. horizontal angulation
5. receptor exposure
Patient preparation
Infection control procedures
Preparation of treatment area and supplies
Patient is seated
Patient is prepared
Exposure Sequence for Receptor Placements
anterior exposure first, then posterior due to the anterior being easier for the patient to tolerate and get used to